The Role Of A Multidisciplinary Care Team In Treatment
Keep in mind that the optimal treatment strategy for mCRPC is different for each person and that its a complicated disease to treat. Thats why its important to assemble a team of doctors and specialists to keep your treatment and you on track.
Your team should include an experienced urologist, advises Cookson, as well oncologists who are comfortable with the newer treatments and know how to use them.
A study published in July 2015 in the Journal of Urology agrees, finding that with so many new treatments coming on board, doctors have to juggle a lot of factors when figuring out your best next steps from what kind of symptoms you have to your personal preferences, as well as any other health conditions that may have to be taken into account when coming up with a treatment strategy.
Its also important for your care team to review the medicines youve already taken for prostate cancer, and plan the sequence of the medicines youll take next. Getting the order right is important because certain drugs can make subsequent treatments more, or less, effective.
Your care team should also watch you closely to determine whether you have any resistance to any medicines, so that they can make changes quickly if necessary.
Ideally, your care team should possess expertise in distinct domains of cancer care, such as imaging, chemotherapy, radiation, and surgery, according to a study published in the Annals of Oncology in August 2015.
Overexpression Of Mutated Androgen Receptor
Expression of AR is often increased in hormone-refractory prostate cancer cases . However, mice that overexpress the wild-type AR in the prostate develop focal PIN lesions with age, suggesting that increased levels of AR may be permissive, but insufficient to drive tumorigenesis . A mouse prostate cancer model using probasin promoter-driven expression of the AR mutation E231G has been described . This missense mutation, located in the N-terminal domain of the AR, results in increased responsiveness to coactivators in TRAMP cell lines . Prostate tissues of transgenic mice that overexpress wild-type AR or a ligand-binding domain AR mutation appear normal, while AR-E231G mice rapidly develop PIN and invasive adenocarcinoma in the ventral lobe of the prostate. Inflammation accompanied invasive lesions, and metastases were detected in the lungs of AR-E231G transgenic mice after 1 year . This model is the first to provide in vivo evidence of AR as an oncogenic factor. Because increased AR signaling is thought to contribute to tumor progression , further biochemical analyses of this model may provide critical insight into the effects of increased AR-coactivator interactions in prostate tumor progression.
Susan F. Slovin MD, PhD, in, 2016
Metastatic Hormone Sensitive Prostate Cancer
This form of prostate cancer can be an initial diagnosis but more often refers to cases where surgeries or other initial treatments to remove tumors from the prostate havent succeeded in stopping its progression.
Notably, too, these cases are defined by metastasis, meaning it has started to spread to other structures in the body, such as bones or the lymph nodes. However, the development of castration resistance is part of the eventual and expected progression of the diseaseeven while on ADT.
Recommended Reading: Can Cycling Irritate The Prostate
Mechanisms Of Resistance In Castration
Thenappan Chandrasekar, Joy C. Yang, Allen C. Gao, Christopher P. Evans
Department of Urology, University of California, Davis, CA, USA
Correspondence to:
Keywords: Castration-resistant; disease progression; drug resistance; prostatic neoplasms
Submitted Dec 21, 2014. Accepted for publication Feb 28, 2015.
doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2223-4683.2015.05.02
Quality Of Life With Mcrpc

According to a review published in the British Medical Journal in October 2016, you may not experience pain or other symptoms at this stage of cancer, or you may experience many. Its different for everyone. So along with treating the cancer itself, be sure to talk to your doctors about any symptoms and side effects youre experiencing in order so that the right ways to alleviate them can be found. You should also ask your care team about options for palliative care.
Because it can be very stressful to have advanced prostate cancer, and tough to talk about what it all means for your future, the ASCO urges men to have an open and honest conversation with their care team. Discuss what youre worried about, and whats important to you. There are many ways to look for and get emotional support.
Additional reporting by Andrea Peirce
Recommended Reading: Does Cialis Shrink An Enlarged Prostate
What Types Of Hormone Therapy Are Used For Prostate Cancer
Hormone therapy for prostate cancer;can block the production or;use of androgens . Currently available treatments can do so in several ways:
- reducing;androgen production by the testicles
- blocking the action of androgens throughout;the body
- block androgen production throughout the body
Treatments that reduce androgen production by the testicles are the most commonly used hormone therapies for prostate cancer;and the first type of hormone therapy that most men with prostate cancer receive. This form of hormone therapy includes:
Treatments that block the action of androgens in the body are typically used when ADT stops working. Such treatments include:
Treatments that block the production of androgens throughout the body include:
Enzalutamide And Androgen Receptor Inhibitors
In response to the many AR mediated mechanisms of resistance found leading to development of CRPC, there has been development of a new generation of androgen-receptor signaling inhibitors. The main agent in this class is enzalutamide , which has been demonstrated to have a multi-pronged approachâpreventing testosterone binding to AR, AR nuclear translocation, AR binding to DNA, and co-activator recruitment . While the AFFIRM III trial demonstrated a 4.8-month survival benefit over placebo in CRPC patients who had failed docetaxel and the PREVAIL trial demonstrated an overall survival and radiographic progression-free survival over placebo in chemotherapy-naïve CRPC patients , not all the patients benefited from treatmentâa subset of patients continued to progress, indicating that there are significant resistance mechanisms that need to be identified and addressed.
