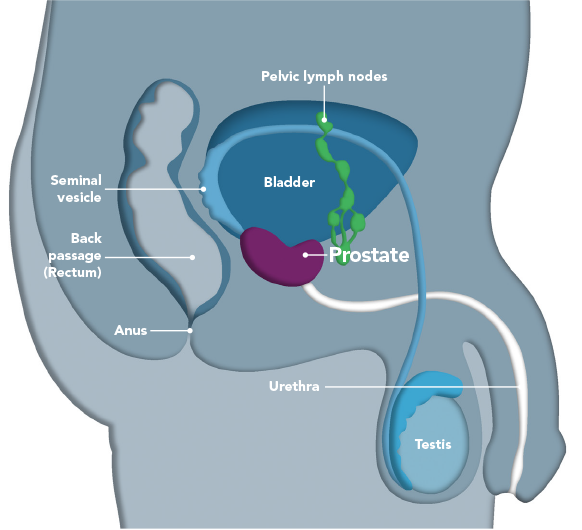
Prostate Gland Anatomy Zones
The prostate tissue is made up of many branching ducts surrounded by connective tissue and muscles known as the stroma. These ducts contain the cells that make the prostatic fluid. The prostate has a left lobe, right lobe, a base that sits at the lower part of the bladder, and an apex where the gland narrows at the urethra. It is divided up into four anatomy zones:
- Anterior fibromuscular zone: a thick muscle and fibrous tissue covering of the apex there are no ducts in this part of the prostate
- Peripheral zone: This is the largest area of the prostate and the one closest to the rectum. Most of the fluid producing ducts are located here, and it is most easily felt in a digital rectal exam . This is where a majority of prostate cancers arise.
- Central zone: This is the area around the ejaculatory ducts, which run from the seminal vesicles to the portion of the urethra surrounded by the prostate .
- Transition zone: This is the area around the prostatic urethra and the part of the prostate that enlarges with age, also known as benign prostatic hyperplasia.
The Prostate Boosts Your Sexual Capability
Prostate gland secretions comprise a large portion of seminal fluid and proper function of the gland is crucial to sexual capability in men.
The prostate contributes around 20-30% to the total seminal volume. The prostatic fluid contains substances that allow the sperm cells to live. One of these substances is the PSA, which makes the semen more fluid. This prostate role ensures that the sperm cells survive until it encounters an ovary to form an egg-cell.
What Is Prostate Cancer
This diagram shows the location of the prostate, in front of the rectum and just below the bladder.
This diagram shows the location of the prostate, in front of the rectum and just below the bladder.
Cancer is a disease in which cells in the body grow out of control. When cancer starts in the prostate, it is called prostate cancer. Not including skin cancer, prostate cancer is the most common cancer in American men.
Don’t Miss: Cialis For Prostatitis
How Does The Prostate Play A Role In Male Fertility
The prostate gland is essential for reproduction and male fertility due to the prostatic fluid it produces.
The components of the prostatic fluid ensure that sperm is healthy and is able to fertilize eggs. Prominent components of prostatic fluid include:
- The enzyme prostate-specific antigen , which thins or loosens up semen so that sperm can travel more freely
- Prostatic acid phosphatase, an enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of energy-rich compounds present in seminal fluid and may also increase sperms motility
- Citric acid, which may help maintain osmotic-electrolytic equilibrium in semen
- Zinc, which is important for semen coagulation
- Spermine, which is ultimately responsible for semens unique odor and may play a role in sperm motility and helping sperm fertilize eggs, according to an article published in Endocrine Reviews.
- Prostatic inhibin, or prostatic secretory protein, a protein that plays a role in regulating cell growth
Additionally, prostatic fluid is alkaline , and research published in July 2015 in the journal PLoS One suggested that the pH level of sperm can play a role in reproduction, helping maintain the viability of sperm and successful fertilization.
Infertility may develop if there are changes to the composition or secretion of the prostatic fluid.
Read Also: Can Prostatitis Go Away On Its Own
Gene And Protein Expression
About 20,000 protein coding genes are expressed in human cells and almost 75% of these genes are expressed in the normal prostate. About 150 of these genes are more specifically expressed in the prostate with about 20 genes being highly prostate specific. The corresponding specific proteins are expressed in the glandular and secretory cells of the prostatic gland and have functions that are important for the characteristics of semen. Some of the prostate specific proteins, such as the prostate specific antigen , and the Prostatic acid phosphatase.
