Newly Approved Prostate Cancer Scan Can Detect Cells That Have Spread To Lymph Nodes
Thomas Hope , MD, and Peter Carroll, MD, stand at the PACS workstation where the images from the PSMA PETs are viewed and interpreted. The imaging technique received FDA approval in 2020.
A revolutionary new diagnostic method for prostate cancer can detect prostate cancer cells that have spread to lymph nodes both inside and outside the pelvis, according to the UC San Francisco and UCLA team whose earlier work led to the tests FDA approval.
The test, which is now available at UCSF and UCLA, makes cancer cells light up on positron emission tomography with a radioactive compound developed more than a decade ago in Germany. The method, known as PSMA PET imaging, should become more widely available as commercial firms enter the market.
This is a game changer, said Peter Carroll, MD, MPH, professor in the UCSF Department of Urology and a senior researcher for the study. It will lead to more refined treatment for men with high-risk prostate cancer at the time of diagnosis, as well as for previously treated men whose cancers recur.
The key to this improved PET imaging approach is an injectable formulation containing a small amount of Gallium 68 PSMA-11. Within the body the diagnostic agent attaches to a protein called the prostate-specific membrane antigen , which is abundant on prostate cells that are cancerous, but not on normal tissue. Gallium 68 PSMA-11 emits positron particles detectible with PET imaging, highlighting tissue to which cancer has spread.
Endpoints And Statistical Analysis
For statistical testing SPSS 16.0.01 was used and a p< 0.05 was a priori deemed significant.
Endpoints of the present study, that were determined for patients with and without lymph node involvement on MRL, were: distant metastases-free survival and overall survival . For DMFS, deaths were censored. Survival rates were estimated with the Kaplan-Meier method, and the unstratified log-rank statistical analysis was used to test for differences.
How Quickly Does Prostate Cancer Spread
A bone scan can tell doctors whether cancer has spread to bones. When prostate cancer spreads to distant areas, it usually affects bones first. Radionuclide dye is injected into the body and images of the bones are taken over a few hours. The dye makes the cancer cells easier to see.
MRIs and transrectal ultrasounds can show where prostate cancer is spreading. MRIs can also show whether it has spread to other parts of the body. These tests can give doctors a good idea of how much cancer is present in the prostate. In general, however, if the cancer has spread beyond the prostate gland, it will be more aggressive and more difficult to treat.
If the cancer is detected early, it can be controlled with a medication. If a cancer is slow to grow, it can stay within the prostate for many years without causing any symptoms. In these cases, the goal of treatment is to limit bone metastasis, alleviate symptoms, and prevent further complications.
Don’t Miss: How To Milk Your Own Prostate
Multivariable Analysis Of Ln+
We used multivariate logistic regression to evaluate whether the association between age and LN+ at the time of diagnosis was independent of other known risk factors. Sex, race, year of operation, tumor grade, and LNE were used as covariates of the adjusted model. Age remained a significant predictor of LN+ in all T stages , and young MIBC patients were more likely to have LN+. Compared with the reference group , patients with T2 and T4 stages, aged < 50years, were more likely to have LN+, and the adjusted OR was 1.805 and 1.492 , respectively. The probability of LN+ was the highest in the 5059-year age group with T3, and the adjusted OR was 1.407 .
