Role Of Terminologies In Health Care
A terminology is the body of terms used with a particular technical application in a subject of study, theory, or profession. Terminologies vary in their purposes, scopes, and structures. This is especially true in health care where there is a high degree of specialization. Although there exists a nearly universal terminology for human anatomy that is taught to a variety of health professions, there is a wide array of specialized terminologies used in health-care settings. Nursing, for example, has three major terminologies: NANDA International , the Nursing Interventions Classification , and the Nursing Outcomes Classification . The nursing terminologies provide sets of terms to describe nursing judgments, treatments, and nursing-sensitive patient outcomes.
Terminologies in health-care support the documentation of observations, treatments, and outcomes that clinicians put in the patient chartwhich is increasingly performed using electronic health record systems. Although there exist a fair number of major or standard terminologies like the NIC and NOC, there are many more terminologies developed for specific purposes. A local terminology is one that is created for a specific purpose by a single organization, such as a laboratory, hospital, clinic, or pharmacy. For example, a local terminology may be used by the laboratory supporting a large health system to provide user friendly terms to physicians who order the tests.
Andreas Charalambous, … Daniel Kelly, in, 2018
Nursing Care Plan For Prostate Cancer 3
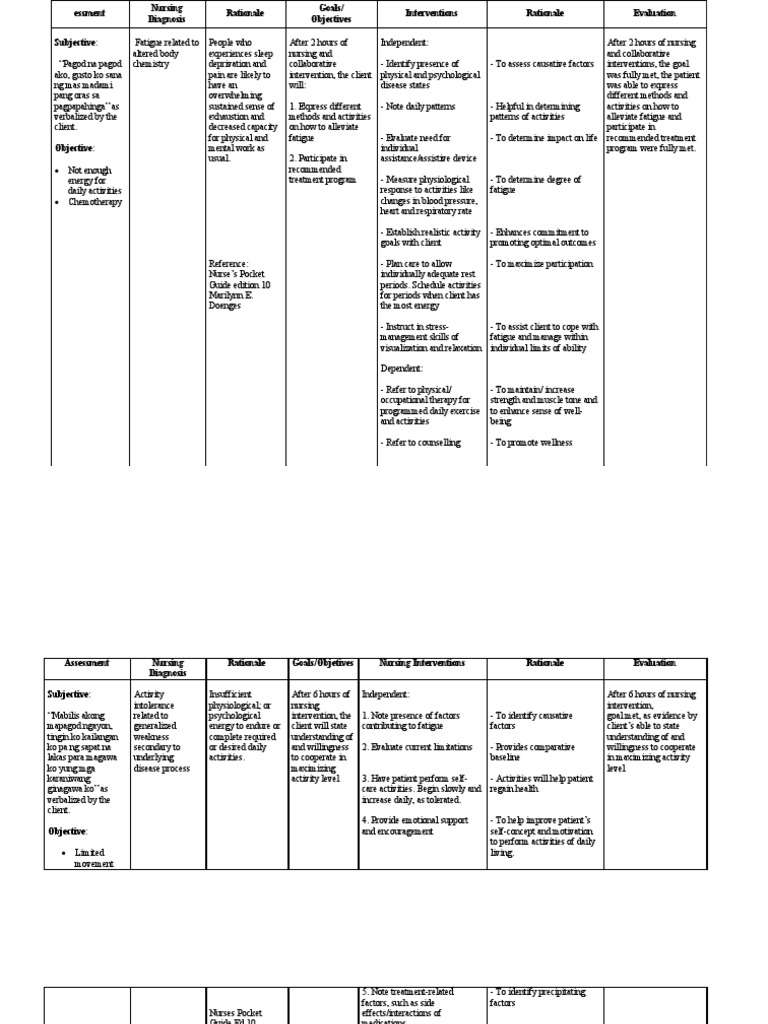
Nursing Diagnosis: Risk for Deficient Fluid Volume related to difficulty controlling bleeding, restricted intake preoperatively, post-obstructive diuresis, and vascular nature of surgical area secondary to prostate cancer.
