Mechanism Of Action Of Parp Inhibitors
The original rationale for using PARPi as a cancer treatment is that PARPi can sensitize tumor cells to therapies that cause DNA damage, such as chemo or radiotherapy. The inhibition of PARP-mediated repair of DNA damage produced by chemotherapy or radiotherapy, may result in an increased of therapeutic potency .
Almost two decades ago, two groups described the important concept of Synthetic Lethal interaction between PARP inhibition and BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutation, which represented a new therapeutic option for BRCA-mutant tumors .
SL means that a defect in either one of two genes has little effect on the organism, but a combination of defects in both genes results in cell death.
Carriers of deleterious heterozygous germline mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes have high risk of different types of cancer, such as PCa . BRCA1 and BRCA2 are tumor-suppressor genes involved in transcriptional regulation and, as stated before, are critical to the repair of DSBs in the DNA molecule, playing a key role in the HR pathway . Cells with functional loss in these genes are unable to repair errors in DNA, depending on PARPs ability to detect these damages and activate alternative repair pathways.
PARPi antitumor activity is based on the concept of synthetic lethality, in which two separate molecular pathways, which are not lethal when disrupted individually, cause cell death when inhibited simultaneously .
PARPi Trapping Potency.
Ddr Mutations And Prostate Cancer
A number of studies have reported the frequencies of somatic and germline mutations in DDR genes at several disease stages of PCa, but whether or not patient mutation status indicates clinical benefit has yet to be seen . In 2015, Robinson et al. evaluated 150 cases of mCRPC and found that 22.7% of tumors harbored deleterious DDR germline or somatic mutations in BRCA1, BRCA2, ATM, CDK12, FANCA, RAD51B, and RAD51C . Pritchard et al. found that 11.8% of screened patients with mCRPC had at least one germline mutation in a DDR gene , and Abida et al., in 2017, found that 27% of screened patients across all stages of PCa possessed germline or somatic alterations in either BRCA1/2, ATM, and CHEK2 . The recent PROfound trial screened 4,425 patients with mCRPC for 15 genes with direct or indirect roles in HR. A total of 2,792 patients were successfully sequenced, and qualifying alterations were found in 778 of 2,792 patients . These reported frequencies in sequenced patients have been corroborated by several other studies in mCRPC , as seen in .
