Biochemical Recurrence After Locoregional Treatment
Biochemical recurrence can occur as PSA recurrence after definitive local treatment or as PSA persistence after definitive treatment. Per the National Comprehensive Cancer Network definition, persistence is the failure of PSA to become undetectable after surgery, whereas the European Association of Urology definition is PSA > 1.0 ng/mL within 4 to 8 weeks after surgery and has consistently been associated with poor oncological outcomes . Risk factors for PSA persistence include higher pre-operative PSA levels, advanced pathological T stage and International Society of Urological Pathology grade, positive surgical margins, and pathologic node-positive status . Therefore, it is essential to use effective imaging for staging workup in order to help identify these patients. Currently, there is a prospective study that aims to assess whether PSMA PET/CT should replace conventional imaging for the initial staging of patients with high-risk features .
After confirming BCR, imaging is used to assess for the presence of local or distant disease. However, conventional imaging modalities are limited by low sensitivity. For instance, both scintigraphy and 18-F sodium fluoride PET imaging visualize osteoblastic activity and thus do not indicate the full extent of disease activity or volume. Given these limitations, other tracers have been developed to more accurately characterize BCR.
Do We Have Prognostic Subgroups
The analysis of prognostic factors of metastasized patients led to the CHAARTED criteria and to the LATITUDE criteria to trigger systemic treatment, Table 1 . The analysis of combined risk factors in a large cohort suggested that patients with both paraaortic nodes and bony metastases have the same prognosis as patients with visceral metastases . However, this was not clinically tested and significant confounders might be present . Currently, there is no consensus on further prognostic subgroups for metastatic prostate cancer beyond the CHARTED or LATITUDE definition .
More Options Lead To More Questions
Elisabeth Heath, M.D., director of prostate cancer research at Karmanos Cancer Institute in Detroit, agreed that the ARASENS results should have an immediate impact on how this form of the disease is treated.
Speaking at the ASCO symposium, Dr. Heath, who was not involved in the study, highlighted an important difference between ARASENS and other trials that tested androgen receptorblocking drugs in men with this form of prostate cancer. In those other trials, she explained, some participants received docetaxel prior to treatment with the androgen receptorblocking drugs rather than at the same time.
Based on the ARASENS results, Dr. Heath said, giving all three treatments simultaneously looks to be the preferred option for some patients.
Dr. Karzai noted that despite there being multiple options to treat metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer, many questions remain. We don’t have guidelines on who should start with what drug and whether one drug is better than another for a patient, she said.
She also pointed out that more research is needed on how the order in which the drugs are given impact their effectiveness and the frequency of side effects.
Additionally, she said, the survival improvement in the ARASENS trial was seen in patients whose cancer had spread in multiple areas beyond the prostate .
We dont know if people with lower-volume benefit from as much as the patients with higher-volume disease do, she said.
Recommended Reading: Green Light Photovaporization Of The Prostate
Nhs England Commissions Radiotherapy For Men With Low Volume Metastatic Prostate Cancer
19 Nov 2020
Men with prostate cancer that has spread to a small number of parts of their body can now receive prostate radiotherapy through the NHS in England. This decision was made following a recommendation from the Clinical Priorities Advisory Group based on evidence from the STAMPEDE trial.
In July 2020, the Clinical Priorities Action Group looked at the evidence on various treatments for a wide range of diseases. This included giving radiotherapy to men whose prostate cancer has spread to only a small number of parts of their body. They recommended this treatment should be the top priority out of the six specialised treatments they examined. Based on this recommendation, NHS England have decided to approve radiotherapy for this group of men.
This decision was based on evidence from the STAMPEDE trial, which found that for men with disease which had spread to just a small number of places within the body at the time of diagnosis, radiotherapy significantly improved how long men lived for. After 3 years, 81% of men with low metastatic burden in the radiotherapy group were still alive, compared to 73% of men in the standard treatment group. Radiotherapy also delayed the disease getting worse.
