Who Is More Likely To Have Prostate Cancer Recurrence
In general, the further your cancer has spread and the more aggressive it is, the more likely it is to recur. Specific factors include:
- Tumor size: In general, the larger the tumor, the more likely it is to recur.
- Gleason score: A higher Gleason score means a more aggressive cancer and a higher rate of recurrence.
- Cancer staging: Staging refers to how far the cancer has spread. Higher stage cancers have spread further at initial treatment and have higher rates of recurrence.
- Involvement of the lymph nodes: Prostate cancer that has entered the lymph nodes prior to treatment is more likely to recur.
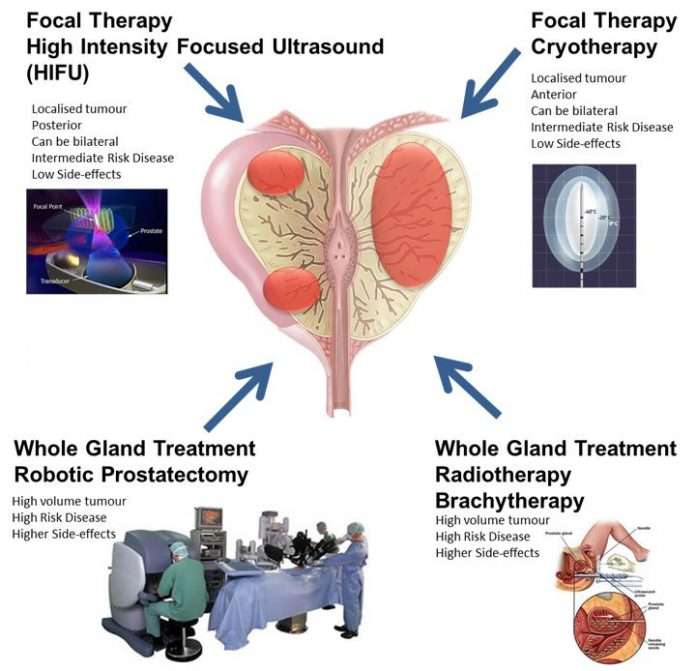
What Is The Best Treatment For Prostate Cancer
Depending on each case, treatment options for men with prostate cancer might include:
- Observation or Active Surveillance for Prostate Cancer.
- Surgery for Prostate Cancer.
- Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer.
- Cryotherapy for Prostate Cancer.
- Hormone Therapy for Prostate Cancer.
- Chemotherapy for Prostate Cancer.
Treating Advanced Prostate Cancer
It is very important for patients with advanced prostate cancer to seek care from a comprehensive cancer center like Roswell Park, Dr. Chatta says. The single biggest thing is, we have a whole team of people attacking this problem, which is clearly beyond the bandwidth of one or two people. When you have a whole team, that makes for better care.
Treatment for advanced prostate cancer may include a number of different approaches, including hormone therapy, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, radiopharmaceuticals and targeted therapy. However, the mainstay of treatment continues to be hormone therapy, which aims to block interactions between androgens and the androgen receptor on cells. At any given stage, whether it has spread to lymph nodes or bone, the bread and butter of prostate cancer treatment is to knock down testosterone, Dr. Chatta says. It is the main fuel for prostate cancer.
Recommended Reading: How To Reduce Your Chances Of Getting Prostate Cancer
Asian Or Pacific Islander Ethnic Background Was Associated With Favorable Os
Several studies have reported that for localized and locally advanced PCa patients, Black men consistently have a higher mortality rate than do men of other ethnicities. One possible reason for this finding is that Black men are less likely to be treated with a curative intent than are White men . However, in our study, Black men presented survival times similar to those of White men. This phenomenon might be explained by the fact that in the metastatic stage, there are few proactive treatments available to significantly change the oncological outcome of these patients. Interestingly, our study demonstrated that patients with an Asian or Pacific Islander background were associated with a better OS than White men, which is consistent with previous reports showing that Asian men have superior survival in de novo metastatic PCa than do men of other races . Therefore, genomic diversities rather than treatments are most accountable for the different survival times between races . It is known that allelic imbalance at 13q14 and 13q21 is significantly higher in Japanese patients than in Caucasians . The frequency of the TMPRSS2-ERG fusion in Chinese patients is significantly lower than those patients from Western countries . Furthermore, differences in diet and other lifestyle factors may also affect survival .