Frequencies of germline vs. somatic mutations in DNA damage repair genes and evidencebased clinical applications in prostate cancer
| Gene . |
|---|
Parp Inhibitors: From Bench To Bedside
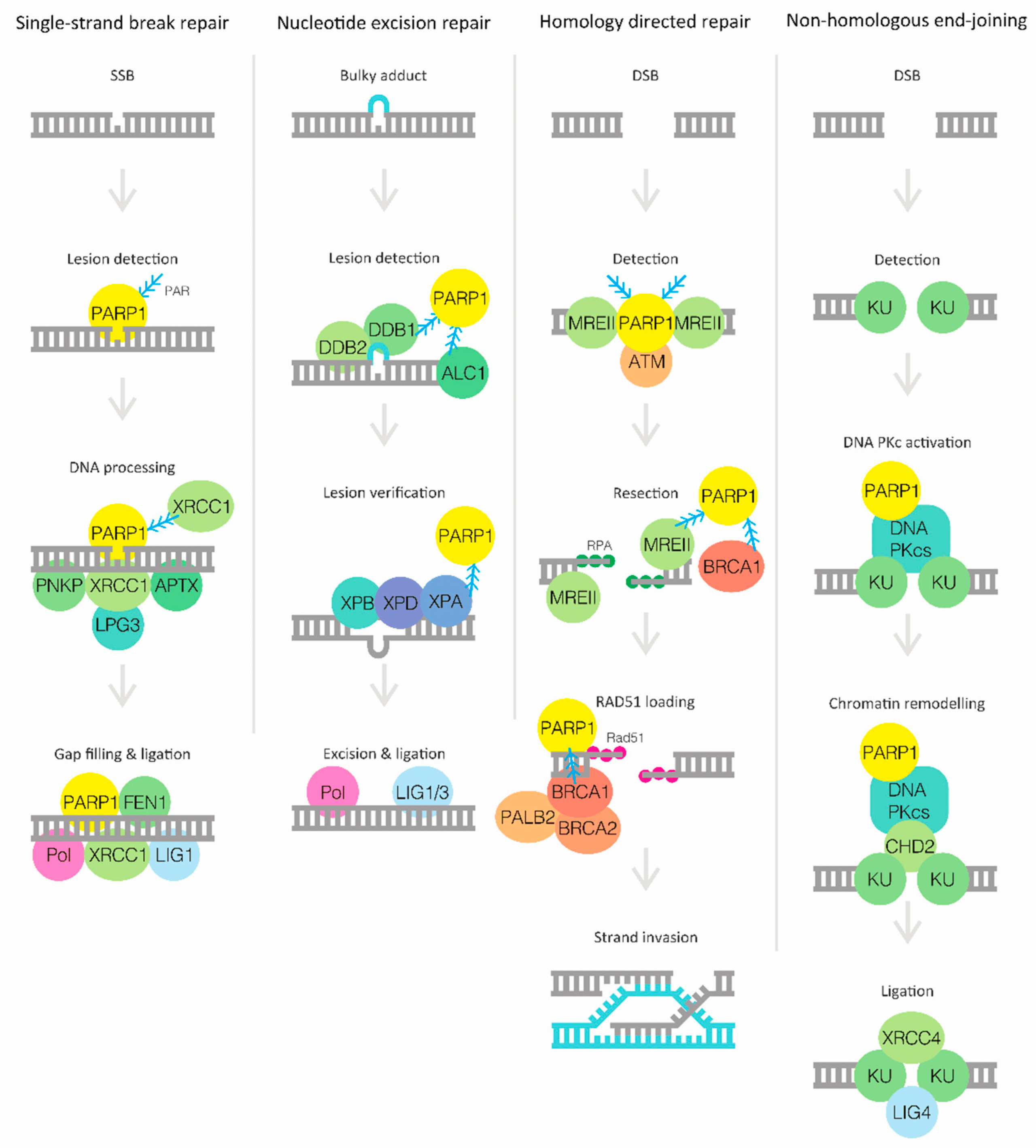
Poly polymerases , a family of enzymes sharing a catalytical domain whose main function is to add poly-ADP-ribose chains to other proteins as signaling transmitter and/or to regulate transcription. PARP1, predominantly, and PARP2, are critical to DNA single-strand break repair. They detect ssDNA breaks, bind to them and synthesize PAR using NAD+, initiating the call for DNA repair mediators and effectors, which then will require PARP1/2 to be removed from the site of damage for the ssDNA repair process to properly ensue. PARP inhibitors are drugs that compete with NAD+ to bind to the enzyme, and therefore prevent proper activation of the ssDNA break repair cascade.
Unrepaired ssDNA breaks will progress to double-strand DNA breaks. However, cells have specific pathways to repair toxic dsDNA breaks, including the error-prone non-homologous end joining and microhomology-mediated end joining pathways and the preferred, error-free, homologous recombination repair pathway.
Recommended Reading: Psa Test Vs Prostate Exam
Mechanisms Of Intrinsic And Acquired Resistance To Parp Inhibitors
Similar to other targeted therapies, resistance to PARPi has been observed in most patients with advanced tumors . There are several mechanisms for resistance proposed so far that demonstrate how tumor cells stop responding to the cytotoxic effects of PARPi, and can be grouped as follows:
Parp Inhibitors And Prostate Cancer: What Urologists Need To Know
Urology Times staffUrology Times Journal
In this interview, Emmanuel S. Antonarakis, MD, provides an overview of rucaparib and olaparib , discusses the key trials that led to their approvals, and explains the urologists role in their use.
In May 2020, the FDA approved the oral poly polymerase inhibitors rucaparib and olaparib for the treatment of metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. These 2 novel treatments represent the first approvals in this class of medications for prostate cancer. In this interview, Emmanuel S. Antonarakis, MD, provides an overview of these treatments, discusses the key trials that led to their approvals, and explains the urologists role in their use. Antonarakis is a professor of oncology and urology at the Johns Hopkins Sidney Kimmel Comprehensive Cancer Center in Baltimore, Maryland. Antonarakis has served as a paid advisor to AstraZeneca, Merck, Clovis Oncology, Janssen, and Pfizer.