Desired Outcomes:
To view this video please enable JavaScript, and consider upgrading to a web browser thatsupports HTML5 video
- The patient will demonstrate adequate hydration as evidenced by stable vital signs, palpable peripheral pulses, excellent capillary refill, moist mucosal membranes, and urine output within the normal range.
- The patient will demonstrate the absence of active bleeding.
Prevention Of Prostate Cancer
The following measures can help prevent or decrease the risk of developing prostate cancer.
- Consume a healthy diet. A diet reduced in dairy and calcium, for example, may help minimize the risk of prostate cancer. The following foods may help reduce the risk of prostate cancer: broccoli, brussels sprouts, and kale, fish, soy, olive oil, which contains omega-3 fatty acids.
- Choose healthy foods over supplements. To date, no studies reported a decreased risk of prostate cancer with supplement use. As an alternative, eat meals that are high in vitamins and minerals to keep the vitamin levels in check.
- Exercise regularly. Exercise can also help the patient reduce weight, which is important because obesity has been linked to prostate cancer according to a 2016 study. Aim for 30 minutes of exercise most days of the week with the doctors consent.
- Consult with the healthcare provider regarding the risk of developing prostate cancer. According to certain studies, 5-alpha reductase inhibitors such as finasteride and dutasteride may reduce the overall risk of prostate cancer. These medications are intended to prevent prostate enlargement and hair loss.
However, some evidence suggests that men who take these drugs may be at a higher risk of developing a more serious form of prostate cancer . Advise the patient to check with the doctor if he/she is concerned about the risk of developing prostate cancer.
You May Like: What Is The Natural Cure For Prostate Cancer
Treatment For Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Treatment for BPH involves pharmacologic and surgical interventions and they are the following:
> > > All Natural Technique Fixes Enlarged Prostate Watch Here< <
Surgical procedures to remove the diseased prostate are usually necessary. Surgical procedures are not always necessary. If the disease is caused by bacterial infections, a doctor can treat the symptoms using alpha-blockers or surgery. Physical therapy, relaxation exercises, and warm baths are all recommended. A physician may also prescribe antibiotics to cure the infection. A bacterial infection can also cause a recurrence of the condition.
An enlarged prostate can be uncomfortable for both men and women. Some of the symptoms of an enlarged male reproductive organ include a weakened urine stream, urgent need to urinate, and urinary tract infections. BPH can also cause damage to the kidneys. A sudden inability to urinate can be life-threatening, as it can lead to bladder and kidney damage. Unfortunately, most men with enlarged prostrates put up with the symptoms for years before they seek treatment. However, many of the men with symptoms finally decide to go to a doctor for proper gynecological evaluation and to begin enlarged prostatic therapy.
Read Also: What Is A Prostate Massage
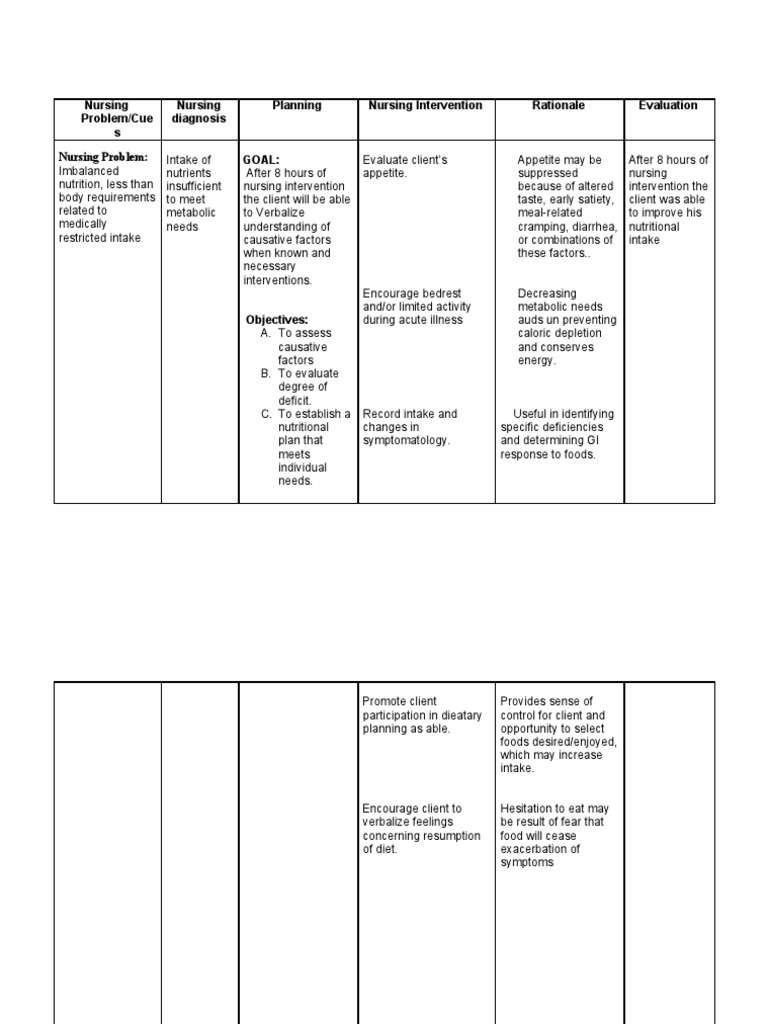
Nursing Diagnosis Prostate Cancer
