Chances Of Developing Metastatic Prostate Cancer
About 50% of men diagnosed with local prostate cancer will get metastatic cancer during their lifetime. Finding cancer early and treating it can lower that rate.
A small percentage of men arent diagnosed with prostate cancer until it has become metastatic. Doctors can find out if its metastatic cancer when they take a small sample of the tissue and study the cells.
The Ajcc Tnm Staging System
A staging system is a standard way for the cancer care team to describe how far a cancer has spread. The most widely used staging system for prostate cancer is the AJCCTNM system, which was most recently updated in 2018.
The TNM system for prostate cancer is based on 5 key pieces of information:
- The extent of the main tumor *
- Whether the cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes
- Whether the cancer has spread to other parts of the body
- The PSA level at the time of diagnosis
- The Grade Group , which is a measure of how likely the cancer is to grow and spread quickly. This is determined by the results of the prostate biopsy .
*There are 2 types of T categories for prostate cancer:
- The clinical T category is your doctors best estimate of the extent of your disease, based on the results of the physical exam and prostate biopsy, and any imaging tests you have had.
- If you have surgery to remove your prostate, your doctors can also determine the pathologic T category . The pathologic T is likely to be more accurate than the clinical T, as it is done after all of your prostate has been examined in the lab.
Numbers or letters after T, N, and M provide more details about each of these factors. Higher numbers mean the cancer is more advanced. Once the T, N, and M categories have been determined, this information is combined in a process called stage grouping to get the overall stage of the cancer.
Treatment For Metastatic Prostate Cancer
Treatment for prostate cancer that has spread to the bones and/or other organs in the body is aimed at relieving symptoms and slowing the cancers growth. Treatment may include:
- Hormone therapy to slow cancer growth.
- Radiation therapy to shrink tumours and ease pain.
- Chemotherapy to stop the growth of cancer cells.
- Surgery to remove blockages that are causing problems .
Recommended Reading: What Age To Check Prostate Cancer
Surgical Treatment For Cn1 Patients
The rationale supporting local treatment in advanced cancers is based on the principle of tumor volume reduction and local control. The benefit of radiation therapy in addition to systemic treatment in cN1 PCa patients has been demonstrated by different studies, both in a subgroup analysis of RCT and in a population based setting . In the setting of surgery, a survival benefit of RP in patients with nodal involvement detected during surgery has led to the abandonment of frozen LN section .
The first study to specifically analyze the role of prostatectomy in cN1 patients was reported by Moschini et al. oncological outcomes of 50 cN1 M0 patients undergoing RP + PLND were compared to 252 patients with cN0, M0 disease. The authors reported no difference between groups in CSS and OS. The only significant predictors of CSM were the number of positive nodes and pathologic Gleason score 810 vs. < 7 . Both groups were comparable in adjuvant ADT or RT. Although demonstrating promising results, the study lacked of a control group of cN1 patients treated with RT and/or ADT and such comparison is still missing.
Table 1. Summary of advantages and disadvantages of LND in cN1 patients.
What Factors Increase The Chance Of Cancer Recurrence
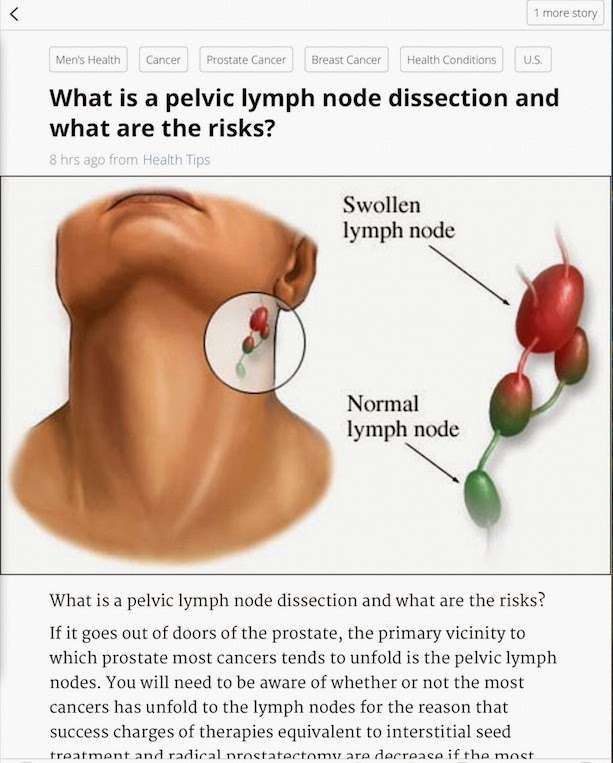
The likelihood of metastasis occurring increases with higher grade and stage of the cancer as the more aggressive and developed the cancer is, the higher the chance of it breaking out of the prostate. More specifically:
- High Gleason grades
- High clinical stages
- Positive surgical margins .