Don’t Miss: How To Prevent Enlarged Prostate
Clinical Testing For Hrr Mutations In Prostate Cancer
Multiple studies have now confirmed the high prevalnece of HRR-associated gene mutations in advanced prostate cancer . This enrichment in late-stage disease has led to some controversy with regards to the use of archival, primary prostate tumor biopsies for genomic profiling once patients have developed mCRPC. As part of the screening process for the randomized PROFOUND trial of olaparib, over 4000 patients underwent next-generation sequencing targeted profiling the overall rate of HRR-associated genes mutations was 27%, with no differences observed based on the use of a primary vs metastatic sample for NGS testing . Similarly, in a study pursuing targeted NGS from 470 primary tumors of patients who all later developed mCRPC, the prevalence of these mutations was similar to what has been reported for metastatic biopsy cohorts . Moreover, a recent study comparing primary tumor biopsies and cfDNA samples acquired later at the time of mCRPC also confirmed that BRCA2, ATM and CDK12 defects are already present in the primary tumors of these patients . This is different to the study of alterations in AR or tumor suppressors such as TP53, RB1 or PTEN, which seem to evolve as a result of hormonal therapy-induced selective pressure.
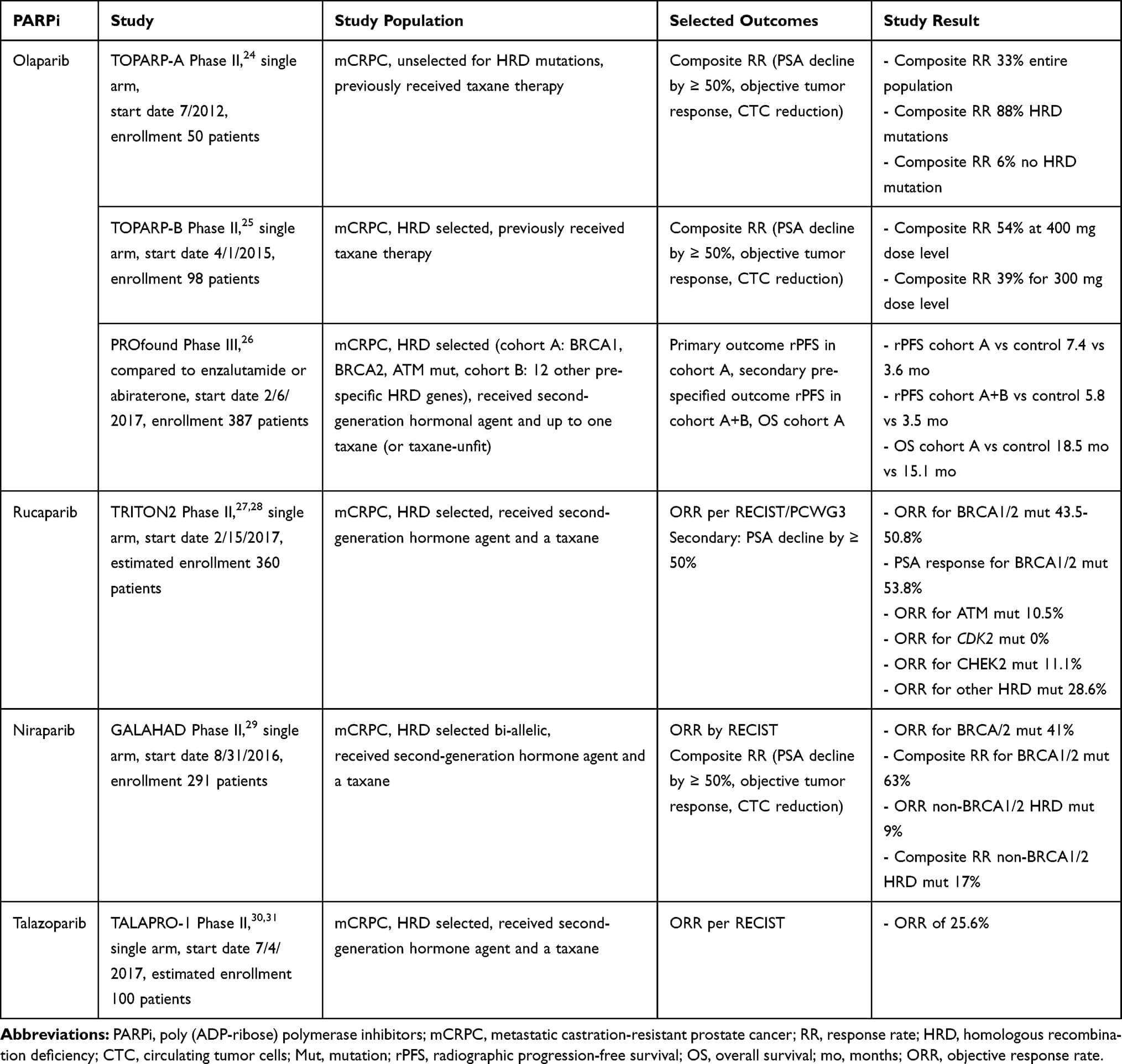
Pivotal Clinical Trials Of Parp Inhibitors In Mcrpc
Olaparib
Olaparib became FDA approved on May 19, 2020, for the treatment of mCRPC following progression on enzalutamide or abiraterone, based on the results of the prospective, open-label, randomized, phase 3 PROFOUND trial.28 At 206 sites in 20 countries, 4425 patients were screened for alterations in 15 prespecified genes, and 778 of 2792 had qualifying DDR mutations based on NGS from primary or metastatic tumor tissues. Patients with 1 or more alterations in BRCA1, BRCA2, or ATM were assigned to cohort A while those with alterations in the other 12 genes were assigned to cohort B. Patients were randomized 2:1 to receive standard-dose olaparib or the prespecified physicians choice of enzalutamide or abiraterone . The primary end point was PFS, with secondary end points of overall response rate and OS. A total of 162 and 83 patients were randomized to receive olaparib and control treatment, respectively, in cohort A, while 94 and 48 patients received olaparib and control treatment, respectively, in cohort B.
