How Is Prostate Cancer Staged
Prostate cancer is one of the most common types of cancer that develops in men and is the second leading cause of cancer deaths in American men, behind lung cancer and just ahead of colorectal cancer. The prognosis for prostate cancer, as with any cancer, depends on how advanced the cancer has become, according to established stage designations.
The prostate gland is a walnut-sized gland present only in men, found in the pelvis below the bladder. The prostate gland wraps around the urethra and lies in front of the rectum. The prostate gland secretes part of the liquid portion of the semen, or seminal fluid, which carries sperm made by the testes. The fluid is essential to reproduction.
The term to stage a cancer means to describe the evident extent of the cancer in the body at the time that the cancer is first diagnosed.
- Clinical staging of prostate cancer is based on the pathology results, physical examination, PSA, and if appropriate, radiologic studies.
- The stage of a cancer helps doctors understand the extent of the cancer and plan cancer treatment.
- Knowing the overall results of the different treatments of similarly staged prostate cancers can help the doctor and patient make important decisions about choices of treatment to recommend or to accept.
Prostate Cancer Is Common With Aging
After skin cancer, prostate cancer is the most common cancer in men. About 1 in 7 men will be diagnosed with prostate cancer in their lifetime. And these are just the men who are diagnosed. Among very elderly men dying of other causes, a surprising two-thirds may have prostate cancer that was never diagnosed.
Only 1 in 36 men, though, actually dies from prostate cancer. That’s because most prostate cancers are diagnosed in older men in whom the disease is more likely to be slow-growing and non-aggressive. The majority of these men eventually pass away from heart disease, stroke, or other causes — not their prostate cancer.
How Is Advanced Prostate Cancer Treated
The primary treatment of prostate cancer is prostatectomy, which is a surgery to remove a part of the prostate gland or the entire prostate gland in younger patients.
Androgen deprivation therapy is usually the choice of treatment of metastatic prostate cancer. Also known as hormone therapy, it is also used for treating patients who are unfit or unwilling to undergo surgery or/and radiation therapy.
Examples of hormone therapies for advanced prostate cancer include
- Abiraterone
Don’t Miss: Does Enlarged Prostate Affect Ejaculation
Risk Of Prostate Cancer
About 1 man in 8 will be diagnosed with prostate cancer during his lifetime.
Prostate cancer is more likely to develop in older men and in non-Hispanic Black men. About 6 cases in 10 are diagnosed in men who are 65 or older, and it is rare in men under 40. The average age of men at diagnosis is about 66.
What Is Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer can develop when cells in the prostate start to grow in an uncontrolled way.
Some prostate cancer grows too slowly to cause any problems or affect how long you live. Because of this, many men with prostate cancer will never need any treatment.
But some prostate cancer grows quickly and is more likely to spread. This is more likely to cause problems and needs treatment to stop it spreading.
Don’t Miss: What Happens To The Prostate Later In Life
Staging Spread And Survival Rates
As with all cancers, doctors use the term stage to describe the characteristics of the primary tumor itself, such as its size and how far prostate cancer has spread when it is found.
Staging systems are complicated. The staging system for most cancers, including prostate cancer, uses three different aspects of tumor growth and spread. It’s called the TNM system, for tumor, nodes, and metastasis:
- T, for tumor describes the size of the main area of prostate cancer.
- N, for nodes, describes whether prostate cancer has spread to any lymph nodes, and how many and in what locations.
- M, for metastasis, means distant spread of prostate cancer, for example, to the bones or liver.
Using the TNM system, each man’s prostate cancer can be described in detail and compared to other men’s prostate cancer. Doctors use this information for studies and to decide on treatments.
