Other Drugs And Therapies
Many other pharmacologic interventions have been studied in patients with CP/CPPS, with variable results.29 Pentosan polysulfate is commonly used to treat patients with painful bladder syndrome/interstitial cystitis to replenish the glycosaminoglycan layer of the bladder. PBS/IC and CP/CPPS are thought to be related conditions, and pentosan polysulfate has been tested in an RCT for CP/CPPS.33 The results showed some clinical benefit in the treatment arm, but the change in total NIH-CPSI score was not statistically significant.
Several natural therapies have also been used for CP/CPPS, including saw palmetto and its extract, bee pollen extract and quercetin. A review of trials using these products suggests potential for each of them to have a therapeutic role,34 and a recent multicenter RCT has demonstrated statistically significant symptomatic improvement in patients receiving bee pollen extract.35
A number of other procedures have been employed to treat men with CP/CPPS, including transurethral microwave thermotherapy, transurethral needle ablation, spinal cord stimulation, pudendal nerve block or decompression, transurethral prostate resection, electromagnetic therapy and acupuncture. Assessment of each of these options is beyond the scope of this Review, but the data on transurethral microwave thermotherapy in particular is encouraging.1,46,47
Chronic Prostatitis/chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome
| Chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome |
|---|
| Other names |
The cause is unknown. Diagnosis involves ruling out other potential causes of the symptoms such as bacterial prostatitis, benign prostatic hypertrophy, overactive bladder, and cancer.
Recommended treatments include multimodal therapy, physiotherapy, and a trial of alpha blocker medication or antibiotics in certain newly diagnosed cases. Some evidence supports some non medication based treatments.
Read Also: How To Check For Enlarged Prostate At Home
Measurement Of Superoxide Dismutase Malondialdehyde And Gsh Levels
After the mice were sacrificed, the mouse prostate tissues were homogenized and then placed in phosphate-buffered saline . The homogenates were centrifuged at 2,500 rpm/min for 10 min at 4°C, and the supernatants were extracted for further analysis of oxidative stress levels. Superoxide dismutase and malondialdehyde contents were measured according to the corresponding detection kits . The data were further analyzed according to the instructions to calculate the protein content.
Read Also: Where Does Prostate Cancer Spread
Identification Of Diagnostic Markers For Chronic Prostatitis
As mentioned above, although COX-2 and IL-1 could discriminate inflammatory tissues from normal controls, they were universally expressed on epithelial cells and infiltrated inflammatory cells. Thus, identifying novel markers that are specifically expressed on inflammatory cells instead of epithelial cells would help us better evaluate the inflammation status.
Based on the correlations between these top DEGs and immune processes, we selected eight of them to perform IHC validation . Notably, we found that CXCR4, CD44, and OLFM4 were expressed only on the inflammatory cells of the CNP models , and the epithelial cells of both the CNP models and negative controls rarely expressed these proteins, highlighting their roles in serving as potential therapeutic targets. Taken together, these results highlight the diagnostic roles of CD44, OLFM4, and CXCR4 in discriminating CNP models from normal controls, which also hold therapeutic potential.