AR point mutations are also important mechanisms of resistance to enzalutamide, just as in the development of CRPC. The Phe876Leu mutation in the LBD of AR has been reported to make enzalutamide into an agonist of AR, though the clinical relevance of this change has not been documented . Similar effects were noted for the first generation anti-androgens bicalutamide and flutamide.
Don’t Miss: Can A Ct Scan Detect Prostate Cancer
Index Patient : Asymptomatic Or Minimally Symptomatic Mcrpc Without Prior Docetaxel Chemotherapy
This patient represents a common clinical presentation seen in the CRPC setting today. These patients are characterized as having a rising PSA in the setting of castrate levels of testosterone, documented metastatic disease on radiographic imaging and no prior treatment with docetaxel chemotherapy for CRPC. The key distinction between this patient and Index Patients 3 and 4 is symptom status. Specifically, this patient is defined as having no symptoms or mild symptoms attributable to his prostate cancer. However, one must then consider whether the patient requires regular opioid pain medications for symptoms thought to be attributable to documented metastases to achieve this level of pain control. In general, if patients require regular narcotic medications for pain relief, they are not included in this category. Acknowledging these important definitions, the panel makes the following guidelines statements:
Guideline Statement 5
Clinicians should offer abiraterone plus prednisone, enzalutamide, docetaxel, or sipuleucel-T to patients with asymptomatic or minimally symptomatic mCRPC with good performance status and no prior docetaxel chemotherapy.
Discussion
Guideline Statement 6
Clinicians may offer first- generation anti-androgen therapy, ketoconazole plus steroid or observation to patients with asymptomatic or minimally symptomatic mCRPC with good performance status and no prior docetaxel chemotherapy who do not want or cannot have one of the standard therapies.
Discussion
What Is Metastatic Castration
This is a form of advanced prostate cancer in the prostate gland. This form of cancer doesnt respond to hormone treatment;that lowers testosterone.
At this stage, it;can spread to other parts of the body, so its best to find prostate cancer early, and learn more about provenge treatment. Its important to keep in mind that at this point there are treatment options as well.
Don’t Miss: When To Get A Prostate Biopsy
New Generation Hormonal Therapies
These therapeutic options arise after understanding that serum testosterone does not necessarily extrapolate to the prostate. We can have low levels of testosterone in the blood and higher levels of intraprostatic androgen levels. Thus, castration resistant prostate cancer is not always caused by androgen independence. It is sometimes caused by a different response from the prostate tissue to the available androgens. These new hormonal therapy agents interfere with new androgen receptor pathways that form in castration resistant prostate cancer. Others inhibit enzymes that block androgen synthesis. Abiraterone is perhaps one of the most important members of this group. It inhibits an enzyme called CYP17A1. By doing so, it blocks testosterone synthesis.
Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors In Mcrpc
This class of drugs fall into the category of immunotherapydrugs that boost the immune system to fight cancer. ICIs have significantly improved outcomes in a number of types of metastatic cancer, but were previously thought not to have much promise in mCRPC. This is still true, by and large, but a small proportion of mCRPCs may have a feature that is associated with a high probability of response to immunotherapy drugs. This feature is known as mismatch repair deficiency or microsatellite instability, and is quite rare in prostate cancer . Patients whose tumors have this feature should be offered an ICI called pembrolizumab .
Another potential marker of sensitivity to ICIs is loss of the gene CDK12, a mutation seen in about 7% of mCRPC patients. A small study demonstrated that 33% of these patients experience reduction in PSA levels in response to ICIs.
There are now multiple clinical trials exploring ICIs in combination with other drugsincluding targeted therapy, hormonal drugs, or drugs that block the blood supply to tumors, as well as PARP inhibitors.
Read Also: Will Blood Test Show Prostate Cancer
Treatment By Stage Of Prostate Cancer
Different treatments may be recommended for each stage of prostate cancer. Your doctor will recommend a specific treatment plan for you based on the cancers stage and other factors. Detailed descriptions of each type of treatment are provided earlier on this same page. Clinical trials may also be a treatment option for each stage.