Further information
Contact Us
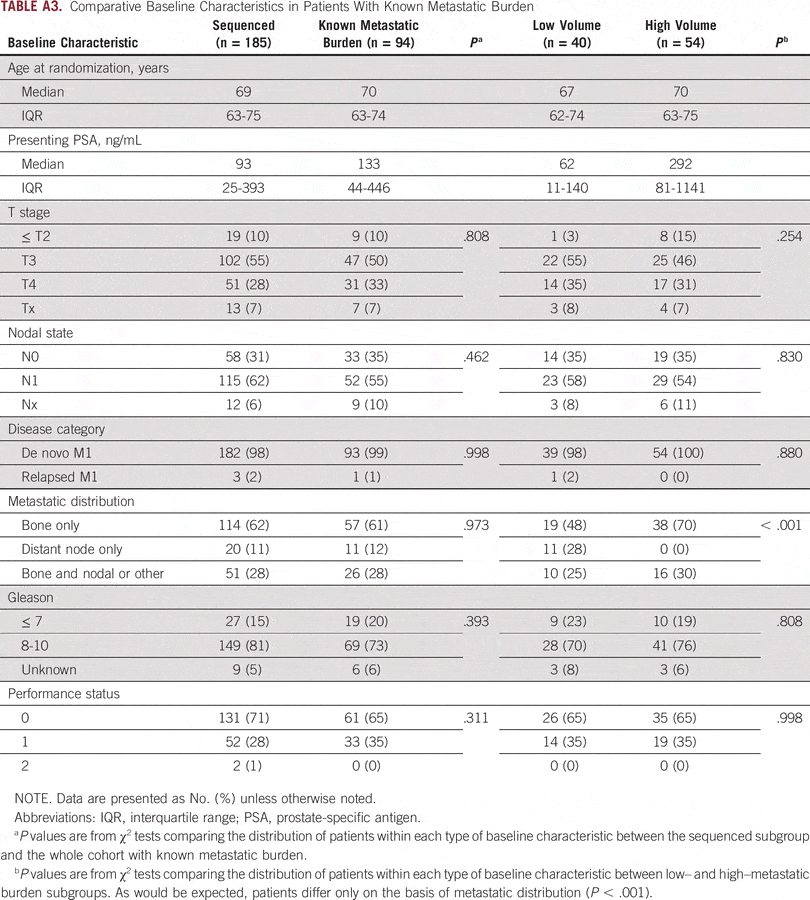
Patient Characteristics And Staging
STAMPEDE trial
From 2013 to 2016, men with newly diagnosed metastatic prostate cancer confirmed by bone scan and soft tissue imaging were included. A PET scan was not performed. Imaging should have been done within 12 weeks of starting ADT . Patients had received no previous radical treatment, presented without significant cardiovascular disease, and had no contraindications to radiotherapy. Metastatic burden was classified according to the CHAARTED-definition . High metastatic burden was defined as 4+ bone metastases with one or more outside the vertebral bodies or pelvis, or visceral metastases, or both. All other patients were considered to have low metastatic burden . Patients were represented with 90% T3+ cancers, 64% N1 disease, and 29% distant nodes . Bone metastases were detected in 89%, visceral metastases in 10%. Initial median PSA level before ADT was ~97ng/mL . A Gleason score of 810 was detected in 79% . WHO performance score was 0 in 71% . Low metastatic burden was classified in 42% of patients .
HORRAD trial
From 20042014, men with PSA > 20ng/ml with bone metastases on bone scan were included. In contrast to the STAMPEDE trial, patients were subdivided into < 5, 515, or more bone lesions.
Don’t Miss: Is Whey Protein Good For Prostate
When To Treat Prostate Cancer Metastases With Ablative Radiation
Selecting Patients for Metastasis Directed Therapy – Definitions of Oligometastatic Prostate Cancer
Quantitative cutoffs based on the number of metastatic foci are often used to define the oligometastatic state for simplicity as well as association with disease outcome. Nine prospective clinical trials have numerically defined the oligometastatic state in prostate cancer three allowed up to three metastases, two up to four, three up to five, and one up to 10. The literature of other published retrospective reviews generally included five or fewer metastatic foci.
As detection methods continue to evolve, technological differences between studies must be taken into consideration when evaluating outcomes of MDT patients with five or fewer lesions detectable with leading-edge methods may represent a population with a lower disease burden than those identified using conventional imaging alone.
The Role Of The Urologist
Management of mHSPC has traditionally been in the domain of the urologist. Since ADT was standardised as a first-line option for these patients many years ago, it has been the urologist who has been the primary specialist overseeing their care until the emergence of castration-resistance. However, the upfront use of Docetaxel chemotherapy and ARPIs has led to changes in patterns of care, with medical oncologists playing an increasing role in the primary management of mHSPC. Whilst Docetaxel is most often administered by medical oncologists, it is also administered by urologists in some countries, especially in the Asia-Pacific region . The increasing role for well tolerated oral ARPIs combined with ADT for mHSPC, also means that urologists can continue to play a key role in the management of mHSPC, provided they are willing to become facile with the safe use and monitoring of these agents . Ultimately, these patients are best managed in multidisciplinary teams, taking into account patient and disease factors, as well as access and affordability issues .
You May Like: What Is Gleason 6 Prostate Cancer
Additional Local Treatment Of Distant Metastases
Additional local treatment of metastases is currently under investigation and optimal patient selection, i.e., maximal number of distant lesions needs to be defined. This is not addressed by the two discussed trials. Both trials contain patients with low metastatic burden but not oligometastatic disease, where metastases-directed treatment might be reasonable to improve progression-free survival and should be discussed individually in an interdisciplinary tumor board.