However, most prostate cancers are cured with surgery. As an example, using my results from operations performed on over 2,300 men with a variety of stages and grades, 96.3% of operations resulted in full cancer cure. Some combinations of minor prostate cancer had a 100% cancer cure rate, but the higher you go, the lower the full cancer cure rate.
The commonest sites of recurrence of prostate cancer following surgery are:
- the prostate bed 80% of recurrence cases
- lymph nodes 15% of cases
- bones 5% of cases.
Recommended Reading: How To Stimulate Male Prostate
Mechanisms Of Lymph Node Metastasis
Tumor-associated lymphatic vessels serve as a route for lymph node metastasis
Lymph node. Metastases of tumor cells through lymphatic vessels to lymph nodes.
Local extension of tumor cells from the primary tumor into the surrounding lymphatics through a process called permeation is one means through which tumor cells can enter into the lymphatic vessels . In addition, tumor cells can be stimulated by cytokines produced by the lymphatic vessels, which promote chemotactic diffusion of tumor cells into the lymphatics . Finally, many tumors have the ability to secrete growth factors that induce the growth of new lymphatic vessels from a precursor, a process called lymphangiogenesis .
What Is Cancer Of The Lymph Nodes
When cancer originates in the lymph nodes or other areas of the lymphatic system, its referred to as lymphoma.2 The most common types are hodgkins lymphoma and non-hodgkins lymphoma. In rare instances, theres also a chance for the development of lymphoma of the skin. If youre wondering, Is lymphoma hereditary, we cover this question in our latest blog article.
People with hodgkins lymphoma usually experience enlarged lymph nodes with a small number of Reed-Sternberg cells present surrounded by normal immune cells. With classic hodgkins lymphoma, which accounts for 9 out of 10 cases of this type of cancer, there are four subtypes that may develop.3 These are:
- Nodular sclerosis hodgkins lymphoma is the most common and tends to start in the lymph nodes in the neck or chest. Though it is more prevalent in teens and young adults, it can develop at any age.
- Mixed cellularity hodgkins lymphoma is the second most common subtype and occurs mainly in the lymph nodes found in the upper half of the body. Its mostly detected in people with HIV infection and affects mostly children and the elderly.
- Lymphocyte-rich hodgkins lymphoma is a rarer subtype and usually occurs in the upper half of the body in a few lymph nodes.
- Lymphocyte-depleted hodgkins lymphoma is the rarest subtype of this type of cancer and occurs mainly in older people with HIV infection. Its mostly found in lymph nodes in the stomach, spleen, liver, and/or bone marrow.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Know If You Have A Prostate Infection
Lymph Node Removal: The Procedure
The procedure of lymph node removal depends on the underlying disease as well as on the localization of the affected lymph nodes. In the case of cancer, besides surgical removal of the primary tumor and any metastases, the surrounding lymph nodes need to be removed too, as there is a high possibility that they also contain tumor cells. This is a complicated process, because sometimes whole clusters of grouped lymph nodes need to be removed.