Rucaparib
A multicenter, randomized, open-label, phase 3 study is ongoing and randomizing patients with mCRPC who have BRCA1/2 or ATM gene mutations and have progressed on 1 prior NHT for mCRPC to rucaparib monotherapy or investigators choice of abiraterone, enzalutamide, or docetaxel . The primary end point will be radiographic PFS.
Talazoparib
Niraparib
Also Check: How To Massage Prostate Externally
Adverse Events And Tolerability
Despite presenting a very high safety profile, PARPi have demonstrated, in phase III clinical trials, some adverse effects, of which fatigue, gastrointestinal symptoms, and myelosuppression are the most common . The main adverse reactions of these drugs are usually mild to moderate, can be managed with dose reductions, and do not require discontinuation of treatment. Fatigue is the most frequently observed adverse effect, and it seems to be transversal to all PARPi. GI adverse effects are extremely common and tend to occur in all patients treated with PARPi. Nausea is the most prevalent adverse effect, occurring in 76% of patients treated with olaparib, 75% with rucaparib, 74% with niraparib, and 49% of patients treated with talazoparib, followed by vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, and abdominal pain.
Hematologic toxicity usually appears early after the start of treatment with PARPi and tends to resolve a few months after taking the drugs. Anemia is the main hematological adverse event, occurring in 44% of patients treated with olaparib, 50% with niraparib, 37% with rucaparib, and in 53% of patients treated with talazoparib. Of all the PARPi, niraparib is correlated with the highest hematological toxicity .
According to prostate cancer studies, in the PROFOUND trial, the most common adverse events were hematological , gastrointestinal , and fatigue or asthenia . The GALAHAD and TRITON2 studies also found that anemia is the most frequent adverse event, 17.925% .
