Treatment Of Prostate Cancer
Treatment of prostate cancer depends on many factors, including your age, your overall health and the growth and spread of the cancer when it is diagnosed. Some men who have slow growing tumours may not need treatment right away and some may never need treatment.
Other types of prostate cancer are aggressive and can quickly spread to other parts of the body, making treatment difficult. Common treatment options include watchful waiting or expectant management , radiation therapy , chemotherapy, surgery and hormone therapy.
The Jamaica Cancer Society currently has the largest and most-organised screening clinic for prostate cancer in Jamaica. The JCS is a non-profit, non-governmental organisation that was formed in 1955 to initiate and engage in activities for the prevention and control of cancer in Jamaica.
The head office is located in Kingston, with three branches in the parishes of St Ann/St Mary, Manchester, and St Elizabeth. Screening services are provided by volunteer members of the Jamaica Urological Society. Recommendations for screening are annual visits commencing at age 40.
Males presenting for screening have digital rectal examinations and PSA. Men with abnormal PSAs and DREs are recommended for confirmatory transrectal ultrasound guided biopsies. All men diagnosed with prostate cancer are referred for treatment at a urology clinic of their choice.
DID YOU KNOW?
· All men are at risk of developing prostate cancer and the risk increases as they grow older
Are There Prostate Cancer Risk Factors To Consider
Cancer researchers have identified several factors that could increase a mans risk of developing prostate cancer. In considering whether any of these risk factors apply to you, remember that having one or more of them does not mean you will get the disease. However, you should be sure to get all the prostate cancer screenings your physician recommends. It is also important to know that men without these risk factors may also have prostate cancer.
Psa Screening For Prostate Cancer: A Controversial History
The history of the role of the prostate-specific antigen test for prostate cancer is controversial.
The prostate-specific antigen blood test was created in the late 1980s, and tests for elevated levels of the antigen. Elevated levels can be suggestive of prostate cancer. The test itself is insufficient for diagnosing prostate cancer and was initially proposed as a marker of prostate cancer recurrence or disease progression. But doctors quickly began using it for cancer screening throughout the United States. By 1992, PSA testing as a cancer screen was at its peak.
Also, in the late 1980s, surgeons in the United States and Europe perfected the technique of radical prostatectomy, which involves removal of the prostate gland and any cancer within it. Initially, it seemed like an ideal situation: Men could have a simple blood test and prostate cancers that had not spread outside of the prostate gland could be cured.
But as time wore on, problems emerged that had not been anticipated when PSA screening was introduced:
You May Like: How To Insert A Prostate Toy
How Does The Doctor Know I Have Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer tends to grow slowly over many years. Most men with early prostate cancer dont have changes that they notice. Signs of prostate cancer most often show up later, as the cancer grows.
Some signs of prostate cancer are trouble peeing, blood in the pee , trouble getting an erection, and pain in the back, hips, ribs, or other bones.
If signs are pointing to prostate cancer, tests will be done. Most men will not need all of them, but here are some of the tests you may need:
PSA blood test: PSA is a protein thats made by the prostate gland and can be found in the blood. Prostate cancer can make PSA levels go up. Blood tests will be done to see what your PSA level is and how it changes over time.
Transrectal ultrasound : For this test, a small wand is put into your rectum. It gives off sound waves and picks up the echoes as they bounce off the prostate gland. The echoes are made into a picture on a computer screen.
MRI: This test uses radio waves and strong magnets to make detailed pictures of the body. MRI scans can be used to look at the prostate and can show if the cancer has spread outside the prostate to nearby organs.
Prostate biopsy: For a prostate biopsy, the doctor uses a long, hollow needle to take out small pieces of the prostate where the cancer might be. This is often done while using TRUS or MRI to look at the prostate. The prostate pieces are then checked for cancer cells. Ask the doctor what kind of biopsy you need and how its done.
Genetic Testing For Prostate Cancer
You may hear a lot about genetics or genomics. Both terms are related to genes and cell DNA, but they are different. These tests are being used to learn more about the DNA of cancer cells, and link DNA mutations with treatments. In the future, genetic testing may be the first step doctors take when diagnosing prostate cancer.
Also Check: How Many Radiation Treatments For Prostate Cancer
No Symptoms In Early Stages
The problem is, early stage prostate cancer is a silent lurker with no symptoms. However, a growing tumor will eventually cause symptoms. Since many noncancerous conditions like infection or normal age-related prostate enlargement can cause similar symptoms, only a doctor can tell the difference.
Here are 10 prostate cancer warning signs you should pay attention to. To help you remember them, I have divided them into three categories: urinary function, sexual function, and pain.
