The Natural History And Molecular Biology Of Low Grade Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer develops with age in the majority of men, including those from all races and regions. In Caucasians, the chance of harboring prostate cancer is approximately the same as ones age thirty percent of men in their 30s, 40% in their 40s, 80% in their 80s . Most of these are microfoci and low grade, particularly in younger men. The high prevalence of microfocal prostate cancer has been confirmed in autopsy studies of Caucasians, Asians, and other ethnic groups going back more than 50 years. A recent autopsy study in Japanese and Russian men who died of other causes showed that overall 35% of both groups had prostate cancer, and 50% of the cancers in Japanese men aged > 70 were Gleason score 7 or above .
Nomograms Predict Survival Advantages Of Gleason Score 3+4 Over 4+3 For Prostate Cancer: A Seer
- 1Department of Urology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing, China
- 2Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, The First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing, China
Background: Different proportions of Gleason pattern 3 and Gleason pattern 4 lead to various prognosis of prostate cancer with Gleason score 7. The objective of this study was to compare the survival outcomes of Gleason score 3+4 and 4+3 based on data from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results cancer registry database, and to investigate independent prognosis-associated factors and develop nomograms for predicting survival in Gleason score 7 prostate cancer patients.
Methods: A retrospective study was conducted on 69,116 cases diagnosed as prostate adenocarcinoma with Gleason score 7 between 2004 and 2009. Prognosis-associated factors were evaluated using univariate and multivariate Cox regression analysis, and a 1:1 ratio paired cohort by propensity score matching with the statistical software IBM SPSS, to evaluate prognostic differences between Gleason score 3+4 and 4+3. The primary cohort was randomly divided into training set and validation set . Based on the independent factors of prognosis, nomograms for prognosis were established by the training group and validated by the validation group using R version 3.5.0.
Can The Gleason Score On My Biopsy Really Tell What The Cancer Grade Is In The Entire Prostate
Because prostate biopsies are tissue samples from different areas of the prostate, the Gleason score on biopsy usually reflects your cancers true grade. However, in about 1 out of 5 cases the biopsy grade is lower than the true grade because the biopsy misses a higher grade area of the cancer. It can work the other way, too, with the true grade of the tumor being lower than what is seen on the biopsy.
You May Like: Can Prostate Cancer Affect Women
Technique Of Focal Therapy
A variety of techniques have been described, all involving the use of directed energy and image guidance. These include high intensity focused ultrasound , MR guided ultrasound, laser ablation, cryosurgical ablation, focal photodynamic therapy, electroporation, various forms of radiation. Ultimately, which of these therapies becomes widely used will be a reflection of precision of treatment, morbidity, cost, and availability and convenience. The principles and methods used with these directed energies have been described previously. The experience with these technologies used for focal therapy is summarized in the table below, in chronological order.
Most of the focal therapy data lacks robust endpoints. In most published studies, follow-up biopsies were usually not systematic, and in most studies the majority of patients were not biopsied. This is a potential source of bias, in that PSA and MRI may misidentify as responders some patients with residual disease. In patients having a biopsy, the rate of positive biopsies ranged from 14% to 50% . Further, most authors only biopsied the treated area. Biopsies of the untreated area were selective based on mpMRI.
How Do I Know The Gleason Grade Is Accurate
Assigning the correct Gleason score is a skill just like any other that is developed through experience and practice. It is often prudent to have the biopsy material referred for a second opinion at a reference center to confirm the accuracy of the initial Gleason score that was assigned.
References:
You May Like: What Type Of Doctor Does Prostate Exams
Prostate Cancer Stages And Other Ways To Assess Risk
After a man is diagnosed with prostate cancer, doctors will try to figure out if it has spread, and if so, how far. This process is called staging. The stage of a prostate cancer describes how much cancer is in the body. It helps determine how serious the cancer is and how best to treat it. Doctors also use a cancerâs stage when talking about survival statistics.
The stage is based on tests described in Tests to Diagnose and Stage Prostate Cancer, including the blood PSA level and prostate biopsy results.