First Parp Inhibitor To Demonstrate Clinical Benefit In Combination With A New Hormonal Agent In This Setting
AstraZeneca and MSDs Lynparza in combination with abiraterone and prednisone or prednisolone has been recommended for marketing authorisation in the European Union for the treatment of adult patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer for whom chemotherapy is not clinically indicated.
The Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use of the European Medicines Agency based its positive opinion on results from the PROpel Phase III trial which were published in NEJM Evidencein June 2022.
In the trial, Lynparza in combination with abiraterone and prednisone or prednisolone, reduced the risk of disease progression or death by 34% versus abiraterone alone . Median radiographic progression-free survival was 24.8 months for Lynparza plus abiraterone versus 16.6 months for abiraterone alone. Results also showed that Lynparza in combination with abiraterone extended median rPFS by almost one year, with a median rPFS of 27.6 months versus 16.4 with abiraterone alone, as assessed by blinded independent central review .
Updated results also showed a favourable trend in improved overall survival with Lynparza plus abiraterone versus abiraterone alone, however the difference did not reach statistical significance at the time of this data cut-off .
Notes
Despite the advances in mCRPC treatment in the past decade with taxane and new hormonal agent treatment, there is high unmet need in this population.5,7,8,12
References
Adrian Kemp
Read Also: Does Frequent Sex Help Prevent Prostate Cancer
Dna Repair Pathways Defects Are Early Drivers
To assess better the type, nature, and frequency of DNA repair pathway mutations, a study evaluated 504 tumor specimens from 451 patients through targeted sequencing. The frequency of mutations in the PI3K, RAF kinase family, and the WNT pathway was similar to prior reports. In addition, new insights regarding HRR machinery in carcinoma prostate were evident. First, around 22% of all cases had a somatic mutation in the gene involved in HRR, with mutations in the BRCA-2 gene being the most common . Second, among patients undergoing germline testing, 19% had a germline pathogenic mutation in an HRR gene. Third, nearly 27% of patients had some HRR gene alteration when cotested with germline and somatic assays. Fourth, germline analysis alone accounted for only half of these patients. Fifth, although many gene mutations showed enrichment with progressive stages , phosphatase and tensin homolog , and ataxia telangiectasia mutated ), the prevalence of mutations in TP53 and BRCA2 was relatively uniform. Taken together, these findings imply that nearly 1/3rd of patients have targetable HRR mutations which are better detected by cotesting on somatic as well as germline assays. Furthermore, BRCA2 mutations seem to be early oncogenic drivers of disease.
Palb2 And Bard1 Alterations And Mutational Signatures In Advanced Prostate Cancer
We first assessed the frequency of PALB2 and BARD1 alterations in advanced prostate cancer. We restricted our analysis to alterations that were likely to lead to loss of function, and therefore considered only nonsense and frameshift mutations as well as deep deletions. The SU2C cohort is comprised of metastatic prostate cancer cases and 3 of 429 cases had a presumed deleterious PALB2 alteration while 5 of 429 cases had a predicted deleterious BARD1 alteration . PALB2 alterations were observed in 14 and 8 of screened and randomized PROfound patients, respectively, whereas BARD1 mutations were present in 11 and 3 screened and randomized patients, respectively . In the TRITON2 trial, 2 of 193 enrolled patients had a PALB2 mutation and no patients had a BARD1 mutation.
Recommended Reading: Is It Painful To Have Prostate Biopsy
Parp Combinations May Further Improve Outcomes
Adding the PARP inhibitor Zejula to the anti-androgen drug Zytiga may be a new first-line treatment for patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer with homologous recombination deficiency. The phase 3 MAGNITUDE clinical trial compared the Zejula-Zytiga combination to Zytiga alone in 423 men with mCRPC and biomarkers of HRR. The combination significantly reduced the risk of radiographic progression or death by 27% and the median time to cancer progression was 16.5 months for Zejula treated patients compared to 13.7 months for Zytiga alone. The combination was most effective in patients with BRCA1/2 alterations. Among these high-risk patients, the treatment combination reduced the risk of progression or death by 47% .14
Results are similar the PROpel clinical trial that combined the PARP inhibitor Lynparza with Zytiga as 1st-line treatment for men with mCRPC with or without HRR gene mutations.12 In the PROpel study, researchers randomly assigned 796 to treatment with Xytiga with our without Lynparza. The interim analysis showed that the combination therapy significantly delayed cancer progression regardless of patients HRR mutational status, to a median of 24.8 months with the addition of Lynparza compared to 16.6 months for Zytiga alone. It is not yet clear if survival is improved.13
References:
