Turp / Greenlight Pvp Laser / Thermotherapy
Transurethral resection of the prostate has long been the mainstay of enlarged prostate surgery, but less invasive alternatives are now available, with the potential for equal results. With TURP, the obstructing portion of the enlarged prostate tissue is removed. Although effective, TURP requires hospitalization and catheterization for 48 hours or more and comes with risks associated with anesthesia; bleeding during and after the operation; and, in rare cases, fluid absorption that can be life-threatening.
Prostate LaserOne alternative that has emerged is laser enlarged prostate surgery. Like TURP, the so-called GreenLight PVP Laser Therapy aims to create a channel in the urethra through which men can urinate more freely but the surgery is considerably less invasive. Instead of cutting tissue out, the newer technique creates the channel by vaporizing the tissue using laser energy. Thus far, almost every study has shown that when done by experienced urologists, the laser enlarged prostate surgery produces results that are equal to those with TURP, but without the severe side effects and risks. It is an outpatient procedure with minimal to no bleeding, no risk of fluid absorption, and catheterization only overnight, if at all.
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Prevalence And Risk Factors
The risk of BPH increases year by year after a man turns 40, but estimates on the prevalence of BPH among age groups vary.
Twenty percent of men in their fifties have BPH, while 60 percent of men in their sixties have it, and 70 percent of men in the their seventies do, according to the Prostate Cancer Foundation.
In its Andrology Handbook, however, the American Society of Andrology states that about 50 percent of men have BPH at age 50 and 90 percent at age 90. A report published in July 2017 in the Asian Journal of Urology, on the other hand, notes that 8 to 60 percent of men have BPH at age 90.
Aside from increased age, risk factors for BPH include:
- Family history of BPH
Doctors advise men to seek medical care if they experience the above complications.
What To Think About
Unless surgery is required because of a complication, choosing a treatment is largely up to you and your doctor. If complications arise, surgery may be needed.
The extent to which treatment improves your symptoms depends partly on how bad your symptoms are and how much you are bothered by them. If you are not bothered by your symptoms before treatment, you are less likely to notice much improvement after treatment.
Surgery offers the best chance for improving the symptoms but also has the risk of causing other problems.
Recommended Reading: Prostate Meds Side Effects
What Are The Symptoms Of Benign Prostate Hypertrophy
The symptoms of BPH can include:
- inability to completely empty the bladder when peeing
- poor urine flow
- urgent need to pee, which can disturb sleep at night
- dribbling of urine at the end of peeing
- bladder infections
