Prostate Cancer Metastatic To The Cervical Lymph Nodes
Luis Sepúlveda
Abstract
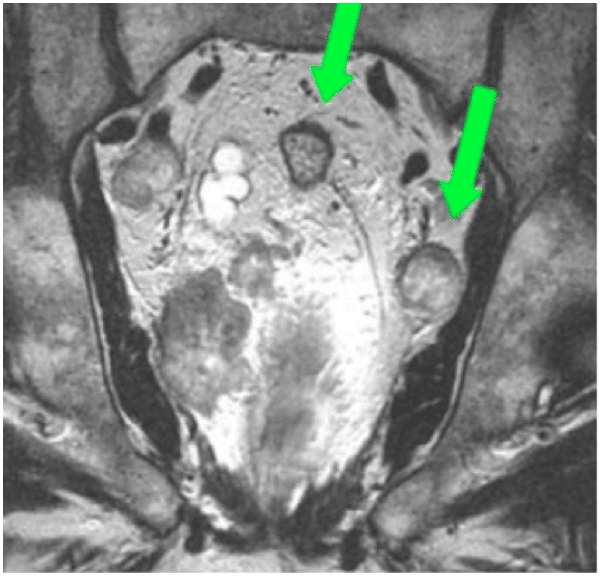
Prostate cancer is the most common cancer in men, often presenting with regional lymph node or bone metastasis and rarely with supradiaphragmatic lymph node involvement. Most metastatic cancers involving the cervical lymph nodes are from cancers of the upper aerodigestive tract. In this report, we describe two cases with cervical lymph node enlargement due to metastatic prostate cancer as the initial clinical presentation: a 43-year-old male, initially misdiagnosed with a tumor of the upper aerodigestive tract and an 87-year-old male with right lobe pneumonia and cervical lymph node enlargement, initially attributed to be an acute inflammatory lymph node reaction. To the best of our knowledge, there are less than 50 cases reported in the literature of adenocarcinoma of prostate metastatic to the cervical lymph nodes and only one case presenting in men younger than 45 years. The authors intend to highlight the importance of digital rectal exam and PSA test in case of persistent left cervical lymph node enlargement, including men younger than 45 years of age.
1. Introduction
In Europe, carcinoma of the prostate is the most common solid neoplasm and the second most common cause of cancer death in men . With a peak incidence between the ages of 70 and 74 years, less than 0.1% of all patients with prostate cancer are younger than 50 years of age . The most common metastatic site is the lymph nodes, usually those of the pelvis and retroperitoneum.
Endpoints And Statistical Analysis
For statistical testing SPSS 16.0.01 was used and a p< 0.05 was a priori deemed significant.
Endpoints of the present study, that were determined for patients with and without lymph node involvement on MRL, were: distant metastases-free survival and overall survival . For DMFS, deaths were censored. Survival rates were estimated with the Kaplan-Meier method, and the unstratified log-rank statistical analysis was used to test for differences.
What If You Have Metastatic Castration
This means you have a type of metastatic prostate cancer thatâs able to grow and spread after you had hormone therapy to lower your testosterone levels.
Still, most people with mCRPC stay on androgen deprivation therapy because it might still be effective against some prostate cancer cells.
Your doctor may recommend adding other treatments like:
- Treatments to ease symptoms like pain
You could also find out if a clinical trial might be right for you.
Some people with mCRPC simply choose to try active surveillance or watchful waiting.
You May Like: Why Do People Get Prostate Cancer
Open Access License / Drug Dosage / Disclaimer
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License . Usage and distribution for commercial purposes requires written permission. Drug Dosage: The authors and the publisher have exerted every effort to ensure that drug selection and dosage set forth in this text are in accord with current recommendations and practice at the time of publication. However, in view of ongoing research, changes in government regulations, and the constant flow of information relating to drug therapy and drug reactions, the reader is urged to check the package insert for each drug for any changes in indications and dosage and for added warnings and precautions. This is particularly important when the recommended agent is a new and/or infrequently employed drug. Disclaimer: The statements, opinions and data contained in this publication are solely those of the individual authors and contributors and not of the publishers and the editor. The appearance of advertisements or/and product references in the publication is not a warranty, endorsement, or approval of the products or services advertised or of their effectiveness, quality or safety. The publisher and the editor disclaim responsibility for any injury to persons or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content or advertisements.
What Is Metastatic Prostate Cancer
Sometimes cancer cells will escape the prostate and grow quickly, spreading to nearby tissue, or metastasizing. Nearby lymph nodes are often the first destination for a spreading cancer. If prostate cancer has spread to your lymph nodes when it is diagnosed, it means that there is higher chance that it has spread to other areas of the body as well.
