Your Mri Scan Will Provide You With The Stage Of Your Prostate Cancer
In patients who are subsequently diagnosed with prostate cancer, the MRI scan provides the stage of the cancer, with the letter T used to indicate the stage of the tumour. Stage means how far the cancer has spread. Although the stage can be assessed by digital rectal examination, it is more accurately assessed by an MRI scan.
Citations & Data Usage Policy
Users must abide by the TCIA Data Usage Policy and Restrictions. Attribution should include references to the following citations:
Data Citation
Choyke P, Turkbey B, Pinto P, Merino M, Wood B. . Data From PROSTATE-MRI. The Cancer Imaging Archive.
TCIA Citation
Clark K, Vendt B, Smith K, Freymann J, Kirby J, Koppel P, Moore S, Phillips S, Maffitt D, Pringle M, Tarbox L, Prior F. The Cancer Imaging Archive : Maintaining and Operating a Public Information Repository, Journal of Digital Imaging, Volume 26, Number 6, December, 2013, pp 1045-1057.
What Body Areas Are Seen During An Mri Of The Abdomen And Pelvis
Body organs that can be seen during an MRI of the abdomen and pelvis include:
- Stomach, intestines , liver, gallbladder, pancreas, and spleen. These organs help break down the food you eat and get rid of waste through bowel movements.
- Kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra . These organs make urine and allow you to urinate.
Also Check: Pi Rads 5 Prostate Cancer
Pet/mri Basics And Image Acquisition
PET/MRI imaging systems can be either in tandem or integrated. Tandem systems have the MRI and PET machines located either in adjacent rooms or side-by-side in the same room with a moveable patient table between . Tandem PET/MRI units such as the Phillips Ingenuity were the initial systems developed because the magnetic field generated by the MRI machine did not interfere with the PET unit. Due to the large footprint and cumbersome nature of tandem PET/MRIs, these have largely been supplanted by their integrated counterparts. A major hurdle of integrated or simultaneous systems is the fact that the photomultiplier tubes used in traditional PET scanners cannot function within a strong magnetic field. The development of avalanche photodiodes, photon detectors insensitive to magnetic changes, was the breakthrough that allowed development of and commercialization of modern integrated PET/MRIs . While one drawback of avalanche photodiodes is the inability to measure time of flight, silicon photomultiplier detectors have been developed to circumvent this limitation .
Existing relevant experience on the multi-faceted use of PET/MRI in prostate cancer is summarized in Table 1.
Table 1
Prostate Cancer Risk Prediction Algorithm Could Help Targeted Testing For Men At Greatest Risk
Cambridge scientists have created a comprehensive tool for predicting an individual’s risk of developing prostate cancer, which they say could help ensure that those men at greatest risk will receive the appropriate testing while reducing unnecessaryand potentially invasivetesting for those at very low risk.
CanRisk-Prostate, developed by researchers at the University of Cambridge and The Institute of Cancer Research, London, will be incorporated into the group’s CanRisk web tool, which has now recorded almost 1.2 million risk predictions. The free tool is already used by health care professionals worldwide to help predict the risk of developing breast and ovarian cancers.
Prostate cancer is the most common type of cancer in men. According to Cancer Research UK, more than 52,000 men are diagnosed with the disease each year and there are more than 12,000 deaths. Over three-quarters of men diagnosed with prostate cancer survive for over ten years, but this proportion has barely changed over the past decade in the U.K.
Testing for prostate cancer involves a blood test that looks for a protein known as a prostate-specific antigen that is made only by the prostate gland however, it is not always accurate. According to the NHS website, around three in four men with a raised PSA level will not have cancer. Further tests, such as tissue biopsies or MRI scans, are therefore required to confirm a diagnosis.
More information:Journal of Clinical Oncology
Read Also: Can You Get Prostate Cancer Without A Prostate
Why Shouldnt I Have The Assessment
The MRI procedure is loud and noisy mild side effects include feeling warm, queasy, skin rashes, headaches and dizziness. Despite these factors, patients are usually allowed to return home on the same day and resume their usual activities Note that this is impacted if patients have undergone sedation during their scan.
Patients can discuss sedation with their doctors far ahead of their scan date. Patients who have had a sedative will need to be accompanied for 24 hours following their scan and should avoid driving or operating heavy machinery.
