Further Testing For Advanced Cancer
If there’s a significant chance the cancer has spread from your prostate to other parts of the body, further tests may be recommended.
These include:
- an MRI scan, CT scan or PET scan these scans build a detailed picture of the inside of your body
- an isotope bone scan, which can tell if the cancer has spread to your bones a small amount of radiation dye is injected into the vein and then collects in parts of the bone where there are any abnormalities
Why Is A Prostate
A PSA blood test is performed to detect or rule out prostate cancer. The amount of PSA in the blood is often higher in men who have prostate cancer. However, an elevated PSA level does not necessarily indicate prostate cancer. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has approved the PSA blood test for use in conjunction with a DRE to help detect prostate cancer in men age 50 or older and for monitoring men with prostate cancer after treatment. However, much remains unknown about how to interpret a PSA blood test, its ability to discriminate between cancer and problems such as BPH and prostatitis, and the best course of action if the PSA level is high.
When done in addition to a DRE, a PSA blood test enhances detection of prostate cancer. However, the test is known to have relatively high false-positive rates. A PSA blood test also may identify a greater number of medically insignificant lumps or growths, called tumors, in the prostate. Health care providers and patients should weigh the benefits of PSA blood testing against the risks of follow-up diagnostic tests. The procedures used to diagnose prostate cancer may cause significant side effects, including bleeding and infection.
Tests To Diagnose And Stage Prostate Cancer
Most prostate cancers are first found as a result of screening. Early prostate cancers usually dont cause symptoms, but more advanced cancers are sometimes first found because of symptoms they cause.
If prostate cancer is suspected based on results of screening tests or symptoms, tests will be needed to be sure. If youre seeing your primary care doctor, you might be referred to a urologist, a doctor who treats cancers of the genital and urinary tract, including the prostate.
The actual diagnosis of prostate cancer can only be made with a prostate biopsy .
On this page
Read Also: Does Regular Ejaculation Help Prostate
Data Analysis And Algorithm For Identification Of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer
Gene expression data were downloaded and analyzed using ABI Quantstudio 6 software . The mean cycle threshold value from triplicate PCR was used as the gene expression level of each gene . The housekeeping gene beta-actin was measured and used to normalize each gene in the classifier .
For the identification of clinically significant and insignificant PCa by the 24-Gene Classifier in the urine samples, CtS of the 24 genes was used in the following Urine Clinically Significant Cancer Algorithm:
CUrineCSC = AH+
* 24 are gene 1 and gene 1 cross clinically insignificant PCa regression coefficients through gene 24 and gene 24 cross clinically insignificant PCa regression coefficients. The sample was diagnosed as clinically significant PCa when the Urine Clinically Significant Cancer D Score was > 0, whereas the sample was diagnosed as clinically insignificant PCa when the D Score was 0.
The diagnostic method of clinically significant and insignificant PCa by the 24-Gene Classifier in the prostate tissue specimens is described in the Supplementary Data.
Screening For Prostate Cancer
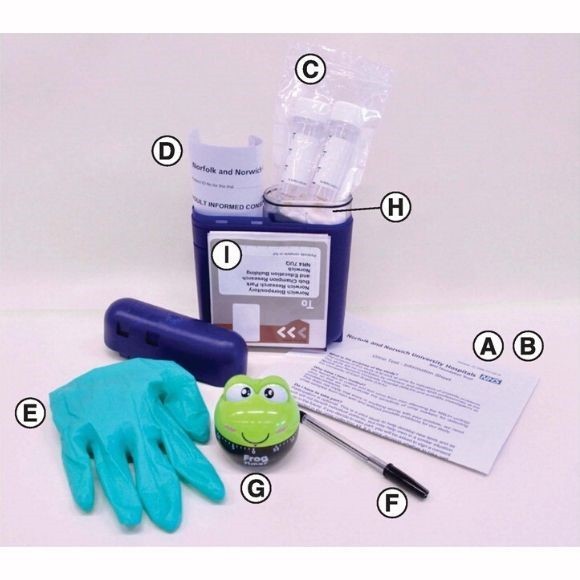
There is no national screening programme for prostate cancer in the UK. This is because there isnt a reliable test that can pick up prostate cancer that needs treatment at an early stage.
