Questions To Ask Your Doctor
To help understand the progression of prostate cancer, discuss these questions with your doctors:
- What is my Gleason score?
- Has the cancer spread outside my prostate?
- Whats my prostate cancer stage?
- Are other tests needed to determine my cancer stage?
- What are the treatment options for my stage of cancer?
- Can I avoid treatment right now and go on active surveillance?
General Prostate Cancer Survival Rate
According to the American Cancer Society:
- The relative 5-year survival rate is nearly 100%
- The relative 10-year survival rate is 98%
- The 15-year relative survival rate is 91%
Note: Relative survival rate means the percentage of patients who live amount of years after their initial diagnosis.
Keep in mind, however, that because the compiled list figures are of cancers diagnosed up to 15 years ago, you may have an even greater chance of survival than these indicate due to advances in prostate cancer treatment technology
Read Also: How Do They Test For Prostate Infection
Is Prostate Cancer Curable
Prostate cancer is the most common type of cancer among men, second only to skin cancer. Learning that one has any type of cancer isnt easy, but the first question on most patients minds after diagnosis is, is prostate cancer curable?
The short answer is yes, prostate cancer can be cured, when detected and treated early. The vast majority of prostate cancer cases are discovered in the early stages, making the tumors more likely to respond to treatment. Treatment doesnt always have to mean surgery or chemotherapy, either. Non-invasive radiation therapy can effectively treat prostate cancer; in the case of Pasadena CyberKnife, radiosurgery treatment generally takes less than a week, and you can typically resume your normal activities the same day you receive treatment.
You May Like: Prostate Cancer Shortness Of Breath
Treatments To Control And Prevent Symptoms Caused By The Spread Of Prostate Cancer To The Bones
Palliative External beam radiotherapy
Radiopharmaceuticals: Strontium-89 , samarium-153
Radium-223 dichloride is now licensed and called Xofigo. This is not widely available in the UK but BPC is one of a relatively small number of specialist centres using this treatment.
Zolidronic acid a bisphosphonate given by a 15 minute intravenous infusion every 34 weeks. It reduces the risk of bone complications, including pain and fractures.
Xgeva : this is a newly licensed drug available at BPC.
Pain medications
Surgery may be undertaken to treat bone fractures or to relief the pressure on the spinal cord by bone metastases.
Stages Of Prostate Cancer
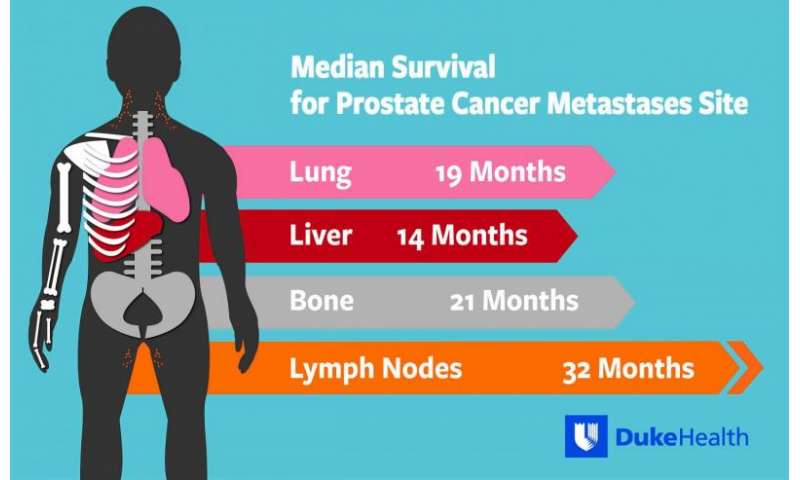
In order to determine the stage of a patients prostate cancer, most doctors start by using the TNM staging system, which helps describe different aspects of the cancers growth.
- T the T category measures the size and extent of the Tumor
- N the N category measures whether and how far the cancer has spread to the Lymph Nodes
- M the M category whether the cancer has spread to other organs in the body (a process called Metastasis
The score for each of these categories is determined based on a pre-determined set of criteria. Your doctor cannot feel or see the tumor with a score of T1. A score of T3 means that the tumor has begun to grow outside of the prostate.