As far as survival rates for prostate cancer go, however, the staging system is pretty simple. As we’ve mentioned, in terms of survival rates, men with prostate cancer can be divided into two groups:
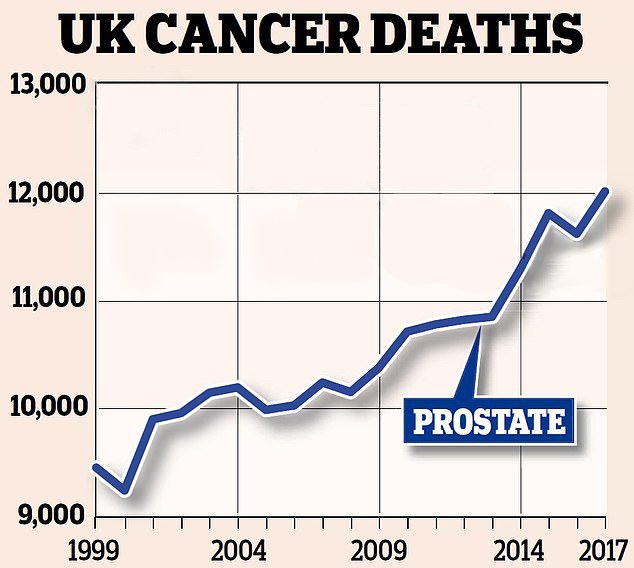
Prostate Cancer Deaths To Hit Highest Numbers In Two Decades
Cancer Facts and Figures
Im here today because my cancer was caught early. We need to educate more men about this disease, and why early testing is crucial to survival. The fact that Im still here today is proof.
- Family history of prostate cancer
- African American ancestry
- Family history of the BRCA 1 or 2 gene mutations
- Military veterans
About ZERO The End of Prostate Cancer
You May Like: Does Enlarged Prostate Affect Ejaculation
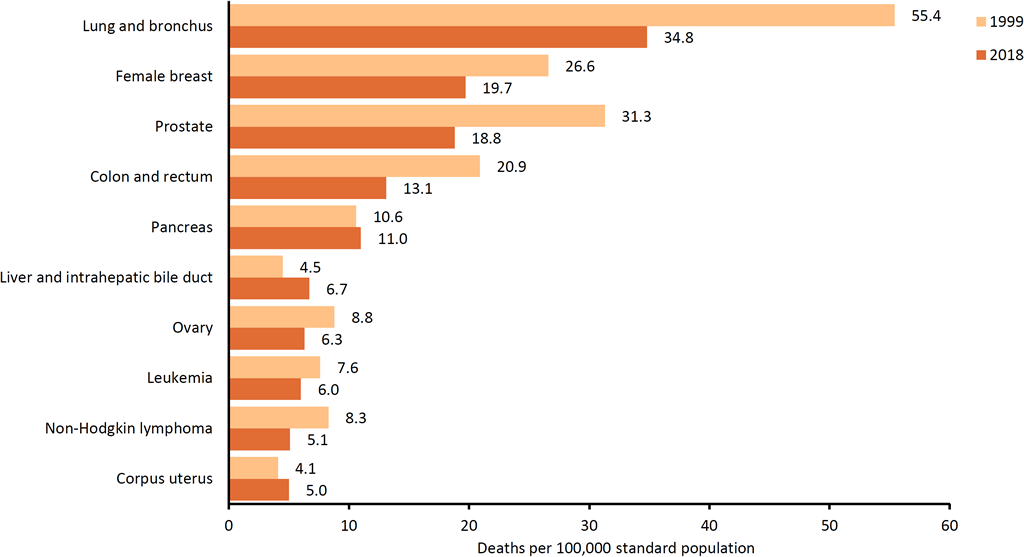
What Were The Leading Causes Of Cancer Death In 2019
Lung cancer was the leading cause of cancer death, accounting for 23% of all cancer deaths. Other common causes of cancer death were cancers of the colon and rectum , pancreas , female breast , prostate , and liver and intrahepatic bile duct . Other cancers individually accounted for less than 5% of cancer deaths.
In 2019
- 139,603 people died of lung cancer .
- 51,896 people died of colorectal cancer .
- 45,886 people died of pancreatic cancer .
- 42,281 females died of breast cancer.
- 31,638 males died of prostate cancer.
- 27,959 people died of liver and intrahepatic bile duct cancer .
NOTES: Deaths were classified using the International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision. Cancer deaths were identified using underlying cause-of-death codes C00-C97 .
National Center for Health Statistics, National Vital Statistics System, Mortality Data.
Prostate Cancer Now Kills More People Than Breast Cancer: Cause For Alarm
As epidemiologists, we are not alarmed by the apparent increase in deaths from prostate cancer, heres why
Jason Oke
For the first time in the UK, the number of deaths from prostate cancer has exceeded the numbers of deaths from breast cancer. According to figures from the UKs Office for National Statistics , more men died of prostate cancer than women died from breast cancer .