Also Check: Prostate Cancer Stage 7 Treatment
How Is The Gleason Score Derived
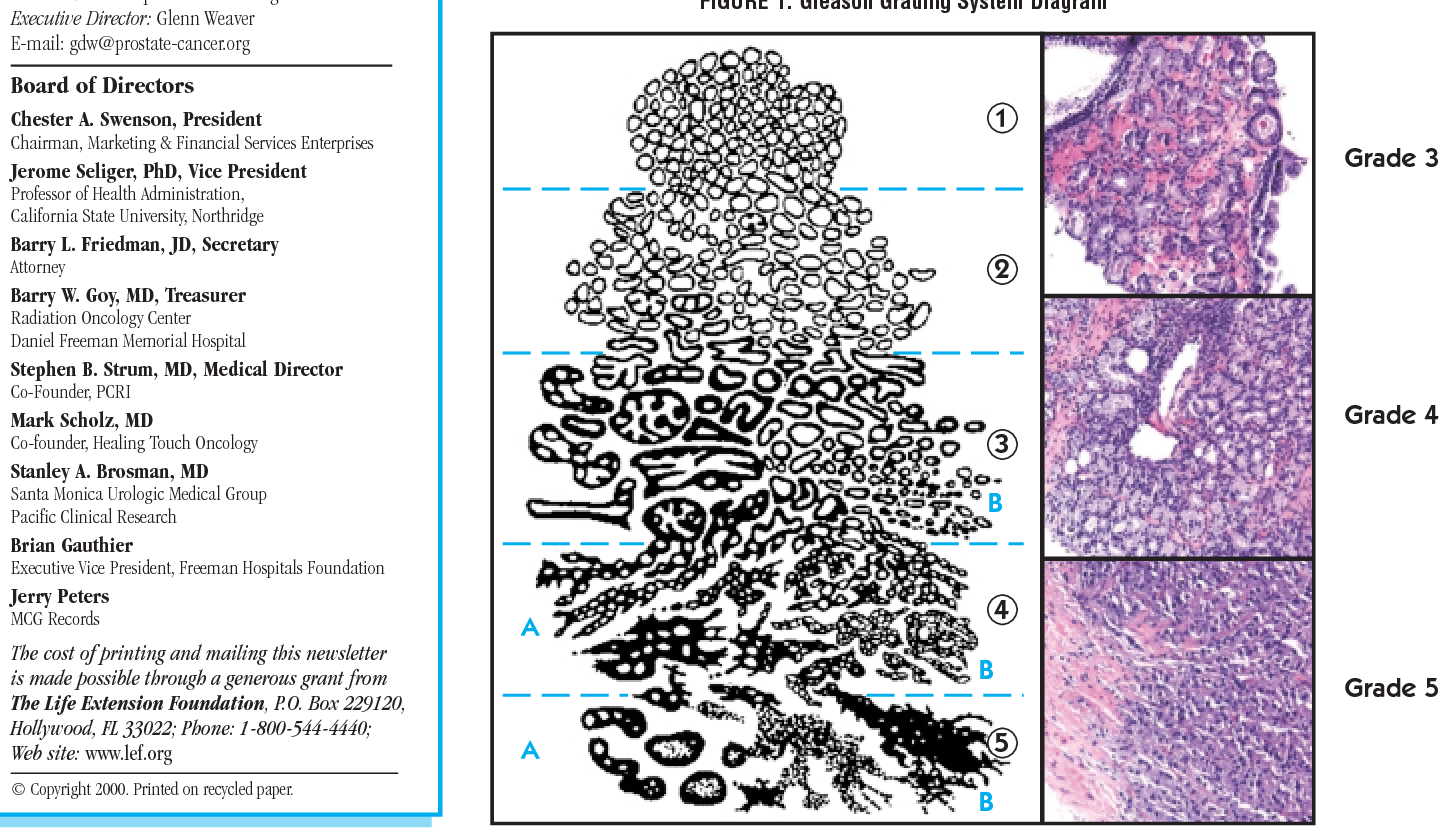
The pathologist looking at the biopsy sample will assign one Gleason grade to the most predominant pattern in your biopsy and a second Gleason grade to the second most predominant pattern. For example: 3 + 4. The two grades will then be added together to determine your Gleason score. Theoretically, Gleason scores range from 2-10. However, since Dr. Gleasons original classification, pathologists almost never assign scores 2-5, and Gleason scores assigned will range from 6 to 10, with 6 being the lowest grade cancer.