Urethral Cancer Is A Disease In Which Malignant Cells Form In The Tissues Of The Urethra
The urethra is the tube that carries urine from the bladder to outside the body. In women, the urethra is about 1½ inches long and is just above the . In men, the urethra is about 8 inches long, and goes through the prostategland and the to the outside of the body. In men, the urethra also carries .
Urethral cancer is a rare cancer that occurs more often in men than in women.
Recommended Reading: Womenâs Bladder Leakage Protection
Recommended Reading: Can You Milk Your Prostate
How To Reduce Prostate Size
This article was medically reviewed by . Dr. Litza is a board certified Family Medicine Physician in Wisconsin. She is a practicing Physician and taught as a Clinical Professor for 13 years, after receiving her MD from the University of Wisconsin-Madison School of Medicine and Public Health in 1998.There are 13 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been viewed 65,131 times.
The prostate gland is a part of the male reproductive system that can enlarge with age, putting uncomfortable pressure on the urethra. This can cause urinary difficulties, urinary tract infections , and even bladder stones. By making lifestyle changes and using medication, most men can reduce their urinary troubles. A few men, though, may need to consider minimally invasive or traditional surgery options to feel their best.
Questions To Ask The Doctor
- What treatment do you think is best for me?
- Whats the goal of this treatment? Do you think it could cure the cancer?
- Will treatment include surgery? If so, who will do the surgery?
- What will the surgery be like?
- Will I need other types of treatment, too?
- Whats the goal of these treatments?
- What side effects could I have from these treatments?
- What can I do about side effects that I might have?
- Is there a clinical trial that might be right for me?
- What about special vitamins or diets that friends tell me about? How will I know if they are safe?
- How soon do I need to start treatment?
- What should I do to be ready for treatment?
- Is there anything I can do to help the treatment work better?
- Whats the next step?
Recommended Reading: What Is The Latest Treatment For Enlarged Prostate
Where Prostate Cancer Spreads
If left untreated, diagnosed prostate cancer can grow and possibly spread outside of the prostate to local tissues or distantly to other sites in the body. The first sites of spread are typically to the nearby tissues.
The cancer can spread down the blood vessels, lymphatic channels, or nerves that enter and exit the prostate, or cancer could erode directly through the capsule that surrounds the prostate.
The seminal vesicles are a site of particularly common early spread. More extensive local spread can occur with cancer invading the nearby bladder or rectum.
Further advancement of cancer can occur when cancer cells enter the blood vessels and lymphatic channels. Once cancer has entered into these vessels, prostate cancer cells can seed into virtually any other part of the body.
Prostate cancer is known to have a particular affinity for spreading or metastasizing to the bones especially the lower spine, pelvis, and femur. Other organs such as the liver, brain, or lungs can also be the sites of spread, but these are much rarer.
You May Like: Is There A Blood Test For Prostate
What Causes Prostate Cancer And Am I At Risk
Every man is at risk for prostate cancer as he ages. Although prostate cancer can affect younger men, about 6 out of 10 cases are diagnosed in men over the age of 65. The average age of diagnosis is 66. After non-melanoma skin cancer, prostate is the most common cancer diagnosed in men in the United States. The American Cancer Society estimates there will be 248,530 new cases of prostate cancer each year.
Although there are several known risk factors for getting prostate cancer, no one knows exactly why one man gets it and another doesnt. Some important risk factors for prostate cancer are:
Dont Miss: Can You Still Have Sex With Prostate Cancer
Recommended Reading: Are Eggs Bad For Prostate
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer may not cause any signs and symptoms in the early stages. Hence, it is advisable for men over 50 years of age with or without other risk factors to consult with a doctor to be screened for prostate cancer.
