What Questions Should I Ask My Healthcare Provider
If you have prostate cancer, you may want to ask your healthcare provider:
- Why did I get prostate cancer?
- What is my Gleason score? What is my Grade Group? What do these numbers mean for me?
- Has the cancer spread outside of the prostate gland?
- What is the best treatment for the stage of prostate cancer I have?
- If I choose active surveillance, what can I expect? What signs of cancer should I look out for?
- What are the treatment risks and side effects?
- Is my family at risk for developing prostate cancer? If so, should we get genetic tests?
- Am I at risk for other types of cancer?
- What type of follow-up care do I need after treatment?
- Should I look out for signs of complications?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Prostate cancer is a common cancer that affects males. Most prostate cancers grow slowly and remain in the prostate gland. For a small number, the disease can be aggressive and spread quickly to other parts of the body. Men with slow-growing prostate cancers may choose active surveillance. With this approach, you can postpone, and sometimes completely forego, treatments. Your healthcare provider can discuss the best treatment option for you based on your Gleason score and Group Grade.
What Stages Have To Do With Cancer Spread
Cancers are staged according to tumor size and how far it has spread at the time of diagnosis. Stages help doctors decide which treatments are most likely to work and give a general outlook.
There are different types of staging systems and some are specific to certain types of cancer. The following are the basic stages of cancer:
- In situ. Precancerous cells have been found, but they havent spread to surrounding tissue.
- Localized. Cancerous cells havent spread beyond where they started.
- Regional. Cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes, tissues, or organs.
- Distant. Cancer has reached distant organs or tissues.
- Unknown. Theres not enough information to determine the stage.
- Stage 0 or CIS. Abnormal cells have been found but have not spread into surrounding tissue. This is also called precancer.
- Stages 1, 2, and 3. The diagnosis of cancer is confirmed. The numbers represent how large the primary tumor has grown and how far the cancer has spread.
- Stage 4. Cancer has metastasized to distant parts of the body.
Your pathology report may use the TNM staging system, which provides more detailed information as follows:
T: Size of primary tumor
- TX: primary tumor cant be measured
- T0: primary tumor cant be located
- T1, T2, T3, T4: describes the size of the primary tumor and how far it may have grown into surrounding tissue
N: Number of regional lymph nodes affected by cancer
M: Whether cancer has metastasized or not
How Is Prostate Cancer Staged
Prostate cancer is one of the most common types of cancer that develops in men and is the second leading cause of cancer deaths in American men, behind lung cancer and just ahead of colorectal cancer. The prognosis for prostate cancer, as with any cancer, depends on how advanced the cancer has become, according to established stage designations.
The prostate gland is a walnut-sized gland present only in men, found in the pelvis below the bladder. The prostate gland wraps around the urethra and lies in front of the rectum. The prostate gland secretes part of the liquid portion of the semen, or seminal fluid, which carries sperm made by the testes. The fluid is essential to reproduction.
The term to stage a cancer means to describe the evident extent of the cancer in the body at the time that the cancer is first diagnosed.
- Clinical staging of prostate cancer is based on the pathology results, physical examination, PSA, and if appropriate, radiologic studies.
- The stage of a cancer helps doctors understand the extent of the cancer and plan cancer treatment.
- Knowing the overall results of the different treatments of similarly staged prostate cancers can help the doctor and patient make important decisions about choices of treatment to recommend or to accept.
Read Also: How Long Can You Take Lupron For Prostate Cancer
Blood Tests Before And During Chemotherapy Treatment
Blood tests are needed to assess the health of the patient as well as ensuring that he/she will be able to cope with possible side-effects. For example, blood tests can detect liver problems, which could mean that chemotherapy is unsuitable for the patient unless the liver recovers. Chemotherapy chemicals are metabolized in the liver which could be harmed if it is not working properly.
Before chemotherapy it is important to test the patients blood count because the treatment will reduce the number of red and white blood cells, as well as platelets. If a blood test reveals a low blood count the doctors may decide to delay treatment.
Researchers at the Paul Papin Cancer Center in Angers, France, reported that measuring drug levels in patients blood and adjusting them for optimal dosing can substantially reduce severe toxicity and improve efficacy in colorectal cancer.
Regular blood tests will continue during the treatment period so that the medical team can keep an eye on blood count and the state of the patients liver. As you may read under side-effects further down this page, there is a risk that chemotherapy may lower white, red, and platelet blood level counts.
Monitoring the patients blood can also provide doctors with important data on how well the chemotherapy is working.
How Long Is A Course Of Chemotherapy
In the majority of cases for best results the patient will need regular chemotherapy over a specific period. A protocol plan is drawn up which specifies when treatment sessions will occur and for how long.