|
Figure 3 Immunohistochemistry analyses of the immune-related markers, CD44, CXCR4, and OLFM4 between prostate tissues derived from chronic nonbacteria prostatitis and negative controls. Note: For the control set, no or few inflammatory cells infiltrated, while for the CNP model set, the arrow pointed out the inflammatory nest. |
Treatment Approaches To Cp/cpps
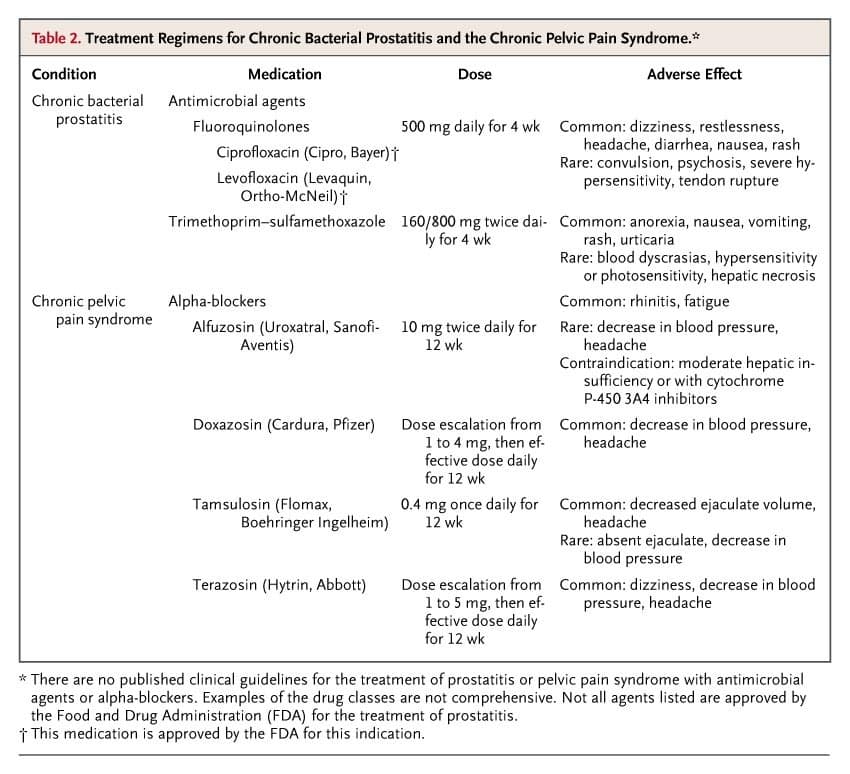
Antibiotics are largely ineffective in the treatment of CP/CPPS as the chronic nature of the syndrome is thought not to be completely attributable to an ongoing active or latent bacterial infection . Despite this, up to almost 80% of CP/CPPS patients receive antibiotics as treatment at some point during their disease course, more than 7 times that of non-CP/CPPS patients, and many receive multiple rounds of antibiotics despite lack of efficacy . Many other monotherapies have been applied in prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trials, including anti-inflammatory drugs, finasteride, phytotherapies, alpha-receptor blockers, antianxiolytics, and the interstitial cystitis drug pentosan polysulfate. No single drug has been able to show consistent, significant benefit in CP/CPPS patients .
You May Like: What Happens When Hormone Treatment For Prostate Cancer Stops Working
Records Of The Variables
From the available records that we obtained from the CP/CPPS patients according to some studies of the risk factors for CP/CPPS and the pain of CP/CPPS , the 11 variables were about basic information, lifestyle, and medical history were selected for further analysis. The sedentary lifestyle was defined as sitting or lying down when took part in an activity, such as reading, watching television, driving . Holding back urine was defined as that waiting until the last second to go to the bathroom to pee . In China, the main contraceptive method was the use of condoms, so in our study, the contraceptive method was set as the use of condoms. The questionnaire of the Self-Rating Anxiety Scale was used to judge whether patients with CP/CPPS had the diagnosis of anxiety. When the scores of SAS was more than 50, the patients were diagnosed with anxiety . 100 ml of beer per week differed significantly from 100 ml of liquor or spirits. To accurately assess the alcohol intake of patients, we uniformly defined the patients alcohol intake as grams of alcohol intake per week. According to the number of cigarettes daily in Pauls study, we divided smokers into two groups: daily smoker of< 10 cigarettes and daily smoker of10 cigarettes . Skewed data were log-transformed or coded as categorical variables, and the detailed information was presented in Additional file : Table S1.
The Biological Cause Of An Enlarged Prostate
Researchers have revealed the biological irritants responsible for prostate inflammation.
When we are young, our bodies effectively break down irritating free radicals, protecting us from their harmful effects. But as we age, this natural mechanism stops working as efficiently. Free radicals remain in our body, provoking inflammation that is often concentrated in the prostate. The prostate becomes swollen, compressing the urethra and pushing up against the bladder.
Guarding the prostate from free radical damage by boosting your antioxidant defense helps reduce prostate inflammation, allowing you to urinate predictably and painlessly.