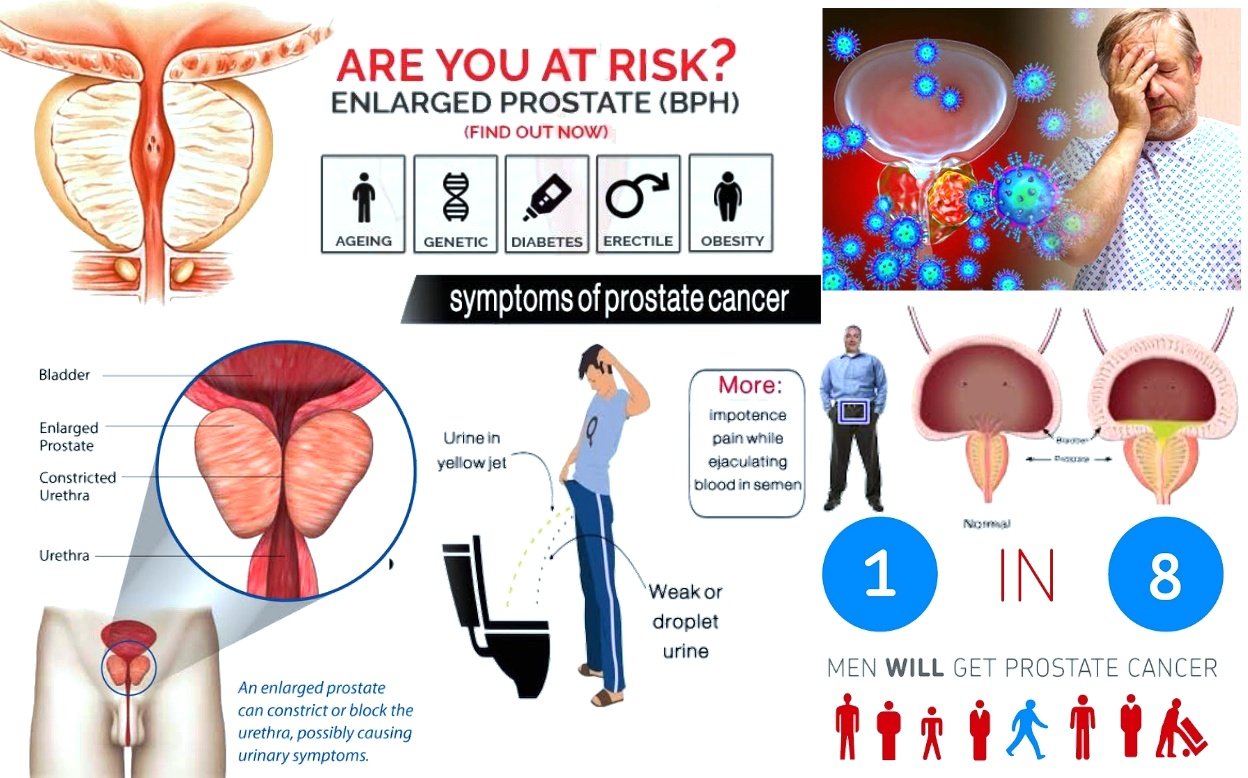
There are usually no symptoms at the start, even after the prostate has started to enlarge. The first sign of BPH is usually problems with urinating, because the enlarged prostate is squeezing and narrowing the urethra.
This is because the enlarged prostate is squeezing and narrowing the urethra.
Occasionally, BPH interferes with the ability to have sex, causing impotence or painful orgasms.
What Causes Bph At What Age Do Men Develop The Condition
Medical professionals do not have a good understanding of what causes an enlarged prostate.
BPH generally begins in a man’s 30s, evolves slowly, and most commonly only causes symptoms after 50.
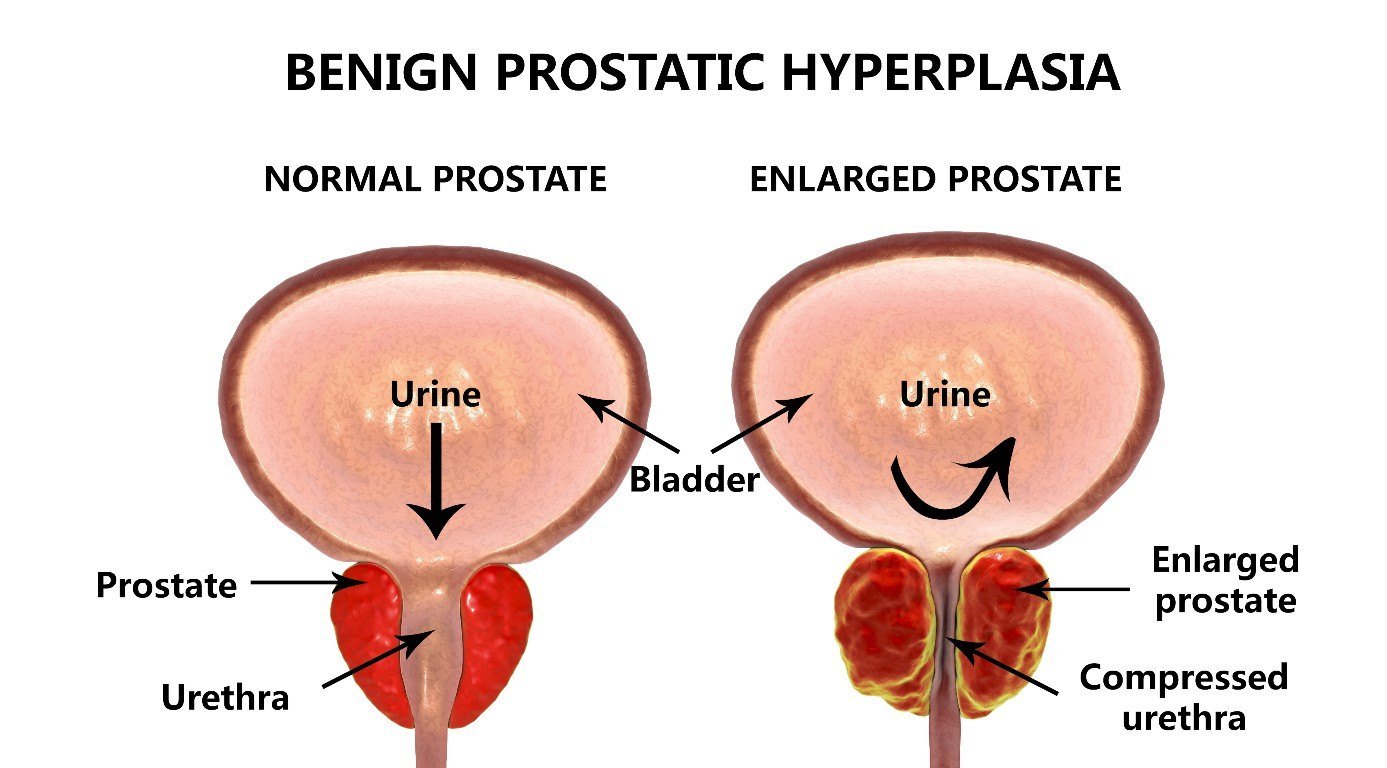
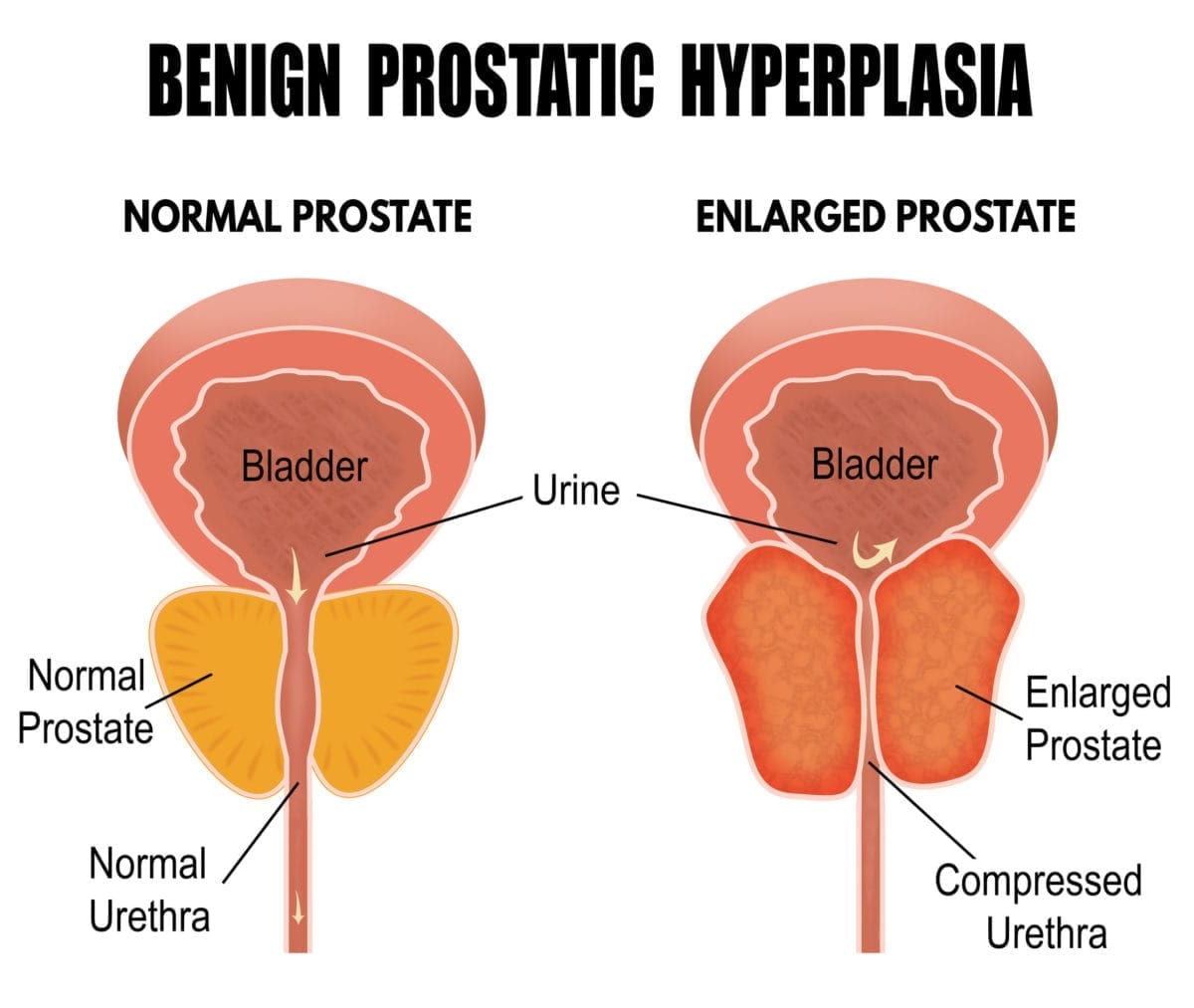
In benign prostatic hyperplasia, the prostate gland grows in size. It may compress the urethra, which courses through the center of the prostate. This can impede the flow of urine from the bladder through the urethra to the outside. Lower urinary tract symptoms from BPH can be due to one of the factors: dynamic, static, and compensatory. Dynamic factors are related to the tone of the muscle surrounding the prostate and the outlet of the bladder whereas static factors are related to the enlargement of the prostate tissue. Dynamic and static symptoms are prostate-related symptoms. Compensatory factors are the result of changes that occur in the bladder as a result of the bladder working harder to push urine past the bladder neck and prostate.