A course of chemotherapy may be just a one-day treatment, or can last for a few weeks it will depend on the type and stage of the cancer . If the patient requires more than one course of treatment there will be a rest period for his/her body to recover. This could be a one-day treatment followed by a weeks rest period, followed by another one-day treatment followed by a three-week rest period, etc. This may be repeated many times.
Read Also: What Is Perineural Invasion In Prostate Cancer
Pearls And Other Issues
PSA Testing: The Pros and the Cons
Prostate Specific Antigen is a protein produced by the prostate and is abundant in semen. Its natural function is to divide seminogelin in the semen, which helps in liquefaction. The expression of PSA is androgen-regulated.
It was originally used as a prostatic tissue stain to help determine the etiology of tumors of unknown origin. Later, serum levels of PSA were used as a prostate cancer screening tool because serum PSA levels start to increase significantly about seven to nine years before the clinical diagnosis of malignancy. While a good indicator of prostatic disorders, PSA elevation is not specific for cancer as it is also elevated in benign prostatic hyperplasia, infection, infarction, inflammation and after prostatic manipulation. It also cannot reliably distinguish between low risk/low grade disease and high risk/high grade cancers.
About 80% of the patients currently diagnosed with prostate cancer are initially investigated due to an elevated serum PSA.
While it unquestionably increases prostate cancer detection rates, the value of PSA testing is less clear in avoiding overtreatment, improving quality of life and lengthening overall survival which is why routine PSA screening for prostate cancer remains quite controversial.
PSA testing became widely available in the United States in 1992, and since then, prostate cancer detection rates have increased substantially.
The Current USPSTF Recommendation
Against PSA Screenings
How To Tell If Your Cancer Has Metastasized
Prostate cancer metastasis may be suspected if you have specific symptoms such as new lower back pain or elevated liver enzymes. These may be signs your cancer has spread to your spine or your liver, respectively. If your prostate-specific antigen levels continue to rise despite treatment, especially if they are rising particularly fast, this may be a sign that cancer is metastasizing somewhere in your body.
You May Like: Does An Enlarged Prostate Affect A Man Sexually
What Is Localized Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is the abnormal growth of cells in the prostate gland. Localized prostate cancer has not spread outside the gland. Early prostate cancer usually doesnt cause symptoms.
Prostate cancer is the most common cancer in men. Most men who get it are older than 65. If your father, brother, or son has had prostate cancer, your risk is higher than average.
Men of African descent have the highest rates of both prostate cancer and deaths from it.
About 21,000 men are diagnosed with prostate cancer in Canada every year.footnote 1 In the United States, about 12 out of 100 men in the U.S. will be diagnosed with prostate cancer sometime in their lifetime.footnote 2 But most men who are diagnosed with prostate cancer dont die from prostate cancer.
Unlike many other cancers, prostate cancer is usually slow-growing. When prostate cancer is found earlybefore it has spread outside the glandit may be cured with radiation or surgery.
Prostate cancer that has grown beyond the prostate is called advanced prostate cancer. Treatment choices are different for that stage of cancer.
Recommended Reading: Can Prostatitis Go Away On Its Own
Metastatic Spinal Cord Compression
Metastatic spinal cord compression happens when cancer cells grow in or near to the spine and press on the spinal cord. MSCC isnt common, but you need to be aware of the risk if your prostate cancer has spread to your bones or has a high risk of spreading to your bones. The risk of MSCC is highest if the cancer has already spread to the spine. Speak to your doctor or nurse for more information about your risk.
MSCC can cause any of the following symptoms.
- Pain or soreness in your lower, middle or upper back or neck. The pain may be severe or get worse over time. It might get worse when you cough, sneeze, lift or strain, or go to the toilet. It might get worse when you are lying down. It may wake you at night or stop you from sleeping.
- A narrow band of pain around your abdomen or chest that can move towards your lower back, buttocks or legs.
- Pain that moves down your arms or legs.
- Weakness in your arms or legs, or difficulty standing or walking. You might feel unsteady on your feet or feel as if your legs are giving way. Some people say they feel clumsy.
- Numbness or tingling in your legs, arms, fingers, toes, buttocks, stomach area or chest, that doesnt go away.
- Problems controlling your bladder or bowel. You might not be able to empty your bladder or bowel, or you might have no control over emptying them.
Dont wait
It is very important to seek medical advice immediately if you think you might have MSCC.
Read more about metastatic spinal cord compression .
Recommended Reading: Cranberry Juice And Prostate
Symptoms Of Metastatic Cancer
Metastatic cancer may or may not cause symptoms, and the potential symptoms may vary depending on the type of cancer and where its spread.
In general, however, there are certain symptoms that tend to come with metastatic cancer, including:
- Fatigue
- Pain
- Difficulty breathing
There may also be symptoms specific to the site where the cancer has spread. For example:
- Cancer that has spread to a bone may cause pain and an increased risk of fractures.
- Cancer that has spread to the brain may cause headaches, seizures or dizziness.