After calculating the TNM categories, doctors will combine the TNM score with the patients Gleason score and PSA levels assigning of a specific stage to the patients cancer.
Prostate cancer prognosis and survival rates can help give patients an idea of their chances of surviving the disease based on the stage and time of diagnosis. While some patients may find this information helpful, others may not want to know.
Don’t Miss: Does Prostatitis Go Away Without Treatment
Outlook For Locally Advanced Prostate Cancer
Many men with;locally advanced prostate cancer;have treatment that aims to get rid of their cancer. For some men, this treatment can be very successful and they may live for many years without their cancer coming back or causing them any problems. For others, treatment may be less successful and the cancer may come back. If this happens, you might need further treatment. Read more about;the risk of your cancer coming back.
Some men with;locally advanced prostate cancer;will have treatment that aims to help keep their cancer under control rather than get rid of it completely. For example, if you have;hormone therapy;on its own, it can help to keep the cancer under control, usually for several years. And there are other treatments available if your hormone therapy stops working.
How To Make The Right Treatment Decision
Current expert guidelines for treatment of localized prostate carcinoma recommend potentially curative therapy for patients whose life expectancy is at least 10 years., Patients with limited life expectancy are more likely to die from health conditions other than prostate cancer. Men with a life expectancy of more than 10 years are more likely to die from progressive prostate cancer. This 10-year rule enjoys broad acceptance among urologists and radiation oncologists.,
Conservative management proved to be an acceptable treatment option for men with low-grade Gleason scores, clinically localized disease, and life expectancies of less than 10 years. Increasing age was described as a risk factor for receiving inadequate treatment for prostate cancer. Thus, older men have been shown to receive potentially curative therapy less often than younger men., Radical prostatectomy is preferred treatment in men younger than 70 years, whereas radiation therapy is applied predominantly in patients older than 70 years. Conservative therapy such as watchful waiting or androgen deprivation by luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone analogs is preferentially applied in men older than 80 years. Watchful waiting or hormonal therapy is used to treat 82% of men older than 80 years.
Read Also: Does Cialis Shrink The Prostate
Most Patients Did Not Progress
With active surveillance, the patients had physical exams and PSA tests every six months, with biopsies recommended every one to two years.
Over an average of two and a half years of follow-up, 43 of the study participants showed evidence of cancer progression and received treatment.
In two patients, cancer spread beyond their prostate.
The study is published in the April issue of the Journal of Urology.
The findings support the idea that some men with prostate cancer may not need treatment, American Cancer Society Deputy Chief Medical Officer Len Lichtenfeld, MD, tells WebMD.
He says the addition of a second biopsy should help refine the search for men who are appropriate candidates for active surveillance, but he also agrees that the strategy of watchful waiting is not without its risks.
âThe real advance will be when we have tests that will tell us with a high degree of accuracy when treatment is needed and when it is not,â he says.
A great deal of research is being done to identify genetic tests or tumor markers that can do this, but Lichtenfeld says it will be years before these tests are validated.
Outlook For Men With Localised Prostate Cancer
Most;localised prostate cancer;is slow-growing and may not need treatment or shorten a mans life. For many men who have treatment for localised prostate cancer, the treatment will get rid of the cancer. For others, treatment may be less successful and the cancer may come back. If this happens, you might need further treatment.
Also Check: Does Enlarged Prostate Cause Constipation
Don’t Miss: How To Pleasure A Woman After Prostate Surgery
About Half Of Men Older Than 50 Have An Enlarged Prostate Here Are Some Of The Basic Facts You Need To Know About This Common Condition
As men age, many experience prostate gland enlargement. This condition is known as benign prostatic hyperplasia .
The prostate gland surrounds the urethra, the hollow tube that carries urine out of the body. When the prostate gets bigger, it can squeeze or partially block the urethra, which leads to problems urinating.
BPH is quite common in older men. In fact, the condition impacts about 50% of men between the ages of 51 and 60. For men 80 and older, the prevalence of BPH is approximately 90%, according to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases.
