> > > This Simple Morning Test Will Fix Your Prostate
Another type of prostate issue is chronic prostatitis, or chronic pelvic pain syndrome. This condition causes pain in the lower back and groin area, and may cause urinary retention. Symptoms include leaking and discomfort. In severe cases, a catheter may be required to relieve the symptoms. If the problem is unresponsive to other treatments, your doctor may suggest a surgical procedure. If these do not work, your symptoms could progress and become chronic.
An acute bacterial infection can cause a burning sensation. Inflammation of the prostate can affect the bladder and result in discomfort and other symptoms. This is the most common urinary tract problem in men under 50, and the third most common in men over 65. The symptoms of acute bacterial prostatitis are similar to those of CPPS. Patients may experience a fever or chills as a result of the infection.
You May Like: Blood Clots In Urine After Prostate Surgery
Treatment Procedure And Collection Of Treatment Plan Data
For the patients in Group 1, 248 out of 255 treatment plans were created using a 3DCRT technique with typically one anteriorposterior field and two opposed lateral fields . All fields had a photon beam energy of 15 MV and were individually shaped with a multi-leaf collimator and wedges were used, whenever judged to be appropriate. Seven treatment plans in Group 1 were 7-field IMRT plans with a photon beam energy of 6 MV. For the patients in Group 2, all 253 treatment plans were created using a VMAT technique with two 360-degree arcs each using a photon beam energy of 6 MV.
The prescribed dose was in all cases 70 Gy in 2-Gy fractions . Treatment plan objectives included that the PTV should be covered by the 95% isodose and that the CTV mean dose should be 70 Gy. For patients in Group 1, the planning instructions were to minimize the rectal dose. In Group 2, the rectal treatment planning objectives were to keep the relative rectal volume receiving at least 35 Gy below 50% and that the relative rectal volume receiving at least 63 Gy should be minimized. The dose levels of 35 and 63 Gy correspond to 50 and 90% of the 70-Gy prescription dose, respectively. Figure 1 shows a sagittal view of one 3DCRT ST treatment plan and of one VMAT ST treatment plan.
Fig. 1
Etical approval was granted as indicated in the article.
> > > One Crazy Prostate Trick All Men Over 40 Should Try
Symptomatic treatment of an enlarged prostate usually involves a combination of medication and lifestyle changes. A diet rich in fruits and vegetables may be the best option if you suffer from chronic urination. It will help the body adjust to the increased size of the prostate. Also, taking regular urination intervals will help retrain the bladder to function properly. Inactivity also contributes to urine retention, and cold temperatures can increase the urge to urinate.
Invasive treatment of enlarged prostate includes medication that relieves the pressure on the urethra and bladder. However, if the condition is severe, it may require surgical intervention. If treatment is not successful, the enlarged prostate can become a potentially life-threatening disease. As the hormone levels in the body change, the enlarged prostate can lead to various complications, including urinary retention and even cancer. This is why it is critical to see a doctor for further evaluation.
Also Check: Prostate Health Foods To Eat And Foods To Avoid
Also Check: How To Touch My Prostate
Does Prostate Radiation Affect The Colon
Radiotherapy for prostate cancer can cause bowel problems for some men. Radiation can cause the lining of the bowel to become inflamed which then leads to symptoms such as: loose and watery bowel movements
How long does rectal bleeding last after radiation?