In the developing embryo, at the hind end lies an inpouching called the cloaca. This, over the fourth to the seventh week, divides into a urogenital sinus and the beginnings of the anal canal, with a wall forming between these two inpouchings called the urorectal septum. The urogenital sinus divides into three parts, with the middle part forming the urethra the upper part is largest and becomes the urinary bladder, and the lower part then changes depending on the biological sex of the embryo.
Don’t Miss: Is Zinc Good For Prostate
Prostate Zones And Prostate Cancer All You Need To Know
Prostate carcinoma is a serious health problem for men all around the globe. In fact, the disease is affecting around 1 in every 6 men.
Those who suspect they have cancer do a prostate biopsy and MRI screening. The sooner you detect the illness, the easier it can be to manage it.
But, its critical to understand the prostate zones when you want to know more about them. Identifying the zone can help you learn more about the male body and its cancer susceptibility. This is a detailed review of the zones and their connection to prostate cancer.
Functions The Prostate Gland Performs
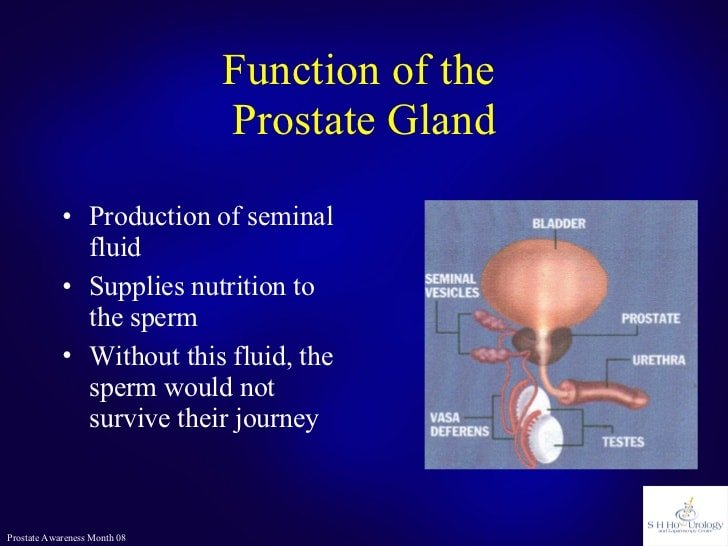
The prostate is something that every man knows about, but few realize the various functions this walnut-sized gland is responsible for in the male reproductive system. Weve put together a list of 10 amazing functions the prostate gland performs based on information from bewellbuzz.com.
It helps produce semen.
The main function of the prostate is to help produce semen. It makes an alkaline fluid which mixes with sperm during ejaculation to create semen. The alkaline fluid helps to protect the sperm once it reaches a womans vagina as this is an acidic environment.
It produces prostate-specific antigen .
The prostate produces a fluid called prostate-specific antigen which also helps the sperm by acting like a glue to attach it to a womans cervix. The glue then dissolves and the sperm is free to swim into the uterus to find an egg.
The high levels of PSA in a man can also be an indication of prostate cancer. Men over a certain age should have their PSA levels checked on a yearly basis. This is done through a simple blood test.
It pumps sperm.
As well as helping to make semen, the prostate gland helps to pump out sperm during intercourse. The pumping action ensures that the sperm can travel far enough into the uterus to possibly find an egg. This experience helps make sex pleasurable for men.
Its the G-spot.
It acts as a filter.
It creates erections.
It controls urine flow.
Also Check: Zinc Prostrate
Can Male Menopause Be Treated
If your testosterone levels are low, hormone replacement therapy may help relieve symptoms, such as the loss of interest in sex, depression and fatigue. However, replacing male hormones can make prostate cancer worse, and may make atherosclerosis worse, also.
You should receive a complete physical examination and laboratory tests should be performed before starting hormone replacement therapy. There are still many unanswered questions about how many middle-aged men could benefit from hormone replacement therapy. Talk to your healthcare provider about all the pros and cons of this treatment and what the best option is for you.
What Does My Prostate Do
It is a small gland that is part of the male reproductive system. Its supposed to be about the shape and size of a walnut.
It rests below your bladder and in front of your rectum. It surrounds part of the urethra, the tube in your penis that carries pee from your bladder.
The prostate helps make some of the fluid in semen, which carries sperm from your testicles when you ejaculate.