You May Like: Is Cialis Good For Enlarged Prostate
Also Check: What Does Prostate Cancer Look Like
How Prostate Cancer Is Diagnosed And Staged
Cancer staging helps you and your doctor understand how advanced your cancer is and how much it has spread at the time of diagnosis. Knowing your cancer stage also helps your doctor determine the best treatment options for you and estimate your chance of survival.
The most widely used staging system for cancer is the TNM system that classifies cancer from stage 1 to stage 4.
TNM stands for:
- Tumor: the size and extent of the tumor
- Nodes: the number or extent of nearby lymph node involvement
- Metastasis: whether cancer has spread to distant sites in the body
The TNM scale is used for many types of cancer. When a doctor uses it to determine your prostate cancer stage, theyll consider several other factors as well, including:
- grade groups
Understanding Your Pathology Report: Prostate Cancer
When your prostate was biopsied, the samples taken were studied under the microscope by a specialized doctor with many years of training called a pathologist. The pathologist sends your doctor a report that gives a diagnosis for each sample taken. Information in this report will be used to help manage your care. The questions and answers that follow are meant to help you understand medical language you might find in the pathology report from your prostate biopsy.
Recommended Reading: How Is Prostate Cancer Causes
How Do Doctors Find Out Your Grade Group
The pathologist grades each sample of prostate cancer cells from 3 to 5 based on how quickly they are likely to grow or how aggressive the cells look. You may hear this score being called the Gleason grade.
Doctors then work out an overall Gleason score by adding together the 2 most common Gleason grades. So for example, if the most common Gleason grade is 3, and the second most common is 4, then the overall Gleason score is 7. Or they might write the scores separately as 3 + 4 = 7. This combined score is now called the Grade Group.
There are 5 Grade Groups. Grade Group 1 is the least aggressive and Grade Group 5 is the most aggressive.
This is how the Gleason score and Grade Groups match up and what it means:
| Gleason score |
|---|
Important Takeaway Message About As
From our viewpoint at the Sperling Prostate Center, AS is a good thing for the right patient. This Johns Hopkins study shows the diagnostic inadequacy of the TRUS biopsy to determine who those men are.
Who wants to wake up from radical prostatectomy only to learn that the cancer was worse than originally thought? The fact is, at the time of surgery, nearly 25% of study patients with Gleason 3+4 cancer were harboring more dangerous disease than their doctors found using TRUS biopsy.
We have to ask, what if these men had undergone a 3T multiparametric MRI scan before they had a biopsy? And, if the 3T mpMRI had picked up significant lesions, what would an in-bore MRI-guided targeted biopsy have found? Many published studies have shown that real-time MRI-guided biopsies are superior over TRUS biopsies at detecting significant cancer using fewer needles.
At our Center, we support AS patients by offering
- The most accurate imaging to detect significant disease
- The most precise biopsy method, superior to fusion-guided biopsy, for accurate diagnosis
- A monitoring protocol using PSA plus periodic 3T mpMRI scans to pick up any cancer changes as early as possible, to facilitate decision-making at each step along the way.
Patel HD, Tosoian JJ, Carter HB, Epstein JI. Adverse Pathologic Findings for Men Electing Immediate Radical Prostatectomy: Defining a Favorable Intermediate-Risk Group. JAMA Oncol. 2017 Jul 13. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.1879.
Also Check: How To Remove Prostate Cancer
What Are Grade Groups
Grade Groups are a new way to grade prostate cancer to address some of the issues with the Gleason grading system.
As noted above, currently in practice the lowest Gleason score that is given is a 6, despite the Gleason grades ranging in theory from 2 to 10. This understandably leads some patients to think that their cancer on biopsy is in the middle of the grade scale. This can compound their worry about their diagnosis and make them more likely to feel that they need to be treated right away.
Another problem with the Gleason grading system is that the Gleason scores are often divided into only 3 groups . This is not accurate, since Gleason score 7 is made up of two grades , with the latter having a much worse prognosis. Similarly, Gleason scores of 9 or 10 have a worse prognosis than Gleason score 8.