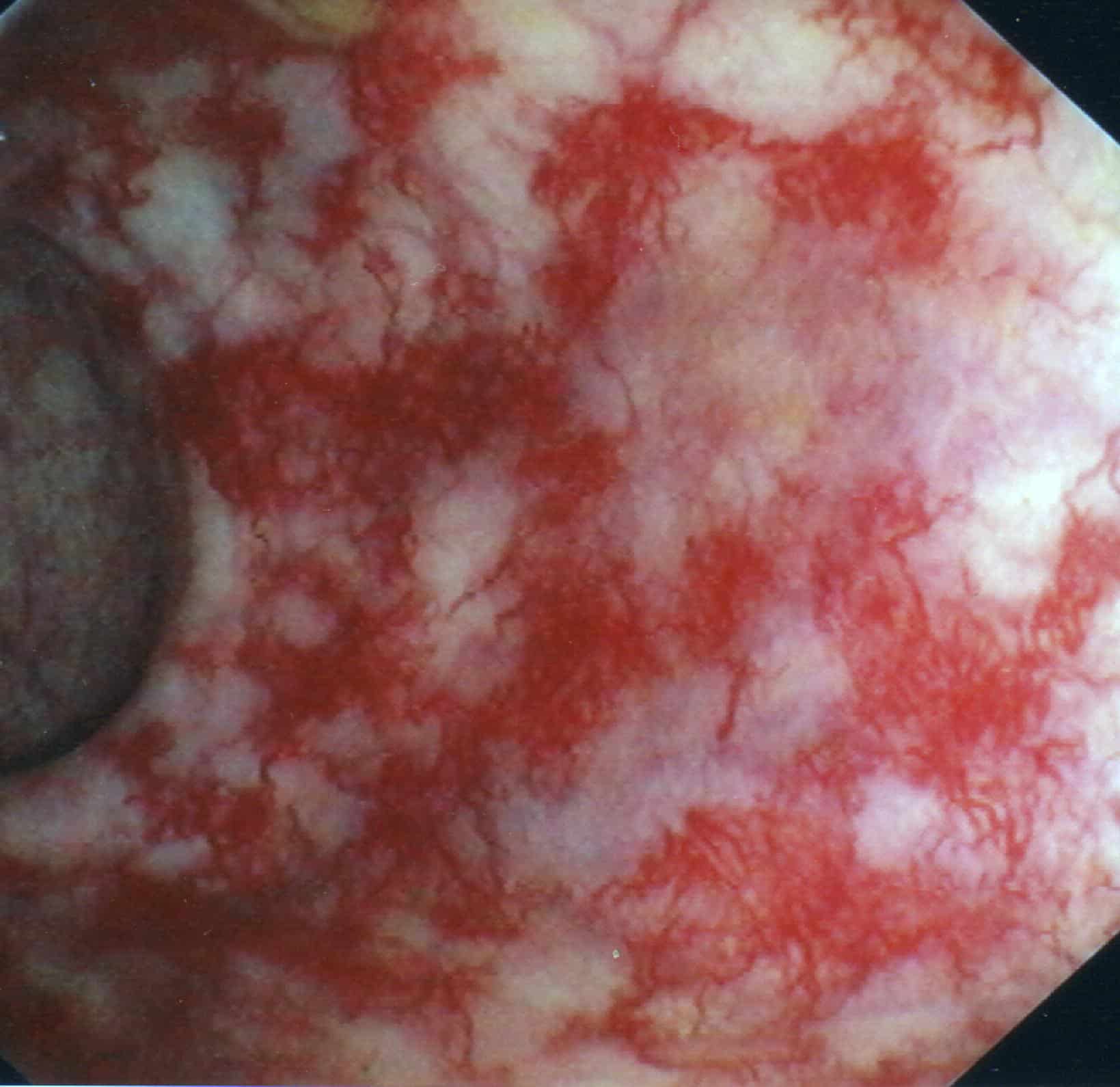
The severity of bowel dysfunction symptoms But 23% of men who undergo modern radiation therapy for prostate cancer will suffer from the most severe bowel dysfunction symptoms, like rectal bleeding. In some cases, rectal bleeding can last for months or even years after radiation therapy is completed.
How long does rectal bleeding last after prostate?
All of 12 patients treated with APC showed improvement within 2 months and bleeding stopped in 5 patients . However, 2 or 3 sessions of treatment were needed to stop or relieve bleeding in 5 patients .
Incidence Of Rectal Bleeding In Contemporary Studies
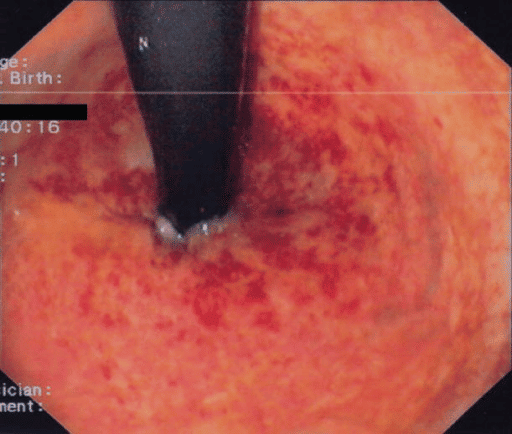
Table summarizes the results of contemporary studies that examined the incidence of late rectal complications after prostate brachytherapy. It should be emphasized that the lack of uniform reporting criteria make it difficult to directly compare the rates of late rectal complications after brachytherapy.
| Study |
|---|
This chart illustrates long-term rectal complication rates for patients with localized prostate cancer treated with permanent interstitial seed implantation from 1998 to 2006 at The University of Texas M. D. Anderson Cancer Center.