Also Check: External Prostate Massage For Prostatitis
Why Do Men Have A Prostate
The prostate is a small gland in men that helps make semen. Located just below the bladder in front of the rectum, it wraps around the tube that carries urine and semen out of the body. It tends to grow larger as you get older. If your prostate gets too large, it can cause a number of health issues.
Medication For Urinary Problems
Your doctor may suggest various medications to help ease your urinary problems, including:
- medications to reduce the tone of the muscles of the urethra and prostate to minimise any constriction to urine flow caused when these muscles contract
- medication to reduce the size of the prostate gland. These medications work by blocking the action of male hormones produced by the prostate gland
- medications to relax the bladder, making unwanted contractions less likely and reducing the symptoms of urgency and frequency of urination
- the over-the-counter preparation ‘saw palmetto’ is sometimes used. This may help some men, especially if frequent urination at night is a problem.
However, recent reviews of the evidence for using saw palmetto as a treatment for mild or moderate urinary symptoms did not show any improvement, compared to no treatment, in men with BPH.
Also Check: Define Prostate
Who Might Get An Enlarged Prostate
BPH is common and cannot be prevented. Age and a family history of BPH are two things that increase the chances you might get it. A few stats on that:
- Some 8 out of every 10 men eventually develop an enlarged prostate.
- About 90% of men over the age of 85 will have BPH.
- About 30% of men will find their symptoms bothersome.
What Are The External Male Reproductive Structures
Most of the male reproductive system is located outside of your abdominal cavity or pelvis. The external parts of the male reproductive system include the penis, the scrotum and the testicles.
Penis
The penis is the male organ for sexual intercourse. It has three parts:
- The root: This is the part of the penis that attaches to the wall of your abdomen.
- The body or shaft: Shaped like a tube or cylinder, the body of the penis is made up of three internal chambers. Inside these chambers theres a special, sponge-like erectile tissue that contains thousands of large spaces that fill with blood when youre sexually aroused. As the penis fills with blood, it becomes rigid and erect, which allows for penetration during sex. The skin of the penis is loose and elastic, allowing for changes in penis size during an erection.
- The glans: This is the cone-shaped end of the penis. The glans, which is also called the head of the penis, is covered with a loose layer of skin called foreskin. This skin is sometimes removed in a procedure called circumcision.
The opening of the urethra the tube that transports both semen and urine out of the body is located at the tip of the glans penis. The penis also contains many sensitive nerve endings.
Semen, which contains sperm, is expelled through the end of the penis when a man reaches sexual climax . When the penis is erect, the flow of urine is blocked from the urethra, allowing only semen to be ejaculated at orgasm.
Scrotum
Recommended Reading: What Is The Definition Of Prostate Gland
How Does The Male Reproductive System Function
The entire male reproductive system is dependent on hormones. These are chemicals that stimulate or regulate the activity of your cells or organs. The primary hormones involved in the functioning of the male reproductive system are follicle-stimulating hormone , luteinizing hormone and testosterone.
FSH and LH are produced by the pituitary gland. Its located at the base of your brain and its responsible for many functions in your body. FSH is necessary for sperm production . LH stimulates the production of testosterone, which is necessary to continue the process of spermatogenesis. Testosterone is also important in the development of male characteristics, including muscle mass and strength, fat distribution, bone mass and sex drive.
Actions For This Page
- The prostate gland is a male reproductive organ that produces fluids to feed and protect sperm cells.
- Many men experience urinary changes as they age. In many cases, these changes do not need specific treatment.
- When urinary changes cause problems, they can be treated successfully by lifestyle changes, medication, surgery or a combination of the three.
- For problems such as blood in the urine, pain on urination, inability to urinate or uncontrollable urine flow, see your doctor promptly.
Recommended Reading: How Effective Is Chemotherapy For Prostate Cancer
What Does The Prostate Do
The prostate produces a fluid that mixes with sperm to make semen. The fluid is kept in a tube-shaped gland that sits behind the bladder. This gland is called the seminal vesicle. During sex, the muscle tissue helps force prostate fluid and sperm into the urethra.
The sex hormone testosterone controls how the prostate works. Testosterone is responsible for things like your sex drive, getting an erection, and muscle development.
The prostate also produces a protein called prostate-specific antigen . This helps to make semen more watery. A blood test can measure PSA. This is called a PSA test. Doctors use it to help diagnose different prostate problems, including cancer.
