Does Restaging A Cancer Change The Original Stage
When a cancer is staged again after the initial staging, it is sometimes referred to as restaging. Often the same tests that were done when the cancer was first diagnosed are done again.
With any type of restaging, the new stage classification is added to the original stage, but it doesnt replace it. The stage assigned at diagnosis is still the one that is most important when discussing statistics like survival rates .
What Goes Into The Stage: The Tnm System
There are different types of systems used to stage cancer, but the most common and useful staging system for most types of cancer is the TNM system.
The American Joint Committee on Cancer and the Union for International Cancer Control maintain the TNM classification system as a way for doctors to stage many different types of cancer based on certain common standards.
In the TNM system, the overall stage is determined after the cancer is assigned a letter or number to describe the tumor , node , and metastasis categories.
- T describes the original tumor.
- N tells whether the cancer has spread to the nearby lymph nodes.
- M tells whether the cancer has spread to distant parts of the body
If Treatment Does Not Work
Recovery from cancer is not always possible. If the cancer cannot be cured or controlled, the disease may be called advanced or terminal.
This diagnosis is stressful, and for many people, advanced cancer may be difficult to discuss. However, it is important to have open and honest conversations with your health care team to express your feelings, preferences, and concerns. The health care team has special skills, experience, and knowledge to support patients and their families and is there to help. Making sure a person is physically comfortable, free from pain, and emotionally supported is extremely important.
People who have advanced cancer and who are expected to live less than 6 months may want to consider hospice care. Hospice care is designed to provide the best possible quality of life for people who are near the end of life. You and your family are encouraged to talk with the health care team about hospice care options, which include hospice care at home, a special hospice center, or other health care locations. Nursing care and special equipment, including a hospital bed, can make staying at home a workable option for many families. Learn more about advanced cancer care planning.
After the death of a loved one, many people need support to help them cope with the loss. Learn more about grief and loss.
Don’t Miss: Cialis Prostatitis
When Prostate Cancer Spreads Where It Goes Matters A Lot
And if the cancer progresses or spreads beyond his prostate? We can treat it then, Callaghan said.
The study shows that you have no business treating low-grade prostate cancer in someone with a life expectancy of less than 15 years because the side effects outweigh any benefits, said urological surgeon Dr. Peter Albertsen of the University of Connecticut Health. The Oxford scientists reported that 46 percent of men who had their prostate removed were using adult diapers six months later . Similarly, only 12 percent of men who got surgery and 22 percent who had radiation could sustain an erection, compared to 52 percent of the monitoring group.
An estimated 180,890 men in the US will be diagnosed with prostate cancer this year, according to the American Cancer Society. Some 26,120 will die of it in 2016, almost always because it has spread to a vital organ.
In an editorial accompanying the study, radiation oncologist Dr. Anthony DAmico of Brigham and Womens Hospital focused on the finding that men who opted for monitoring were more than twice as likely to develop metastatic prostate cancer. That is, malignant cells reached the bones, lung, liver, or brain.
Garnick agreed: The intermediate-risk men we would never assign to active monitoring. If the increased metastases came from these patients, it would explain those differences and even more strongly encourage the role of active management in truly low-risk prostate cancer.
How To Tell If Your Cancer Has Metastasized
Prostate cancer metastasis may be suspected if you have specific symptoms such as new lower back pain or elevated liver enzymes. These may be signs your cancer has spread to your spine or your liver, respectively. If your prostate-specific antigen levels continue to rise despite treatment, especially if they are rising particularly fast, this may be a sign that cancer is metastasizing somewhere in your body.
Read Also: Does An Enlarged Prostate Affect A Man Sexually
Advanced Prostate Cancer Life Expectancy And Prognosis
Typically, each stage of prostate cancer has different prognosis. In general, the advanced stages of the disease are much more difficult to treat than when the disease is still at early stage not yet spread. What are factors that affect the outlook and life expectancy of patient? The following are some statistics for each stage of this disease.