Similarly, our finding that late rectal complications tend to occur within the first 2 years after implantation agrees with findings from other studies. For example, Snyder et al and Kaye et al reported no episodes of chronic radiation proctitis after the third year postimplantation., Gelblum and Potters reported a peak incidence of rectal complications at 8 months after implantation, and no patients had rectal symptoms at 42 months. Snyder et al observed an increased incidence of radiation proctitis the first year after implantation 14% of their patients developed symptoms in the first year, and 72% had symptoms in the second year, whereas the majority reported symptom resolution after the third year. Likewise, Hu and Wallner observed that no patients developed rectal bleeding after 28 months.
You May Like: How Long Can A Prostate Infection Last
Faq: Radiation Therapy For Prostate Cancer
Why would I choose radiation therapy?
Radiation therapy, including external beam radiation therapy and brachytherapy, is an alternative form of treatment for prostate cancer. EBRT may be used after other treatments, such as surgery, to manage cancer that has recurred or is at high risk of recurrence. Radiation therapy has an excellent record of success, providing long-term disease control and survival rates equivalent to other treatments, including surgery.
How should I expect to feel during radiation therapy?
Undergoing external beam radiation therapy is similar to having a routine X-ray. Radiation cannot be seen, smelled or felt. Generally, side effects don’t appear until the second or third week of treatment. Because radiation therapy is a local treatment, only the areas of the body where it is directed will experience side effects. Most patients will experience some or all of the following:
- Increase in the frequency of urination
- Urinary urgency
- Softer and smaller volume bowel movements
- Increased frequency of bowel movements
- Worsening of hemorrhoids or rectal irritation with occasional scant blood and fatigue
Many questions may arise during radiation therapy treatment. Your doctors will be available to answer questions throughout your treatment.
How should I expect to feel after radiation therapy?
Swelling Bruising Or Tenderness Of The Scrotum
Symptoms generally resolve on their own within three to five days. Oral anti-inflammatory medications such as ibuprofen are usually sufficient for pain relief, if necessary. You should avoid hot tubs and Jacuzzis for at least two to three days after the procedure. Postpone bike riding until the tenderness is gone.
Also Check: How Do You Do A Prostate Ultrasound
Prostate Radiation Vs Robotic Prostatectomy
It is not possible to decide which treatment is better or more effective radiation or robotic prostatectomy, due to the fact that everybody has different stages of prostate cancer and other health-related issues. Below are enumerated pros and cons for each type of treatment, but every patient needs to take into account what his doctor is telling and suggesting.
Change In Radiation Dose Distribution May Reduce Late Rectal Bleeding
We were unable to process your request. Please try again later. If you continue to have this issue please contact .
Men with shorter rectums who receive intermediate to high doses of radiation are more likely to experience rectal bleeding following radiation treatment for prostate cancer, according to study findings presented at the Annual Meeting of the American Association of Physicists in Medicine.
Thus, considering rectum length and radiation therapy dose may help predict a patients risk for experiencing late rectal bleeding, which occurs in approximately one in 10 men with prostate cancer who undergo radiation, according to the researchers.
Radiation dose distribution can be designed for each individual patient, and while it covers the prostate, it often comes in contact with the rectum or the bladder too, study researcher Joseph O. Deasy, PhD, chair of the department of medical physics at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, said during a press conference. By reducing the dose to the edge of the area being irradiated in men with shorter rectums, possibly using better treatment image guidance, we can significantly reduce the risk of late-stage rectal bleeding.
The researchers identified 1,001 men who were treated with a variety of radiation therapy techniques for prostate cancer . The men received between 70 Gy to 86 Gy at 2 Gy per fraction between 1991 and 2007 at five participating hospitals.