Nursing Diagnosis: Impaired Urinary Elimination related to mechanical obstruction , catheter/balloon pressure and irritation, loss of bladder tone due to preoperative overdistension or prolonged decompression secondary to prostate cancer as evidenced by urgency, hesitation, dysuria, incontinence, retention, suprapubic soreness, and bladder fullness
Desired Outcomes:
There Are Different Types Of Treatment For Patients With Prostate Cancer
Different types of treatment are available for patients withprostate cancer. Some treatments are standard , and some are being tested in clinical trials. A treatment clinical trial is a research study meant to help improve current treatments or obtain information on new treatments for patients with cancer. When clinical trials show that a new treatment is better than the standard treatment, the new treatment may become the standard treatment. Patients may want to think about taking part in a clinical trial. Some clinical trials are open only to patients who have not started treatment.
Also Check: Does Ginseng Affect The Prostate
Interventions By Cancer Type Or Radiation Site
Breast radiation: Advise the patient to avoid bras with underwires, nylon, or lace. Instead, recommend a breathable cotton bra or camisole. Tell patients they may use deodorant but should avoid shaving the armpits to avoid skin irritation.
Head or neck: If the patient complains of dry mouth, suggest an oral mouthwash, such as a solution of 1 qt of water, 1 tsp of salt, and 1 tsp of baking soda. Instruct the patient to swish it in the mouth and spit it out, repeating several times a day. Some patients may need a prescription mouthwash. If appropriate, advise patients to see a dentist before radiation treatment starts to check for severely decayed teeth or an oral infection, as these could be a source of infection during treatment.
Brain tumor: Assess the patient for neurologic impairment, such as a change in level of consciousness, speech, vision, balance, or strength. Check for numbness, tingling, and seizures. Recognize that any change from baseline assessment findings requires intervention.Bone involvement: Assess the patients pain level effectiveness of pain management interventions and extremity strength, numbness, tingling, and range of motion. Caution patients that a bone tumor impairs bone integrity, setting the stage for fractures.
Pelvic cancer: For younger patients with pelvic cancers , provide information about sexuality and possible infertility before radiation treatment begins. As appropriate, teach them about banking sperm or egg-harvesting options.
Risk For Deficient Fluid Volume
Chronic retention is commonly referred to as either high or low-pressure retention. High-pressure chronic retention commonly occurs in bladder outflow obstruction as a result of high detrusor pressures required to overcome the obstruction. The persistence of this high pressure causes reflux and subsequent hydronephrosis. Over time this can result in an insidious deterioration in renal function. Following catheterization, the client may undergo post-obstructive diuresis characterized by increased urine output in the following 24 to 72 hours.
You May Like: When To Get Prostate Test
Keeping Personal Health Records
You and your doctor should work together to develop a personalized follow-up care plan. Be sure to discuss any concerns you have about your future physical or emotional health. ASCO offers forms to help keep track of the cancer treatment you received and develop a survivorship care plan when treatment is completed.