Patients with metal implants or similar may require an initial X-ray. Patients with metal plates, artificial joints, pacemakers, nerve stimulators, dental bridges, surgical wires, medical screws or rods, prosthetic heart valves, some tattoo inks, intrauterine devices, implantable cardioverter-defibrillators, penile implants, eye, cochlear or drug pump implants, tubal ligation or brain aneurysm clips may be precluded.
Tests To Diagnose And Stage Prostate Cancer
Most prostate cancers are first found as a result of screening. Early prostate cancers usually dont cause symptoms, but more advanced cancers are sometimes first found because of symptoms they cause.
If prostate cancer is suspected based on results of screening tests or symptoms, tests will be needed to be sure. If youre seeing your primary care doctor, you might be referred to a urologist, a doctor who treats cancers of the genital and urinary tract, including the prostate.
The actual diagnosis of prostate cancer can only be made with a prostate biopsy .
On this page
Recommended Reading: Does Prostate Cancer Have A Cure
Also Check: What Does Hormone Therapy Do For Prostate Cancer
Treatment Planning For Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy is one of the main prostate cancer treatment methods that can be used in low stage up to high stage of disease and even in bone metastasis of prostate cancer. According to patients condition and stage of disease, radiation therapy performs alone or in combination with other therapy methods like surgery or hormonal therapy.
There are two kinds of radiation therapy methods: External beam radiation therapy and Brachytherapy . Radiation therapy can use in low risk patients for curing the cancer completely and it calls radical radiotherapy. In higher stage of prostate cancer and when bone metastasis are existence and patients suffer from pain radiation therapy is used for shrinking cancerous cells on nerves systems and bones to decrease pain . After radical prostatectomy radiation therapy is useful for preventing and decreasing cancer recurrence and distal metastasis. In intermediate to high risk patients, radiation therapy can be used in combination with hormonal therapy before or after radical prostatectomy . MR images can be used reliably for treatment planning of radiation therapy.
Also Check: Stage 2 Prostate Cancer Definition
Atlas Of Laparoscopic And
More than 700 illustrations with one entirely image-based chapter featuring educational case studies. Radiologists will learn how to optimally perform and interpret prostate MRI. And referring physicians will learn to integrate it into day-to-day practice. This book is an essential resource for radiologists and radiology residents, as well as urologists, oncologists. MRI technicians, and other medical practitioners who treat patients with genitourinary disorders.
Although prostate cancer is the second leading cause of cancer death in men in the USA, it can be treated successfully if detected early. Prostate MRI has emerged as the most precise, state-of-the-art imaging modality for prostate cancer diagnosis and management.
Thereby creating an immediate demand for radiologists to become proficient in its use. The ultimate guide to help learn and implement prostate MRI. Essential text and first of its kind for the emerging technique of prostate MRI Information on performing and interpreting the MRI examination including diagnosis, staging and treatment planning.
Clinical pearls on the optimization and application of prostate MRI for risk assessment, disease staging, MRI-targeted biopsy, recurrent disease, and active surveillance Emerging utilization of PET and PET/MRI for primary prostate cancer evaluation More than 650 illustrations with one entirely imagebased chapter featuring educational case studi.
You May Like: How Do You Stop Urine Leakage After Prostate Surgery
How Do I Prepare For A Prostate Ultrasound
You dont need to do much to prepare for a prostate ultrasound. Its an outpatient procedure that usually takes less than an hour. Your doctor may refer you to a hospital or clinic that has the proper ultrasound equipment for this test. You may also need to sign a consent form before the test.
Some possible instructions that your doctor might give you before the test include:
- Dont eat for a few hours before the test.
- Take a laxative or enema to help clear out your intestines a few hours before the test.
- Stop taking any medications that can thin your blood, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or aspirin, about a week before the procedure. This is usually recommended if your doctor plans to take a biopsy of your prostate.
- Dont wear any jewelry or tight clothes to the clinic on the day of the procedure.
- Take any medications recommended to help you relax during the procedure. Your doctor may recommend a sedative, such as lorazepam .
- Make sure someones available to take you home in case your doctor gives you a sedative.