Table 4 Association of age and rate of LN+
What Causes Prostate Cancer And Am I At Risk
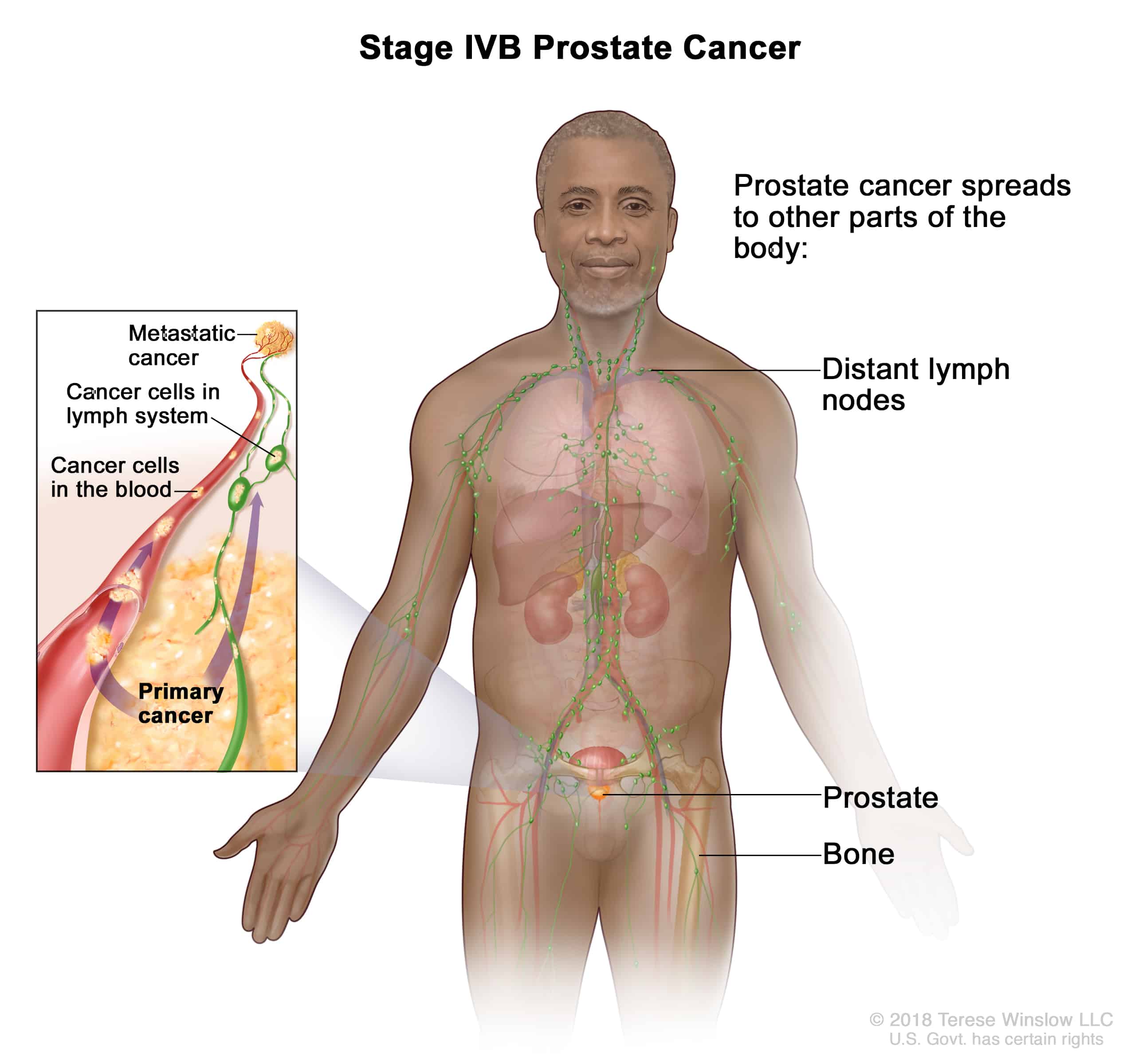
Every man is at risk for prostate cancer as he ages. Although prostate cancer can affect younger men, about 6 out of 10 cases are diagnosed in men over the age of 65. The average age of diagnosis is 66. After non-melanoma skin cancer, prostate is the most common cancer diagnosed in men in the United States. The American Cancer Society estimates there will be 248,530 new cases of prostate cancer each year.
Although there are several known risk factors for getting prostate cancer, no one knows exactly why one man gets it and another doesnt. Some important risk factors for prostate cancer are:
Dont Miss: Can You Still Have Sex With Prostate Cancer
You May Like: What Are The Symptoms Of Prostate Cancer Quizlet
Receiving Treatment For Prostate Cancer That Has Spread
At Moffitt Cancer Center, the experts within our Urologic Oncology Program treat patients with all stages of prostate cancer, including advanced-stage cancers that have metastasized to other areas of the body. Our multispecialty team collaborates as a tumor board, ensuring each patient receives a treatment plan tailored to his unique needs. For individuals with metastatic prostate cancer, treatment plans aim to alleviate symptoms, slow the rate of cancer growth and shrink tumors to help improve quality of life.
Medically reviewed by Monica Chatwal, MD.
If you have been diagnosed with prostate cancer, whether early stage or late stage, you can find the treatment you require at Moffitt. We welcome patients with or without a referral to fill out a new patient registration form or call to schedule an appointment.
What Are The Treatments For Prostate Cancer
There are many different ways to treat prostate cancer. For prostate cancer, it is important that you get a second opinion and you will most likely be consulting multiple types of healthcare providers before making a final decision. You should talk to both urologists and radiation oncologists to hear about the benefits and risks of surgery, hormonal therapy and radiation in your particular case. If your prostate cancer has already spread at the time of diagnosis, you will also need a medical oncologist to talk about chemotherapy. The most important thing is to review your options and make a decision that best suits your lifestyle, beliefs and values.