Bladder And Urinary Troubles
A prostate tumor that has grown significantly in size may start to press on your bladder and urethra. The urethra is the passage the carries urine from your bladder out of your body. If the tumor is pressing on your urethra, you might have trouble passing urine.
One of the common areas for prostate cancer to spread to is the bladder, because the two organs are close. This can cause additional problems with urination and bladder function.
Some symptoms your bladder and urethra are being affected by cancer include:
- urinating more frequently
- getting up in the middle of the night to pee
- having blood in your urine or semen
- feeling like you have to urinate often and not actually passing anything
Its not as common, but prostate cancer can also spread to your bowel. The cancer first spreads to the rectum, which is the part of your bowel closest to the prostate gland.
Symptoms of cancer thats spread to the bowels include:
- stomach pain
Don’t Miss: Is Fish Oil Linked To Prostate Cancer
Current Psa Screening Recommendations
PSA-based screening refers to testing healthy men without symptoms.
Until recently, physician societies disagreed on screening recommendations, but with the publication of the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Guideline in May 2018, all the major physician groups are broadly in agreement, including the American College of Physicians , the American Cancer Society , American Urological Association , and American Society of Clinical Oncology :
- They advise supporting men so that they make informed decisions about screening that reflect their personal preferences and values.
- Routine screening is not recommended in men between ages 40 and 54 of average risk.
- For men ages 55 to 69 years, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force concluded with moderate certainty that the net benefit of PSA-based screening is small for some men, making the decision up to the judgment of the physician and the values of the patient.”
- For men 70 years and older, they recommend against routine screening because the expected harms are thought to outweigh the benefits.
- Your doctor should not screen you unless you express a preference for it.
- A discussion of the benefits and harms of screening should include a family history of prostate cancer, race or ethnicity, any medical conditions that affect your overall health and lifespan, and your values about risk and benefit.
- If you have less than a 10-year life expectancy, screening is not recommended.
Can Prostate Cancer Be Prevented
There are no clear prevention strategies for prostate cancer. There is some conflicting evidence that a healthy diet composed of low fat, high vegetables and fruits may help reduce your risk of prostate cancer. Routine screening, with PSA blood test and physical exam, is important to detect prostate cancer at an early stage. A healthy diet and regular exercise are also critical in maintaining good health and preventing disease in general.
You May Like: Side Effects Of Prostate Supplements
Don’t Miss: Can You Get An Erection Without A Prostate
Have Any Of These Symptoms Visit Norman Urology
Theres no sense in worrying needlessly come see us at Norman Urology. We take urological care seriously for both men and women. Whether you have a benign condition or something more serious, you can count on superior, specialized care from experienced, compassionate professionals.
Reach out to us today to schedule an appointment. We cant wait to meet you.
How Do You Know If You Have Prostate Cancer
Theres no way of knowing if you have prostate cancer without visiting your doctor, as most men with early prostate cancer dont have any symptoms. And if you do have symptoms they can be caused by other things.
And you cant check for prostate cancer yourself.
You may want to speak to your GP if you’re over 50 , even if you don’t have any symptoms. These are all things that can increase your risk of prostate cancer. Your GP can give more information or tests if necessary.
If youre not sure about what to say to your GP, print and fill out this form and show it to them. This will help you have the conversation.
I thought I could be at risk after learning that African Caribbean men are more likely to get prostate cancer than white men.
Recommended Reading: Does Prostate Milking Prevent Cancer
Unfortunately Some People Can Have Cancer Without Any Symptoms Which Means Re
If breast cancer is diagnosed at an early enough stage, its treatable. Prostate cancer is one of the most common types of cancer diagnosed in men. Recognize these common warning signs of prostate cancer. Getting a diagnosis of bladder cancer can be a difficult time. Roughly 21,000 women a year are diagnosed with ovarian ca. Colon cancer is the third deadliest cancer affecting both men and women in the united states. The earlier the detection of prostate cancer. But hearing the words can still be scary. Although screenings for prostate cancer are one tool for early detecti. The earlier the detection of prostate cancer, the better the patients chance of survival is. Specifically, they form in your liver, which is an organ that cleans your blood and helps your body process nutrients. Prostate cancer is one of the most common types of cancer diagnosed in men. Ovarian cancer occurs when there are mutations of abnormal cells in the ovaries.
Part of what makes colon cancer so deadly is that it often goes relatively unnoticed because of a lack of early symptoms. Compared to other types of cancer, such as lung cancer,. Being armed with information is vital to begin the fight. The earlier the detection of prostate cancer. Here are 10 more facts about prostate cancer.
Prostate Cancer: Where Can You Find A Helping Hand
This is your one-stop source for information on prostate cancer. You can easily search for support groups, doctors, and clinical trials. And, your donation to the PCF funds prostate cancer research, with 84 cents of every dollar going toward their research mission.