Prostate cancer can cause the following signs and symptoms in the later stages
Dont Miss: Radiation For Metastatic Prostate Cancer
Active Surveillance And Watchful Waiting
If prostate cancer is in an early stage, is growing slowly, and treating the cancer would cause more problems than the disease itself, a doctor may recommend active surveillance or watchful waiting.
Active surveillance. Prostate cancer treatments may seriously affect a person’s quality of life. These treatments can cause side effects, such as erectile dysfunction, which is when someone is unable to get and maintain an erection, and incontinence, which is when a person cannot control their urine flow or bowel function. In addition, many prostate cancers grow slowly and cause no symptoms or problems. For this reason, many people may consider delaying cancer treatment rather than starting treatment right away. This is called active surveillance. During active surveillance, the cancer is closely monitored for signs that it is worsening. If the cancer is found to be worsening, treatment will begin.
ASCO encourages the following testing schedule for active surveillance:
-
A PSA test every 3 to 6 months
-
A DRE at least once every year
-
Another prostate biopsy within 6 to 12 months, then a biopsy at least every 2 to 5 years
Treatment should begin if the results of the tests done during active surveillance show signs of the cancer becoming more aggressive or spreading, if the cancer causes pain, or if the cancer blocks the urinary tract.
Also Check: What Happens When A Man Loses His Prostate
What Happens When Prostate Cancer Is Left Untreated
While most men undergo some form of treatment for their prostate cancer, some men today choose to not be treated for their prostate cancer. Instead, they may choose to have their healthcare providers monitor their cancer.
Known as active surveillance, it is common when the cancer is expected to grow slowly based on biopsy results, confined to the prostate, not causing any symptoms, and/or small. In active surveillance, healthcare providers will initiate cancer treatment only if cancer starts growing.
Others men may choose to not undergo cancer treatment because of a short life expectancy or other serious medical problems. They may feel that the risks or side effects of cancer treatment outweigh their potential benefits.
This option is certainly OK and reasonable in the right circumstancesrequiring a careful and thoughtful discussion with your healthcare provider and family.
Stem Cell Or Bone Marrow Transplant
A stem cell transplant, sometimes called bone marrow transplant, replaces damaged blood-forming cells with healthy ones. The procedure takes place following large-dose chemotherapy or radiation therapy to kill cancer cells and to stop your stem cells from producing cancerous cells.
Stem cell transplants can be used for several types of cancer, including multiple myeloma and some kinds of leukemia.
Don’t Miss: Is Colon Cancer The Same As Prostate Cancer
What To Expect If Prostate Cancer Spreads
Metastatic cancer from the prostate can be different for every patient. In most cases, prostate cancer is slowly growing. The patient may not expect the prostate cancer severity to increase when test results show a slow growth rate and stability.
It is, however, important to understand what to expect in a case where prostate cancer progression results in metastasis.
It is important to note that when prostate cancer spreads, the cancerous cells may start to develop tumors in various areas of the body. This means what you should expect largely depends on where the cancerous cells start to form new tumors.
If cancer spreads to nearby tissue, you may experience problems with bladder function. Problems with the bladder can lead to stress urinary incontinence and similar issues. Some men also complain about erection problems when the tumor affects surrounding tissues. In cases where cancer spreads toward the lungs, the patient may experience trouble breathing and pain in the chest. Prostate cancer weight loss is also relatively common among patients with metastasis. The weight loss can have a sudden onset, and the patient may lose excessive weight in just a short period.
Detecting Prostate Cancer Progression
However, recent advances in imaging technology have given doctors better tools to find those stray cancer cells. We now have more sophisticated scans to pick these up before surgery, which only became available in the last 12 to 15 months, he says. Only time will tell if these will increase cure rates.
Men who have been diagnosed with prostate cancer undergo certain tests to see if the cancer has spread, including X-rays and CT, MRI and prostate-specific PET scans. Patients have these tests periodically in the years after initial treatment to keep tabs on the disease.
Symptoms such as bone pain and broken bones may also signify cancer spread. If prostate cancer patients experience those, they should alert their doctor, who may order the appropriate scans. However, the goal of newer imaging techniques is to pick up the cancer well before any symptoms develop.