This is also a good time to talk with your doctor about who will lead your follow-up care. Some survivors continue to see their oncologist, while others transition back to the care of their primary care doctor or another health care professional. This decision depends on several factors, including the type and stage of cancer, side effects, health insurance rules, and your personal preferences.
If a doctor who was not directly involved in your cancer care will lead your follow-up care, be sure to share your cancer treatment summary and survivorship care plan forms with them and with all future health care providers. Details about your cancer treatment are very valuable to the health care professionals who will care for you throughout your lifetime.
The next section in this guide is Survivorship. It describes how to cope with challenges in everyday life after a cancer diagnosis. Use the menu to choose a different section to read in this guide.
Diagnosis Of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Diagnosing BPH involves a variety of techniques and are listed below:
- Digital rectal examination DRE is the most significant part of a physical exam when diagnosing BPH. The healthcare provider can easily assess for size, contour, presence of nodules or areas suggestive of malignancy, just by performing this exam.
Laboratory studies involves the following:
- Urinalysis utilized to assess for presence of bacteria, blood, WBCs, protein or glucose that can suggest for urinary retention caused by BPH.
- Urine culture Utilized to exclude infections of the urinary tract when abnormal findings where first detected in urinalysis
- Prostate-specific antigen PSA is an enzyme and cancer marker for Prostate cancer. Though BPH does not cause prostate cancer, men with the former diagnosis are also at risk for the latter.
- Electrolytes, Blood urea nitrogen and creatinine These studies are useful to evaluate renal health, especially for those patients who have high post void residual urine volumes.
- Ultrasound Ultrasound of the whole abdomen, including the kidneys and thru the transrectal approach will help to evaluate the bladder, prostate size, and signs of renal insufficiency.
- Endoscopy of the lower urinary tract Involves the direct visualization of the structures to assess for internal structures.
Other tests include:
Also Check: Secondary Cancers From Prostate Cancer
Prostate Cancer: A Guide To Diagnosis
Key learning points:
Prostate cancer is the most common cancer in men
Current diagnostic tests for prostate cancer can give false negatives and false positives and are therefore currently unsuitable for a national screening programme
Men need support to make an informed decision on whether or not to be tested for prostate cancer
Prostate cancer is the most common cancer in men. Every year over 44,000 men are diagnosed with the disease in the UK and it kills more than 10,000. With no national screening programme, diagnosing prostate cancer remains one of the biggest challenges facing health professionals.
Nurses play a vital role in ensuring that all men concerned about prostate cancer are armed with the information they need to make an informed decision about testing.
Signs and symptoms
Most early stage prostate cancers do not cause any symptoms, mostly because either the tumour is small or in the outer part of the prostate and is therefore not putting any pressure on the urethra.
Risk factors
Due to the fact that most men with early stage prostate cancer will not have any symptoms, being aware of a mans risk is essential. There are three key risk factors to think about:
1. What is the mans ethnicity?
We know that in the UK one in four black men will be diagnosed with prostate cancer, which is double the risk of a white man .
2. Does he have a family history of prostate cancer?
3. How old is he?
What to do after an assessment?
The pros and cons of the PSA test
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Bph Nursing Care Plans Diagnosis And Interventions
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia NCLEX Review and Nursing Care Plans
The prostate is a walnut-shaped organ located between the male penis and bladder.
Its primary function is the production of seminal fluid, which serves as the transport medium of the sperm during intercourse.
In benign prostatic hyperplasia or benign prostatic hypertrophy, the prostate enlarges and in turn causes obstruction problems.
Because of its anatomical placement, urinary problems arise which in turn significantly affects the patient.
The condition is more common in men above 50 years of age.
Also Check: Do Women Have A Prostate Gland
Signs Of Prostate Cancer Include A Weak Flow Of Urine Or Frequent Urination
These and other signs and symptoms may be caused by prostate cancer or by other conditions. Check with your doctor if you have any of the following:
- Weak or interrupted flow of urine.
- Sudden urge to urinate.
- Frequent urination .
- Trouble starting the flow of urine.
- Trouble emptying the bladder completely.
- Pain or burning while urinating.
- Blood in the urine or semen.
- A pain in the back, hips, orpelvis that doesn’t go away.