Active Surveillance
Surgery
Surgery is a common form of treatment for men with prostate cancer. Surgery attempts to cure prostate cancer by removing the entire prostate and getting all of the cancer out of the body. An attempt at a surgical cure for prostate cancer is usually done with early stage prostate cancers. However, sometimes surgery will be used to relieve symptoms in advanced stage prostate cancers.
Talk to your surgeon about their complication rates before your operation. With surgery, urinary incontinence and impotence are often most severe right after the operation and generally get better with time. There are things that your providers can recommend to help you with either of these problems. Talk to your urologist about your options.
Radiation
Hormonal Deprivation Therapy
Chemotherapy
Recommended Reading: How To Detect Prostate Cancer Early
Treating Prostate Cancer That Doesnt Go Away Or Comes Back After Treatment
If your prostate-specific antigen blood level shows that your prostate cancer has not been cured or has come back after the initial treatment, further treatment can often still be helpful. Follow-up treatment will depend on where the cancer is thought to be and what treatment youve already had. Imaging tests such as CT, MRI, or bone scans may be done to get a better idea about where the cancer is.
Does Radiation Shorten Your Life
“Rapidly dividing cells, such as cancer cells, are more affected by radiation therapy than normal cells. The body may respond to this damage with fibrosis or scarring, though this is generally a mild process and typically does not cause any long-term problems that substantially affect quality of life.”
Don’t Miss: How To Test For Prostate Cancer Yourself
Will Treatment Cause Erectile Dysfunction
Radical prostatectomy is a surgery to remove the prostate gland. When your surgeon removes the gland, they may damage the nerves and blood vessels that run along it. If theyre damaged enough, you wont be able to get an erection following the procedure.
Today, doctors can do nerve-sparing surgery, which helps prevent permanent ED. Your surgeon can still touch those nerves and blood vessels, causing ED as a temporary side effect. Many men have trouble getting an erection for a few weeks, months, or even years after their procedure.
Radiation therapy also damages blood vessels and the nerves that control erection. Up to half of men who have radiation for prostate cancer experience ED afterward. In some men, this symptom will improve with time. Sometimes radiation side effects dont appear until a few months after the treatment. If ED starts late, it may not be as likely to go away.
A few treatments can help with ED until youre able to have erections on your own again.
Additional treatments include the following:
Correlation With Dominant Tumor Location
Dominant lesions on RP: 50 R lobe, 44 L lobe, 31 bilateral. 15/50 R lobe and 18/44 L lobe dominant tumors had LN metastasis on the contralateral side. Only 4% of cases were associated with anterior dominant tumors. 3040% of LN metastases occur contralateral to the dominant tumor. LN metastasis is overwhelmingly associated with high grade, high stage and large volume disease. LN positivity is rarely associated with anterior dominant tumors.
Keywords:
Also Check: When Should A Man Go For A Prostate Exam
Symptoms Of Prostate Cancer Spread To The Bones
The most common place for prostate cancer to spread to is the bones. This can include the:
The most common symptom if cancer has spread to the bone is bone pain. It is usually there most of the time and can wake you up at night. The pain can be a dull ache or stabbing pain.
Your bones might also become weaker and more likely to break .
When prostate cancer spreads to the spine, it can put pressure on the spinal cord and cause spinal cord compression. This stops the nerves from being able to work properly. Back pain is usually the first symptom of spinal cord compression.
Spinal cord compression is an emergency. You should contact your treatment team immediately if you are worried you might have spinal cord compression.