You might also like to know more about how fast prostate cancer spreads and what are the most common sites /organs of the body for the metastasis of this cancer in this section, before continuing
One thing you need to clearly understand that there is no any statistic that can be detail enough to tell you about what will happen. In other words, this statistic is only purposed for general information! In fact, each case of cancer is unique. So, there is always a chance and a hope for anyone who diagnosed with cancer.
Advanced prostate cancer symptoms
The symptoms of the disease are more likely to occur when the disease at advanced stage. This is the most challenging for doctors, because the early warning signs that are more likely to not occur will increase the number of patients diagnosed with the disease at later stages.
Once the cancerous tumor is bigger in size and also spreads to nearby sites or even other distinct organs of the body, there will be more complications that can be generated. These may include:
Understanding n-years survival statistics
The major factors that affect the outlook of patients
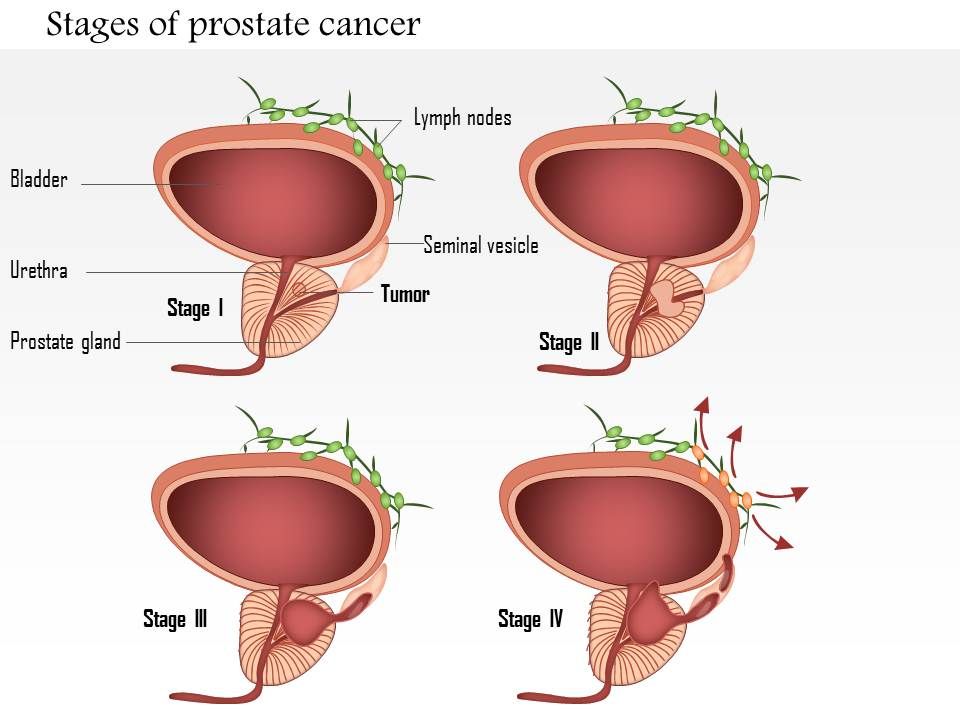
The Stages Of Prostate Cancer: What You Need To Know
After a prostate cancer diagnosis, your oncologist will refer to the stage of your cancer. All cancers are categorized into four distinct stages, each of which identifies the progress of the growth of cancerous cells within clinically defined standards. These stages help doctors determine the most appropriate care for each patient based on his or her condition, and can also provide easy-to-understand context for your diagnosis. Learn more about the stages of prostate cancer, how each stage will affect your treatment plan and the survival rates for each stage, then contact Regional Cancer Care Associates to schedule a consultation.
You May Like: Do Females Have Prostate Cancer
Screening Information For Prostate Cancer
Screening for prostate cancer is done to find evidence of cancer in otherwise healthy adults. Two tests are commonly used to screen for prostate cancer:
-
Digital rectal examination . A DRE is a test in which the doctor inserts a gloved, lubricated finger into the rectum and feels the surface of the prostate through the bowel wall for any irregularities.