Read Also: Can An Mri Detect Prostate Cancer
Histologic Correlation Of T2wi And Dwi
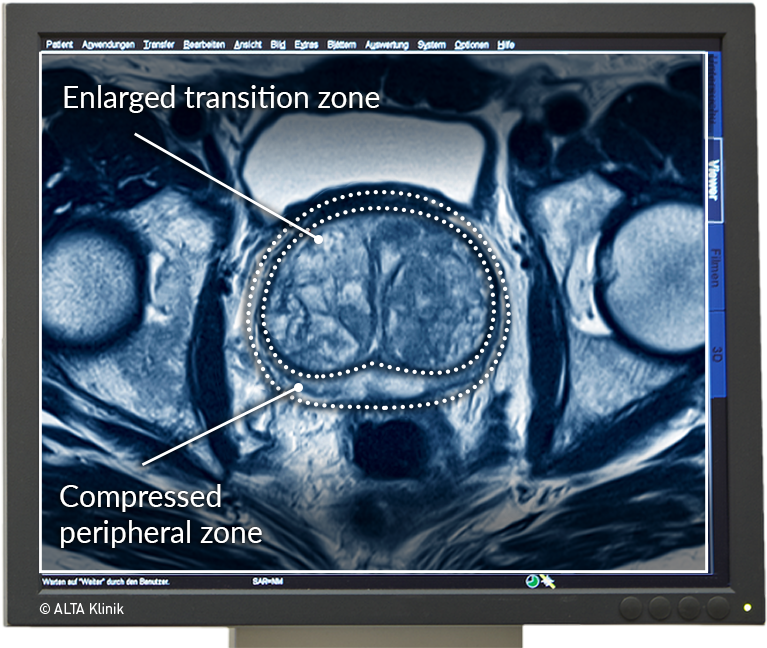
To summarize, healthy PZ tissue on T2WI and DWI appears as a region with both high T2 and high ADC. When luminal space and stromal matrix is lost to cancer, which consists of highly compacted cells, water diffusion becomes generally more restricted and macromolecular content increases. Water molecules encountering membrane boundaries and macromolecules within cancerous zones demonstrate observable decreases in both T2 and ADC . Two recent studies by Wang et al. and Gibbs et al. utilized histological measurements of cancer cell density to obtain inverse relationships between prostate cancer tumor cellularity and ADC values.
Healthy CG contains not only the same tissue components as the PZ but also more smooth muscle cells within the stromal matrix and frequently regions of benign prostatic hyperplasia . There are two histological types of BPH â glandular and stromal. The former appear as hyperintense nodules and the latter appear as hypointense nodules, which can occasionally mimic the appearance of cancer. However, the typical stromal tissue is curvilinear or band-like as it permeates between the glandular elements of BPH. Since muscle tissue has one of the lowest T2 values, healthy CG appears more hypointense and heterogeneous than the surrounding PZ on T2WI of the normal prostate, making CG tumor detection more difficult.
Also Check: Does Drinking Cause Prostate Cancer
Also Check: Folic Acid And Prostate Cancer
What Does The Equipment Look Like
The traditional MRI unit is a large cylinder-shaped tube surrounded by a circular magnet. You will lie on a table that slides into a tunnel towards the center of the magnet.
Some MRI units, called short-bore systems, are designed so that the magnet does not completely surround you. Some newer MRI machines have a larger diameter bore, which can be more comfortable for larger patients or those with claustrophobia. “Open” MRI units are open on the sides. They are especially helpful for examining larger patients or those with claustrophobia. Open MRI units can provide high quality images for many types of exams. Open MRI may not be used for certain exams. For more information, consult your radiologist.
Most prostate MRI exams use high-field MRI magnets because they provide higher-quality images. However, men with metal implants may undergo low-field prostate MRI because the implants may otherwise interfere with imaging.
Surgery For Prostate Cancer
There are many types of surgery for prostate cancer. Some are done to try to cure the cancer others are done to control the cancer or make symptoms better. Talk to the doctor about the kind of surgery planned and what you can expect.
Side effects of surgery
Any type of surgery can have risks and side effects. Be sure to ask the doctor what you can expect. If you have problems, let your doctors know so they can help you.
Also Check: What Is Sbrt For Prostate Cancer
Also Check: Prostate Cancer 9 Gleason Score
Imaging Tests For Prostate Cancer
Imaging tests use x-rays, magnetic fields, sound waves, or radioactive substances to create pictures of the inside of your body. One or more imaging tests might be used:
- To look for cancer in the prostate
- To help the doctor see the prostate during certain procedures
- To look for spread of prostate cancer to other parts of the body
Which tests you might need will depend on the situation. For example, a prostate biopsy is typically done with transrectal ultrasound and/or MRI to help guide the biopsy. If you are found to have prostate cancer, you might need imaging tests of other parts of your body to look for possible cancer spread.