Free Prostate Cancer Early Detection Event
The Buffalo Sabres and Roswell Park are partnering up once again to provide free prostate early detection screening to all eligible men, 45-70 years old. The event will take place on Monday, November 7, 2022 at KeyBank Center..
Recommended Reading: When Do You Have Your First Prostate Exam
How Does Prostate Cancer Spread
Cancer cells sometimes break away from the original tumor and go to a blood or lymph vessel. Once there, they move through your body. The cells stop in capillaries — tiny blood vessels — at some distant location.
The cells then break through the wall of the blood vessel and attach to whatever tissue they find. They multiply and grow new blood vessels to bring nutrients to the new tumor. Prostate cancer prefers to grow in specific areas, such as lymph nodes or in the ribs, pelvic bones, and spine.
Most breakaway cancer cells form new tumors. Many others don’t survive in the bloodstream. Some die at the site of the new tissue. Others may lie inactive for years or never become active.
Remission And The Chance Of Recurrence
A remission is when cancer cannot be detected in the body and there are no symptoms. This may also be called having no evidence of disease or NED.
A remission can be temporary or permanent. This uncertainty causes many people to worry that the cancer will come back. Although there are treatments to help prevent a recurrence, such as hormonal therapy and radiation therapy, it is important to talk with your doctor about the possibility of the cancer returning. There are tools your doctor can use, called nomograms, to estimate someone’s risk of recurrence. Understanding your risk of recurrence and the treatment options may help you feel more prepared if the cancer does return. Learn more about coping with the fear of recurrence.
In general, following surgery or radiation therapy, the PSA level in the blood usually drops. If the PSA level starts to rise again, it may be a sign that the cancer has come back. If the cancer returns after the original treatment, it is called recurrent cancer.
When this occurs, a new cycle of testing will begin again to learn as much as possible about the recurrence, including where the recurrence is located. The cancer may come back in the prostate , in the tissues or lymph nodes near the prostate , or in another part of the body, such as the bones, lungs, or liver . Sometimes the doctor cannot find a tumor even though the PSA level has increased. This is known as a PSA recurrence or biochemical recurrence.
Also Check: What Type Of Doctor Does Prostate Exams
Treatments To Help Manage Symptoms
Advanced prostate cancer can cause symptoms, such as bone pain. Speak to your doctor or nurse if you have symptoms there are treatments available to help manage them. The treatments above may help to delay or relieve some symptoms. There are also specific treatments to help manage symptoms you may hear these called palliative treatments. They include:
This is the team of health professionals involved in your care. It is likely to include:
- a specialist nurse
- a chemotherapy nurse
- a diagnostic radiographer
- a therapeutic radiographer
- other health professionals, such as a dietitian or physiotherapist.
Your MDT will meet to discuss your diagnosis and treatment options. You might not meet all the health professionals straight away.
Your main point of contact might be called your key worker. This is usually your clinical nurse specialist , but might be someone else. The key worker will co-ordinate your care and help you get information and support. You may also have close contact with your GP and the practice nurses at your GP surgery.
Treatments For Prostate Cancer Spread To Bones
If prostate cancer spreads to other parts of the body, it nearly always goes to the bones first. Bone metastasis can be painful and can cause other problems, such as fractures , spinal cord compression , or high blood calcium levels, which can be dangerous or even life threatening.
If the cancer has grown outside the prostate, preventing or slowing the spread of the cancer to the bones is a major goal of treatment. If the cancer has already reached the bones, controlling or relieving pain and other complications is also a very important part of treatment.