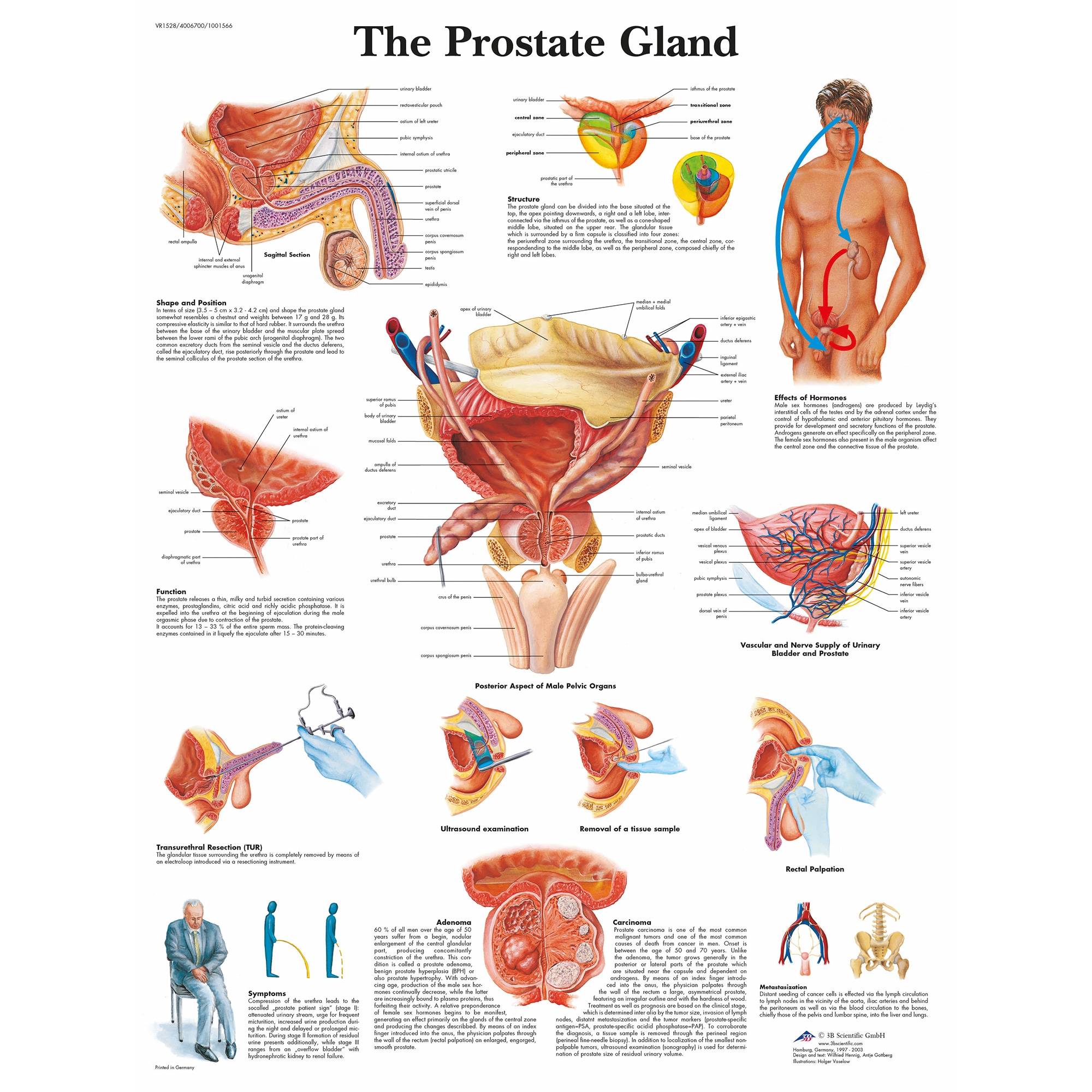
Normal Anatomy And Radiographic Appearance
The normal prostate gland surrounds the most proximal aspect of the urethra and lies ventral to the rectum and caudal to the urinary bladder, typically within the pelvic canal. In many dogs, especially neutered dogs, the normal prostate gland is not visible radiographically. With slight enlargement, whether normal or abnormal, the prostate gland is recognized radiographically by its round shape and soft tissue opacity and by the relation of the gland to the organs around it. The absolute normal size of the prostate gland is dependent on the age, size and neuter status of the dog being imaged.1 Inability to see the normal prostate gland is influenced by the fact that it is usually in direct contact with the rectum, resulting in the dorsal border of the prostate gland being effaced, especially if the rectum contains feces. A full rectum may also obscure the prostate gland on the ventrodorsal view. Also, if the shape or position of the prostate gland is altered, it may not be recognizable other than as a nondescript opacity between the bladder, rectum, and pelvis.2
The normal prostate gland is not visible in the cat because of its location on the dorsal lateral surfaces of the mid pelvic urethra and its small size, measuring normally only about 10mm in length.3 Prostatic diseases causing clinical signs in cats are very rare and will not be considered further in this chapter.