Read Also: Where Is A Mans Prostate
You May Like: How To Cure Prostate Enlargement
What Are The Odds You Will Get Prostate Cancer
What are Prostate Cancer Risk Factors? One man in six will get prostate cancer. But which men and why? What makes some men predisposed to prostate cancer, while others are never diagnosed? Age, race, lifestyle, family history, where you live, and what you eat can be risk factors. Having one or more of the risk factors described on this page is not a guarantee that you will get prostate cancer, but it does mean your chances of developing prostate cancer are higher.
Prostate Seed Brachytherapy Or High Dose Rate Radiation
SHORT TERM
Immediately after the procedure, patients may have some perineal discomfort and even some bruising for a few days. Patients often experience increased urinary frequency, urgency, weak stream and nighttime urination. These effects are at their greatest for 4-6 weeks after brachytherapy and will dissipate over the following 3-6 months.
LONG TERM
Late effects are much less common than early effects, but can be more serious and long lasting. Urinary stricture or incontinence are rare, but can occur particularly in patients who have significant urinary problems prior to treatment. Loss of potency can occur and is directly related to the patients age and erectile function prior to treatment. Rectal inflammation, called proctitis, can occur, but infrequently becomes serious enough to require treatment.
Read Also: Can Pelvic Ultrasound Detect Prostate Cancer
Proton Beam Radiation Therapy
Proton beam therapy focuses beams of protons instead of x-rays on the cancer. Unlike x-rays, which release energy both before and after they hit their target, protons cause little damage to tissues they pass through and release their energy only after traveling a certain distance. This means that proton beam radiation can, in theory, deliver more radiation to the prostate while doing less damage to nearby normal tissues. Proton beam radiation can be aimed with techniques similar to 3D-CRT and IMRT.
Although in theory proton beam therapy might be more effective than using x-rays, so far studies have not shown if this is true. Right now, proton beam therapy is not widely available. The machines needed to make protons are very expensive, and they arent available in many centers in the United States. Proton beam radiation might not be covered by all insurance companies at this time.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Know If You Have A Swollen Prostate
How Do You Choose
Choosing which of the Prostate Cancer Treatments depends upon many factors. The type of cancer, whether or not the cancer has spread , a patients age, general health status, and prior prostate cancer treatments the patient may have undergone. There are three standard prostate cancer treatments for men with organ-confined prostate cancer: Active Surveillance, Surgery and Radiation Therapy .
We suggest consultations with several specialist who can describe the pros and cons of each prostate cancer treatment. So plan to schedule consults with experts in each field of treatment. A Urologist is a trained surgeon who can review the surgical options for a prostatectomy. A Radiologist is a medical doctor who can lead you through the options of external beam or brachytherapy, seed implants. If your cancer is more advanced, you may also want to meet with a Medical Oncologist, an expert in the treatment of various types of cancer.
Recommended Reading: Do You Have To Get A Prostate Exam
Do You Have Signs Of Prostate Cancer
What are Prostate Cancer Symptoms? To quote Wikipedia, “A symptom is a departure from normal function or feeling which is noticed by a patient, reflecting the presence of an unusual state, or of a disease.” In this case Prostate Cancer. The early stages of Prostate Cancer, usually have no signs or symptoms. So if you have symptoms, a possible sign of more advanced cancer, it is important that you be tested. Be aware that these symptoms can also be a signs of non-cancerous conditions such as BPH, Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy, or another condition known as Prostatitis. If you have symptoms, we recommend that you have them checked by a physician.
Uncertainty About Radiation For People With A Higher Risk Of Recurrence
After a diagnosis of early-stage breast cancer, radiation therapy following a lumpectomy is used to reduce the chance that the cancer will come back in the same breast. There are multiple options for breast radiation therapy, including whole-breast radiation and partial-breast radiation, Dr. Salerno said, and the decision of which treatment is most appropriate is made jointly between a patient and their radiation oncologist.
For whole-breast radiation, previous studies have shown that 3 weeks of treatment at slightly higher doses is as safe and effective as conventional whole-breast radiation over 56 weeks.