-
PSA blood test. There is controversy about using the PSA test to look for prostate cancer in people with no symptoms of the disease. On the one hand, the PSA test is useful for detecting early-stage prostate cancer, especially in those with many risk factors, which helps some get the treatment they need before the cancer grows and spreads. On the other hand, PSA screening may find very-slow-growing prostate cancers that would never threaten someone’s life. As a result, screening for prostate cancer using PSA may lead to treatments that are not needed, which can cause side effects and seriously affect a person’s quality of life.
ASCO recommends that people with no symptoms of prostate cancer and who are expected to live less than 10 years do not receive PSA screening. For those expected to live longer than 10 years, ASCO recommends that they talk with their doctor to find out if the test is appropriate for them.
Other organizations have different recommendations for screening:
What Is The Life Expectancy Of A Man With Prostate Cancer
The life expectancy of a man with prostate cancer is favorable. Most of the aged men detected of prostate cancer die of other comorbidities. The life expectancy is as follows:
- Almost 100% of men who have early-stage prostate cancer will survive more than 5 years after diagnosis.
- Men with advanced prostate cancer or whose cancer has spread to other regions have lesser survival rates. About one-third will survive for 5 years after diagnosis.
The longer-term survival rates for early-stage prostate cancer include:
- The relative 10-year survival rate is 98%.
- The relative 15-year survival rate is 96%.
By Frederik Joelving, Reuters Health
4 Min Read
NEW YORK Even without treatment, only a small minority of men diagnosed with early-stage prostate cancer die from the disease, Swedish researchers reported Friday.
Drawing from a national cancer register, they estimated that after 10 years prostate cancer would have killed less than three percent of these men.
What the data is showing is that for most patients with low-risk cancer, there is no need to panic, said Grace Lu-Yao, a cancer researcher who was not involved in the new study. Prostate cancer really is no longer a fatal disease.
The Swedish findings jibe with earlier results, including a large US study.
You May Like: What Is Perineural Invasion In Prostate Cancer
Gleason Score For Grading Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is also given a grade called a Gleason score. This score is based on how much the cancer looks like healthy tissue when viewed under a microscope. Less aggressive tumors generally look more like healthy tissue. Tumors that are more aggressive are likely to grow and spread to other parts of the body. They look less like healthy tissue.
The Gleason scoring system is the most common prostate cancer grading system used. The pathologist looks at how the cancer cells are arranged in the prostate and assigns a score on a scale of 3 to 5 from 2 different locations. Cancer cells that look similar to healthy cells receive a low score. Cancer cells that look less like healthy cells or look more aggressive receive a higher score. To assign the numbers, the pathologist determines the main pattern of cell growth, which is the area where the cancer is most obvious, and then looks for another area of growth. The doctor then gives each area a score from 3 to 5. The scores are added together to come up with an overall score between 6 and 10.
Gleason scores of 5 or lower are not used. The lowest Gleason score is 6, which is a low-grade cancer. A Gleason score of 7 is a medium-grade cancer, and a score of 8, 9, or 10 is a high-grade cancer. A lower-grade cancer grows more slowly and is less likely to spread than a high-grade cancer.
How Does Tumor Grade Affect A Patients Treatment Options
Doctors use tumor grade and other factors, such as cancer stage and a patients age and general health, to develop a treatment plan and to determine a patients prognosis . Generally, a lower grade indicates a better prognosis. A higher-grade cancer may grow and spread more quickly and may require immediate or more aggressive treatment.
The importance of tumor grade in planning treatment and determining a patients prognosis is greater for certain types of cancer, such as soft tissue sarcoma, primary brain tumors, and breast and prostate cancer.
Patients should talk with their doctor for more information about tumor grade and how it relates to their treatment and prognosis.