Signs and symptoms of BPH include lower urinary tract symptoms of weak urine stream, difficulty starting the urine stream , straining to urinate, inability to completely empty the bladder, inability to urinate , blood in the urine , leakage of urine , decreased urine flow , and post-void dribbling of urine.
BPH may also be related to the development of bladder stones, recurrent urinary tract infections, and backup of urine in the kidneys .
Recommended Reading: Is Turmeric Good For Prostate
Causes Of Benign Prostate Enlargement
The exact cause of benign prostate enlargement is unknown, but research suggests that hormones probably play an important role in the condition’s development.
Hormones are powerful chemicals that can have a wide range of effects on the cells of the body.
One theory is that as some men get older, the levels of a type of hormone called dihydrotestosterone increases, which may stimulate the growth of the prostate.
Another theory suggests that two hormones, testosterone and oestrogen, play a role. Younger men produce high levels of testosterone and much smaller levels of oestrogen. But as men get older, their levels of testosterone decrease, which means they then have a higher proportion of oestrogen in their body. It’s been suggested that the relative increase in oestrogen may stimulate prostate growth.
What Is Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Benign prostatic hyperplasiaalso called BPHis a condition in men in which the prostate gland is enlarged and not cancerous. Benign prostatic hyperplasia is also called benign prostatic hypertrophy or benign prostatic obstruction.
The prostate goes through two main growth periods as a man ages. The first occurs early in puberty, when the prostate doubles in size. The second phase of growth begins around age 25 and continues during most of a mans life. Benign prostatic hyperplasia often occurs with the second growth phase.
As the prostate enlarges, the gland presses against and pinches the urethra. The bladder wall becomes thicker. Eventually, the bladder may weaken and lose the ability to empty completely, leaving some urine in the bladder. The narrowing of the urethra and urinary retentionthe inability to empty the bladder completelycause many of the problems associated with benign prostatic hyperplasia.
Read Also: Does Enlarged Prostate Cause Constipation
Lifestyle Changes For Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
If you have only very mild symptoms from BPH, your doctor may recommend certain lifestyle changes to manage your BPH. These include:
- Reducing your liquid intake, especially before leaving the house or sleeping
- Avoiding caffeine, alcohol, and certain medication that may make you urinate more
- Training the bladder to keep urine flowing longer
- Exercising your pelvic floor muscles
- Preventing or treating constipation
What Increases Your Risk
Men who are older than 50 have a higher risk for benign prostatic hyperplasia .
The hormone testosterone, which is produced mainly by the testicles, is needed in order for BPH to develop. Men who have their testicles removed before puberty never develop BPH. Men who have their testicles removed after puberty rarely develop BPH.
A vasectomy does not increase your risk of BPH.
Read Also: Definition Of Prostate
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Treatment
A wide variety of treatments are available for enlarged prostate, including medication, minimally invasive therapies and surgery. The best treatment choice for you depends on several factors, including:
- The size of your prostate
- Your age
- Your overall health
- The amount of discomfort or bother you are experiencing
If your symptoms are tolerable, you might decide to postpone treatment and simply monitor your symptoms. For some men, symptoms can ease without treatment.
