What Happens After The Exam
When abnormalities are found with the rectal exam, the doctor will order a PSA test. After the results for PSA testing are returned, the doctor will analyze the measurements of prostate-specific antigen in the patients blood.
The findings of the PSA test determine what the doctor will do next.
If the doctor suspects prostate cancer, other tests may be requested. A transrectal ultrasound is often requested. This gives the doctor a visual view of the patients prostate gland.
Cancerous growths can be observed through this type of ultrasound test. The test is also relatively quick to perform. Men may experience discomfort when an ultrasound is performed. The discomfort should not last long, however.
A prostate biopsy is sometimes done. This helps to provide a more accurate test for cancer. A colonoscopy is sometimes needed too. This is especially the case when prostatic carcinoma is suspected.
Risks And Benefits Of Prostate Cancer Screening
There are two main benefits of prostate cancer screening.
One is potentially preventing death from prostate cancer. Many men have prostate cancer without experiencing symptoms, so screening can potentially identify prostate cancer early on when it can be treated more easily.
Another benefit of screening and early detection is potentially catching prostate cancer in its early stages, allowing for more effective treatment. Earlier treatment can help prevent prostate cancer from spreading beyond the prostate , which can cause several symptoms.
Unfortunately, there are drawbacks to prostate cancer screening. The DRE is not very sensitive or specific. This means that people who have prostate cancer can still have a normal DRE, while patients with an abnormal DRE may not have prostate cancer. For these reasons, healthcare providers are no longer performing DRE alone for routine prostate cancer screening and relying instead on the PSA test .
PSA testing also has limitations in screening for prostate cancer. Elevated PSA levels do not only occur in prostate cancer. Prostatitis or an enlarged prostate can also cause PSA levels outside the normal range. Abnormal test results can ultimately lead to undue anxiety and further testing that may prove unnecessary .
Another problem with the PSA test is the potential for overdiagnosis and overtreatment. Screening uncovers patients with prostate cancer who would otherwise never have had any issues resulting from the disease.
What Clinical Trials Are Open
Clinical trials that are currently open and are recruiting can be viewed at www.ClinicalTrials.gov.
This content is provided as a service of the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, part of the National Institutes of Health. The NIDDK translates and disseminates research findings to increase knowledge and understanding about health and disease among patients, health professionals, and the public. Content produced by the NIDDK is carefully reviewed by NIDDK scientists and other experts.
The NIDDK would like to thank:Steven A. Kaplan, M.D., Weill Cornell Medical College Michel A. Pontari, M.D., Temple University School of Medicine
Recommended Reading: What Is Perineural Invasion In Prostate Cancer
What If We Find Something
A rectal exam can give us an indication that cancer may be present but discovering a lump is not a cancer diagnosis. If the examiner finds the surface of your prostate to be hard and lumpy or your PSA levels are higher than expected you may be referred for additional tests. If you haven’t already seen a Consultant Urologist they may conduct another rectal exam to check the GP’s initial assessment.
The next step is usually to have an MRI scan so an image of your prostate can be examined. If necessary, you may then be referred for a biopsy to take a sample from your prostate. Even then, finding cancer cells in your prostate doesn’t necessarily mean you’ll need cancer treatment. Find out more on the truth about prostate cancer diagnosis here.
*Reference: NHS England
What Happens After The Dre
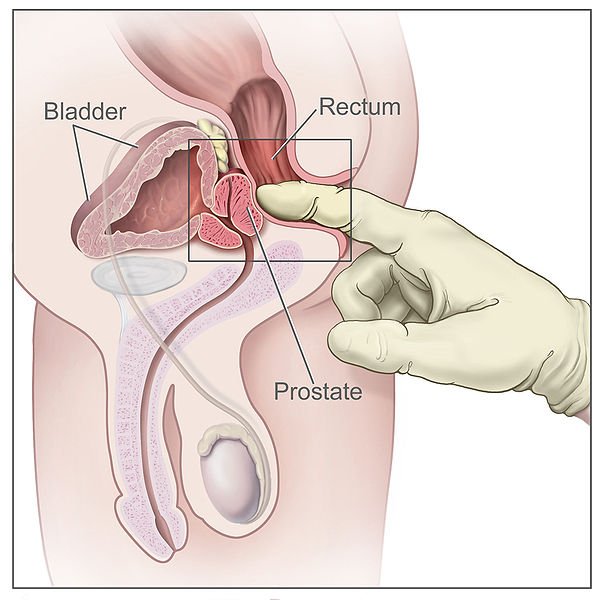
If any abnormalities are found during the DRE, the doctor may order more tests and possibly schedule a prostate biopsy to see if there are any signs of cancer present.
If there are no signs of prostate cancer found during screening, the results of the PSA blood test may help to determine the time between future prostate cancer screenings. PSA levels vary by age and other factors.
Ultimately, you and your doctor will decide how often you should be screened since your diet, health and lifestyle habits are all factors on the timing and frequency of your prostate cancer screenings. Be sure to consult with your doctor if you notice any changes in your health.
