What Does It Mean If My Biopsy Report Also Mentions Atrophy Adenosis Or Atypical Adenomatous Hyperplasia
All of these are terms for things the pathologist might see under the microscope that are benign , but that sometimes can look like cancer.
Atrophy is a term used to describe shrinkage of prostate tissue . When it affects the entire prostate gland it is called diffuse atrophy. This is most often caused by hormones or radiation therapy to the prostate. When atrophy only affects certain areas of the prostate, it is called focal atrophy. Focal atrophy can sometimes look like prostate cancer under the microscope.
Atypical adenomatous hyperplasia is another benign condition that can sometimes be seen on a prostate biopsy.
Finding any of these is not important if prostate cancer is also present.
What Is A Bad Gleason Score For Prostate Cancer
Gleason scores aren’t good or bad, per se. They predict how quickly your prostate cancer might grow. Tumors with higher Gleason scores are likely to grow quickly. And Gleason scores aren’t the only factors healthcare providers consider when creating your treatment plan.
What other factors do healthcare providers consider?
Providers consider the results of other tests and additional biopsy information. For example, when you had your biopsy, your healthcare provider obtained several samples or cores from your prostate. They checked how many cores contained cancer and whether most of the cells in the cores were cancerous cells.
Other factors may include:
Figure 2 Why Understaging May Occur
When the prostate is removed, a pathologist examines slices of the gland for evidence of cancer. A. Under a microscope, the pathologist can distinguish tiny tumors, consisting of clumps of visibly abnormal cells. B. With current imaging technology, it is not yet possible for a pathologist to identify micrometastases individual cancer cells shed from the primary tumor that have gone on to seed adjacent tissue. In this image, for example, cancer cells have already penetrated the capsule and migrated to adjacent tissue, even beyond the margin of tissue removed during surgery.
Individual prostate cancer cells can spread to more remote areas of the body in three ways . Whats more, they can do so without being detected with our current technology, essentially escaping under the radar. So its always possible even if you are diagnosed with early-stage prostate cancer that the cancer has already spread and will manifest in the coming years. How likely is it that an early-stage prostate cancer will become active without treatment? A small study provides some clues .
Also Check: Diet For Prostate Cancer Radiation Treatment
What Is Advanced Prostate Cancer
When prostate cancer spreads beyond the prostate or returns after treatment, it is often called advanced prostate cancer.
Prostate cancer is often grouped into four stages.
- Stages I & II: The tumor has not spread beyond the prostate. This is often called early stage or localized prostate cancer.
- Stage III: Cancer has spread outside the prostate, but only to nearby tissues. This is often called locally advanced prostate cancer.
- Stage IV: Cancer has spread outside the prostate to other parts such as the lymph nodes, bones, liver or lungs. This stage is often called advanced prostate cancer.
When an early stage prostate cancer is found, it may be treated or placed on surveillance . If prostate cancer spreads beyond the prostate or returns after treatment, it is often called advanced prostate cancer. Stage IV prostate cancer is not curable, but there are many ways to control it. Treatment can stop advanced prostate cancer from growing and causing symptoms.
There are several types of advanced prostate cancer, including:
Biochemical Recurrence
If your Prostate Specific Antigen level has risen after the first treatment but you have no other signs of cancer, you have biochemical recurrence.
Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer
- Lymph nodes outside the pelvis
Tests To Identify Prostate Cancer Stage
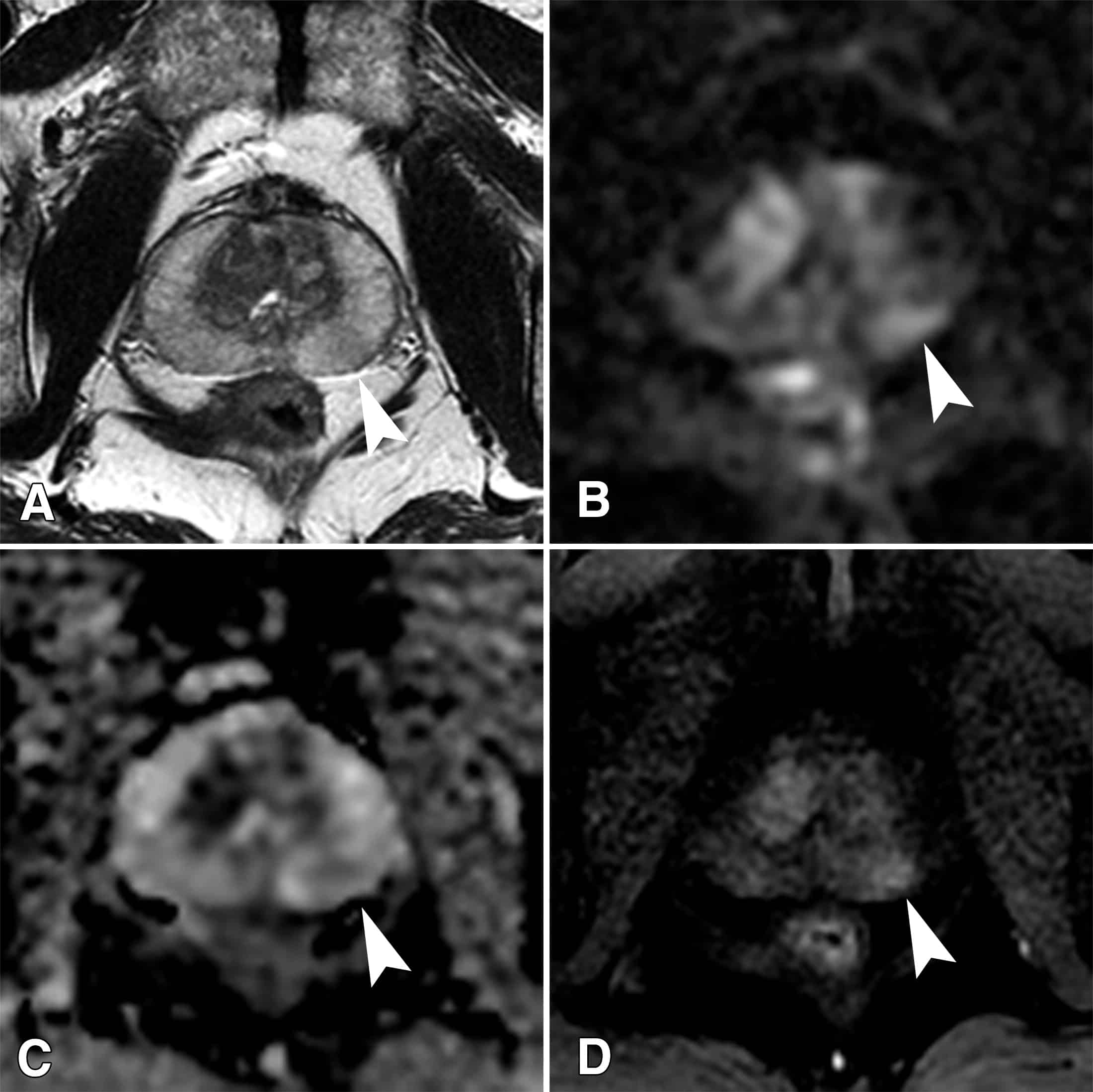
After a prostate cancer diagnosis, your doctor will do tests to see how far the cancer has spread. Not all men need every test. It depends on the results of your biopsy, a test that checks tissue from your prostate gland for cancer. Tests that help your doctor figure out the stage of your prostate cancer include:
- CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis to see if the cancer has spread
- Nuclear medicine bone scan to see if the cancer has spread to your bones
- Surgery to check the lymph nodes in your pelvis for prostate cancer spread
You May Like: Are Tomatoes Good For Prostate
Stage 2 Prostate Cancer
In stage 2, the tumor is still confined to your prostate and hasnt spread to lymph nodes or other parts of your body. A doctor may or may not be able to feel the tumor during a prostate exam, and it may appear on ultrasound imaging. The survival rate is still near 100 percent.