Tests And Diagnosis For Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Your doctor will start by asking detailed questions about your symptoms and doing a physical exam. This initial exam is likely to include:
- Digital rectal exam. The doctor inserts a finger into the rectum to check your prostate for enlargement.
- Urine test. Analyzing a sample of your urine can help rule out an infection or other conditions that can cause similar symptoms.
- Blood test. The results can indicate kidney problems.
- Prostate-specific antigen blood test. PSA is a substance produced in your prostate. PSA levels increase when you have an enlarged prostate. However, elevated PSA levels can also be due to recent procedures, infection, surgery or prostate cancer.
- Neurological exam. This brief evaluation of your mental functioning and nervous system can help identify causes of urinary problems other than enlarged prostate.
After that, your doctor might recommend additional tests to help confirm an enlarged prostate and to rule out other conditions.
These additional tests might include:
If your condition is more complex, your doctor may recommend:
You May Like: What Is Perineural Invasion In Prostate Cancer
Treating Benign Prostate Enlargement
Treatment for an enlarged prostate is determined by the severity of your symptoms.
If you have mild to moderate;symptoms, you won’t receive any immediate medical treatment, but you’ll have regular check-ups to carefully monitor your prostate.
You’ll probably also be advised to make;lifestyle changes, such as limiting your caffeine and;alcohol intake, and exercising regularly,;to see if they improve your symptoms.
As well as;lifestyle changes, medication is usually recommended to treat moderate to severe symptoms of benign prostate enlargement.;Finasteride and dutasteride are medications;that are commonly used. They block the effects of a hormone called dihydrotestosterone on the prostate gland, which can reduce the size of the prostate and improve associated symptoms.
Alpha blockers may also be prescribed. They help to relax your bladder muscles, making it easier to pass urine. Tamsulosin and alfuzosin are two alpha blockers commonly used to treat benign prostate enlargement.
Surgery is usually only recommended for moderate to severe symptoms of benign prostate enlargement that have failed to respond to medication.
Read more about treating benign prostate enlargement
Who Is More Likely To Develop Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Like we mentioned in the previous section, there are several uncontrollable risk factors that account for your chance of getting an enlarged prostate . Here are the three most important factors:
How can benign prostatic hyperplasia be prevented?
While there are uncontrollable risk factors for BPH such as family history and age, there are some that can be controlled or managed by men:
ObesityIt is important to maintain a healthy lifestyle to manage the risk of BPH, and a healthy diet is a necessity to achieve it. Nutrition also goes hand in hand with avoiding obesity.
Physical activityRegular exercise is another major component of a healthy lifestyle, and a great way to avoid obesity and the complications it brings, including those associated with BPH.
If you already have BPH, there are certain habits you can maintain to avoid further complications.
Don’t Miss: External Prostate Massage For Prostatitis
What Are Medications And Surgery Procedures That Treat Bph
There are several different ways to treat BPH, and the treatment may vary with the different factors. Alpha-blockers and PDE-5 inhibitors commonly treat the dynamic factors associated with BPH, whereas 5-alpha reductase inhibitors and surgical interventions treat the static factors, and anticholinergics and beta 3-adrenoceptor agonists treat the compensatory factors.
Men should carefully weigh the risks and benefits of each of these options. Although surgical intervention tends to produce the most significant impact on symptoms, it is associated with greater risk and is typically reserved for individuals who fail medical therapy, either by lack of adequate symptom improvement or side effects of the medication.
Medical treatment of BPH is usually reserved for men who have an elevated AUA-SI :
Surgery or office procedures may also be used to treat BPH, most commonly in men who have not responded satisfactorily to medicine or those who have more severe problems, such as a complete inability to urinate, kidney problems due to the BPH, recurrent urinary tract infections, recurrent bladder stones, or gross hematuria .
Tests That Are Often Done
- A digital rectal examination checks the size and firmness of the prostate. But the size of the prostate does not always determine the severity of the symptoms.
- A urinalysis and urine culture check for a urinary tract infection that might be the cause of the symptoms.
- A prostate-specific antigen test helps check for prostate cancer, which can cause the same symptoms as BPH.
Recommended Reading: Viagra Bph
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Medication
If you have mild to moderate BPH, your doctor will likely prescribe one or more drugs to stop the growth of or shrink the prostate and reduce symptoms.