Read Also: Perineural Invasion Prostate Cancer
How A Doctor Performs A Prostate Exam
The male reproductive system relies on a healthy prostate to function. The prostate is a relatively small gland. It is the size of a chestnut . The prostate produces a fluid that combines with sperm.
The prostate fluid helps to nourish sperm. In turn, reproduction is possible, and semen can survive in the acidic environment of the vagina.
There are times when a prostate may give a man problems. Several complications have been linked to the prostate gland. Benign prostatic hyperplasia is generally considered the most common type of prostate condition.
Other common issues that men are concerned about include prostate cancer and prostatitis.
Prostate screening is one of the first diagnostic tools used to detect these problems.
While men generally find this to be an uncomfortable procedure, its benefits need to be considered.
We take a look at how a prostate exam is done. The post also considers why a prostate exam is done.
Are You Seeing Prostate Cancer Becoming More Prevalent In Younger Patients
Its pretty rare. Its less common that men in their 40s have prostate cancer, but, we also are very rarely screening them. The young men who come in to be screened tend to have one of those high-risk features. They most likely had a father who had prostate cancer, so theyre nervous about it. Or theyre African-American, and theyve been flagged by their health care providers.
If youre young, your quality of life is even more important to you right now. We know that, if diagnosed with low-grade prostate cancer, a person will need treatment at some time in life. If we can delay treatmentwhich could negatively impact urinary or sexual functionby several years, then we should do that and obviously discuss that there is a low but possible chance of metastasis developing during that time.
Also Check: Perineural Invasion Meaning
Preparing For A Prostate Exam
Theres nothing special that you need to do to prepare for a prostate exam. Tell your doctor if you have anal fissures or hemorrhoids, as a DRE may aggravate these conditions.
If you decide to get a prostate cancer screening, your doctor will likely order a blood test, so inform the person drawing your blood if youre prone to dizziness.
Your doctor may ask you to sign a consent form before performing a cancer screening.
What Are Some Common Uses Of The Procedure
Your doctor uses MRI to evaluate prostate cancer and see if it is limited to the prostate. Mp-MRI provides information on how water molecules and blood flow through the prostate. This helps determine whether cancer is present and, if so, whether it is aggressive and if it has spread.
Occasionally, MRI of the prostate is used to evaluate other prostate problems, including:
- infection or prostate abscess.
- some older cardiac defibrillators and pacemakers
Tell the technologist if you have medical or electronic devices in your body. These devices may interfere with the exam or pose a risk. Many implanted devices will have a pamphlet explaining the MRI risks for that particular device. If you have the pamphlet, bring it to the attention of the scheduler before the exam. MRI cannot be performed without confirmation and documentation of the type of implant and MRI compatibility. You should also bring any pamphlet to your exam in case the radiologist or technologist has any questions.
If there is any question, an x-ray can detect and identify any metal objects. Metal objects used in orthopedic surgery generally pose no risk during MRI. However, a recently placed artificial joint may require the use of a different imaging exam.
Also Check: Periprostatic
What Are The Limitations Of Mri Of The Prostate
High-quality images depend on your ability to remain perfectly still and follow breath-holding instructions while the images are being recorded. If you are anxious, confused or in severe pain, you may find it difficult to lie still during imaging.
A person who is very large may not fit into certain types of MRI machines. There are weight limits on the scanners.
Implants and other metallic objects can make it difficult to obtain clear images. Patient movement can have the same effect.
A very irregular heartbeat may affect the quality of images. This is because some techniques time the imaging based on the electrical activity of the heart.
MRI cannot always distinguish between cancer and inflammation or the presence of blood products within the prostate. Blood may sometimes appear due to a prostate biopsy. To avoid confusing any bleeding with cancer, your doctor may wait six to eight weeks after prostate biopsy to perform prostate MRI. This will allow any remnants of bleeding to resolve.
MRI typically costs more and may take more time to perform than other imaging methods. Talk to your insurance provider if you have concerns about the cost of MRI.
Deciding If You Need A Prostate Screening
You May Like: Do Females Have Prostate Cancer
What Do The Results Mean
PSA levels may be above the baseline for various reasons other than prostate cancer.
Other factors that can raise PSA levels include:
- older age
- an enlarged prostate â because of benign prostatic hyperplasia , for example
- prostatitis, which is inflammation and swelling of the prostate
Also, people with obesity may have lower PSA readings.
In addition, some medications may reduce PSA levels, including:
- 5-alpha reductase inhibitors, which can help treat BPH
- aspirin, which some people take regularly as a blood thinner
- statins, which help manage cholesterol levels
- thiazide diuretics, a kind of water pill that can help reduce high blood pressure
Some herbal medicines and supplements can also lower PSA levels. Tell the doctor about any medications and supplements before undergoing the test.