How Do Doctors Find Metastatic Prostate Cancer
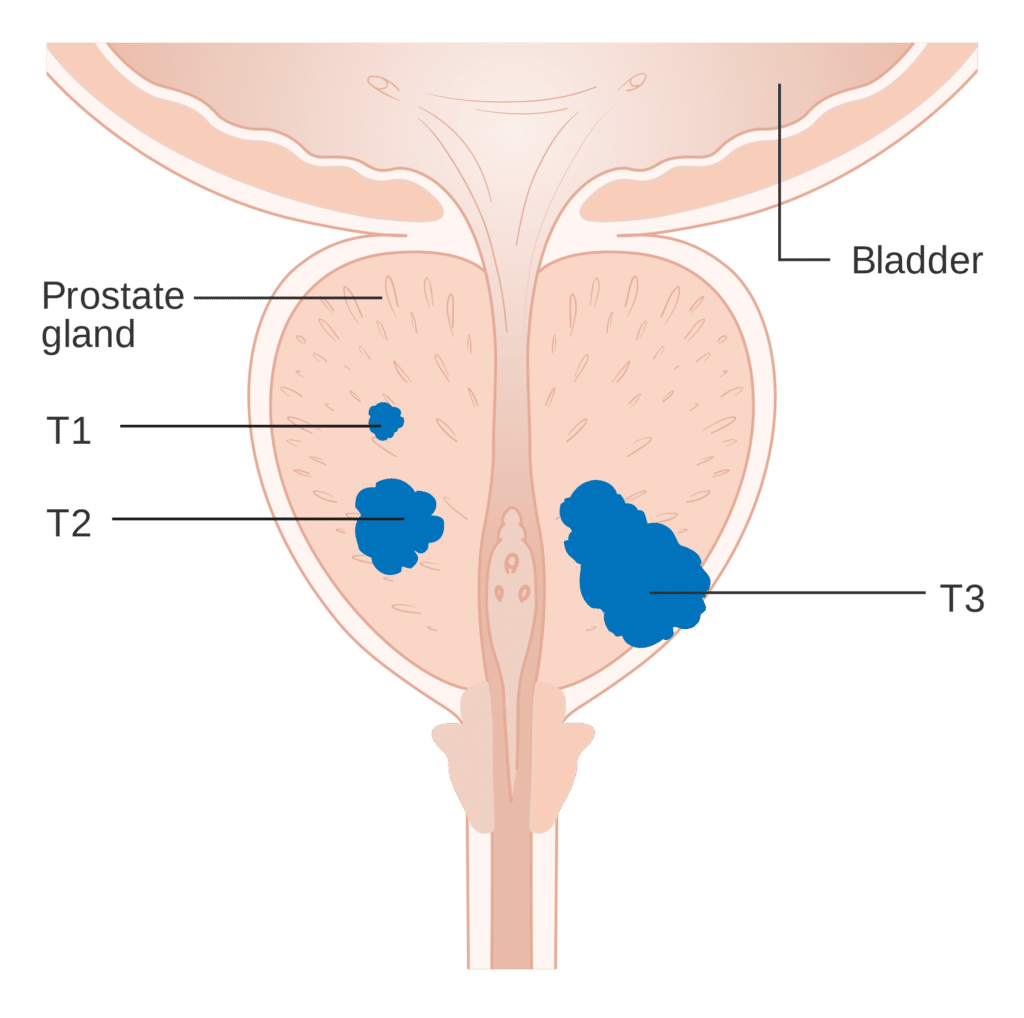
When you are diagnosed with prostate cancer, your doctor will order tests such as:
These tests may focus on your skeleton and in your belly and pelvic areas. That way doctors can check for signs that the cancer has spread.
If you have symptoms such as bone pain and broken bones for no reason, your doctor may order a bone scan. It can show if you have signs of cancer spreading to your bones.
Your doctor will also ask for blood tests, including a check of PSA levels, to look for other signs that the cancer is spreading.
PSA is a protein made by the prostate gland. A rise in PSA is one of the first signs your cancer may be growing. But PSA levels can also be high without there being cancer, such as if you have an enlarged prostate, a prostate infection, trauma to the perineum, or sexual activity.
Don’t Miss: How To Get Rid Of Prostate Infection Naturally
Treatments To Help Manage Symptoms
Advanced prostate cancer can cause symptoms, such as bone pain. Speak to your doctor or nurse if you have symptoms there are treatments available to help manage them. The treatments above may help to delay or relieve some symptoms. There are also specific treatments to help manage symptoms you may hear these called palliative treatments. They include:
This is the team of health professionals involved in your care. It is likely to include:
- a specialist nurse
- a chemotherapy nurse
- a diagnostic radiographer
- a therapeutic radiographer
- other health professionals, such as a dietitian or physiotherapist.
Your MDT will meet to discuss your diagnosis and treatment options. You might not meet all the health professionals straight away.
Your main point of contact might be called your key worker. This is usually your clinical nurse specialist , but might be someone else. The key worker will co-ordinate your care and help you get information and support. You may also have close contact with your GP and the practice nurses at your GP surgery.
How Does The Doctor Know I Have Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer tends to grow slowly over many years. Most men with early prostate cancer dont have changes that they notice. Signs of prostate cancer most often show up later, as the cancer grows.