The PSA score for stage 2 is less than 20 ng/mL.
Stage 2 cancer is further divided into three phases depending on the grade group and Gleason scores:
- Gleason score: 6 or less
What If My Biopsy Shows Cancer
If the biopsy shows prostate cancer, your doctor will determine how likely your cancer is to grow quickly and spread. Sometimes, prostate cancer grows slowly over many years. But other times, it grows quickly.
Your doctor can use your PSA level, Gleason score, and tumor score to determine your risk level. The following pages give more information about Gleason score, T-score, and prostate cancer risk levels.
Gleason Score
The Gleason score is a common scale used to determine how fast your prostate cancer is likely to grow. Gleason scores can range from 2 to 10, but most often range from 6 to 10. The higher the Gleason score, the more likely your cancer is to grow and spread.
Tumor Score
The T-score tells how far your prostate cancer has grown.
- T1: The cancer is too small to be felt during a digital rectal exam or seen in an imaging test . The cancer is found from a biopsy done after a man has a high PSA level or has surgery for problems urinating. The cancer is only in the prostate gland.
- T2: The cancer can be felt during a digital rectal exam and may be seen in an imaging test. The cancer is still only in the prostate gland.
- T2a: The cancer is in one-fourth of the prostate gland .
- T2b: The cancer is in more than one-fourth of the prostate gland , but has not grown into the other side of the prostate gland.
- T2c: The cancer has grown into both sides of the prostate gland.
Risk Level
| Risk Level* |
|---|
Dont Miss: Msk Precise For Prostate Cancer
Don’t Miss: Healthy Choice Naturals Prostate Care
What Is The Normal Gleason Score
Theoretically, Gleason scores range from 2-10. However, since Dr. Gleasons original classification, pathologists almost never assign scores 2-5, and Gleason scores assigned will range from 6 to 10, with 6 being the lowest grade cancer.
Otherwise, is a Gleason score of 9 a death sentence?
Not all men with Gleason 8-10 disease are going to do badly after treatment. There is a perception among a lot of patients especially when they get diagnosed that having a high Gleason score of 8, 9, or 10 is essentially a death sentence, regardless of how they get treated. This is not actually the case at all.
Although, is Gleason score the same as PSA? A Gleason score of 8 or higher, accompanied by a PSA level of higher than 20 ng/ml and a more advanced tumor stage, signifies a high risk of advancing cancer. In high-risk cases, the prostate cancer tissue looks very different from normal tissue.
So too, what is a Gleason score of 7 mean?
A Gleason score of 7 is a medium-grade cancer, and a score of 8, 9, or 10 is a high-grade cancer. A lower-grade cancer grows more slowly and is less likely to spread than a high-grade cancer.
What if prostate biopsy is positive?
If prostate cancer is found on a biopsy, it will be assigned a grade. The grade of the cancer is based on how abnormal the cancer looks under the microscope. Higher grade cancers look more abnormal, and are more likely to grow and spread quickly.
28 Related Questions Answered
Ethics Approval And Informed Consent
This study was approved by the regional Swedish Ethics Review Authority in Stockholm, Sweden . In registry-based studies, such as this one, the requirement for informed consent is typically waived because the benefits to patients and the health care in general outweigh potential liabilities. The data handling complied with relevant data protection and privacy regulation .
Also Check: What Is Salvage Radiation For Prostate Cancer
Gleason Prostate Cancer Score
1960s as a way to measure how aggressive your prostate cancer may be.
A pathologist determines your Gleason score by looking at a biopsy of your prostate tissue under a microscope. They grade the cells in the biopsy on a scale of 1 to 5. Grade 1 cells are healthy prostate, whereas grade 5 cells are highly mutated and dont resemble healthy cells at all.
