At What Point Are Prostate Cancer Patients Cured
Nov. 1, 1999 â Patients with prostate cancer whose prostate-specific antigen blood levels return to normal range and stay there for at least 5 years after radiation therapy have a high likelihood of being cured of their cancer, according to this study that appears in the Oct. 15 issue of Cancer, a journal published by the American Cancer Society.
Prostate cancer is the most common cancer in men, and the second most fatal. According to figures from the American Cancer Society, 179,300 men will be diagnosed with prostate cancer in 1999, and 37,000 will die from the disease. Although prostate cancer has few, if any, symptoms in its early stages, it is highly treatable. Therefore, the American Cancer Society recommends annual PSA screening and digital rectal examinations in all men aged 50 and older.
In patients who are diagnosed with prostate cancer and undergo treatment, including surgery or radiation therapy, PSA testing is used to determine the effectiveness of treatment. PSA levels below 4.0 are considered normal.
These authors found that patients have a high likelihood of cure if their PSA levels remain normal for about three and a half years following treatment, and rarely have treatment failure if they do well for four years after radiation therapy. In those patients in whom radiation treatment failed, 95% had increasing PSA levels during the first four years after treatment.
Show Sources
Read Also: Stage 2 Prostate Cancer Treatment
Aggressive Prostate Cancer Definition And 3 Indisputable Facts To Know
Do you know that prostate cancer can be aggressive and non-aggressive? Yes, it can and this depends on the stage in which the disease is. Prostate cancer is an abnormal growth of the cells of the prostate. These growths often lead to tumor that can metastasize to other organs of the body. Understanding the stages of the prostate cancer will enable your doctor to determine if the cancer is aggressive or not. This article defines aggressive prostate cancer and provides you with 3 indisputable facts that are linked with the condition.
3 Facts about aggressive prostate cancer
1.Aggressive prostate cancer is diagnosed on individuals whose cancers have metastasized beyond the localized region of the prostate. Biopsy, Bone scans and X-rays are applied to detect the aggressiveness of the cancer. Diagnosis for this classification of cancer is not that difficult because the symptoms are evidently seen in the patients.
Below Are Other Related Articles Among 1,000+Prostate Cancer Articles On This HUGE 4+ Year Old Prostate Cancer Victory Authority Website:
Also Check: Is There A Cure To Prostate Cancer
What Increases Your Risk
A risk is anything that makes you more likely to get a particular disease. Being older than 50 is the main risk for prostate cancer. About 6 out of 10 new prostate cancers are diagnosed in men who are 65 and older.footnote 3
Your chances of getting the disease are higher if other men in your family have had it. Your risk is doubled if your father or brother developed prostate cancer. Your risk also depends on the age at which your relative was diagnosed. Most men who get prostate cancer have no family history of the disease.
Don’t Miss: How Many Stages Of Prostate Cancer Are There
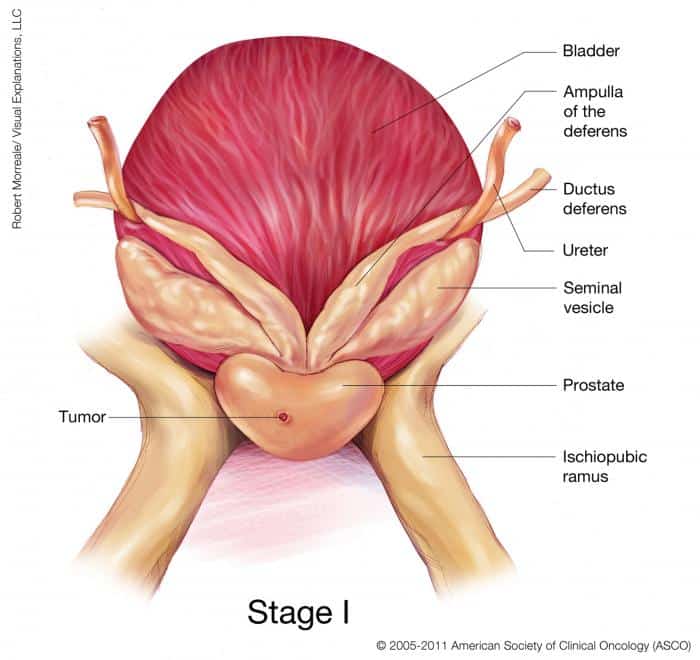
Understanding Prostate Cancers Progression
To determine the appropriate treatment, doctors need to know how far the cancer has progressed, or its stage. A pathologist, the doctor trained in analyzing cells taken during a prostate biopsy, will provide two starting pointsthe cancers grade and Gleason score.