Selected Reference
American Joint Committee on Cancer. AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 7th ed. New York, NY: Springer 2010.
Related Resources
Read Also: What Happens If You Have Prostate Cancer
What Is The Treatment For Advanced Prostate Cancer
No matter where prostate cancer spreads, its still treated as prostate cancer. Its harder to treat when it reaches an advanced stage.
Treatment for advanced prostate cancer involves targeted and systemic therapies. Most men need a combination of treatments and they may have to be adjusted from time to time.
Prostate Cancer Treatments How Long Can You Live With Prostate Cancer
The treatments for cancer will be determined after a diagnosis and staging is complete. There will be a lot of information to think about before discussing care alternatives with medical doctors. If an individual has been recently diagnosed, then many prostate cancer treatments are available.
ManagementBasic prostate cancer treatments imply the active surveillance of the cancer and wary waiting. Active surveillance is a care option that involves monitoring the cancer consuming specific blood tests and many ultrasounds.This is normally done at standard interims to determine if the cancer is flourishing. Wary waiting will be less intensive with evaluation and basing government decisions on the symptoms of the patient. The option to use any form of management technique is often done in early stages.
SurgeryA common medicine that is meant to medication cancer is surgery. This is often a medication alternative when the cancer is at the T1 or T2 stage and has not spread outside the gland. The most frequent type of surgery for cancer is announced revolutionary prostatectomy.In this activity, the surgeon is lifting the prostate gland along with some of the encircling material. There are many modes this action can be done discussing options with your doctor will be a good thing.
Any prostate cancer treatments that are considered will take into account the current senility of the patient, lifespan anticipations, and the point or stage of the cancer.
Don’t Miss: What Is Perineural Invasion In Prostate Cancer
The Prostate Cancer Research Institute Uses Colors To Describe The Stages
The Prostate Cancer Research Institute , which is dedicated to helping educate patients and caregivers about prostate cancer, has developed a staging system using colors.
Unlike the other staging systems designed for healthcare professionals making treatment decisions, such as the AJCC TNM system, this one is a simplified system targeted at patients. Its designed to help educate men with prostate cancer so that they have a better understanding of their disease, enabling for improved communication with their healthcare provider.
The PCRI system involves taking a six question quiz, using information from your medical records, to determine the likely stage of prostate cancer you have. Knowing more about your stage of prostate cancer is intended to put you in a better position to start the conversation about treatment options with your healthcare professional.
This PCRI prostate cancer staging system has five stages as follows:
- Sky – A low-risk stage that requires active surveillance
- Teal – An intermediate-risk stage with three sub-levels – low, basic and high
- Azure – A high-risk stage
- Indigo – A stage covering men with relapsed disease with three sub-levels – low, basic and high
- Royal – An advanced stage of disease where the prostate cancer has spread outside of the pelvic lymph nodes or developed resistance to certain medications. This stage also has three sub-levels – low, basic and high
Gleason Prostate Cancer Score
1960s as a way to measure how aggressive your prostate cancer may be.
A pathologist determines your Gleason score by looking at a biopsy of your prostate tissue under a microscope. They grade the cells in the biopsy on a scale of 1 to 5. Grade 1 cells are healthy prostate, whereas grade 5 cells are highly mutated and dont resemble healthy cells at all.
The pathologist will calculate your Gleason score by adding together the number of the most prevalent type of cell in the sample and the second most prevalent type of cell.
For example, if the most common cell grade in your sample is 4 and the second most common is 4, you would have a score of 8.
A Gleason score of 6 is considered low-grade cancer, 7 is intermediate, and 8 to 10 is high-grade cancer.