The pathologist will calculate your Gleason score by adding together the number of the most prevalent type of cell in the sample and the second most prevalent type of cell.
For example, if the most common cell grade in your sample is 4 and the second most common is 4, you would have a score of 8.
A Gleason score of 6 is considered low-grade cancer, 7 is intermediate, and 8 to 10 is high-grade cancer.
How Is The Gleason Score Derived
The pathologist looking at the biopsy sample will assign one Gleason grade to the most predominant pattern in your biopsy and a second Gleason grade to the second most predominant pattern. For example: 3 + 4. The two grades will then be added together to determine your Gleason score. Theoretically, Gleason scores range from 2-10. However, since Dr. Gleasons original classification, pathologists almost never assign scores 2-5, and Gleason scores assigned will range from 6 to 10, with 6 being the lowest grade cancer.
Recommended Reading: What Is Neoplasm Of Prostate
Cytokine Release Syndrome 9crs
Cancers with Gleason scores of 8 to 10 are more poorly differentiated or high-grade. These cancers are likely to grow and spread more quickly.
A Gleason score of 7 can be made up of either 3+4=7 or 4+3=7, depending on whether the pattern 3 or pattern 4 is predominant. There is a big difference between these two grades.
· Gleason score 3+4=7 tumors still have a good prognosis , although not as good as a Gleason score 6 tumor.
- A Gleason score 4+3=7 tumor is more likely to grow and spread than a 3+4=7 tumor, yet not as likely as a Gleason score 8 tumor.
New Diagnosis: Where Do I Start
You are not alone. The good news is that most prostate cancers are slow-growing and that with early detection and treatment, it can be cured. Increasing your knowledge by reviewing sections such as Coping with cancer, Choosing your treatment as well as other areas of the web site helps relieve the stress and helps make decisions clearer.
Over the last 12 months, approximately 4,600 Quebecers were diagnosed with prostate cancer. This represents an average of 12 men per day. You are definitely not alone in your fight against prostate cancer. The good news is that we know most prostate cancers are slow-growing, which means that with early detection and treatment, it can even be cured.
Once diagnosed, men will go through understandable and normal reactions, such as fear, denial, anger, helplessness and feeling of loss of control over their life. Once reality sets in, a constructive way to deal with the disease is to learn as much as you can about it. Increasing your knowledge about prostate cancer helps relieve the natural fear of the unknown, and makes the decision-making process easier.
Frequently Asked Questions
Click here for the full list of prostate cancer-related FAQs.
Questions about survival
Talk to your doctor about your prognosis. A prognosis depends on many factors, including:
- how the cancer responds to treatment
We are here for you
Recommended Reading: Do Tomatoes Help Prevent Prostate Cancer
If Treatment Does Not Work
Recovery from cancer is not always possible. If the cancer cannot be cured or controlled, the disease may be called advanced or terminal.
This diagnosis is stressful, and for many people, advanced cancer may be difficult to discuss. However, it is important to have open and honest conversations with your health care team to express your feelings, preferences, and concerns. The health care team has special skills, experience, and knowledge to support patients and their families and is there to help. Making sure a person is physically comfortable, free from pain, and emotionally supported is extremely important.
People who have advanced cancer and who are expected to live less than 6 months may want to consider hospice care. Hospice care is designed to provide the best possible quality of life for people who are near the end of life. You and your family are encouraged to talk with the health care team about hospice care options, which include hospice care at home, a special hospice center, or other health care locations. Nursing care and special equipment, including a hospital bed, can make staying at home a workable option for many families. Learn more about advanced cancer care planning.
After the death of a loved one, many people need support to help them cope with the loss. Learn more about grief and loss.
Gleason Score Vs Grade Groups
The International Society of Urological Pathology released a revised prostate cancer grading system in 2014. The grade group system seeks to simplify Gleason scores and give a more accurate diagnosis.