Alpha blockers are a type of medication that relax the smooth muscles of the bladder neck and prostate, helping to improve urine flow and reduce blockage. These medicines include Uroxatral , Cardura , Flomax , and Rapaflo .
Typically prescribed for erectile dysfunction, phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors like Cialis can help reduce lower urinary tract symptoms by relaxing smooth muscles.
Another type of drug called 5-alpha reductase inhibitors ;Proscar and Propecia
Avodart ;can slow and even reverse prostate growth by blocking the production of DHT.
Nonmedication Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Treatment Options
If you have moderate to severe BHP, you’re unresponsive to medication, or you have BPH complications, your doctor will likely opt for minimally invasive treatments or surgery.
Minimally invasive procedures, which can destroy enlarged prostate tissue or widen the urethra, include:
- Transurethral microwave thermotherapy
- Transurethral needle ablation ” rel=”nofollow”>Urology Care Foundation does not recommend)
Surgery may be necessary if medication and minimally invasive procedures are ineffective. Surgical procedures for BPH include:
- Transurethral resection of the prostate
- Laser surgery
- Transurethral incision of the prostate
You May Like: Does An Enlarged Prostate Affect A Man Sexually
How Is Bph Diagnosed
Your doctor will ask you about your symptoms. He or she will do a rectal exam to check your prostate. For this, your doctor will put a gloved, lubricated finger into your rectum. He or she will feel the size of your prostate gland.
Your doctor may do blood or urine tests to make sure that your prostate problem is benign. An ultrasound exam or a biopsy of the prostate may also help in the ;diagnosis.
What Are The Causes Of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
The prostate gland is a walnut-sized gland located at the base of your bladder. The urethra-a tube that passes urine out from your body passes through the center of the prostate.
Therefore, the enlargement of the prostate can lead to urine flow blockage. In many men, the prostate keeps growing throughout life, eventually causing blockage of urine flow or other urinary symptoms.
Experts do not know the exact cause of prostate enlargement, but it can occur due to hormonal imbalance as men get older.
You May Like: Can Prostate Cancer Go Away
Robotic Assisted Simple Prostatectomy
A simple prostatectomy is a procedure performed for BPH which involves removing the adenoma, or enlarged obstructing prostate tissue all at the same time. It is for men with extremely large prostate glands and differs from a radical prostatectomy, which is performed for cancer. Traditionally a simple prostatectomy is performed in an open fashion through a lower abdominal incision. This procedure can also be done minimally invasively using the DaVinci robot. One of the benefits of the robotic approach is that small veins which tend to bleed during the open operation are compressed, reducing blood loss and the need for transfusion.
What are the benefits of robotic simple prostatectomy?
- Extremely large prostates can be approached in a minimally invasive fashion eliminating the need for an open incision.
- Other benefits may include decreased pain, hospital stay, blood loss and catheterization time.
Boston Medical Center is a 514-bed academic medical center located in Boston’s historic South End, providing medical care for infants, children, teens and adults.
One Boston Medical Center Place Boston, MA 02118
How Is It Treated
As a rule, you don’t need treatment for BPH unless the symptoms bother you or you have other problems such as backed-up urine, bladder infections, or bladder stones.
Although home treatment cannot stop your prostate from getting larger, it can help reduce or control your symptoms. Here are some things you can do that may help reduce your symptoms:
- Practice “double voiding.” Urinate as much as you can, relax for a few moments, and then urinate again.
- Avoid caffeine and alcohol. They make your body try to get rid of water and can make you urinate more often.
- If possible, avoid medicines that can make urination difficult, such as over-the-counter antihistamines, decongestants , and allergy pills. Check with your doctor or pharmacist about the medicines you take.
If home treatment does not help, BPH can be treated with medicine. Medicine can reduce the symptoms, but it rarely gets rid of them. If you stop taking medicine, symptoms return.
If your symptoms are severe, your doctor may suggest surgery to remove part of your prostate. But few men have symptoms or other problems severe enough to need surgery.
Read Also: Does Enlarged Prostate Cause Constipation
What And Where Is The Prostate
The prostate gland, which is found only in men, is an important part of the reproductive system. It secretes a fluid that is part of semen and keeps sperm alive and healthy.
The prostate is found behind the base of the penis and underneath the bladder. The urethra runs through the middle of the prostate.