Talking To Andrew’s Doctor
For fifteen months, Andrew responded really well to treatment and was feeling reasonably good. But then he developed a very bad;spinal cord compression. He was unable to walk and at that point it was clear that things were very serious. He spent nearly a month in hospital and his consultant told us that the cancer was back with a vengeance and that they wanted to fast track him home.
Andrew didnt want to know how long he might have. I know that he knew what the score was but that he just didnt want to speak about it.
Andrew didnt want to know how long he might have.
I asked Andrews doctor how long he might live for. She told me that she could give me some indication of how long Andrew might live for if I wanted to know. I wasnt sure that I wanted to know if Andrew didnt it might have created a barrier between us.
I wanted to know what I should expect. But I wasnt sure that I wanted to know how long Andrew would live for if he didn’t know.
But I wanted to know what I should expect. I needed to plan what was going to happen when he came home, the arrangements that would need to be made and whether I needed to speak to other members of our family and friends. At this point I think I felt quite out of control, so speaking to the consultant was my way of regaining some of that control and it helped me to plan for his homecoming.
Its difficult to accept that cancer takes its own route at its own pace.
Recommended Reading: Enlarged Prostate Sexuality
What Happens Without Treatment
Physicians will sometimes talk about a particular diseases natural history or typical progression if it is left untreated indefinitely.
With regard to prostate cancer, most cases of the disease are discovered while the cancer is still confined to the prostate itself. This is called local disease or localized disease.
The disease is easiest to treat while it is confined to the prostate. At this stage, surgery and radiation are most likely to be curative and completely kill or remove whatever cancer cells are present.
If left untreated, however, prostate cancer can proceed on a number of different paths.
Types Of Cancers That Are More Likely To Go Undetected

Some cancers are more easily detected than others. For example, certain types of skin cancer can be diagnosed initially just by visual inspection though a biopsy is necessary to confirm the diagnosis.
But other cancers can form and grow undetected for 10 years or more, as one study found, making diagnosis and treatment that much more difficult.
This table provides an overview of common cancers that often display little or no symptoms early on, and how theyre typically detected and diagnosed:
| Type of cancer |
|---|
You May Like: External Prostate Massage For Prostatitis
Survival Rates For Bladder Cancer
Survival rates can give you an idea of what percentage of people with the same type and stage of cancer are still alive a certain amount of time after they were diagnosed. They cant tell you how long you will live, but they may help give you a better understanding of how likely it is that your treatment will be successful.
Keep in mind that survival rates are estimates and are often based on previous outcomes of large numbers of people who had a specific cancer, but they cant predict what will happen in any particular persons case. These statistics can be confusing and may lead you to have more questions. Talk with your doctor about how these numbers may apply to you, as he or she is familiar with your situation.
Managing Bone Pain And Weakness
Symptoms like nausea, hot flashes, and pain can usually be relieved with medication. Some people find that complimentary treatments like acupuncture or massage help manage side effects.
Your doctor may also recommend orthopedic surgery to stabilize your bones, relieve pain, and help prevent bone fractures.
Dont Miss: How To Massage Your Own Prostate Gland
Don’t Miss: Does Enlarged Prostate Cause Constipation
Stomach Cancer Untreated Life Expectancy
Nutrition in cancer care health professional. Nutrition plays major roles in many aspects of cancer development and treatment. Malnutrition is a common problem in cancer patients.
Stages of liver damage ehow. You may also like. Stages of liver disease. Stages of liver damage; end stage liver disease life expectancy; what is end stage liver disease? You may also like. Does anyone know someone close to you that has. My mom has stage 4 stomach cancerwhat is the life expectancy? By randb on sat jul 28, 2007 1200 am. Quote reply. Free cancer essays and papers 123helpme. Free cancer papers, essays, and research papers. These results are sorted by most relevant first . You may also sort these by color rating or essay. Stomach cancer survival statistics ctca. Race for life; search events; more survival statistics for stomach cancer. There is information about. A quick guide to what’s on this page; about the. Cancer life expectancy. Stomach cancer life expectancy info. Try a new search on alot!