Early-stage prostate cancer
Early-stage prostate cancer usually grows very slowly and may take years to cause any symptoms or other health problems, if it ever does at all. As a result, active surveillance or watchful waiting may be recommended. Radiation therapy or surgery may also be suggested, as well as treatment in clinical trials. For those with a higher Gleason score, the cancer may be faster growing, so radical prostatectomy and radiation therapy are often recommended. Your doctor will consider your age and general health before recommending a treatment plan.
ASCO, the American Urological Association, American Society of Radiation Oncology, and the Society of Urologic Oncology recommend that patients with high-risk early-stage prostate cancer that has not spread to other areas of the body should receive radical prostatectomy or radiation therapy with hormonal therapy as standard treatment options.
Locally advanced prostate cancer
Watchful waiting may be considered for older adults who are not expected to live for a long time and whose cancer is not causing symptoms or for those who have another, more serious illness.
Androgen Receptor Splice Variants
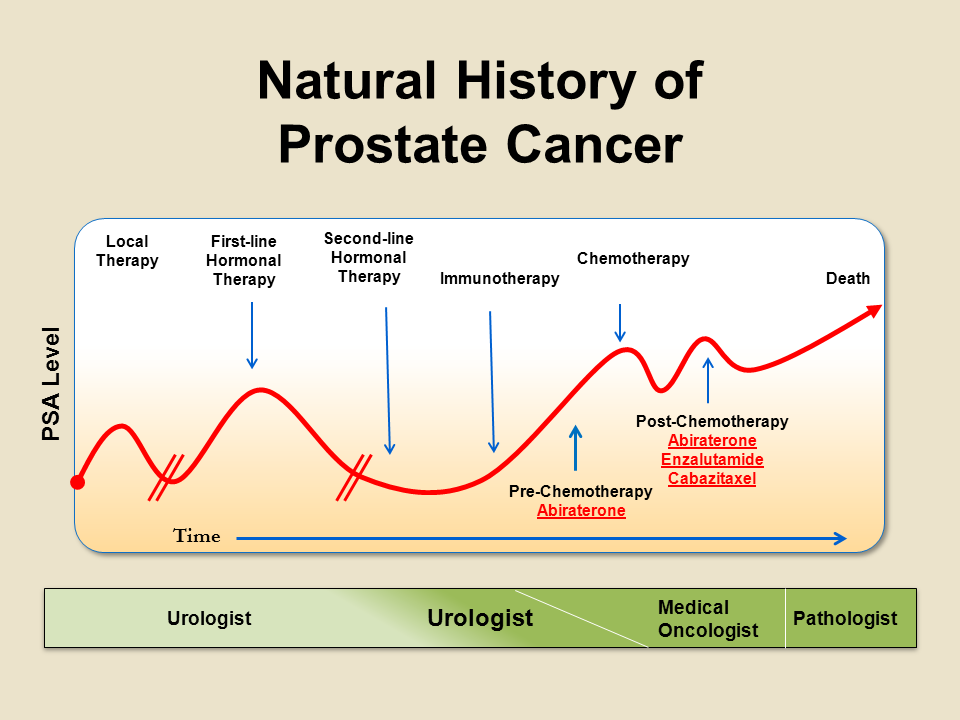
ARVs are truncated versions of the wild type AR that are constitutively active. The truncated portion is typically the C-terminal ligand-binding domain , though at least one variant, ARV8, was reported to have loss of the DNA binding domain . The loss of the LBD makes these variants ligand-independent. The true functional implication of ARVs is not yet completely understood, as direct measurement of the variants has been limited by lack of variant-specific antibodies, requiring proxy assessment using transcribed RNA levels. However, transcribed RNA levels may not be reflective of protein levels, suggesting some degree of post-translational modification .
The role of ARVs in clinical CRPC is being established however. While some CRPC cell lines demonstrate low levels of ARVs, CWR22Rv1 in particular demonstrates almost equal levels of ARV and full-length AR . Hornberg et al. demonstrated that there were higher levels of ARV expression in CRPC bone metastases compared to hormone-sensitive prostate cancer bone metastases, and that ARV expression was associated with poorer prognosis.
Recommended Reading: How Is Prostate Surgery Performed
Hormones And Prostate Cancer
Most prostate cancer today is diagnosed at an early stage when the cancer is still confined to the prostate gland. Men typically have surgery to remove the cancerous prostate gland or radiation treatment to destroy the cancerous cells in the gland.