The imaging tests used most often to look for prostate cancer spread include:
What Is An Mri Of The Lumbar Spine
MRI stands for magnetic resonance imaging, and lumbar spine MRI uses magnetic imaging technology and radio waves to take detailed pictures of the inside of your body near the lumbar region of your spine. This cross-sectional imaging method made possible with MRI machines also captures pictures of the soft tissues, muscles and organs in that part of your body.
Read Also: What Is Prostate Gland Hypertrophy
Preparing For Your Mri Scan
Before you go to your appointment, or when you arrive, you fill in a safety checklist. This asks about:
- any operations youve had
- whether you have any metal implants or other metals in your body
An MRI scan uses strong magnetism which could affect any metal in your body. This includes:
- pacemakers or an implantable defibrillator
- surgical clips, pins or plates
- cochlear implants
- metal fragments anywhere in your body for example from an injury, dental fillings and bridges
You can still have an MRI scan if you have some metals in your body, but your doctor and radiographer decide if its safe for you. Tell the scanner staff about any metals in your body.
Some people feel claustrophobic or closed in when theyre having an MRI scan. Contact the department before your test if youre likely to feel like this. The hospital staff can take extra care to make sure youre comfortable and that you understand whats going on. Your doctor can give you medicine to help you relax if you need to.
The radiographers let you know whether you need to empty your bowels of any poo or gas before having the scan. In some departments you might be given an enema. An enema is a liquid filled pouch that has a nozzle that you can put into your back passage and it helps to empty your bowels.
Will The Mri Be Done With An Endorectal Coil Or An External Pelvic Coil
Some radiology practices use an endorectal coil a probe-like device covered with latex which is inserted into the rectum and helps provide high-quality images of the prostate. With a newer, high-quality MRI system, endorectal coils are not necessary and an external pelvic coil can be used instead, eliminating patient discomfort while maintaining high quality images.
You May Like: What Is Gleason 8 Prostate Cancer
When You Need Themand When You Dont
It is normal to want to do everything you can to treat prostate cancer. But its not always a good idea to get all the tests that are available. You may not need them. And the risks from the tests may be greater than the benefits.
The information below explains why cancer experts usually do not recommend certain imaging tests if you are diagnosed with early-stage prostate cancer. You can use this information to talk about your options with your doctor and choose whats best for you.
How is prostate cancer usually found?
Prostate cancer is cancer in the male prostate gland. It usually grows slowly and does not have symptoms until it has spread. Most men are diagnosed in the early stages when their doctor does a rectal exam or a PSA blood test. PSA is a protein made in the prostate. High levels of PSA may indicate cancer in the prostate.
If one of these tests shows that you might have prostate cancer, you will be given more tests. These tests help your doctor find out if you actually have cancer and what stage your cancer is.
What are the stages of prostate cancer?
Prostate cancer is divided into stages one to four . Cancer stages tell how far the cancer has spread.
Stages I and II are considered early-stage prostate cancer. The cancer has not spread outside the prostate. However, stage II cancer may be more likely to spread over time than stage I cancer. In stages III and IV, the cancer has already spread to other parts of the body.
Imaging tests have risks.
Local Staging Of Prostate Cancer
Determining the extension of prostate cancer and local staging is one of the main roles of a radiologist after detection of prostate cancer. Staging of prostate cancer is very important in therapy decision making as well as prognosis determination. Imaging techniques play a significant role in staging of prostate cancer and MRI is the most accurate imaging modality used for prostate cancer staging . High resolution MR images especially with the use of endorectal coil can show with high accuracy whether the tumor is confined to prostate gland or there is involvement of prostate capsule and extra capsular extension that is considered the T component of TNM staging system. Extension of tumor to periprostatic fat, invasion to neurovascular bundles and involvement of seminal vesicles and Denonvilliers fascia are well detected by MRI .4).
Biopsy Proven Prostate Cancer, Stage T3, Gleason Score 8.
A)Axial T2w. image of prostate gland: A hyposignal tumoral mass is evident in peripheral zone in right base of prostate. B) Axial T2w. image of prostate gland in more cephalic level: Involvement of seminal vesicles by prostate cancer is noted. C) Coronal T2w. image of prostate gland: Involvement of seminal vesicles is well shown.
Axial T2w. image of prostate gland: A hyposignal tumoral mass is noted at the right side of prostate. The capsule of prostate is disrupted with invasion of tumor to periprostatic fat, neurovascular bundle and Denonvilliers fascia.
Also Check: Isotope Treatment For Prostate Cancer