- Cancer that has spread to a lung may cause difficulty breathing or shortness of breath.
- Cancer that has spread to the liver may cause jaundice and abdominal swelling.
Receiving Treatment For Prostate Cancer That Has Spread
At Moffitt Cancer Center, the experts within our Urologic Oncology Program treat patients with all stages of prostate cancer, including advanced-stage cancers that have metastasized to other areas of the body. Our multispecialty team collaborates as a tumor board, ensuring each patient receives a treatment plan tailored to his unique needs. For individuals with metastatic prostate cancer, treatment plans aim to alleviate symptoms, slow the rate of cancer growth and shrink tumors to help improve quality of life.
Read Also: What Is Perineural Invasion In Prostate Cancer
Distant Metastatic Prostate Cancer
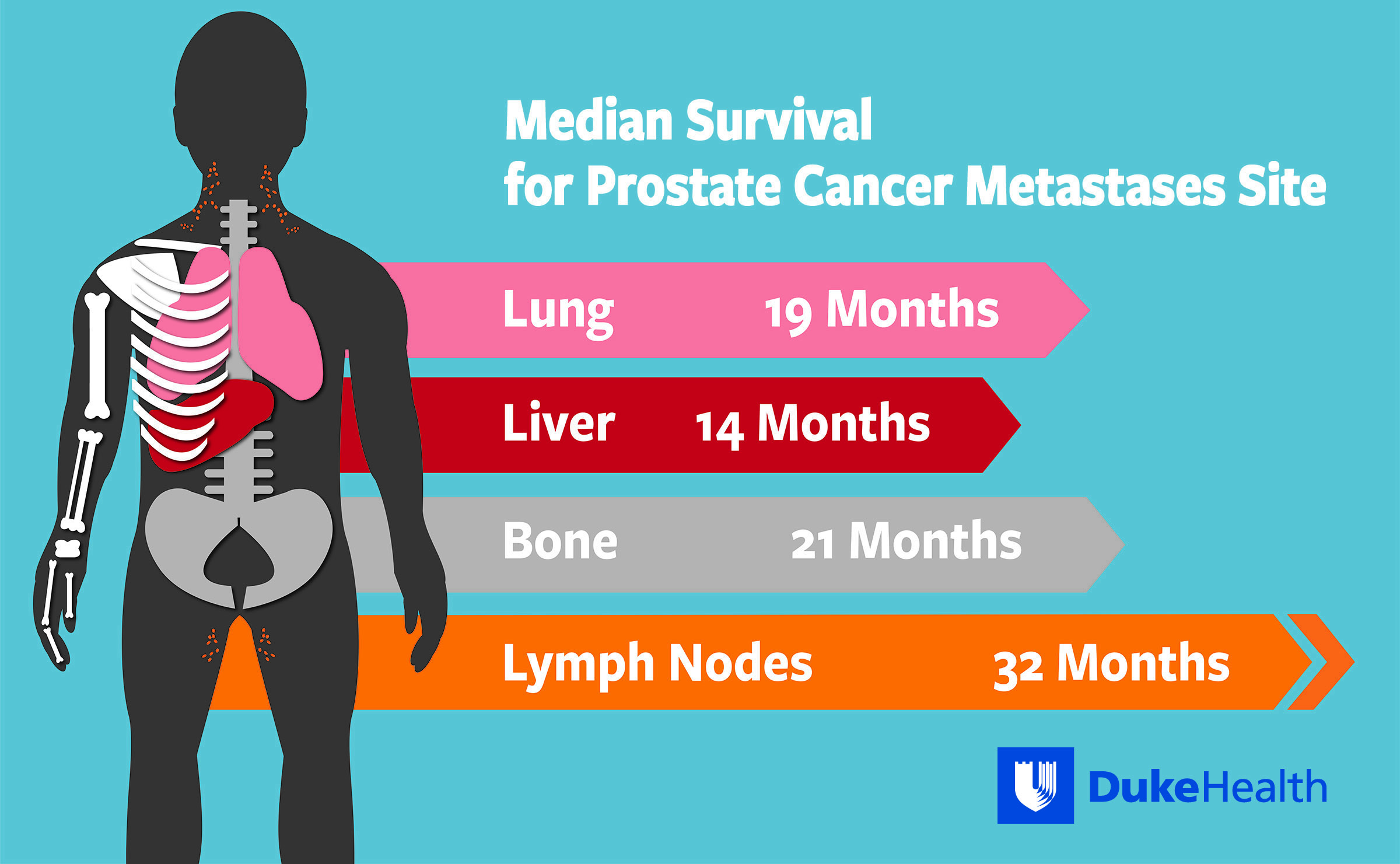
Distant metastatic prostate cancer is more advanced, having spread to areas outside the pelvic region. The most common distant places where prostate cancer spreads include the:
- Bones
- Lungs
- Liver
Less commonly, prostate cancer may spread to the adrenal glands, kidneys, brain, pancreas or another organ. It is important to note that it is still considered prostate cancer when it spreads to other regions, as the cancer cells in distant areas are the same as the original cancer cells in the prostate gland, even if the prostate gland was previously removed. A biopsy may be recommended to confirm this.