Donald E. Thrall DVM, PhD, DACVR , Ian D. Robertson BVSc, DACVR, in, 2016
Read Also: Transitional Zone Prostate
Prostatitis: A Common Prostate Problem In Younger Men
Prostatitis, or prostate inflammation, is the most common prostatic and urinary tract problem for men under age 50, according to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases . It accounts for 2 million doctor visits in the United States each year.
There are several types of prostatitis.
Prostatitis caused by bacteria is known as bacterial prostatitis, and it can cause an acute or chronic infection.
Read Also: What Is A Prostate Vibrator
Facts About The Prostate Gland
The prostate gland is about the size of a walnut. It’s located just below the bladder and it surrounds the urethra. This is a tube that carries urine and semen out of the body. The prostate is partly muscular and partly glandular. It has tubes that open into the prostatic part of the urethra. It is made up of 3 lobes: a middle lobe, left lobe, and right lobe.
Recommended Reading: Is Zinc Good For Prostate
What Does The Prostate Gland Do
09 August 2010
The prostate gland is a male reproductive organ whose main function is to secrete prostate fluid, one of the components of semen. The muscles of the prostate gland also help propel this seminal fluid into the urethra during ejaculation .
The prostate is a muscular gland that weighs about three-fourths of an ounce about the size of a small apricot. It surrounds the urethra just beneath the bladder .
During ejaculation, millions of sperm move from the testes through tubes called the vas deferens into the area of the prostate. At this point, the prostate contracts, closing off the opening between the bladder and the urethra, releasing fluid into the urethra and pushing semen on through.
The fluid excreted by the prostate makes up about one-third of the total volume of semen and contains various enzymes, zinc and citric acid. Though prostate fluid is slightly acidic, another fluid in semen made by the seminal vesicles leaves semen slightly alkaline, or basic. This alkalinity helps protect sperm and prolong their life after they are deposited in the acidic environment of the vagina, according to the biology textbook, “Life: The Science of Biology, Eighth Addition” .
One component of prostate fluid an enzyme called Prostate Specific Antigen also aids in the success of sperm by liquefying semen that has thickened after ejaculation. This thinning action allows sperm to swim more freely, according to the medical reference book “Prostate Specific Antigen” .
Introduction: Anatomy And Function Of The Prostate Gland
The prostate gland is an accessory male reproductive organ, located at the base of the bladder, and surrounding the urethra. It produces prostatic secretions that contain zinc, citric acid, calcium, phosphates, and other enzymes essential for sperm health and motility. At ejaculation, semen passes through the ejaculatory ducts and mixes with secretions from the prostate gland .
Fig. 1. Anatomical zones of the prostate. The prostate consists of four anatomical zones the centreal , peripheral , and transition zones, and the anterior fibromuscular stroma .
Prostatic fluids arise from the epithelial cells lining the ducts that are separated from surrounding stroma by a basement membrane. The epithelium consists of basal, neuroendocrine and secretory cells and it is polarized so that the secretions arise at the luminal aspect of the epithelium including prostatic-specific antigen . Basally located epithelial cells secrete extracellular matrix for the basement membrane and also include the stem and stem progenitor populations. The surrounding fibromuscular stroma consists of smooth muscle cells, fibroblasts, nerves, endothelial cells, immune cells, and blood vessels. The smooth muscle component provides contractility that is required when proteins are exuded from the glands .
Fig. 2. Distribution of cell types within the prostate. The prostate is a glandular organ, consisting of an epithelial and stromal component, separated by a basement membrane.
Tracey S. Chenier, in, 2009
Recommended Reading: What Happens After Chemo For Prostate Cancer