If early-stage cancer comes back after surgery or radiation, or has begun to spread to more distant parts of the body , treatment with hormone-blocking drugs can slow the advance of the cancer and reduce the size of tumors. This helps to prevent symptoms like urinary obstruction, which happens when tumors interrupt the normal flow of urine from the bladder. Hormone therapy can also enhance the effectiveness of radiation therapy and shrink a tumor before surgery.
Male sex hormones fuel prostate cancer. The main hormone that drives prostate cancer is testosterone, which is produced in the testicles.
ADT drastically lowers levels of testosterone and other androgens in the body, and stalls the advance of the cancer in many men but only temporarily. For reasons that remain poorly understood, prostate cancer cells can adapt to lower levels of natural androgens and start to multiply again. The cancer is then said to be castrate resistant.
How Does Cancer Become Resistant To Hormone Therapy
Cancer progression is much more than growing the tumor and metastasis. It involves thousands of processes inside the cell. It all starts with a few mutations to the DNA of a previously normal cell. This cell loses its restraint and starts to divide without limit. Thats only the early start of cancer.;
New cancer cells born programmed to divide rapidly. This rapid division is also disorganized and fosters new DNA mutations. As the DNA continues to mutate, the cell loses its normal functions and looks different from healthy cells. More and more functions are lost or replaced by others, and cancer becomes more aggressive.
Androgen activation and response to testosterone could be one of the functions affected by new DNA mutations. Thus, the resulting cancer cell does not depend on androgens to keep growing. Reducing levels of testosterone, in this case, would not trigger a significant change in growth speed. In other cases, lower testosterone levels are met by an increase of androgen receptors in cancer cells.
Either way, androgen deprivation stops working after a while, and in some cases, it may not work from day one. This is what we call castrate-resistant cancer .
The exact genes and metabolism changes that turn cells into castrate-resistant cancer are still elusive. However, recent studies have shown specific changes in metabolism and genetics.
Also Check: Is Turmeric Good For Prostate
Ar Amplification And Mutations/hypersensitivity Pathway/promiscuous Pathway
Low levels of androgen persist despite androgen blockade with ADT. Within this microenvironment, a subset of cells develop sensitivity to these low levels of androgens either through amplification of the AR or development of AR mutations that lead to activation by molecules other than androgens .
Amplification of the AR has been identified in a significant portion of CRPC cell lines, ranging from 30-80% . This finding is uncommon in hormone naïve prostate cancer and may be due to selective outgrowth of CRPC cells . This amplification enables CRPC to be hypersensitive to low level of androgens, which promotes progression of disease . As 20% of CRPC metastases have evidence of AR amplification, which is absent in hormone-naive metastatic disease, it may also contribute to metastases. In addition, recent studies have shown that exogenous overexpression of AR can lead to CRPC.
Related to this concept, a substitution of valine with leucine at codon 89 results in increased 5α-reductase levels in a subset of CRPC. This results in higher levels of DHT despite low circulating levels of testosterone. This mutation is more commonly observed in the African-American population, and has been associated with more aggressive, early onset prostate cancer .
When Is Hormone Therapy Used
Hormone therapy may be used:
- If the cancer has spread too far to be cured by surgery or radiation, or if you cant have these treatments for some other reason
- If the cancer remains or comes back after treatment with surgery or radiation therapy
- Along with radiation therapy as the initial treatment, if you are at higher risk of the cancer coming back after treatment
- Before radiation to try to shrink the cancer to make treatment more effective
Don’t Miss: How Does The Prostate Produce Seminal Fluid
Index Patient : Symptomatic Mcrpc With Good Performance Status And No Prior Docetaxel Chemotherapy
These patients have a rising PSA in the setting of castrate levels of testosterone, documented symptomatic metastatic disease on radiographic imaging and no prior history of docetaxel chemotherapy for prostate cancer. The definition of symptomatic disease warrants additional explanation to contrast with Index Patient 2. First, the patient must have symptoms that are clearly attributable to the metastatic disease burden, not any other medical condition. Second, if having pain, the patient should require regular opiate pain medications for symptoms attributable to documented metastases in order to achieve an acceptable level of pain control. If patients require regular narcotic medications for pain relief, then they are symptomatic from their prostate cancer and should be included in this category.
Guideline Statement 7
Clinicians should offer abiraterone plus prednisone, enzalutamide or docetaxel to patients with symptomatic, mCRPC with good performance status and no prior docetaxel chemotherapy.
Discussion
Guideline Statement 8
Clinicians may offer ketoconazole plus steroid, mitoxantrone or radionuclide therapy to patients with symptomatic, mCRPC with good performance status and no prior docetaxel chemotherapy who do not want or cannot have one of the standard therapies.
Discussion
Guideline Statement 9
Discussion
Guideline Statement 10
Discussion