- Cancer grade: When the pathologist looks at prostate cancer cells, the most common type of cells will get a grade of 3 to 5. The area of cancer cells in the prostate will also be graded. The higher the grade, the more abnormal the cells.
- Gleason score: The two grades will be added together to get a Gleason score. This score tells doctors how likely the cancer is to grow and spread.
After a biopsy confirms prostate cancer, the patient may undergo additional tests to see whether it has spread through the blood or lymph nodes to other parts of the body. These tests are usually imaging studies and may include a bone scan, positron emission tomography scan or computed tomography scan.
Donât Miss: Best Method To Check Prostate
What Causes Prostate Cancer
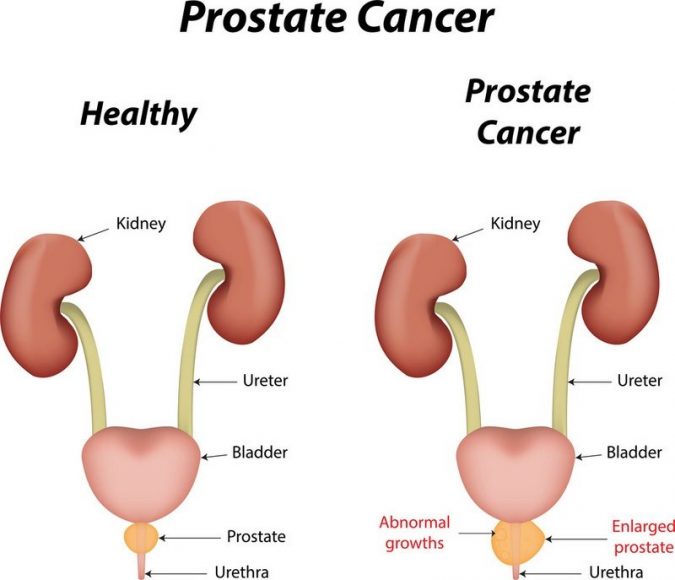
The exact cause of prostate cancer is not known. The tumor arises from cells with abnormal deoxyribonucleic acid changes in the prostate. These abnormal cells rapidly grow and divide, invading surrounding structures and can spread to other parts of the body .
Risk factors
There are certain factors that can increase the risk of prostate cancer. These include
- Age: The risk of prostate cancer increases with age and is most commonly seen after the age of 50.
- Race: African American men have a higher risk of prostate cancer than men of other ethnicities. Cancer in African Americans is also more likely to be aggressive.
- Family history: If a blood relative has prostate cancer, it increases the risk as well. Having a family history of genes that increase the risk of breast cancer or a very strong family history of breast cancer also increases the risk of developing prostate cancer.
- Obesity: Obese people have a higher risk of developing prostate cancer, which is also more likely to be aggressive and recurrent despite treatment.
Also Check: Does Prostate Cancer Affect Sperm Production
How Is Advanced Or Metastatic Prostate Cancer Treated
Advanced or metastatic prostate cancer may be treated with hormone therapy . Some of these treatments may be combined. Other options may include surgery or observation . For either type of cancer, your doctor may suggest a clinical trial
Health Tools help you make wise health decisions or take action to improve your health.
- Cancer: Controlling Cancer Pain
- Cancer: Controlling Nausea and Vomiting From Chemotherapy
Sometimes there are no symptoms of locally advanced or metastatic prostate cancer.
When there are symptoms of locally advanced prostate cancer , they may include urinary problems, such as:
- Not being able to urinate at all.
- Having a hard time starting or stopping the flow of urine.
- Having to urinate often, especially at night.
- Having pain or burning during urination.
Less common symptoms of locally advanced prostate cancer may include:
- Difficulty having an erection.
- Deep and frequent pain in your lower back, belly, hip, or pelvis.
These symptoms also may be caused by an enlarged prostate , an infection in the prostate ( prostatitis
- Swelling in the legs and feet.
How Is Prostate Cancer Diagnosed
A biopsy is when a small piece of tissue is removed from the prostate and looked at under a microscope.
A biopsy is a procedure that can be used to diagnose prostate cancer. A biopsy is when a small piece of tissue is removed from the prostate and looked at under a microscope to see if there are cancer cells.
A Gleason score is determined when the biopsy tissue is looked at under the microscope. If there is a cancer, the score indicates how likely it is to spread. The score ranges from 2 to 10. The lower the score, the less likely it is that the cancer will spread.