One of the major problems with the Gleason score is that some scores can be made up in different ways. For example, a score of 7 can mean:
- 3 + 4. The 3 pattern is the most common in the biopsy and 4 is the second most common. This pattern is considered favorable intermediate risk.
- 4 + 3. The 4 pattern is the most common in the biopsy and 3 is the second most common. This pattern is considered unfavorable and may mean local or metastatic spread.
So, although both situations give a Gleason score of 7, they actually have very different prognoses.
Heres an overview of how the two grading systems compare:
| Cancer grade | |
|---|---|
| grade group 5 | 910 |
Not all hospitals have switched to the grade group system. Many hospitals give both grade group and Gleason scores to avoid confusion until grade groups become more widely used.
Read Also: Wife Gives Husband Prostate Massage
Read Also: How Do You Spot Prostate Cancer
Independent Predictors On Css
Deaths from non-PCa causes were regarded as competing events of cancer-specific mortality. Fine-Gray competing-risk regression models revealed that race, AJCC TNM stage, PSA levels, marital status, treatments, and GP were independent predictors for CSS in the univariate and multivariate analyses . Specifically, GP 5 + 4 was associated with a poorer CSS compared with GP 4 + 5. The GP 4 + 5 group had a lower 3, 5, and 10-year CIF than the GP 5 + 4 group. In the multivariate analysis, the GP 5 + 4 group had a higher risk of CSM than the GP 4 + 5 group . Although the AJCC T stage was not proven to be an independent predictor for OS in the multivariate Cox analyses, the higher T stage indicated higher risks of CSM in the multivariate competing-risk regression . Age at diagnosis was not proven to be significantly associated with CSS. Given that age at diagnosis was a powerful predictor for OS, we included it into the final multivariate competing-risk model.
Figure 4. The CIF curves of CSM before PSM. CIF curves for age at diagnosis CIF curves for race CIF curves for AJCC stage CIF curves for AJCC T stage CIF curves for AJCC N stage CIF curves for AJCC M stage CIF curves for Gleason patterns CIF curves for PSA levels CIF curves for marital status CIF curves for treatments. CIF, cumulative incidence function CSM, cancer-specific mortality PSM, propensity score-matching PSA, prostate-specific antigen.
What Tests Check For Prostate Cancer
Common tests to check for prostate cancer include:
- Digital rectal exam: Your doctor inserts a finger into your rectum and touches your prostate gland. The doctor feels the shape of the prostate gland and checks for any hard spots.
- PSA blood test: This blood test tells how much PSA is in your blood. Many men with prostate cancer have PSA levels that are higher than normal or that have gotten higher over time.
- A high PSA level does not always mean a man has prostate cancer. As men get older, their prostate gland may grow larger over time. This growth, and other health conditions, can cause a high PSA level in men who do not have prostate cancer.
If the test results are not normal, your doctor may recommend more tests, such as a biopsy. During a biopsy, the doctor uses a needle to take out a tiny piece or pieces of the prostate gland. An ultrasound probe may be used to guide the needle. Another doctor called a pathologist looks at the tissue under a microscope to check for cancer cells.
Note
Recommended Reading: Do You Lose Length After Prostate Surgery
British Columbia Specific Information
You are considered a low-risk patient if you have a PSA value that is equal or less than 10 nanograms per millilitre , a Gleason score that is equal or less than 6, and your cancer stage is T1c/T2a. PSA is your prostate specific antigen measured by a blood test, the Gleason score indicates how aggressive the cancer is by looking at tissue biopsy results, and the cancer stage describes how much the cancer has spread.
Active surveillance has been developed to allow for careful management of men with low-risk prostate cancer. For more information, visit BC Cancer Agency Prostate.
Top of the pageDecision Point
You may want to have a say in this decision, or you may simply want to follow your doctors recommendation. Either way, this information will help you understand what your choices are so that you can talk to your doctor about them.