In case of Hodgkin lymphoma , the affected lymph node is removed and the situation is followed up during regular examinations. Non-Hodgkin lymphomas are more aggressive, metastatic, and they require more intensive approach.
Risks Of Radical Prostatectomy
Radical prostatectomy has a low risk of serious complications. Death or serious disability caused by radical prostatectomy is extremely rare.
Important nerves travel through the prostate on the way to the penis. Skilled surgeons can usually protect most of these nerves during radical prostatectomy.
Still, complications from unintended nerve damage can happen after radical prostatectomy. They include:
Urinary incontinence. This means trouble controlling your urine, leaking, or dribbling. If you have incontinence, talk to your doctor about treatments that can help.
Erectile dysfunction . Problems with erections are common after prostatectomy. Still, most men are able to have sex after prostatectomy while using medicines for ED , an external pump, or injectable medications. The younger you are, the higher the chance that youâll be able to get erections after surgery.
Most doctors think you can help yourself regain your ability to get erections if you try to get one as soon as possible once your body has had time to heal â often several weeks after your surgery. This is called âpenile rehabilitation.â Talk to your doctor before you try it.
Much of the skill involved in radical prostatectomy centers on sparing these nerves during the operation. A man undergoing radical prostatectomy by a surgeon at an advanced prostate cancer center has a better chance of keeping their sexual and urinary function.
Other complications of radical prostatectomy include:
Don’t Miss: How To Milk Your Prostate
Open Or Laparoscopic Radical Prostatectomy
In the more traditional approach to prostatectomy, called anopen prostatectomy, the surgeon operates through a single long skin incision to remove the prostate and nearby tissues. This type of surgery is done less often than in the past.
In a laparoscopic prostatectomy, the surgeon makes several smaller incisions and uses special long surgical tools to remove the prostate. The surgeon either holds the tools directly, or uses a control panel to precisely move robotic arms that hold the tools. This approach to prostatectomy has become more common in recent years. If done by experienced surgeons, the laparoscopic radical prostatectomy can give results similar to the open approach.
Risks Of Prostate Surgery
The risks with any type of radical prostatectomy are much like those of any major surgery. Problems during or shortly after the operation can include:
- Reactions to anesthesia
- Blood clots in the legs or lungs
- Damage to nearby organs
- Infections at the surgery site.
Rarely, part of the intestine might be injured during surgery, which could lead to infections in the abdomen and might require more surgery to fix. Injuries to the intestines are more common with laparoscopic and robotic surgeries than with the open approach.
If lymph nodes are removed, a collection of lymph fluid can form and may need to be drained.
In extremely rare cases, a man can die because of complications of this operation. Your risk depends, in part, on your overall health, your age, and the skill of your surgical team.
Don’t Miss: What Are The Long Term Effects Of Removing The Prostate
Limitations Of This Review
This review has several limitations. The studies selected for this review had a certain degree of heterogeneity. PLND was performed by different surgical procedures including open, laparoscopic, and robotic-assisted surgery. Clinical and pathological analyses of lymph nodes varied among studies, due to the different imaging studies and microscopic examinations. As the patients included in this review were treated over a long period of time , the diagnostic accuracy of clinical stage and indication of PLND has been changed over the timeframe of this review. A high heterogeneity was also found when assessing oncologic outcomes. Patients with adjuvant hormone therapy or radiation were included in some studies, but not in others. The oncologic outcome was measured using different survivals, such as biochemical-free, metastatic-free, or CCS. OS, the most important endpoint of cancer therapy, was not assessed in any of the reviewed studies. Therefore, it was difficult to obtain evidence of the clinical benefit of PLND during radical prostatectomy.
How Is Prostate Cancer Diagnosed
A blood test called a prostate-specific antigen test is the most common way to check for prostate cancer. A higher level of PSA may mean that you have prostate cancer or that your prostate cancer has come back.
Your doctor also may do a biopsy. In this test, your doctor takes samples of tissue from your prostate gland or from the area where the cancer may have spread and sends the samples to a lab for testing. A biopsy is the only way to know for sure that you have prostate cancer.