Some signs of prostate cancer are trouble peeing, blood in the pee , trouble getting an erection, and pain in the back, hips, ribs, or other bones.
If signs are pointing to prostate cancer, tests will be done. Most men will not need all of them, but here are some of the tests you may need:
PSA blood test: PSA is a protein thats made by the prostate gland and can be found in the blood. Prostate cancer can make PSA levels go up. Blood tests will be done to see what your PSA level is and how it changes over time.
Transrectal ultrasound : For this test, a small wand is put into your rectum. It gives off sound waves and picks up the echoes as they bounce off the prostate gland. The echoes are made into a picture on a computer screen.
MRI: This test uses radio waves and strong magnets to make detailed pictures of the body. MRI scans can be used to look at the prostate and can show if the cancer has spread outside the prostate to nearby organs.
Prostate biopsy: For a prostate biopsy, the doctor uses a long, hollow needle to take out small pieces of the prostate where the cancer might be. This is often done while using TRUS or MRI to look at the prostate. The prostate pieces are then checked for cancer cells. Ask the doctor what kind of biopsy you need and how its done.
Don’t Miss: Is Radiation For Prostate Cancer Safe
Questions To Ask Your Doctor Or Nurse
- What type of hormone therapy are you offering me and why?
- Are there other treatments I can have?
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of my treatment?
- What treatments and support are available to help manage side effects?
- Are there any lifestyle changes that might help me manage my cancer, symptoms, or side effects?
- How often will I have check-ups and what will this involve?
- How will we know if my cancer starts to grow again?
- What other treatments are available if that happens?
- Can I join any clinical trials?
- If I have any questions or get any new symptoms, who should I contact?
Correlation Of Dominant Tumor Location And Positive Lymph Node Location
On review of RP specimens, 50 dominant tumor masses were located in the right lobe, 44 in the left lobe and 31 in bilateral lobes. Fifteen of 50 right lobe dominant cases showed positive LNs on the left side . Conversely, 18 of 44 left lobe dominant cases showed positive LNs on the right side .
15/50 right lobe dominant cancers had positive lymph nodes in the left pelvis 18/44 left lobe dominant cancers showed positive lymph nodes in the right pelvis .
Unifocal large volume high grade tumor with lymph node metastasis only on the right side Multifocal small volume low grade tumor with bilateral lymph node metastases Anterior dominant, relatively small volume grade 4+3=7 tumor with lymph node metastasis on the right side.
Dominant tumors were located in posterior/posterolateral prostate in 102 , both anterior and posterior in 18 and anterior only in 5 cases, respectively. Sixty dominant RP tumors extended from apex through base, 45 cases were located primarily in the apex to mid gland and 19 cases in the mid to base. Thirteen of 16 cases without EPE or SVI had dominant tumors localized to the apex-mid prostate.
Also Check: Life Expectancy After Metastatic Prostate Cancer
Spreading To Lymph Nodes Helps Cancer Metastasize
The researchers first asked whether cancer in the lymph nodes of mice helps tumors metastasize to the lungs, one of the most common places cancer spreads to.
They implanted groups of melanoma cells under the skin of mice and let them form tumors. In some mice, the cancer spread to the lymph nodes, and in other mice, it didnt. After several weeks, the researchers injected melanoma cells that dont spread to lymph nodes into the veins of the mice and then checked their lungs for cancer.
There were far more tumors in the lungs of mice that had cancer in their lymph nodes than in mice that didnt, they found.
So, it appears that spreading to lymph nodes helps cancer metastasize to the lungs, Dr. Engleman said.
Lymph Nodes And What They Do
Lymph vessels send lymph fluid through nodes throughout the body. Lymph nodes are small structures that work as filters for foreign substances, such as cancer cells and infections. They contain immune cells that can help fight infection by attacking and destroying germs that are carried in through the lymph fluid. Lymph nodes are located in many parts of the body, including the neck, armpit, chest, abdomen , and groin. They contain immune cells that can help fight infection by attacking and destroying germs that are carried in through the lymph fluid.
There are hundreds of lymph nodes throughout the body. Each lymph node filters the fluid and substances picked up by the vessels that lead to it. Lymph fluid from the fingers, for instance, works its way toward the chest, joining fluid from the arm. This fluid may filter through lymph nodes at the elbow, or those under the arm. Fluid from the head, scalp, and face flows down through lymph nodes in the neck. Some lymph nodes are deep inside the body, such as between the lungs or around the bowel, to filter fluid in those areas.
Don’t Miss: Plant Based Diet And Prostate Cancer