Sabr May Facilitate Delay Of Adt Initiation
Controversially, the favorable safety profile and durable lesion control afforded by SABR has led to interest in using this approach to forestall initiation of ADT, in so called oligorecurrent men, in order to avoid unpleasant side effects including hot flashes, fatigue, and sexual dysfunction. The shining example of this approach is the STOMP trial, which randomized men with 3 or fewer extracranial prostate cancer metastases to surveillance alone or SABR to all detectable foci of disease. With a median follow-up of 36 months they observed that median ADT-free survival in men receiving SABR was 21 months vs 13 months with surveillance alone. The clinical relevance of this finding remains a point of active disagreement amongst experts. Those in favor of early ADT initiation may cite the TOAD trial , which showed an overall survival benefit with immediate initiation of ADT as compared to a recommended 2 year delay. Those opposed may cite the overall lack of impact on development of metastases with early ADT in the analysis of US Department of Defense patients by Moul et al. and the results of EORTC 30891, which showed similar prostate cancer-specific survival in men not suitable for local treatment receiving early vs delayed ADT. Despite the controversy, an ADT backbone is the standard of care in men with metastatic disease and other novel approaches including MDT are still best evaluated under the auspices of a clinical trial.
Don’t Miss: External Radiation For Prostate Cancer
Asco Gu : Targeted Therapy In The Context Of Low Volume Metastatic Prostate Cancer
- 4 or more bone lesions and
- one or more lesion in any Bony structure beyond the spine or pelvis
- or visceral disease
- Synchronous which is primary and oligometastatic
- Metachronous which is primarily followed by oligometastatic relapse
- Oligoprogressive-Which is a progressive event through systemic therapy
An Evolving Standard Of Care
Hormone-sensitive prostate cancer means a patients tumors are still largely being fueled by male sex hormones called androgens. For many years, metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer was treated with ADT alone, which blocks the production of androgens by the testicles.
In 2014, a large clinical trial showed that adding the chemotherapy drug docetaxel to ADT improved survival in men with metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer. Since then, this combination has become the standard of care for this group of patients.
More recently, studies have shown that adding other drugs that block the production or binding of androgensincluding abiraterone , enzalutamide , and apalutamide to ADT also helps people with metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer live longer. In a trial combining apalutamide with ADT, for example, approximately 82% of men were still alive after 2 years compared with 74% of men treated with ADT alone.
Several clinical trials were then launched to see if combining any of these drugs with ADT and docetaxel could build on those survival gains. Results of those studies, however, have been mixed, with one showing an improvement in survival without the disease progressing and another finding no increase in overall survival.
You May Like: How Many Radiation Treatments For Prostate Cancer
Concurrent Adt And Other Systemic Therapies
One goal of MDT in OMPC is to avoid systemic therapy and its associated side effects. However, a more aggressive approach may involve intensification aimed at simultaneously eradicating sites of microscopic metastatic disease in addition to local consolidation with SABR through the use of concurrent ADT, non-castrating antiandrogens such as enzalutamide, chemotherapies such as docetaxel, and even complimentary forms of systemic radiation such as radium-223. No level 1 evidence exists for this treatment paradigm, however retrospective data suggests a possible improvement in distant progression-free survival with the concurrent use of ADT and SABR. Therefore, prospective studies are on-going to address this question.
Treatment Of The Primary Tumour
The last decade has seen much debate amongst prostate cancer specialists in regard to cytoreductive treatment for the primary tumour. Two large trials have revealed answers pertaining to external beam radiotherapy in this space, however, the specific cohorts of patients that would benefit from ERBT and the field of ERBT used should be further refined. Furthermore, studies comparing cytoreductive prostatectomy to standard treatment need to be carried out.
The evidence for ERBT to the primary tumour is primarily derived from the STAMPEDE trial and HORRAD trial with results from the PEACE-1 trial eagerly awaited. The HORRAD trial recruited 432 men with PSA > 20 ng/mL and primary bone metastases on whole body bone scan. These men were randomised to receive ADT with or without ERBT . With median follow up of 47 months, improvement in OS was not shown with added ERBT. However in a subgroup analysis of patients with low metastatic burden , radiotherapy resulted in a non-significant improvement in OS . The STAMPEDE trial randomised 2061 men with newly diagnosed mHSPC to receive standard therapy with or without ERBT . Around 60% of these men had high metastatic burden. Results showed that for all patients, failure free survival was improved but not OS. However, failure free survival and OS were both improved specifically for patients with low metastatic burden .