If and when prostate cancer cells gain access to the bloodstream, they can be deposited in various sites throughout the body, most commonly in bones, and more rarely to other organs such as the liver, lung, or brain. Bone metastases are seen in 85% to 90% of metastatic cases.
No matter where a cancer turns up in the body, it is always identified by the tissue type in which it started. Prostate cancer can metastasize to other organs, but it is always prostate cancer, because it consists of mutated prostate cells.
Men diagnosed with metastatic prostate cancer , will often not undergo local treatments of the primary prostate tumor, such as surgery or radiation. Instead, their therapeutic journey might start with hormone therapy, and from there follow a similar path as men who were diagnosed at an earlier stage and had subsequent disease progression.
Want more information about a prostate cancer diagnosis and treatment options? Download or order a print copy of the Prostate Cancer Patient Guide.
Recommended Reading: Can You Check Your Own Prostate
Stage Iv Prostate Cancer
When prostate cancer spreads, its often found in nearby lymph nodes. If cancer has reached these nodes, it also may have spread to other lymph nodes, the bones, or other organs.
When cancer spreads from its original place to another part of the body, the new tumor has the same kind of abnormal cells and the same name as the primary tumor. For example, if prostate cancer spreads to bones, the cancer cells in the bones are actually prostate cancer cells. The disease is metastatic prostate cancer, not bone cancer. For that reason, its treated as prostate cancer, not bone cancer. Doctors call the new tumor distant or metastatic disease.
The cancer has spread beyond the prostate.
- Stage IVA: The cancer has spread to the regional lymph nodes.
-
Stage IVB: The cancer has spread to distant lymph nodes, other parts of the body, or to the bones.
You May Like: Recovery Time After Green Light Laser Prostate Surgery
How Will My Cancer Be Monitored
Your doctor will talk to you about how often you should have check-ups. At some hospitals, you may not have many appointments at the hospital itself. Instead, you may talk to your doctor or nurse over the telephone. You might hear this called self-management.
You will have regular PSA tests. This is often a useful way to check how well your treatment is working. Youll also have regular blood tests to see whether your cancer is affecting other parts of your body, such as your liver, kidneys or bones.
You might have more scans to see how your cancer is responding to treatment and whether your cancer is spreading.
Your doctor or nurse will also ask you how youre feeling and if you have any symptoms, such as pain or tiredness. This will help them understand how youre responding to treatment and how to manage any symptoms. Let them know if you have any side effects from your treatment. There are usually ways to manage these.
Recommended Reading: Prostate Cancer Symptoms And Treatment
The Ajcc Tnm Staging System
A staging system is a standard way for the cancer care team to describe how far a cancer has spread. The most widely used staging system for prostate cancer is the AJCCTNM system, which was most recently updated in 2018.
The TNM system for prostate cancer is based on 5 key pieces of information:
- The extent of the main tumor *
- Whether the cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes
- Whether the cancer has spread to other parts of the body
- The PSA level at the time of diagnosis
- The Grade Group , which is a measure of how likely the cancer is to grow and spread quickly. This is determined by the results of the prostate biopsy .
*There are 2 types of T categories for prostate cancer:
- The clinical T category is your doctors best estimate of the extent of your disease, based on the results of the physical exam and prostate biopsy, and any imaging tests you have had.
- If you have surgery to remove your prostate, your doctors can also determine the pathologic T category . The pathologic T is likely to be more accurate than the clinical T, as it is done after all of your prostate has been examined in the lab.
Numbers or letters after T, N, and M provide more details about each of these factors. Higher numbers mean the cancer is more advanced. Once the T, N, and M categories have been determined, this information is combined in a process called stage grouping to get the overall stage of the cancer.
Experiments With Tissue Culture & Animal Models Of Prostate Cancer
Experiments with tissue culture and animal models of prostate cancer have revealed the mechanisms of the synthesis of lymphangiogenic growth factors in prostate cancer and their important contribution to lymphangiogenesis in prostate cancer lymph node metastasis.
Signaling pathways for VEGF-C synthesis in prostate cancer
Also Check: Can An Mri Detect Prostate Cancer
Chances Of Developing Metastatic Prostate Cancer
About 50% of men diagnosed with local prostate cancer will get metastatic cancer during their lifetime. Finding cancer early and treating it can lower that rate.
A small percentage of men arent diagnosed with prostate cancer until it has become metastatic. Doctors can find out if its metastatic cancer when they take a small sample of the tissue and study the cells.