You May Like: Does Enlarged Prostate Affect Ejaculation
Histopathologic Grade For Prostate Cancer
An additional factor influencing prognosis is histopathologic grading. Tissue obtained from a needle biopsy or a prostatectomy is graded using the Gleason Grading System. Gleason grades range from 1 to 5. Each specimen is assigned two grades based on the most common and second most common pattern. These numerical values are added to calculate the Gleason Score.
|
Gleason score cannot be assessed |
|
|
Gleason 6 |
|
|
Gleason 8-10 |
Poorly differentiated or undifferentiated |
The 8th edition of the AJCC Cancer Staging Manual took effect on January 1, 2018. A major change is that tumor grading now involves the Gleason Score, as well as the grade group.
| 4 + 4 | |
| 5 | 4 + 5, 5 + 4, 5 + 5 |
Treatments To Control And Prevent Further Cancer Spread In Patients With Castrate Refractory Advanced Prostate Cancer:
At BPC we offer:
- Radium-223
Other treatment options ongoing clinical studies:
- Autologous cellular immunotherapy, which is in late trial stage and although not currently available outside a trial setting in the UK, is likely to be licensed soon.
- Cabozantinib
Dont Miss: Will A Blood Test Show Prostate Cancer
Don’t Miss: Perineural Invasion Meaning
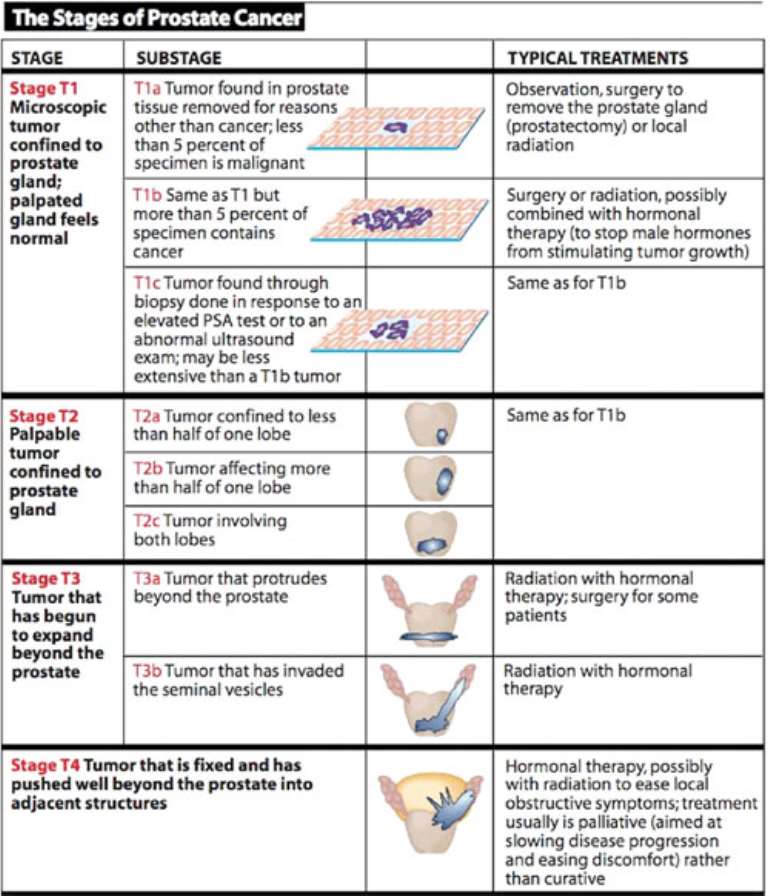
How Prostate Cancer Is Diagnosed And Staged
Cancer staging helps you and your doctor understand how advanced your cancer is and how much it has spread at the time of diagnosis. Knowing your cancer stage also helps your doctor determine the best treatment options for you and estimate your chance of survival.
The most widely used staging system for cancer is the American Joint Committee on Cancers TNM system that classifies cancer from stage 1 to stage 4.
TNM stands for:
- Tumor: the size and extent of the tumor
- Nodes: the number or extent of nearby lymph node involvement
- Metastasis: whether cancer has spread to distant sites in the body
The TNM scale is used for many types of cancer. When a doctor uses it to determine your prostate cancer stage, theyll consider several other factors as well, including:
- grade groups