However, when the trial began a decade ago, this shorter, more intensive course of radiation, known as hypofractionated radiation therapy, had not yet been widely adopted in the United States, according to Lori Pierce, M.D., of the University of Michigan. Dr. Pierce, who was not involved with the trial, provided expert comments on the findings at the ASTRO meeting.
One reason for this slow adoption, Dr. Pierce said, was the uncertainty of whether and how to incorporate a boost of radiation for people who had a higher risk of recurrence.
You May Like: Survival Rates Of Prostate Cancer
What Are The Long Term Effects Of Prostate Radiation
One of the long-term adverse effects of radiation for prostate cancer include rectum inflammation with bleeding. Loss of energy is always accompanied by prostate cancer radiation therapy. It is not uncommon to have patients who complain of fatigue for many weeks after the treatment.
Can rectal bleeding be cured?
Some cases or rectal bleeding are easier to treat than others. Many cases of hemorrhoids can be resolved with simple lifestyle changes and home treatments. Surgery is typically performed on polyps that are found at the time of colonoscopy. These can generally be removed in the same procedure using small biopsy or snaring devices.
What is the life expectancy after prostate removal?
A man might have prostate removal surgery that has an estimated life expectancy of ten years or more and a localized, treatable cancer. Prostate removal is performed with a type of regional or general anesthesia. The person will be numb and drowsy when waking up after having prostate removal surgery performed.
> > > All Natural Technique Fixes Enlarged Prostate Watch Here< <
Surgical procedures to remove the diseased prostate are usually necessary. Surgical procedures are not always necessary. If the disease is caused by bacterial infections, a doctor can treat the symptoms using alpha-blockers or surgery. Physical therapy, relaxation exercises, and warm baths are all recommended. A physician may also prescribe antibiotics to cure the infection. A bacterial infection can also cause a recurrence of the condition.
An enlarged prostate can be uncomfortable for both men and women. Some of the symptoms of an enlarged male reproductive organ include a weakened urine stream, urgent need to urinate, and urinary tract infections. BPH can also cause damage to the kidneys. A sudden inability to urinate can be life-threatening, as it can lead to bladder and kidney damage. Unfortunately, most men with enlarged prostrates put up with the symptoms for years before they seek treatment. However, many of the men with symptoms finally decide to go to a doctor for proper gynecological evaluation and to begin enlarged prostatic therapy.
You May Like: Can Hpv Cause Prostate Cancer
Biologically Effective Dose And Rectal Bleeding In Definitive Proton Therapy For Prostate Cancer
Corresponding Author:
Ronik S. Bhangoo, Molly M. Petersen, Gabriella F. Bulman, Carlos E. Vargas, Cameron S. Thorpe, Jason Shen, William W. Wong, Jean-Claude M. Rwigema, Thomas B. Daniels, Sameer R. Keole, Steven E. Schild, Yi Rong, Todd A. DeWees Biologically Effective Dose and Rectal Bleeding in Definitive Proton Therapy for Prostate Cancer. Int J Part Ther 1 March 2022 8 : 3746. doi:
Radiopharmaceuticals That Target Psma
Prostate-specific membrane antigen is a protein that is often found in large amounts on prostate cancer cells.
Lutetium Lu 177 vipivotide tetraxetan is a radiopharmaceutical that attaches to PSMA, bringing radiation directly to the prostate cancer cells.
This drug can be used to treat prostate cancer that has spread and that has already been treated with hormone therapy and chemotherapy. The cancer cells must also have the PSMA protein. Your doctor will order a PSMA PET scan before you get this drug to make sure the cancer cells have PSMA.
This drug is given as an injection or infusion into a vein , typically once every 6 weeks for up to 6 doses.
Possible side effects
Some of the more common side effects of this drug include:
This drug can lower blood cell counts:
- A low red blood cell count can cause tiredness, weakness, pale skin, or shortness of breath.
- A low blood platelet count can lead to bleeding or bruising more easily than normal, or bleeding that is hard to stop.
- A low white blood cell count can lead to an increased risk of infections, which might show as a fever, chills, sore throat, or mouth sores.
This drug might damage the kidneys. Your doctor or nurse will likely advise you to drink plenty of fluids and to urinate often before and after getting this drug, to help protect the kidneys. Tell your doctor or nurse if you start to pass less urine than is normal for you.
Read Also: Does An Enlarged Prostate Affect A Man Sexually