To account for these differences, the Grade Groups range from 1 to 5 :
- Grade Group 1 = Gleason 6
- Grade Group 2 = Gleason 3+4=7
- Grade Group 3 = Gleason 4+3=7
- Grade Group 4 = Gleason 8
- Grade Group 5 = Gleason 9-10
Although eventually the Grade Group system may replace the Gleason system, the two systems are currently reported side-by-side.
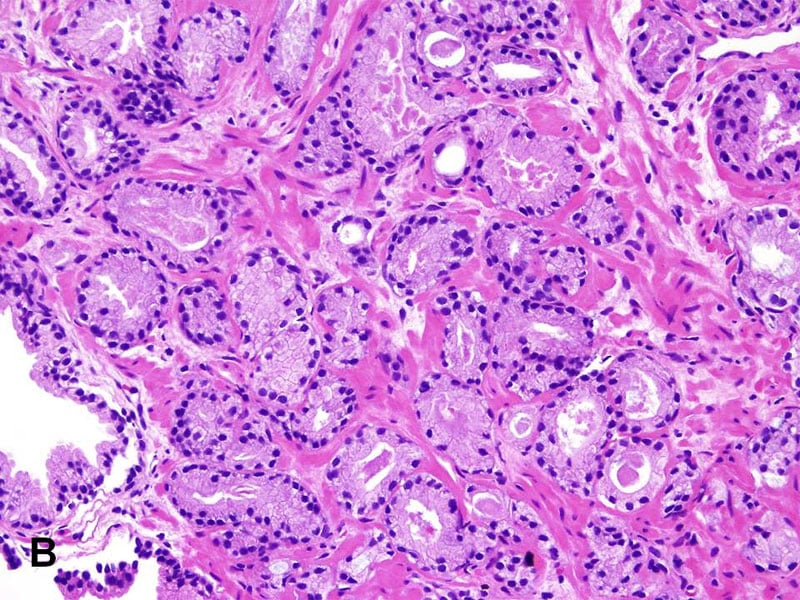
Interobserver Reproducibility Of Percent Pattern 4
It has been documented that interobserver reproducibility for the recognition of Gleason pattern 4 in prostate needle biopsies is not high. In particular, the rate of the agreement between an expert genitourinary pathologist and general pathologists was lower in cases where pattern 4 was scattered among pattern 3 than in those with discrete tumor foci . In a recent study , interobserver reproducibility of percent Gleason pattern 4 in prostate needle biopsy was also assessed in a prospective manner. In 422 biopsy cores received for a second opinion at their institution, 75% of cores were within ±10%, with 32% being a perfect match, between an expert genitourinary pathologist and 1 of 4 genitourinary pathology fellows nearing the end of their fellowship. However, in 88 cases with less than10% tumor involvement of the core, an agreement rate was lower . As a result, the authors did not recommend recording the percentage of pattern 4 in a small focus of Gleason score 7 cancer where grading only a few cancer glands might radically overestimate the amount of pattern 4 in the case.
Don’t Miss: How To Ejaculate From Prostate
What Does It Mean To Have A Gleason Score Of 6 Or 7 Or 8
The lowest Gleason Score of a cancer found on a prostate biopsy is 6. These cancers may be called well-differentiated or low-grade and are likely to be less aggressive – they tend to grow and spread slowly.
Cancers with Gleason Scores of 8 to 10 may be called poorly differentiated or high grade. These cancers tend to be aggressive, meaning they are likely to grow and spread more quickly.
Cancers with a Gleason Score of 7 may be called moderately differentiated or intermediate grade. The rate at which they grow and spread tends to be in between the other 2.
Calculating The Gleason Score
A doctor will use the results of a biopsy to calculate the Gleason score.
During a biopsy, a healthcare professional will take tissue samples from different areas of the prostate. The cancer is not always present in all parts of the prostate. For this reason, they will often collect several samples.
After examining the samples under a microscope, they will identify the two areas with the most cancer cells. They will then assign a score to each of these areas. Then, they will add these scores together to give a combined score, often referred to as the Gleason sum.
It is important to note that sometimes, a doctor will use a different method for calculating the Gleason score.