If you have had prostate cancer before, your doctor may also order a bone scan, CT scan, or MRI to see if it has come back or spread.
Learning that you have cancer that has spread or come back can be very hard. Some people find that it helps to talk about their feelings with their family and friends. You may also want to talk with your doctor or with other people who have had this kind of cancer. Your local Canadian Cancer Society chapter can help you find a support group.
Read Also: How To Know If You Have An Enlarged Prostate
Cancer That Clearly Has Spread
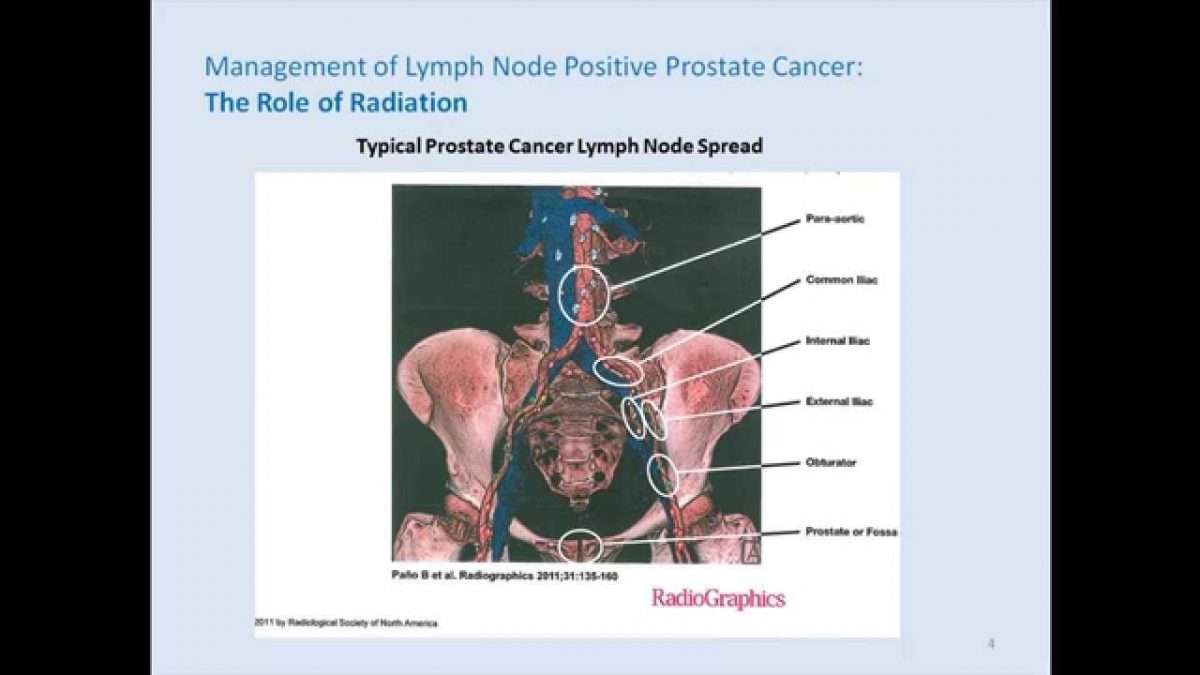
If the cancer has spread outside the prostate, it will most likely go to nearby lymph nodes first, and then to bones. Much less often the cancer will spread to the liver or other organs.
When prostate cancer has spread to other parts of the body , hormone therapy is probably the most effective treatment. But it isnt likely to cure the cancer, and at some point it might stop working. Usually the first treatment is a luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone agonist, LHRH antagonist, or orchiectomy, sometimes along with an anti-androgen drug or abiraterone. Another option might be to get chemotherapy along with the hormone therapy. Other treatments aimed at bone metastases might be used as well.
Stem Cell Or Bone Marrow Transplant
A stem cell transplant, sometimes called bone marrow transplant, replaces damaged blood-forming cells with healthy ones. The procedure takes place following large-dose chemotherapy or radiation therapy to kill cancer cells and to stop your stem cells from producing cancerous cells.