Overall research has shown that current tests dont reduce the number of men dying from prostate cancer. Research is going on to find a new test. Or see if the current test is more effective if used in a different way and can find the cancers that need treatment more accurately.
Recommended Reading: Can You Check Your Own Prostate
Lowering The Risk Of Developing Prostate Cancer
Many risk factors for prostate cancer, such as age and family history, cant be changed or prevented. However, you can take steps to lower your risk of developing advanced or severe disease.
Men can potentially lower their risk of developing prostate cancer by following the Mediterranean diet, engaging in a healthy lifestyle, and maintaining a healthy weight, says Dr. Mehran Movassaghi, a urologist, the director of Mens Health at Providence Saint Johns Health Center, and an assistant professor of urology at Saint Johns Cancer Institute in California.
Optimization Of Tgia And Ria Assay Using Spiked Pca Cells In Control Urine
PCa cells were spiked into the urine of healthy male volunteers for the development and optimization of the TGiA and RiA assays before carrying out the tests in PCa patientsâ urine. From these experiments the fixation and filtration of urine samples, specificity, and sensitivity and automated microscopy of TGiA assay, and the Raman-active Immunolabeling Assay specificity and sensitivity and LOD of the RiA assay were determined ).
Read Also: Is Whey Protein Good For Prostate
How Is The Urine Test Working To Detect Prostate Cancer
The urine test, called Mi-Prostate Score , incorporates blood PSA level and two molecular RNA markers that are considered specific for prostate cancer. Cancer occurs when genes are combined in a different, abnormal way. This test looks for these combinations, that are considered risk signatures, or biomarkers, for prostate cancer.
One marker is a snippet of RNA made from a gene that is overactive in almost all prostate cancers. The second biomarker is considered to be an abnormal fusion between two genes: . The presence of these two biomarkers, or just one, in the urine, can accurately diagnose prostate cancer.
This revolutionary test is not only useful for prostate cancer screening, but also for prostate cancer prediction. It is surprising that this test can predict prostate cancer progression years before it can be detected using other diagnostic methods.
The purpose of developing new tests to detect and determine the location and treatment of prostate cancer is to provide doctors with better technology that makes them able to analyze the genetic makeup of tissue from a biopsy. When a man is told his PSA level is elevated, he wants to know exactly what needs to be done in order to prevent any spread of cancer and to reduce side effects as much as possible. These new tests, especially the urine test, represent medical advancements doctors will rely on when diagnosing and predicting prostate cancer progression.
Advantages Of Tgia And Ria Assays Over Current Urine Cytology Assays
As described, both assays provide a very high level of detection sensitivity . In comparison, the conventional urine cytology tests such as IFA or colorimetric microscopic assays for the detection of urinary PCa cells can only achieve a minimum sensitivity of about 103 cells/mL of the original urine sample, as the traditional cytospin approach requires at least one thousand cells for consistent cell capture from urine, which is often not present in PCa urine specimens. Capturing low numbers of PCa cells from urine using the described filter membrane adapted from the method of Nickens et al.. is an important aspect of this work in increasing the applicability of the TiGA cytology assay whereas the RiA does not require cell capture. Eskra et al. have concluded that while cytology techniques can deliver high specificity, the low sensitivity represents a severe limitation to the practicability of the current approaches. The two new urine cytology assays described in the manuscript offer the specificity of the MIL 38 antibody for the Glypican antigen expressed in PCa cells with the increased sensitivity derived from the improved cell detection technologies described.
Dont Miss: Monoclonal Antibodies For Prostate Cancer
Read Also: What Causes Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Factors In Prostate Cancer Risk For Black Men
The researchers noted that biological and societal causes account for the poorer outcomes for Black men diagnosed with prostate cancer.
Some patients are hard to convince of the importance of screening and preventive medicine, especially if they are healthy, says Dr. Ahmed Eldefrawy, a urologic oncologist with Miami Cancer Institute, part of Baptist Health South Florida.