Recap: Recommendations For Parp Inhibitor Use In Prostate Cancer
ONCOLOGY® Companion
A. Oliver Sartor, MD, discussen treatment options for PARP inhibitor use in patients with prostate cancer.
In a recent OncView discussion, A. Oliver Sartor, MD, a professor of medicine and the C.E. and Bernadine Laborde Professor of Cancer Research at Tulane University School of Medicine as well as the medical director of Tulane Cancer Center, in New Orleans, Louisiana, shared clinical experiences and perspectives regarding the use of PARP inhibitors to treat certain patients with prostate cancer.
To begin the discussion, Sartor talked about baseline testing strategies that he employs to match patients with the best systemic therapy. In terms of molecular testing for metastatic disease, I always to do germline testing. I may want to get additional genetics as well, somatic genetics within the tumor, he said. I also cover family history when I the analysis of a patient.
Testing for both somatic and germline aberrations are important for the treatment of these patients, especially now that targeted therapies are becoming available in this space. Findings like a BRCA mutation, BRCA2, which can often be picked up on primary prostate tissue, important to be able to identify because of treatment implications.
Also Check: What Is The Best Way To Detect Prostate Cancer
Ama Disclaimer Of Warranties And Liabilities
CPT is provided “as is” without warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, including but not limited to, the implied warranties of merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose. No fee schedules, basic unit, relative values or related listings are included in CPT. The AMA does not directly or indirectly practice medicine or dispense medical services. The responsibility for the content of this file/product is with CMS and no endorsement by the AMA is intended or implied. The AMA disclaims responsibility for any consequences or liability attributable to or related to any use, non-use, or interpretation of information contained or not contained in this file/product. This Agreement will terminate upon notice if you violate its terms. The AMA is a third party beneficiary to this Agreement.
Similar Articles Being Viewed By Others
Carousel with three slides shown at a time. Use the Previous and Next buttons to navigate three slides at a time, or the slide dot buttons at the end to jump three slides at a time.
13 July 2020
Sait Ozturk, Deepti Mathur, Ramon Parsons
27 July 2021
Hanqi Lei, Zifeng Wang, Jun Pang
volume 6, Article number: 49
Recommended Reading: Will Radiotherapy Cure Prostate Cancer
Loss Of Rad51 Foci As A Functional Biomarker Of Hrr In Mcrpc
Finally, we studied H2AX/geminin and RAD51/GMN foci by IF in the 52 cases for whom tumor tissue from the same biopsy used for NGS was available . In all 52 cases, H2AX foci were detected in > 40% of GMN-positive cells inter-reader variability was low . Overall, 22 of 52 cases were scored as RAD51 low, using a predefined cutoff of 10% of cells having 5 nuclear RAD51 foci . All 16 tested prostate cancers with deleterious BRCA1/2 alterations had low RAD51 scores this also included all the tumors arising with and without germline mutations and regardless of having detected a biallelic loss . Of the 4 tumors with PALB2 mutations evaluated for RAD51 foci, the 2 with low RAD51 scores were responders in the trial both had biallelic loss neither of the two patients with high RAD51 scores responded to olaparib with neither of these having biallelic loss . Moreover, low RAD51 foci scores associated with response to olaparib: 15 of 22 patients with prostate cancers with low RAD51 foci scores were responders by the trial composite response primary endpoint, compared with 7 of 30 patients with tumors with high RAD51 scores. Patients with low RAD51 foci scores also had longer rPFS and OS from initiation of olaparib therapy when compared with those with high RAD51 foci scores . These data support, for the first time, the validity of the RAD51 assay in mCRPC.