A biopsy is the main tool for diagnosing prostate cancer, but a doctor can use other tools to help make sure the biopsy is made in the right place. For example, doctors may use transrectal ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging to help guide the biopsy. With transrectal ultrasound, a probe the size of a finger is inserted into the rectum and high-energy sound waves are bounced off the prostate to create a picture of the prostate called a sonogram. MRI uses magnets and radio waves to produce images on a computer. MRI does not use any radiation.
Don’t Miss: What Does The Prostate Feel Like
What Kind Of Treatment Will I Need
There are many ways to treat prostate cancer. The main kinds of treatment are observation, active surveillance, surgery, radiation, hormone therapy, and chemo. Sometimes more than one kind of treatment is used.
The treatment thats best for you will depend on:
- Any other health problems you might have
- The stage and grade of the cancer
- Your feelings about the need to treat the cancer
- The chance that treatment will cure the cancer or help in some way
- Your feelings about the side effects that might come with treatment
Does Prostate Cancer Have Any Symptoms
Most men with early prostate cancer dont have any signs or symptoms.
One reason for this is the way the cancer grows. Youll usually only get early symptoms if the cancer grows near the tube you urinate through and presses against it, changing the way you urinate . But because prostate cancer usually starts to grow in a different part of the prostate, early prostate cancer doesnt often press on the urethra and cause symptoms.
If you do notice changes in the way you urinate, this is more likely to be a sign of a very common non-cancerous problem called an enlarged prostate, or another health problem. But its still a good idea to get it checked out. Possible changes include:
- difficulty starting to urinate or emptying your bladder
- a weak flow when you urinate
- a feeling that your bladder hasnt emptied properly
- dribbling urine after you finish urinating
- needing to urinate more often than usual, especially at night
- a sudden need to urinate you may sometimes leak urine before you get to the toilet.
If prostate cancer breaks out of the prostate or spreads to other parts of the body , it can cause other symptoms, including:
- back pain, hip pain or pelvis pain
- problems getting or keeping an erection
- unexplained weight loss.
These symptoms can all be caused by other health problems. But its still a good idea to tell your GP about any symptoms so they can find out whats causing them and make sure you get the right treatment, if you need it.
Also Check: What Foods Can Prevent Prostate Cancer
Symptoms Of Prostate Cancer Spread To The Lymph Nodes
Lymph nodes are part of a system of tubes and glands in the body that filters body fluid and fights infection.
There are lots of lymph nodes in the groin area, which is close to the prostate gland. Prostate cancer can spread to the lymph nodes in the groin area, or to other parts of the body. The most common symptoms are swelling and pain around the area where the cancer has spread.
Cancer cells can stop lymph fluid from draining away. This might lead to swelling in the legs due to fluid build up in that area. The swelling is called lymphoedema.
What Are Grade Groups
Grade Groups are a new way to grade prostate cancer to address some of the issues with the Gleason grading system.
As noted above, currently in practice the lowest Gleason score that is given is a 6, despite the Gleason grades ranging in theory from 2 to 10. This understandably leads some patients to think that their cancer on biopsy is in the middle of the grade scale. This can compound their worry about their diagnosis and make them more likely to feel that they need to be treated right away.
Another problem with the Gleason grading system is that the Gleason scores are often divided into only 3 groups . This is not accurate, since Gleason score 7 is made up of two grades , with the latter having a much worse prognosis. Similarly, Gleason scores of 9 or 10 have a worse prognosis than Gleason score 8.
To account for these differences, the Grade Groups range from 1 to 5 :
- Grade Group 1 = Gleason 6
- Grade Group 2 = Gleason 3+4=7
- Grade Group 3 = Gleason 4+3=7
- Grade Group 4 = Gleason 8
- Grade Group 5 = Gleason 9-10
Although eventually the Grade Group system may replace the Gleason system, the two systems are currently reported side-by-side.
Dont Miss: Prostate Over The Counter Drugs
Recommended Reading: Cancer Of The Prostate Gland
Testing Options For Prostate Cancer
There is no one age for prostate cancer testing, but the American Cancer Society makes recommendations about prostate cancer screenings. According to the ACS, patients in any of these groups should consider asking their doctor about testing:
- Men age 50 or older who have an average risk of prostate cancer and a life expectancy of at least 10 more years
- Men age 45 or older with a high risk, including African-American men and those with a first-degree relative who had prostate cancer before age 65
- Men age 40 or older who have a higher risk, such as more than one first-degree relative diagnosed with prostate cancer at an early age
Expert cancer care
Genetic Testing For Prostate Cancer
You may hear a lot about genetics or genomics. Both terms are related to genes and cell DNA, but they are different. These tests are being used to learn more about the DNA of cancer cells, and link DNA mutations with treatments. In the future, genetic testing may be the first step doctors take when diagnosing prostate cancer.