What Is Metastatic Cancer
Cancer that spreads from where it started to a distant part of the body is called metastatic cancer. For many types of cancer, it is also called stage IV cancer. The process by which cancer cells spread to other parts of the body is called metastasis.
When observed under a microscope and tested in other ways, metastatic cancer cells have features like that of the primary cancer and not like the cells in the place where the metastatic cancer is found. This is how doctors can tell that it is cancer that has spread from another part of the body.
Metastatic cancer has the same name as the primary cancer. For example, breast cancer that spreads to the lung is called metastatic breast cancer, not lung cancer. It is treated as stage IV breast cancer, not as lung cancer.
Sometimes when people are diagnosed with metastatic cancer, doctors cannot tell where it started. This type of cancer is called cancer of unknown primary origin, or CUP. See the Carcinoma of Unknown Primary page for more information.
Don’t Miss: How Does A Doctor Check Your Prostate
Grade: How Aggressive Is The Cancer
The pathology team will take a biopsy sample and prepare it with chemicals, then make extremely fine slices of the tissue to examine under the microscope. If prostate cancer is found when looking at biopsied tissue under a microscope, the pathologist assigns a grade to the cancer. There are 2 grading systems currently in use, which can be confusing for patients.
The classical grading system for prostate cancer is called the Gleason score, which ranges from 6 to 10 .
In 2014, the World Health Organization reorganized the Gleason score with the simpler Grade Group system, ranging from 1 to 5 .
Many medical centers report both the Gleason score and the Grade Group, but there may be some that still only report the old Gleason system.
Both systems attempt to communicate a variety of factors in a way that allows the medical team to communicate and compare cases and strategize treatments.
How Do Doctors Find Metastatic Prostate Cancer
When you are diagnosed with prostate cancer, your doctor will order tests such as:
These tests may focus on your skeleton and in your belly and pelvic areas. That way doctors can check for signs that the cancer has spread.
If you have symptoms such as bone pain and broken bones for no reason, your doctor may order a bone scan. It can show if you have signs of cancer spreading to your bones.
Your doctor will also ask for blood tests, including a check of PSA levels, to look for other signs that the cancer is spreading.
PSA is a protein made by the prostate gland. A rise in PSA is one of the first signs your cancer may be growing. But PSA levels can also be high without there being cancer, such as if you have an enlarged prostate, a prostate infection, trauma to the perineum, or sexual activity.
You May Like: What Does Your Prostate Do For You
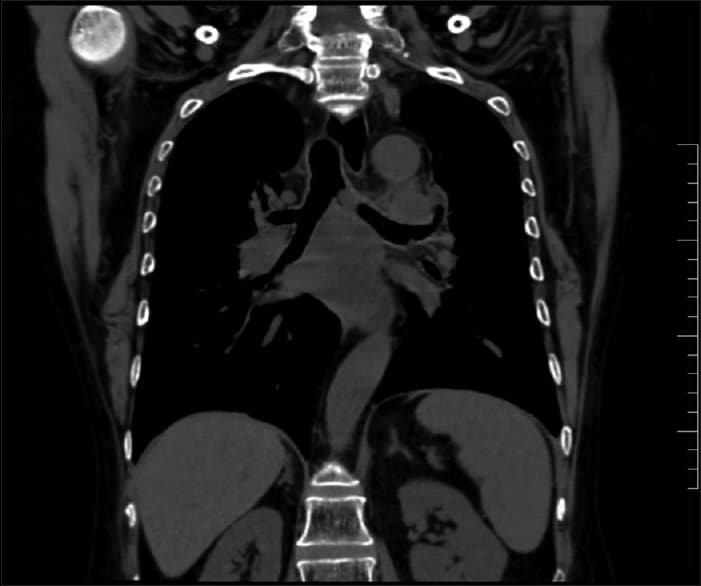
Successful Management Of Prostate Cancer With Bulky Pelvic Lymph Node Metastases After Rapid Development Of Castration
Lixin Mai1, Yonghong Li2, Ping Yang3, Zitong Zhang1, Jianhua Wu1, Fangjian Zhou2, Yang Liu1, Liru He1
1 Department of Urology Oncology, 3 Department of Pathology, Sun Yat-Sen University Cancer Center, State Key Laboratory of Oncology in South China, Collaborative Innovation Center for Cancer Medicine , , China
Correspondence to:
Keywords: Case report castration-resistant chemotherapy prostate cancer radiotherapy
Submitted Mar 09, 2020. Accepted for publication May 14, 2020.
doi: 10.21037/tau-20-725
Treatment For Metastatic Prostate Cancer
Treatment for prostate cancer that has spread to the bones and/or other organs in the body is aimed at relieving symptoms and slowing the cancers growth. Treatment may include:
- Hormone therapy to slow cancer growth.