Treatments such as hormone therapy, chemotherapy, and vaccines may help with this, but other treatments specifically target bone metastasis and the problems it may cause.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Difference Between Bph And Prostate Cancer
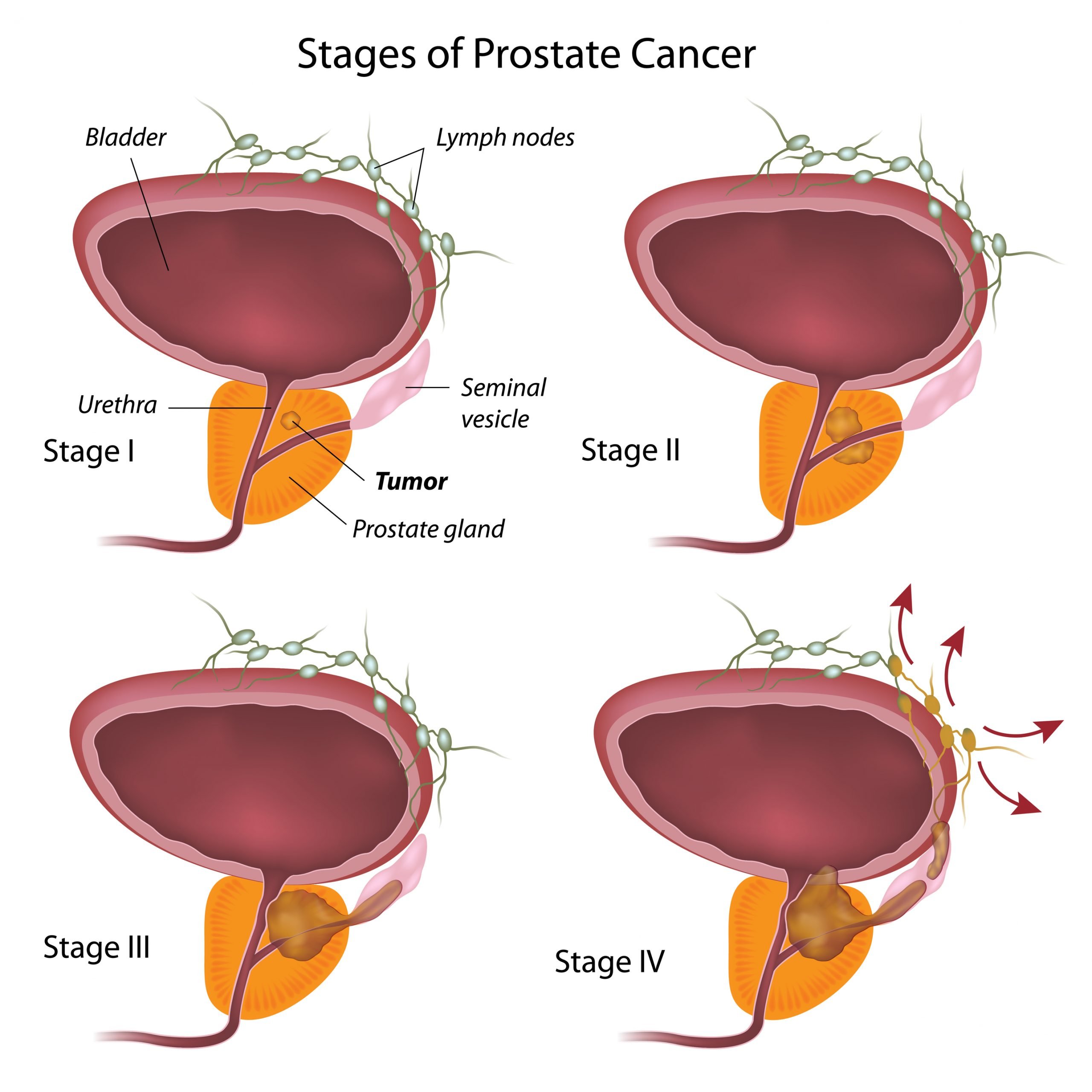
Overview Of The Staging System
After a thorough assessment by your oncologist, your cancer will be assigned a stage between I and IV. Prostate cancer stages are based on the American Joint Committee on Cancer TNM system. Using the TNM system, your oncologist:
- Examines the tumor
- Determines if the cancer has spread to any lymph nodes
- Assesses whether the cancer has metastasized
- Considers the prostate-specific antigen level from blood testing
- Assigns a grade group based on how abnormal the cancer appears under a microscope
With this information in mind, you can better understand how stages are assigned and what they mean for patients in general.
Recommended Reading: What Kind Of Pain Does Prostate Cancer Cause