You May Like: Foods To Avoid With Prostate Issues
Also Check: Gleason 8 Prostate Cancer Prognosis
How Common Is Prostate Cancer
According to the , aside from skin cancer, prostate cancer is the most common type of cancer in men in the United States. Its estimated that about 1 in 8 men will develop prostate cancer at some point in their life.
The ACS estimates that about in the United States will be newly diagnosed with prostate cancer in 2022. Additionally, about 34,500 men in the United States will die from prostate cancer in 2022.
Dont Miss: Prostate Cancer Hormone Therapy Drug Names
How To Protect Yourself Against Prostate Cancer
Throughout the course of recent years, Prostate Cancer has been designated by wellbeing specialists as the biggest secret enemy of men north of 45 years old. In spite of the fact that there have been propels in schooling and overall population mindfulness, men are as yet showing hesitance to recognize the requirement for carefulness in their regular daily existence.
There are various ways that men can console themselves in any case. Here is a rundown of realities and ideas examined from various sources that you ought to be aware of.
One in each 6 men will experience the ill effects of prostate issues in their lives. So there is a compelling reason for the need to feel confined or a casualty. Simply make a move and get to a specialist rapidly at the main sign.
It is nearly 100% sure that speedy activity will prompt fruitful recuperation. The sooner you visit your primary care physician and get alluded to a Urologist, the better your possibilities of fruitful treatment.
There is potential for whats to come. In 2002, researchers at Liverpool University in the UK confined the quality that advances the spread of prostate malignant growth. This data is as yet being investigated to ideally deliver new medications which will help therapy of Prostate disease beyond the ordinary Chemotherapy systems as of now being used.
Dietary propensities are the consistent idea in the greater part of the writing about prostate disease.
Content created and supplied by: AmkJul
Read Also: What Happens When You Get Your Prostate Removed
What Should I Tell My Healthcare Provider Before Taking Finasteride
Before taking finasteride, tell your healthcare provider if you:
- have any other medical conditions, including problems with your prostate or liver
- Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and nonprescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
Recommended Reading: Can A Man With No Prostate Get A Woman Pregnant
Diagnosing Metastatic Spread Outside The Prostate
Overview by Professor Tristan BarrettConsultant Radiologist
Diagnosing metastatic prostate cancer
Accurate staging of prostate cancer is essential to inform prognosis and to stratify patients for appropriate management both at initial presentation, or in the context of suspected recurrent or progressive disease. When prostate cancer metastasises, that is it spreads outside of the prostate gland, it typically affects areas and structures in the immediate vicinity of the prostate gland such as the pelvic lymph nodes, bladder and the seminal vesicles. The spread of disease is classified according to the TNM staging system:
Nodal spread is primarily to four pelvic areas, considered regional nodes: the obturator, internal and external iliac and pre-sacral nodes. When distal metastatic involvement is present, the common site is bone , with involvement of other organs occurring in around 10%, which may include liver, lungs, brain. Clinically low stage disease i.e. PSA < 10 ng/ml, or Gleason grade < 7, or stage T2a, has a low probability of metastases, thus additional imaging tests are not recommended for staging. Current EAU guidelines recommend cross-sectional abdominopelvic imaging and bone-scintigraphy for metastatic screening in patients with predominantly Gleason pattern 4 disease or higher .
Diagnosing metastatic spread
mpMRI scans
Bone scintigraphy
CT scans
You May Like: How To Test For Prostatitis
How Will My Cancer Be Monitored
Your doctor will talk to you about how often you should have check-ups. At some hospitals, you may not have many appointments at the hospital itself. Instead, you may talk to your doctor or nurse over the telephone. You might hear this called self-management.
You will have regular PSA tests. This is often a useful way to check how well your treatment is working. Youll also have regular blood tests to see whether your cancer is affecting other parts of your body, such as your liver, kidneys or bones.
You might have more scans to see how your cancer is responding to treatment and whether your cancer is spreading.
Your doctor or nurse will also ask you how youre feeling and if you have any symptoms, such as pain or tiredness. This will help them understand how youre responding to treatment and how to manage any symptoms. Let them know if you have any side effects from your treatment. There are usually ways to manage these.