Lack of trust in the healthcare system can be seen sometimes, which is understandable given the historical events that happened in the Black population in the past, he told Healthline. Prostate cancer can have no symptoms for many years, losing valuable time when the cancer is curable.
Lack of access is another critical factor and it is far more important in treating advanced diseases, Eldefrawy continued. There are several treatment options for advanced prostate cancer that aim at controlling the disease for years. However, lack or even delay in access to health care can adversely affect the outcome.
Another factor, in my opinion, is patients understanding of the magnitude of the problem and the long-term outcome, he noted. Prostate cancer is slow-growing cancer, a slow killer. It is still lethal cancer even if it will not kill you in a year or two.
The reasons for these differences are multifactorial, but some prostate cancers in Black men have a different genetic profile from the cancers found in other groups, he told Healthline.
Positron Emission Tomography Scan
A PET scan is similar to a bone scan, in that a slightly radioactive substance is injected into the blood, which can then be detected with a special camera. But PET scans use different tracers that collect mainly in cancer cells. The most common tracer for standard PET scans is FDG, which is a type of sugar. Unfortunately, this type of PET scan isnt very useful in finding prostate cancer cells in the body.
However, newer tracers, such as fluciclovine F18, sodium fluoride F18, and choline C11, have been found to be better at detecting prostate cancer cells.
Other newer tracers, such as Ga 68 PSMA-11, 18F-DCFPyl , and Ga 68 gozetotide , attach to prostate-specific membrane antigen , a protein that is often found in large amounts on prostate cancer cells. Tests using these types of tracers are sometimes referred to as PSMA PET scans.
These newer types of PET scans are most often used if its not clear if prostate cancer has spread. For example, one of these tests might be done if the results of a bone scan arent clear, or if a man has a rising PSA level after initial treatment but its not clear where the cancer is in the body. PSMA PET scans can also be used to help determine if the cancer can be treated with a radiopharmaceutical that targets PSMA.
Doctors are still learning about the best ways to use these newer types of PET scans, and some of them might not be available yet in all imaging centers.
Recommended Reading: Is Sex Good For Enlarged Prostate
A Tough Path To The Clinic
Implementing this pre-biopsy testing in clinical practice may not yet be practical because of the limited availability of the T2:ERG test, Dr. Srivastava said.
But Dr. Sanda is hopeful that, based on the studys findings, that may change. Nevertheless, the situation demonstrates that even well-conducted, definitive biomarker studies are really just one step on the pathway to in clinical practice, he added.
This type of work is a key next step to further enhance the utility of urinary markers to refine detection of aggressive prostate cancer, Dr. Srivastava said.
New Urine Test Id’s Prostate Cancer

Genetic Test Finds Prostate Cancer, but Can’t Tell if It’s Deadly
Nov. 28, 2006 – A new urine test can tell prostate cancer from an enlarged prostate — but can’t tell whether the cancer is deadly.
The test, from San Diego-based Gen-Probe, is approved in some European countries but not in the U.S. It detects genetic material — RNA — from prostate cancer gene 3 or PCA3.
PCA3 is found only in the prostate. When prostate cells become cancerous, their PCA3 genes go wild. Prostate cancer cells express 60 to 100 times more PCA3 RNA than normal cells.
That means the PCA3 test can do things the current PSA test can’t do. The PSA test detects prostate-specific antigen, a protein given off by all prostate cells. If a man has an enlarged prostate — a noncancerous condition called benign prostatic hyperplasia or BPH — his PSA level can go up. This often triggers unnecessary biopsies and, sometimes, unnecessary surgery.
“The beauty of this test is it seems to be independent of the BPH component,” Mark Emberton, MD, of the Institute of Urology at University College London, tells WebMD. “But it is not a perfect test. It does not rule out — or rule in — clinically meaningful disease.”
Emberton, who has no financial links to Gen-Probe, reported several studies of the PCA3 test at last week’s annual meeting of the British Association of Urological Surgeons in London.
You May Like: Effects Of Removing Prostate Gland
Prostate Cancer Leading Cause Of Death Among Costa Rican Men
Moreover, difficulties in achieving an erection , pain in the hips, back , chest , weakness or numbness in the legs or feet, or even loss of bladder or bowel control.