High PSA levels alone do not indicate cancer. However, if a DRE also reveals changes, a doctor may recommend a biopsy for a more accurate result.
The PCA3 is another test for prostate cancer that doctors use in some circumstances. Find out more.
Why Is Active Surveillancethe Wait
We utilize active surveillance for men who have been diagnosed with a low-grade prostate cancer. The reason we monitor low-grade prostate cancer using active surveillance, rather than treating it aggressively, is that there are cancers that dont need treatment.
With low-grade prostate cancer, youre more likely to have problems from the treatment than from the prostate cancer. Any treatment we do for prostate cancer is going to affect a mans urinary and sexual function. It may affect it a little bitor a lot. With this type of prostate cancer, we can tell you now that theres very little likelihood the cancer is going to cause you any problems. We have a good and growing amount of evidence that low-grade prostate cancers, on average, progress very slowly and do not appear to spread to the lymph nodes. Active surveillance lets us detect higher grade disease and treat it at that point.
For us to do anything and treat it is going to change your quality of life. I think thats a powerful thing.
You May Like: Perineuronal Net
What Does A Dre Involve
You might have a DRE at your GP surgery or at the hospital.
The doctor or nurse will ask you to lie on your side on an examination table, with your knees brought up towards your chest. They will slide a finger gently into your back passage. Theyll wear gloves and put some gel on their finger to make it more comfortable.
You may find the DRE slightly uncomfortable or embarrassing, but the test isnt usually painful and it doesnt take long.
Personal And Family Medical History
Taking a personal and family medical history is one of the first things a health care provider may do to help diagnose benign prostatic hyperplasia. A health care provider may ask a man
- what symptoms are present
- when the symptoms began and how often they occur
- whether he has a history of recurrent UTIs
- what medications he takes, both prescription and over the counter
- how much liquid he typically drinks each day
- whether he consumes caffeine and alcohol
- about his general medical history, including any significant illnesses or surgeries
Also Check: What Is Perineural Invasion In Prostate Cancer
How Is The Procedure Performed
MRI exams may be done on an outpatient basis.
You will be positioned on the moveable exam table. Straps and bolsters may be used to help you stay still and maintain your position.
Devices that contain coils capable of sending and receiving radio waves may be placed around or next to the area of the body being scanned.
MRI exams generally include multiple runs , some of which may last several minutes.
Your exam may use an endorectal coil. If so, a nurse or doctor will place a disposable cover over the coil. They will lubricate the assembly and insert the coil a short distance into your rectum. After insertion, the doctor inflates the circular balloon that sits around the coil and holds it in place during the exam. When the exam is complete, the doctor deflates the balloon and removes the coil.
If a contrast material is used, a doctor, nurse or technologist will insert an intravenous catheter into a vein in your hand or arm that will be used to inject the contrast material.
You will be placed into the magnet of the MRI unit. The technologist will perform the exam while working at a computer outside of the room.
If a contrast material is used during the exam, it will be injected into the intravenous line after an initial series of scans. More images will be taken during or following the injection.
When the exam is complete, you may be asked to wait while the radiologist checks the images in case more are needed.
Your IV line will be removed after the exam is over.
How Is A Digital Rectal Exam Performed
A DRE is a physical exam of the prostate. The health care provider will ask the patient to bend over a table or lie on his side while holding his knees close to his chest. The health care provider slides a gloved, lubricated finger into the rectum and feels the part of the prostate that lies next to it. The DRE may be slightly uncomfortable, but it is brief. This exam reveals whether the prostate has any abnormalities that require more testing. If an infection is suspected, the health care provider might massage the prostate during the DRE to obtain fluid to examine with a microscope. This exam is usually done first. Many health care providers perform a DRE as part of a routine physical exam for men age 50 or older, some even at age 40, whether or not the man has urinary problems.
Also Check: What Is The Va Disability Rating For Prostate Cancer
Who Interprets The Results And How Do I Get Them
A radiologist, a doctor trained to supervise and interpret radiology exams, will analyze the images. The radiologist will send a signed report to your primary care or referring physician, who will share the results with you.
Follow-up exams may be needed. If so, your doctor will explain why. Sometimes a follow-up exam is done because a potential abnormality needs further evaluation with additional views or a special imaging technique. A follow-up exam may also be done to see if there has been any change in an abnormality over time. Follow-up exams are sometimes the best way to see if treatment is working or if an abnormality is stable or has changed.
Who Should Be Screened
Prostate cancer is most common in older men, and rates are highest in men aged 75-79. Statistics show that ethnicity is a risk factor and black men are more likely to develop it. Youre also more at risk if a close relative has had it before they reached the age of 65.
As it develops without symptoms, its a good idea to get screened from the age of 50.
If you are at a very high risk eg if youve got more than one close relative who has developed prostate cancer before they reached 65, you should start getting screened at 40.
If you are black or you have one close relative who developed prostate cancer at a young age, you should start getting screened at 45.
Recommended Reading: External Prostate Massage Prostatitis