- Radiation therapy to shrink tumours and ease pain.
- Chemotherapy to stop the growth of cancer cells.
- Surgery to remove blockages that are causing problems .
Read Also: 4 3 7 Prostate Cancer
What Is My Outlook
If youre diagnosed with advanced prostate cancer, you may want to know how well your treatment is likely to control your cancer and for how long it will control it. This is sometimes called your outlook or prognosis. But not all men will want to know this.
While it isnt possible to cure advanced prostate cancer, treatments can help keep it under control, often for several years. Treatments will also help manage any symptoms, such as pain.
No one can tell you exactly what your outlook will be, as it will depend on many things such as where the cancer has spread to, how quickly it has spread, and how well you respond to treatment. Some men may not respond well to one treatment, but may respond better to another. And when your first treatment stops working, there are other treatments available to help keep the cancer under control for longer. Speak to your doctor about your own situation and any questions or concerns you have.
Stromal Foxf2 Level Inversely Correlates With Prostate Cancer Grade
Previous studies reported that FOXF2 is highly expressed in the TZ prostate,. Our RNA-in-Situ analysis showed that FOXF2 was expressed in the human prostate stromal but not epithelial cells, and that the expression level was higher in the TZ stroma . To further confirm the higher expression of FOXF2 in the TZ stroma, we FACS-isolated the Lin-Trop2- TZ and PZ stromal cells from 7 pathologist-verified fresh benign prostate tissues from prostate cancer patients who had undergone radical prostatectomy and examined the expression of FOXF2 by qRT-PCR. Figure shows that the expression level of FOXF2 in TZ stroma was approximately 3-fold of that in the PZ stroma. Previously, we showed that the periurethral human TZ tissues share molecular features with the proximal mouse prostate ducts adjacent to the urethra,. A Visium spatial gene expression array revealed that Foxf2 is also highly expressed in the mouse proximal prostate . We previously reported that the stromal cells in the mouse proximal prostate highly express Axin2 and Lgr5,. An RNA-In-Situ duplex analysis of Lgr5 and Foxf2 further confirmed that Foxf2 is specifically expressed by the stromal cells and the expression level is higher in the mouse proximal prostatic ducts than in distal ducts . This indicates that regulation of the expression pattern of Foxf2 is conserved between human and mouse and further supports that the human and mouse prostates share anatomy-associated molecular features.
Don’t Miss: What Contributes To The Successful Treatment Of Prostate Cancer
What Are Lymph Nodes
Lymph nodes are the heart and soul of the immune system, Dr. Engleman said. But they havent gotten as much attention as they deserve, he added.
Lymph, a watery mixture of immune cells and fluid, flows through our bodies via a network of veinlike pipes. Hundreds of lymph nodes are dotted along this network.
Lymph nodes are like sophisticated training centers. Inside, immune cells learn how to fight infections and cancer. Once fully trained, the immune cells leave the lymph nodes to monitor the body for intruders.
To metastasize, cancer cells break off from the primary tumor and travel through the blood or lymph to other organs. If someone is found to have cancer in their lymph nodes, its usually a bad sign that the cancer has or will soon spread to other parts of the body. Most cancer deaths are caused by metastatic cancer.
But its never been clear what cancer cells are actually doing in the lymph nodes.
One of the theories is that, in the lymph node, gain traits that make them metastatic. And then, from there, they go to the distant organ, Dr. Dueck explained.
There is another theory that some cells from the tumor go to the lymph nodes, and some go to the distant organ, she said. With this view, the lymph nodes dont play a critical role in metastasis, she added.
With the necessary models and tools at their disposal, Dr. Englemans team set out to address the long-standing debate about these two theories.
Understanding Prostate Cancers Progression
To determine the appropriate treatment, doctors need to know how far the cancer has progressed, or its stage. A pathologist, the doctor trained in analyzing cells taken during a prostate biopsy, will provide two starting pointsthe cancers grade and Gleason score.
- Cancer grade: When the pathologist looks at prostate cancer cells, the most common type of cells will get a grade of 3 to 5. The area of cancer cells in the prostate will also be graded. The higher the grade, the more abnormal the cells.
- Gleason score: The two grades will be added together to get a Gleason score. This score tells doctors how likely the cancer is to grow and spread.
After a biopsy confirms prostate cancer, the patient may undergo additional tests to see whether it has spread through the blood or lymph nodes to other parts of the body. These tests are usually imaging studies and may include a bone scan, positron emission tomography scan or computed tomography scan.
Also Check: Do Men Need A Prostate
Also Check: Life After Prostate Removal Surgery