The Guardian, like many media outlets, pointed to the changing age demographics as a likely contributor prostate cancer is a disease of the elderly and men are living longer. Others, however, commandeered the media attention to push forward their own hypotheses. Roger Wotton, chairman of Tackle Prostate Cancer, said: Women have screening for breast cancer and this is one reason why mortality rates for prostate cancer are now higher than those for breast cancer. As epidemiologists, we are not alarmed by the apparent increase in deaths from prostate cancer. In this blog, we outline why.
Some clarity can be found by examining the mortality figures stratified by age. The death rate from prostate cancer in men older than 80 years of age is 601 per 100K, whereas the breast cancer mortality rate for women aged 80 or older is 216 per 100K.
The assessment of trends over time should always be made using age- and sex-standardised rates. Without adjusting for differences in population across years, crude numbers can prove to be misleading.
Conflicts of interest: none declared
References
Also Check: Periprostatic
Prostate Cancer Statistics On Life And Death
Prostate cancer is the second most common type of cancer among American men, after skin cancer. According to the American Cancer Society , more than two million U.S. men are prostate cancer survivors.
ACS statistics indicate there will be about 180,890 new cases of prostate cancer in the U.S. in 2016 and about 26,000 deaths. The ACS believes that one in every seven men are diagnosed with the disease during their lifetime. It is more common among older men, and six out of every 10 cases are diagnosed in men ages 65 or older it is rare in men younger than 40. The average age at the time of diagnosis is 66.
Lung cancer is the deadliest type of cancer, while prostate cancer is ranked as the second leading cause of cancer death in American men. One in every 38 men die of prostate cancer.
Prostate cancer can be a serious disease, but most men diagnosed with prostate cancer do not die from it. In fact, more than 2.9 million men in the United States who have been diagnosed with prostate cancer at some point are still alive today, the ACS states.
Are You At Risk
In the UK, about 1 in 8 men will get prostate cancer in their lifetime.
Prostate cancer mainly affects men over 50, and your risk increases with age. The risk is even higher for black men and men with a family history of prostate cancer.
Find out more about your risk.
See and share our infographic on prostate cancer risk.
Read Also: Perineuronal Net
Myth: Prostate Cancer Is For Older Men
Fact: While its true that the majority of men diagnosed with prostate cancer are older, it can strike younger men, too. About 40 percent of all cases occur in men younger than 65, according to the ACS. Its not uncommon at all for men in their fifties and some in their forties to have prostate cancer, says Sartor.
The exact age you should start getting regularly screened for prostate cancer is still an area of confusion and debate. At least start talking to your doctor about PSA testing once youre 50 years old, the ACS recommends. The exception to this is if the disease runs in your family, in which case its a good idea to start PSA screening earlier, at age 40 or 45.
Where Does Prostate Cancer Usually Spread First
If prostate cancer spreads to other parts of the body, it almost always goes to the bones first. These areas of cancer spread can cause pain and weak bones that might break. Medicines that can help strengthen the bones and lower the chance of fracture are bisphosphonates and denosumab.
Also Check: How To Massage A Man’s Prostate
Do Some Groups Experience Higher Rates Than Others
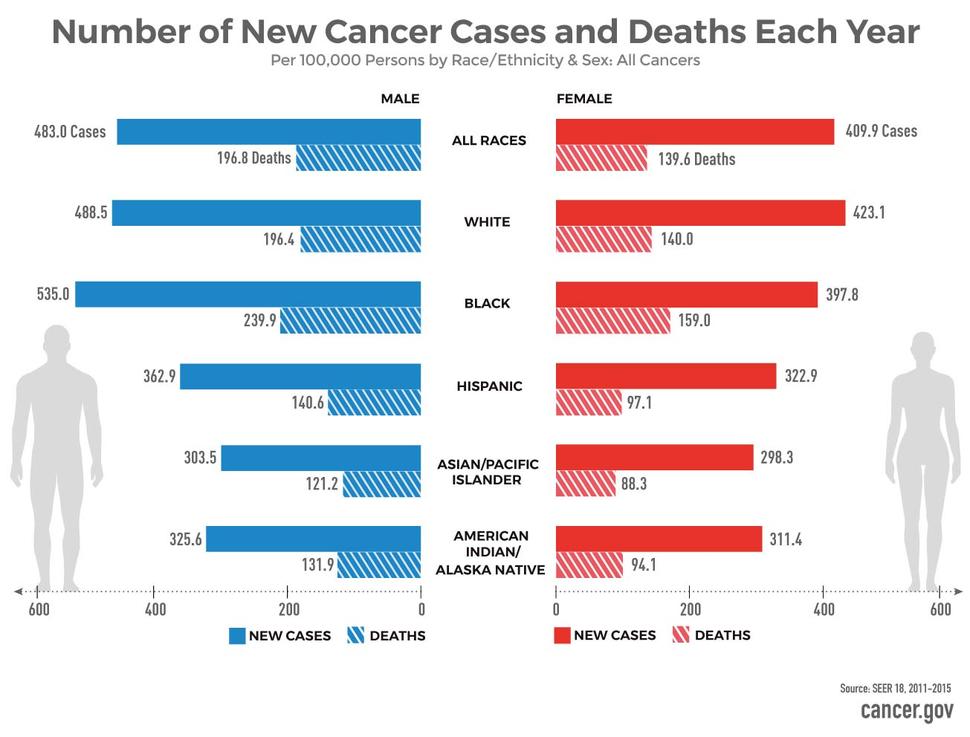