PCRI focuses on improving the lives of prostate cancer patients and caregivers. We love that you can take a prostate cancer staging quiz to find out more about your prognosis. To take it, youll need to know the results of your PSA, biopsy, digital rectal exam, bone scan, and CT scan.
The American Cancer Society is considered the go-to source for reliable cancer information. Their site offers news releases, clinical trial opportunities, online support groups, and more. We especially like their Understanding Health Insurance page, which navigates you through the often complex process of utilizing health insurance for cancer treatments.
Also Check: When Is Prostate Cancer Awareness Month
How Doctors Find Metastatic Prostate Cancer
When you are diagnosed with prostate cancer, your doctor will order tests such as:
These tests may focus on your skeleton and in your belly and pelvic areas. That way doctors can check for signs that the cancer has spread.
If you have symptoms such as bone pain and broken bones for no reason, your doctor may order a bone scan. It can show if you have signs of cancer spread in your bones.
Your doctor will also ask for blood tests, including a check of PSA levels, to look for other signs that the cancer is spreading.
PSA is a protein made by the prostate gland. A rise in PSA is one of the first signs your cancer may be growing. But PSA levels can also be high without there being cancer, such as if you have an enlarged prostate a prostate infection, trauma to the perineum, or sexual activity can also cause PSA level to be high.
If youve been treated, especially if a surgeon removed your prostate, your PSA levels should start to go down. Doctors usually wait seve,ral weeks after surgery before checking PSA levels. A rise in PSA after treatment may suggest the possibility cancer is back or spreading. In that case, your doctor may order the same tests used to diagnose the original cancer, including a CT scan, MRI, or bone scan. The radiotracer Axumin could be used along with a PET scan to help detect and localize any recurrent cancer.
Though very rare, its possible to have metastatic prostate cancer without a higher-than-normal PSA level.
What About Trans People
People born with a prostate can develop prostate cancer. Individuals born without a prostate cannot develop prostate cancer.
Trans women who use hormone therapy such as estrogen may have a lower risk, but the risk is still present.
Anyone born with a prostate should speak to their doctor about screening for prostate cancer.
Recommended Reading: Can Enlarged Prostate Be Cured By Homeopathy
So What Causes Prostate Cancer
The exact cause of prostate cancer is unknown. Most prostate cancers happen by chance, or due to shared environmental and common genetic factors. But what we do know is that prostate cancer happens when some prostate cells become abnormal.
Abnormal cells grow and multiply more quickly than normal cells. And as abnormal cells continue to accumulate, normal cells die and a tumor forms. That tumor can grow and spread to nearby tissue, and those abnormal cells can also spread to other parts of the body.
What Are 5 Common Warning Signs Of Prostate Cancer
In many cases, prostate cancer does not produce clear symptoms in its initial stages of development. In fact, many men may have prostate cancer without even realizing it. However, there are some common warning signs that could indicate a person has prostate cancer. Five of the most common ones include:
Of course, these five symptoms are not the only potential warning signs of prostate cancer. Other possible indicators could include weak urine flow, and unexplained pain deep in the groin area when sitting down. If cancer has spread beyond the prostate, a man may also suffer lower body swelling, abnormal urinary or bowel habits, or inexplicable weight loss.
Its important to note that most of these symptoms are not unique to prostate cancer, and may indicate a different condition that is not life-threatening.