For example, when a biopsy sample has either a large number of high grade cancer cells or shows three different grades of mutation, they will modify the Gleason score to more accurately reflect how aggressive they deem the cancer to be.
A persons Gleason score can technically range from 210, but it is much more likely to range from 610. We will explain why this is in the sections below.
You May Like: How To Get Rid Of Prostate Infection Naturally
Prostate Cancer: The Gleason Score Explained
How aggressive is my prostate cancer? Is it growing slowly or quickly?
If youve been diagnosed with prostate cancerand this year alone nearly 165,000 men nationwide will bethese may be among the first questions youll ask your doctor. And the answers will most likely take into account something called a Gleason score.
The Gleason score is a grading system used by urologists to assess a prostate cancers aggressiveness based on how cells from the tumor look under a microscope. Less-aggressive tumors are more likely to resemble healthy prostate tissue. More-aggressive tumors look less like normal tissue.
The higher the Gleason score, the more aggressive your cancer is likely to beand the greater the chance that it will spread. Doctors use the Gleason score to help choose appropriate treatments.
What Is The Gleason Score
The Gleason grading system estimates the aggressiveness of the cancer by assigning a pattern to the cancer cells depending on their appearance under the microscope. A number from 1 to 5 is used as a measure of how aggressive the cancer looks under the microscope.
- If the cancerous tissue looks much like normal prostate tissue, a grade of 1 is assigned.
- If the cancer cells and their growth patterns look very abnormal, a grade of 5 is assigned.
- Grades 2 through 4 have features in between these extremes.
The most common type of prostate biopsy is a core needle biopsy. For this procedure, the doctor inserts a thin, hollow needle into the prostate gland. When the needle is pulled out it removes a small cylinder of prostate tissue called a core. This is typically repeated several times to sample different areas of the prostate.
Since multiple core biopsy samples are evaluated and prostate cancers in a single patient often have areas with different grades the pathologist assigns two grades to the examined prostate tissue. The first grade is the most common pattern seen after review of all the biopsy specimens and the 2nd grade is assigned to the next most common pattern.
You May Like: What Foods Help Prostate Health
What Does It Mean If My Biopsy Report Mentions The Word Core
The most common type of prostate biopsy is a core needle biopsy. For this procedure, the doctor inserts a thin, hollow needle into the prostate gland. When the needle is pulled out it removes a small cylinder of prostate tissue called a core. This is often repeated several times to sample different areas of the prostate.
Your pathology report will list each core separately by a number assigned to it by the pathologist, with each core having its own diagnosis. If cancer or some other problem is found, it is often not in every core, so you need to look at the diagnoses for all of the cores to know what is going on with you.
What Does It Mean
A Gleason score of 6 is low grade, 7 is intermediate grade, and a score of 8 to 10 is high grade cancer.
Get More Information
Its also important to know whether any cells rated at Gleason grade 5 are present, even in just a small amount, and most pathologists will report this. Having any Gleason grade 5 in your biopsy or prostate puts you at a higher risk of recurrence.
But because many prostate cancer cases are extremely slow-growing, the Gleason system didnt necessarily do a good job of communicating the risks for these cases. Patients with scores of 6 and 7 didnt have a clear picture of the nature of their particular cancer.
Read Also: Does Losing Weight Help Enlarged Prostate
The Number Staging System
There are a few different systems used for staging prostate cancer. A simplified number staging system is described below.
- Stage 1 The tumour is contained in the prostate. The tumour is too small to be felt when a doctor does a rectal examination or to be seen on a scan.
- Stage 2 The tumour is still contained in the prostate, but your doctor can feel it when they do a rectal examination.
- Stage 3 The tumour has started to break through the outer capsule of the prostate and may be in the nearby tubes that produce semen .
- Stage 4 The tumour has spread outside the prostate. It may have spread to areas such as the bladder or back passage . Or it may have spread further, for example to the bones.
Using the numbered staging system described above:
- stage 4 is known as advanced prostate cancer.
See also
The grade of a cancer gives an idea of how quickly the cancer might grow or spread. A doctor decides the grade of the cancer by how the cancer cells look under the microscope.
Doctors look at the grade of the cancer to help them plan your treatment.
Gleason is the most commonly used grading system for prostate cancer.