Cancer death rates differed by cancer type, sex, racial and ethnic group, and residence in an urban or rural county. Healthy People 2030 objectives include reducing death rates for lung cancerexternal icon to 25.1 deaths per 100,000 population, colorectal cancerexternal icon to 8.9 deaths per 100,000 population, female breast cancerexternal icon to 15.3 deaths per 100,000 female population, and prostate cancerexternal icon to 16.9 deaths per 100,000 male population.
| Characteristic | |
|---|---|
| 19.3 | 18.2 |
NOTES: Deaths were classified using the International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision. Cancer deaths were identified using underlying cause-of-death codes C00-C97 . Rates were age-adjusted to the 2000 US standard population. Urban/rural status was based on county of residence, classified using the 2013 NCHS Urban-Rural Classification Scheme for Counties.
National Center for Health Statistics, National Vital Statistics System, Mortality Data.
In 2019
- 1,115 children younger than 15 years old died of cancer.
- 9,084 adolescents and young adults between 15 to 39 years old died of cancer.
- 153,928 adults between 40 to 64 years old died of cancer
- 435,462 adults who were 65 years old or older died of cancer.
Note: Age was not recorded for 12 deaths.
National Center for Health Statistics, National Vital Statistics System, Mortality Data.
Watchful Waiting Vs Active Surveillance
To understand your choices, he explained, its key to know the difference between the two options for men if they do not seek immediate treatmentwatchful waiting and active surveillance.
While both strategies entail not being treated immediately, they are very different. The goal ofwatchful waiting isnt to cure or even treat the disease. Its not a good option for men with low-riskcancer. Its generally for men who, because of advanced age or a medical condition, are likely to die from something else before prostate cancer becomes a mortal threat. If the disease causes symptoms such as pain, these are managed, but the goal isnt cure.
Men with low-risk cancer, on the other hand, are good candidates for active surveillance. The goal here is to cure the cancerif it needs treatment at all. In many cases, these cancers dont even progress, so they dont really need treatmentand may never need treatment. With active surveillance, Dr. Hu explained, treatment is deferred until the time that there is evidence that the disease is progressing.
Current guidelines recommend active surveillance for most men with low-risk prostate cancer.
Don’t Miss: Neurovascular Bundle Invasion Prostate Cancer
Myth: Psa Tests Are Bad For You
Fact: Some prostate cancer experts recommend against regular PSA testing, but not necessarily because of the test itself which is just a simple blood test. PSA screening certainly isnt perfect, but it doesnt pose any actual danger to your health. The real hazard is anxiety and sometimes faulty decision-making when it comes to interpreting and acting on PSA results. According to the ACS, PSA levels usually go above 4 when prostate cancer develops. However, a PSA level between 4 and 10 results in a prostate cancer diagnosis only about 25 percent of the time.
Causes of a high PSA can range from things like bicycling to ejaculation. As a result, some men are given invasive biopsies that arent needed. Or, if they do have cancer, they may be treated aggressively for slow-growing tumors that might never have caused any issues.
Which is not to say that PSA tests arent valuable or that they cant save lives. In the years since theyve been widely used, says Dr. Wei, prostate cancer diagnoses have gone up but the death rate is going down. This is at least in part because PSA tests lead to more investigation, which can find cancer early when its more receptive to treatment. Talk with your doctor about whether and how often you should be screened for prostate cancer.