The spokesman for the College of Pharmacists of Costa Rica, Larry Ramirez, told CRHoy.com that in its initial stage, this type of cancer does not show any symptoms, but they begin to appear in a more advanced stage.
For this reason, he stressed the importance of annual medical check-ups, which are often neglected by men due to shame, male chauvinism, fear, misinformation or being the object of ridicule.
We consider it very important that as a society we work on the social stigmas related to these tests. Masculinity and virility in this case should be focused on looking after the mans own health and wellbeing, Ramirez said.
He reminded that, in order to detect the disease, two tests are necessary, at least once a year: a blood test for prostatic antigen, and the other, which he described as fundamental, a rectal examination by an urologist, which, when performed in time, increases the probabilities of survival.
jg/aph/mem/ale
Most Read In Health News
©News Group Newspapers Limited in England No. 679215 Registered office: 1 London Bridge Street, London, SE1 9GF. “The Sun”, “Sun”, “Sun Online” are registered trademarks or trade names of News Group Newspapers Limited. This service is provided on News Group Newspapers’ Limited’s Standard Terms and Conditions in accordance with our Privacy & Cookie Policy. To inquire about a licence to reproduce material, visit our Syndication site. View our online Press Pack. For other inquiries, Contact Us. To see all content on The Sun, please use the Site Map. The Sun website is regulated by the Independent Press Standards Organisation
Our journalists strive for accuracy but on occasion we make mistakes. For further details of our complaints policy and to make a complaint please click this link: thesun.co.uk/editorial-complaints/
Don’t Miss: What Are The Side Effects Of Super Beta Prostate
How Does Prostate Cancer Screening Work
A doctor can usually perform a prostate cancer screening in an examination room at their office.
To complete a PSA test, a medical professional will take a blood draw and send it to a lab. A doctor can help you prepare for the blood draw. Results are usually available after a few days.
Similarly, a PCA3 test will require you to provide a urine sample. The doctor will send the sample to a lab and get the results back in a few days.
A DRE does not require a lab, so your doctor can provide immediate feedback.
In the early stages, prostate cancer usually doesnt have any symptoms. By the time you notice symptoms, the cancer can advance, making treatment much more difficult.
Before screening became available, one of the most common ways people discovered their prostate cancer was paralysis after the cancer spread to the spine.
So, the main benefit of screening is the ability to detect the disease at an early stage when it is more easily and effectively treatable. Screening can reduce your risk of death from prostate cancer by
You May Like: How Is Prostate Cancer Diagnosed
Why Aren’t Men Screened
A PSA test can give confusing results, which is why routine prostate screening is not yet offered to men.
About 75% or three in every four men who get a positive PSA test result are not found to have cancer when they go for a follow-up biopsy.
And PSA misses the cancer in about 15% of men with prostate cancer.
It also cannot show whether a cancer will probably go on to cause harm.
Read Also: At What Age Should You Have Your Prostate Checked
From Abnormal Result To Unnecessary Biopsy
With many organizations now recommending against routine screening for prostate cancer with the PSA test, its use has , as has the number of prostate biopsies and prostate cancer surgeries.
PSA testing can help identify men who may have prostate cancer. However, the test cannot help distinguish slow-growing, or indolent, cancers that are unlikely to ever cause a man harm from aggressive, potentially lethal cancers.
One of the biggest challenges for researchers has been identifying a way to screen for prostate cancer that can differentiate between indolent and potentially life-threatening cancers.
One approach being tested is to develop ways to better triage care decisions following an abnormal PSA test, including making more informed decisions about whether to pursue a biopsy. Prostate biopsies have risks, including pain, bleeding, and potentially serious infections. And the resulting overdiagnosis and overtreatment of indolent prostate cancers identified via biopsy have their own harms and costs.
The risk of overtreatment remains a valid concern due to the impact of treatment on quality of life, the American Urological Association noted in its most recent consensus statement on PSA screening. These effects can include lasting impairment in urinary, bowl, and sexual function, the statement explains, as well as potential and long-lasting psychological harms.