Stages of liver damage ehow. You may also like. Stages of liver disease. Stages of liver damage; end stage liver disease life expectancy; what is end stage liver disease? You may also like.
Stomach cancer info cancercenter. Also try.
Untreated Prostate Cancer No Death Sentence
By Frederik Joelving, Reuters Health
4 Min Read
NEW YORK – Even without treatment, only a small minority of men diagnosed with early-stage prostate cancer die from the disease, Swedish researchers reported Friday.
Drawing from a national cancer register, they estimated that after 10 years prostate cancer would have killed less than three percent of these men.
What the data is showing is that for most patients with low-risk cancer, there is no need to panic, said Grace Lu-Yao, a cancer researcher who was not involved in the new study. Prostate cancer really is no longer a fatal disease.
With modern screening tests, said Lu-Yao, of the University of Medicine and Dentistry of New Jersey in New Brunswick, many prostate cancers are found that might never have developed into serious disease. In such cases, the slight reduction of risk by surgically removing the prostate or treating it with radiation may not outweigh the substantial side effects of these treatments.
In the Swedish study, published in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute, researchers compared deaths among more than 6,800 men with prostate cancer who underwent treatment — surgery or radiation — or were simply monitored regularly by their doctors, the so-called watchful waiting approach. With watchful waiting, patients are only treated if their cancer progresses.
The Swedish findings jibe with earlier results, including a large US study.
Recommended Reading: Prostate Cancer Ruined My Marriage
What Is The Most Effective Treatment For Prostate Cancer
The choice of treatment for prostate cancer depends on many factors such as the patients prostate cancer risk as calculated from prostate-specific antigen levels, Gleason score, and tumor staging. Patients can discuss the significance of these factors in the choice of treatment with their doctor.
The standard effective treatment choices for men with early-stage prostate cancer are as follows
- Active surveillance: Monitoring the progression/status of the low-risk or early-stage cancer with regular testing and not treating it right away.
- Prostatectomy: Surgical removal of the prostate.;
- Radiation therapy: Use of high-energy waves to destroy cancer cells.
Radiation therapy is one of the most effective treatments for many men with early-stage prostate cancer. It is also the best prostate cancer therapy for older men or those with other co-existing diseases. It can be delivered to the patient in any of the two ways
- External beam radiation: Sending/focusing high-energy waves from an external machine into the tumor.
- Brachytherapy: Placing a radioactive dye in the tumor through an implant or hollow tubes.
For metastatic prostate cancer, androgen deprivation therapy is usually the choice of treatment. ADT is also the only option in patients with prostate cancer who are unfit or unwilling to undergo surgery or/and radiation therapy.
Understanding Prostate Cancers Progression
To determine the appropriate treatment, doctors need to know how far the cancer has progressed, or its stage. A pathologist, the doctor trained in analyzing cells taken during a prostate biopsy, will provide two starting pointsthe cancers grade and Gleason score.
- Cancer grade: When the pathologist looks at prostate cancer cells, the most common type of cells will get a grade of 3 to 5. The area of cancer cells in the prostate will also be graded. The higher the grade, the more abnormal the cells.
- Gleason score: The two grades will be added together to get a Gleason score. This score tells doctors how likely the cancer is to grow and spread.
After a biopsy confirms prostate cancer, the patient may undergo additional tests to see whether it has spread through the blood or lymph nodes;to other parts of the body. These tests are usually imaging studies and may include a bone scan, positron emission tomography scan;or computed tomography scan.
Also Check: Is Viagra Good For Enlarged Prostate
What Is Clinically Localized Prostate Cancer
If you have been diagnosed with prostate cancer and your doctor has indicated that your cancer appears to not have spread beyond the prostate gland, you have what is known as clinically localized prostate cancer. Sometimes, doctors will also call cancer that has spread into the lining of the prostate gland clinically localized.
According to the U.S Department of Health and Human Services, about 90 percent of men with prostate cancer have localized prostate cancer, and it is typically considered low-risk, meaning patients can expect to live long after their diagnosis, in many cases even without treatment.