Reduce The Prostate Cancer Death Rate C08
Objective added to your list.
Objective removed from your list.
Objective added to your list.
Objective removed from your list.
18.3 prostate cancer deaths per 100,000 males
Target:
Baseline:18.8 prostate cancer deaths per 100,000 males occurred in 2018
Reduce the prostate cancer death rate
Read Also: Perineural Invasion In Prostate Cancer
Learn The Facts About Prostate Cancer
Most people dont think prostate cancer is going to happen to them, unless their father or brother had it, says Oliver Sartor, MD, a professor of medicine and urology at the Tulane University School of Medicine in New Orleans.
However, given that about 164,000 men in the United States will be diagnosed with the disease in 2018, according to the American Cancer Society , its likely that you or someone you know will be affected. Prostate cancer is the second leading cause of death from cancer in American men, right behind lung cancer.
But while its a serious disease, and it does take lives, most men dont die from it. In fact, the ACS says that more than 2.9 million Americans whove been diagnosed with prostate cancer are still alive today.
Despite this prevalence, myths and confusion abound when it comes to understanding your own personal level of risk, and what to do when your doctor says you have prostate cancer.
The diagnosis almost always hits people out of the blue, Dr. Sartor says. It’s not what you plan on, and of course it’s very disruptive. For many men, prostate cancer creates a general cognitive dissonance: Why me? What did I do wrong? What am I going to do about it now that my life is being threatened?
Additional reporting by Andrea Peirce
It Was Estimated That In :
- 115,800 Canadian men would be diagnosed with cancer and 44,100 men would die from cancer.
- 110,000 Canadian women would be diagnosed with cancer and 39,300 women would die from cancer.
- On average, 617 Canadians would be diagnosed with cancer every day.
- On average, 228 Canadians would die from cancer every day.
- Lung, breast, colorectal and prostate cancer are the most commonly diagnosed types of cancer in Canada .
- These 4 cancers account for about half of all new cancer cases.
- Prostate cancer accounts for one-fifth of all new cancer cases in men.
- Lung cancer accounts for 14% of all new cases of cancer.
- Breast cancer accounts for one-quarter of all new cancer cases in women
- Colorectal cancer accounts for 12% of all new cancer cases.
Don’t Miss: Prostate Cancer Bone Metastasis Osteoblastic
Reducing The Cancer Burden
Between 30 and 50% of cancers can currently be prevented by avoiding risk factors and implementing existing evidence-based prevention strategies. The cancer burden can also be reduced through early detection of cancer and appropriate treatment and care of patients who develop cancer. Many cancers have a high chance of cure if diagnosed early and treated appropriately.
What Is The Prostate
The prostate is a gland. It is usually the size and shape of a walnut and grows bigger as you get older. It sits underneath the bladder and surrounds the urethra, which is the tube that carries urine out of the body. The prostate’s main job is to help make semen the fluid that carries sperm.
The most common prostate problems are an enlarged prostate, prostatitis and prostate cancer.
Listen to a summary of this page
You May Like: Do Females Have Prostate Cancer
Why Did Cancer Death Rates Change From 1999 To 2019
Previous research suggests that trends in cancer death rates reflect population changes in cancer risk factors, screening test use, diagnostic practices, and treatment advances. More information can be found in the blog post Conversations with Authors: The Annual Report to the Nation. Some examples are highlighted below.
- Cigarette smoking contributes to the development of cancers throughout the body. Fewer people are smoking cigarettes: in 1965, 42% of U.S. adults smoked cigarettes compared to 14% in 2019. About two-thirds of people who smoke want to quit. For more information and quitting resources, visit Tips From Former Smokers.
- Overweight and obesity also contribute to the development of cancers throughout the body, including cancers of the liver, pancreas, and uterus. Some states and communities are providing support that can help people get to and keep a healthy weight. For more information, visit Obesity and Cancer.
- Cancer screening tests can find cancer early, when treatment works best. Screening tests for colorectal cancer can also find polyps, which can be removed before they become cancerous. For more information, visit Cancer Screening Tests.
- Since 2011, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration has approved new treatments for advanced melanoma. For more information, visit the National Cancer Institutes New Therapies Are Changing the Outlook for Advanced Melanoma.external icon