You May Like: Can Prostatitis Cause Swollen Lymph Nodes In Groin
Which Radiotherapy Schedule Should Be Used To Treat The Primary
In STAMPEDE, 55Gy in 20 fractions or 36Gy in 6 weekly fractions were used. The HORRAD trial employed either 70Gy in 35 fractions or 57.76Gy in 19 three weekly fractions. The authors state that this schedule represents an older radiotherapy standard. Therefore, Parker et al. recommend applying the current standard of 60Gy in 20 fractions. However, this CHiP standard and other randomized trials were not tested in locally advanced disease or after transurethral resection, and there remains a risk of slightly increased GU toxicity with hypofractionation. The current German S3 guideline recommends local treatment with moderately hypofractionated or conventionally fractionated RT of the primary with an EQD2 of up to 72Gy, in line with EQD2 of the HORRAD trial .
We discussed this point and recommend a practical approach depending on pre-existing comorbidities, previous surgery , and individual life expectancy. The moderately hypofractionated regimen might be suitable in patients without TURP and with IPSS 12 . This would acknowledge the experience with patients of the CHiP trial with slightly increased genitourinary toxicity . Normofractionated schedules to 7072Gy or hypofractionated schedules with lower EQD2 might be more suitable in patients with an increased risk of toxicity , since evidence of low toxicity can be derived from both trials for locally advanced disease.
A New Standard Of Care For Low
Men diagnosed with metastatic prostate cancer will often not undergo local treatments of the primary prostate tumor, such as surgery or radiation. Primary hormone therapy has long been the standard of care, although recently the addition of docetaxel or abiraterone to ADT has become a standard of care option. In March, the National Comprehensive Cancer Network released its 1.2019 version of guidelines for prostate cancer. For men with low-volume metastatic disease who have not previously been treated with hormone therapy, there is an important update: the option of radiation therapy to the prostate in addition to ADT .
Digging deeper into trial results
This update is based on results of a large randomized controlled trial called STAMPEDE.
But before STAMPEDE, there was another trial called HORRAD, the first study adding RT to ADT in patients with metastatic prostate cancer. In the analysis of all 400+ patients in the HORRAD trial, there was no difference in overall survival. Taken at face value, adding RT didnt work. Case closed?
Not so fast..because when researchers looked at a small subset of patients who had a low number of metastatic disease sites, they saw a suggestion of a survival benefit.
A large European trial
But wait.what about side effects of radiation? The study also assessed toxicity, and found no difference in rates of severe events between the two treatment arms.
Recommended Reading: Are Eggs Bad For The Prostate
Hallmark Six: Tissue Invasion And Metastasis
The potential for invasion into adjacent anatomical structures and spread to distant sites are key attributes of cancer cells. Most manifestations of prostate cancer do not have either of these properties.
Prostate.
RASRAP1AJ Exp Med.Nature.
Urology.BJU Int.
BJU Int.Cancer.
J Urol.Eur Urol.
J Urol.Eur Urol.
Urology.Nat Rev Clin Oncol.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
Cancer.
Cancer.
J Pathol.
J Urol.
Cancer Res.
J Urol.
J Urol.
TMPRSSERGHum Pathol.Urology.Nat Med.
N Engl J Med.Nature.
BJU Int.
J Urol.
Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis.Hum Pathol.
J Natl Cancer Inst.Ann Intern Med.
Ann Intern Med.J Clin Oncol.
J Urol.
How Is Mdt Using Ablative Radiotherapy Delivered
Target Volumes, Dose, and Fractionation
Optimal ablative dosing is contingent on multiple factors including radiobiological properties of prostate cancer cells and dosimetric constraints of adjacent organs at risk. Studies reporting on the use of SABR for the definitive treatment of prostate cancer have utilized regimens with biological effective doses ranging from 168 to 407 Gy with some evidence suggesting BED of 200 Gy is associated with better disease control.
STOMP, the only published prospective randomized trial of MDT in oligometastatic prostate cancer, utilized a dose of 30 Gy in 3 fractions. Other retrospective and observational studies of MDT in oligometastatic prostate cancer utilized doses ranging from 16 to 50 Gy in 1 to 10 fractions (Table 2 with some suggestion that a BED higher than 100 Gy is associated with superior local control.
Toxicity from SABR is generally mild across several lesion locations. Every other day scheduling is often used as it has shown reduced toxicity compared to daily treatments in definitive treatment of the prostate, however even with daily treatments toxicity rates remain low .
Recommended Reading: Is Ejaculation Healthy For The Prostate
Why Treat Prostate Cancer Metastases With Ablative Radiation
Rationale for Metastasis-Directed Therapy in Prostate Cancer
Traditionally, the management of metastatic cancer has been chiefly through systemic treatments while local therapies such as radiation have been used primarily for palliation of symptomatic lesions. Prostate cancer commonly spreads to the bones, causing pain and potentially leading to fractures at weight-bearing sites such as the femoral neck, acetabulum, or vertebral bodies. Radiation is highly effective at reducing pain caused by osseous metastases and can be delivered in one or multiple fractions of external beam radiotherapy or with the systemic radiopharmaceutical radium-223.