Stem cell transplants can be used for several types of cancer, including multiple myeloma and some kinds of leukemia.
Read Also: Can A Prostate Biopsy Spread Cancer
Difficulty Getting An Erection
You might have problems having an erection after a radical prostatectomy. This is impotence. Or you might produce less or no semen. This is known as a dry orgasm.
Impotence is more likely to happen if you are older. Nerve sparing surgery and robotic surgery may reduce the risk for some men. Speak to your doctor before you have surgery to get an idea of your risk of problems afterwards.
There are medicines that can help with erection problems after surgery. You might need a drug like sildenafil or Viagra to help you get an erection. Your doctor or specialist nurse can also refer you to a clinic for people who have sexual problems after treatment. You can store sperm before your operation if you would like to have children in future.
When Does A Lymph Node Need To Be Removed
The condition in which lymph nodes are inflamed and enlarged is called lymphadenitis. This happens most commonly due to a reaction to local infection, or in the case of generalized infections. Inflamed lymph nodes are often very painful, and this discomfort will cause a person to seek medical attention very quickly.
Allergies can also cause an enlargement of the lymph nodes, which are then painless and the swelling would occur rapidly after the contact with the offending allergen. Antihistamines and corticosteroids are used to diminish the effects of an allergy with consequent decrease in size of affected lymph nodes.
The most severe causes of enlarged lymph nodes are malignant tumors. Cancer cells originate from the primary tumor and enter the bloodstream and lymph ducts. On their way, they get caught by the lymph nodes and start reproducing there, thus causing an enlargement of lymph nodes. There are also primary tumors originating from lymph nodes, which are called lymphomas.
For almost all successful cancer treatment plans, it is necessary to remove all the malignant cells, including those located in the lymph nodes, and therefore, different types of cancer are the most common causes of lymph node removal.
Also Check: Can A Man Function Sexually Without A Prostate
Toxicity Of Multimodality Therapy For Ln+ Pca
The great majority of series described in this article focused primarily on oncologic outcomes rather than toxicity or quality of life. Of 98 patients treated with ADT and RT on RTOG 8531, grade 4 toxicities developed in 4. These included two bowel obstructions , one case of cystitis, and one case of hematuria. A recently published review of toxicity outcomes of 35 patient series, with a total of 11,835 patients treated with definitive RT for PCa, revealed a median rate of late grade 2 gastrointestinal and genitourinary toxicities to be 15% and 17%, respectively. Late grade 3 and higher GI and GU toxicities were 2% and 3%, respectively. This analysis included patients who did not receive pelvic RT and who were treated in the previous era before the introduction of intensity-modulated radiation therapy , so it can provide only limited guidance to patients and clinicians when discussing toxicity outcomes with multimodality therapy for LN+ PCa.
Caring For The Catheter
You will be discharged with a Foley catheter, a tube that continuously drains urine from your bladder into a bag and that you will use for seven to 10 days. Before you leave the hospital, your nurse will teach you how to empty and care for your catheter and drainage bag. The catheter works with gravity and should be draining urine at all times, so you have to keep the drainage bag below your bladder at all times, even when you shower. If your urine is not draining, lower the bag and check the connection for kinks or loops. Loops can cause an air lock that prevents drainage. You can also try emptying the bag. Then try briefly disconnecting the catheter from the clear plastic tubing to allow a little air into the system. Your nurse will show you how to do this before your discharge.
To prevent infection, you must keep your catheter clean. This section explains how to clean the catheter, the area around the catheter and the drainage bag. It also explains how to apply your leg bag and secure the catheter to your leg.
We will provide most of the supplies you need to care for your catheter. They include:
- Blue clamp
- StatLock Foley catheter securement device
- Shaving supplies
You should empty the catheter bag when it’s half full. This helps prevent air locks from developing in the tubing.
To apply the leg bag:
Don’t Miss: What Causes Prostate Cancer In Men