What Is Clinically Localized Prostate Cancer
If you have been diagnosed with prostate cancer and your doctor has indicated that your cancer appears to not have spread beyond the prostate gland, you have what is known as clinically localized prostate cancer. Sometimes, doctors will also call cancer that has spread into the lining of the prostate gland clinically localized.
According to the U.S Department of Health and Human Services, about 90 percent of men with prostate cancer have localized prostate cancer, and it is typically considered low-risk, meaning patients can expect to live long after their diagnosis, in many cases even without treatment.
Recommended Reading: How To Massage A Manâs Prostate
You May Like: Prostaglandins Erectile Dysfunction
Should I Have A Psa Test
- The Prostate Cancer Risk Management Programme gives you information on risks and benefits of the PSA test to help you decide whether or not to have it. Go to the website
- Also, an online decision aid called Prosdex provides information, including real-life stories, to help you make a decision on whether or not to have the PSA test.
Stage 3 Pericardial And Testicular Mesothelioma
Doctors and researchers do not clearly define stage 3 pericardial or testicular mesothelioma due to their rare nature.
Only 1% to 2% of mesothelioma cases are pericardial, which means cancer forms within the sac that protects the heart. Therefore, a diagnosis for this disease is unlikely until the late stages, after metastasis to the lungs or chest cavity.
Doctors evaluate testicular mesothelioma tumor characteristics by using staging guidelines for general testicular cancer. For example, doctors more commonly refer to stage 3 testicular mesothelioma as late-stage cancer. This description indicates that cancer has spread beyond the lining of the testicles to other tissues such as lymph nodes or bone.
Dont Miss: What Is Perineural Invasion In Prostate Cancer
Recommended Reading: External Prostate Massage Prostatitis
Prevention Of Colorectal Cancer
We can do quite a lot to lower our chances of developing colorectal cancer:
- Regular screenings especially if you have had colorectal cancer before, you are over 60, there is a family history of this type of cancer, you have Crohns disease. Some experts say screening should start after the age of 50.
- Nutrition make sure your diet has plenty of fiber, fruit, vegetables, and good quality carbohydrates. Keep your consumption of red meat and processed meat down to a minimum, or cut them out altogether. Switch from saturated fats to good quality fats, such as avocado, olive oil, fish oils, and nuts. However, this study found that although vegetarians have an overall lower risk of developing cancers, their risk of developing colorectal cancer is higher than meat eaters.
- Exercise exercise regularly. Moderate, regular exercise has been shown to have a significant impact on lowering a persons risk of developing colorectal cancer.
- Bodyweight keep your bodyweight healthy. Being overweight or obese raises a persons risk of developing many cancers, including colorectal cancer.
Is Going To The Bathroom Frequently A Sign Of Prostate Cancer
Thats one of the challenging things having urinary symptoms is very rarelyalmost nevera sign of prostate cancer. Having urinary symptoms means you should probably be evaluated for an enlarged prostate, also known as benign prostatic hyperplasia . We can treat your urinary symptoms and help you pee better.
If urinary symptoms bring men to the doctor, we can discuss screening for prostate cancer. Thats important because not all men will go to a doctor until theres something wrong with them. And prostate cancer screening really is the only way to detect prostate cancer, because its almost always asymptomatic.
Read Also: How Long Should You Take Lupron For Prostate Cancer
What Is Metastatic Prostate Cancer
Sometimes cancer cells will escape the prostate and grow quickly, spreading to nearby tissue, or metastasizing. Nearby lymph nodes are often the first destination for a spreading cancer. If prostate cancer has spread to your lymph nodes when it is diagnosed, it means that there is higher chance that it has spread to other areas of the body as well.
If and when prostate cancer cells gain access to the bloodstream, they can be deposited in various sites throughout the body, most commonly in bones, and more rarely to other organs such as the liver, lung, or brain. Bone metastases are seen in 85% to 90% of metastatic cases.
No matter where a cancer turns up in the body, it is always identified by the tissue type in which it started. Prostate cancer can metastasize to other organs, but it is always prostate cancer, because it consists of mutated prostate cells.
Men diagnosed with metastatic prostate cancer , will often not undergo local treatments of the primary prostate tumor, such as surgery or radiation. Instead, their therapeutic journey might start with hormone therapy, and from there follow a similar path as men who were diagnosed at an earlier stage and had subsequent disease progression.
Want more information about a prostate cancer diagnosis and treatment options? Download or order a print copy of the Prostate Cancer Patient Guide.