Recommended Reading: Best Prostate Doctor In Usa
Also Check: What Happens If Prostate Cancer Has Spread
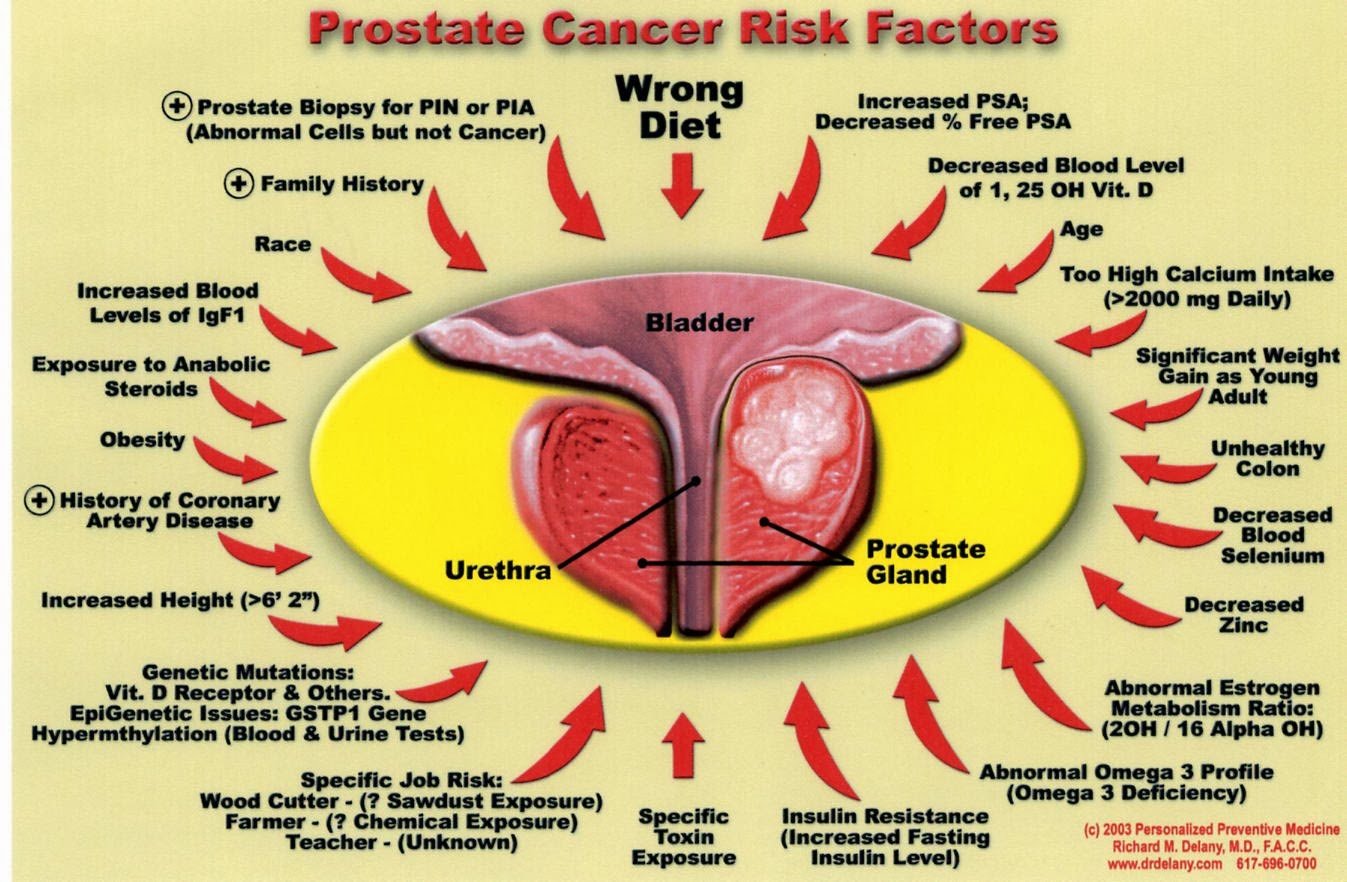
Risk Factors For Prostate Cancer
Because prostate cancer tends to not show symptoms in its early stages, risk factors are another useful tool to identify candidates for screening. The Mayo Clinic notes that risk certainly increases as you grow older, and obese men may be more likely to have prostate cancer that is aggressive or difficult to treat.
For unknown reasons, black men are also at a greater risk of prostate cancer than men of other races. Not only are they more likely to get prostate cancer, but the risk of prostate cancer being aggressive or advanced is also higher.
Finally, your family history or genetics can also help determine your prostate cancer risk. For example, men with close relatives who had prostate cancer are more likely to get it. Also, a family history of breast cancer or the presence of the genes BRCA1 or BRCA2 within the family also raises the likelihood of a man developing prostate cancer.
What Questions Should I Ask My Healthcare Provider
If you have prostate cancer, you may want to ask your healthcare provider:
- Why did I get prostate cancer?
- What is my Gleason score? What is my Grade Group? What do these numbers mean for me?
- Has the cancer spread outside of the prostate gland?
- What is the best treatment for the stage of prostate cancer I have?
- If I choose active surveillance, what can I expect? What signs of cancer should I look out for?
- What are the treatment risks and side effects?
- Is my family at risk for developing prostate cancer? If so, should we get genetic tests?
- Am I at risk for other types of cancer?
- What type of follow-up care do I need after treatment?
- Should I look out for signs of complications?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Prostate cancer is a common cancer that affects males. Most prostate cancers grow slowly and remain in the prostate gland. For a small number, the disease can be aggressive and spread quickly to other parts of the body. Men with slow-growing prostate cancers may choose active surveillance. With this approach, you can postpone, and sometimes completely forego, treatments. Your healthcare provider can discuss the best treatment option for you based on your Gleason score and Group Grade.
Don’t Miss: Is The Prostate Part Of The Urinary System