- Shortness of breath, feeling very tired, fast heartbeat, dizziness, or pale skin caused by anemia.
Other conditions may cause the same symptoms. As men age, the prostate may get bigger and block the urethra or bladder. This may cause trouble urinating or sexual problems. The condition is called benign prostatic hyperplasia, and although it is not cancer, surgery may be needed. The symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia or of other problems in the prostate may be like symptoms of prostate cancer.
Certain Factors Affect Prognosis And Treatment Options
The prognosis and treatment options depend on the following:
- The stage of the cancer .
- The patients age.
- Whether the cancer has just been diagnosed or has recurred .
Treatment options also may depend on the following:
- Whether the patient has other health problems.
- The expected side effects of treatment.
- Past treatment for prostate cancer.
- The wishes of the patient.
Most men diagnosed with prostate cancer do not die of it.
Also Check: Does Cialis Shrink An Enlarged Prostate
Prostate Cancer Nursing Care Plans Diagnosis And Interventions
Prostate Cancer NCLEX Review and Nursing Care Plans
Prostate cancer is the most often diagnosed cancer in men around the world. The American Cancer Society predicts that 268,490 men in the United States will be newly diagnosed with prostate cancer in 2022.
The prostate is a tiny gland that lies behind the bladder and surrounds the urethra in a mans lower abdomen and is controlled by the hormone testosterone.
The prostate gland also generates seminal fluid, also called semen. The sperm-containing substance that escapes the urethra during ejaculation is known as sperm.
Prostate cancer occurs when an abnormal, malignant growth of cells, known as a tumor, arises in the prostate. As the disease progresses, these tumor cells have the potential to spread to other parts of the body.
Because the cancer is made up of prostate cells in these circumstances, it is still called prostate cancer.
> > > One Crazy Prostate Trick All Men Over 40 Should Try
Symptomatic treatment of an enlarged prostate usually involves a combination of medication and lifestyle changes. A diet rich in fruits and vegetables may be the best option if you suffer from chronic urination. It will help the body adjust to the increased size of the prostate. Also, taking regular urination intervals will help retrain the bladder to function properly. Inactivity also contributes to urine retention, and cold temperatures can increase the urge to urinate.
Invasive treatment of enlarged prostate includes medication that relieves the pressure on the urethra and bladder. However, if the condition is severe, it may require surgical intervention. If treatment is not successful, the enlarged prostate can become a potentially life-threatening disease. As the hormone levels in the body change, the enlarged prostate can lead to various complications, including urinary retention and even cancer. This is why it is critical to see a doctor for further evaluation.
A physician can recommend a number of treatments to address an enlarged prostate. An enlarged prostate will require surgery to relieve the symptoms. In most cases, surgical treatment for an enlargement of the penis is enough. Moreover, a doctor may recommend a course of treatment based on symptoms. A TURP procedure is not painful and requires less recovery time than open surgery. The recovery period will be shorter and less traumatic.
Don’t Miss: What Are The Risk Factors Associated With Prostate Cancer
> > > This Simple Morning Test Will Fix Your Prostate
Another type of prostate issue is chronic prostatitis, or chronic pelvic pain syndrome. This condition causes pain in the lower back and groin area, and may cause urinary retention. Symptoms include leaking and discomfort. In severe cases, a catheter may be required to relieve the symptoms. If the problem is unresponsive to other treatments, your doctor may suggest a surgical procedure. If these do not work, your symptoms could progress and become chronic.
An acute bacterial infection can cause a burning sensation. Inflammation of the prostate can affect the bladder and result in discomfort and other symptoms. This is the most common urinary tract problem in men under 50, and the third most common in men over 65. The symptoms of acute bacterial prostatitis are similar to those of CPPS. Patients may experience a fever or chills as a result of the infection.
A bacterial infection can also lead to prostate issues. Acute bacterial infections can be hard to treat. Some men with a bacterial infection may need to take antibiotics to prevent or treat symptoms. Symptoms of the disease include fever and chills, pain in the lower back and the tip of the penis. Some men may have blood in the urine, frequent urination, and blood in the urine. If you suffer from acute bacterial prostatitis, a medical professional should be able to prescribe you the appropriate treatments to prevent the disease.