Also Check: Can You Get An Erection After Prostate Surgery
He Staining Of Human And Cnp Mouse Prostate Tissues
We obtained histological sections from patients who were diagnosed with benign prostatic hypertrophy after surgical treatment and histologically confirmed to have inflammatory cell infiltration and CP/CPPS-like symptoms . The infiltrated inflammatory cells were mainly lymphocytes and neutrophils , a result consistent with previous findings.9,22,23 After establishing the CNP model, we found that many lymphocytes and neutrophils infiltrated the interstitial space of the CNP mice, while little inflammatory cell infiltration was observed in the negative control group . Since COX-2 and IL-1 are recognized markers of chronic prostatitis, we applied IHC to detect their expression nevertheless, weak differences were uncovered between the CNP models and negative controls . Therefore, identifying new and prominent markers for the diagnosis of CNP is warranted. Taking Figure 1 and Supplementary Figure S1 in combination, we established a stable CNP model and revealed some similarities between the clinical patients and CNP models.
|
Figure 1 Hematoxylin-eosin staining showed the inflammatory cell infiltration to the prostate tissues. The prostate tissues were dissected from benign prostatic hypertrophy patients who received surgical treatment, and accompanied with chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome -like symptoms. The lymphocytes and neutrophils were pointed out by the arrows. |
Establishment Of The Chronic Prostatitis/chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome Mouse Model
The most widely accepted animal model of CP/CPPS was established as described in the Methods section in this model, the tissue structure of the mouse prostate changed after the model was successfully established, and a large number of inflammatory cells infiltrated the prostate . According to a previously published article , the inflammatory score was used to assess the inflammatory state, and it was found that the prostate tissue inflammatory score was significantly increased in the EAP group , but the difference in body weight between the two groups was not statistically significant . Von Frey pain behavior test filaments were used to measure the pain of the mice with EAP, and we found that the response frequency was significantly increased in mice with EAP . In this part of the experiment, the mouse CP/CPPS model was shown to have been successfully established, and it was ready for our subsequent research.
FIGURE 2. Successful establishment of the CP/CPPS mouse model. Sections of prostate tissues were stained with HE. Scale bar = 50 m CTL = control EAP = experimental autoimmune prostatitis mice. Inflammatory score and weight in the CTL and EAP groups. n = 6. The Von Frey filament response frequency test in the CTL and EAP groups. n = 6.
After Ningmitai treatment, prostatic inflammation and inflammatory pain-related pathway activity in mice decreased.
Don’t Miss: How To Perform Prostate Massage
Trial To Compare Alfuzosin Versus Placebo In The Treatment Of Chronic Prostatitis/chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome
| The safety and scientific validity of this study is the responsibility of the study sponsor and investigators. Listing a study does not mean it has been evaluated by the U.S. Federal Government. Read our disclaimer for details. |
| First Posted : February 8, 2005Results First Posted : June 12, 2020Last Update Posted : June 12, 2020 |
The two primary objectives of this study are:
- To compare 12 weeks of treatment with alfuzosin versus placebo in newly-diagnosed, alpha-blocker naive CP/CPPS participants with respect to the primary endpoint in the National Institutes of Health Chronic Prostatitis Symptom Index .
- To evaluate the safety and tolerability of 12 weeks of alfuzosin in newly-diagnosed, alpha-blocker naïve CP/CPPS participants.
The proportion of “responders” in each treatment arm will be compared to evaluate the overall safety and efficacy of alfuzosin as compared to placebo. Approximately 270 eligible patients, 135 per treatment arm, will be randomized and followed for a period of twelve weeks after randomization.
| 10 mg of alfuzosin once daily for 12 weeks | Drug: Alfuzosin |
| 10 mg of an identical-looking placebo once daily for 12 weeks | Drug: Placebo |
Our Research Confirms A Natural Approach Is Best
Dr. Jamison reveals new clinical evidence supporting the use of natural remedies for an enlarged prostate.
Scott Jamison, MD, has been a physician for over 30 years and is a leader in integrative medicine currently practicing in St. Louis. He and his team of researchers have been investigating the most effective alternative remedies to reduce prostate inflammation naturally.
“After months of research and testing, we arrived at a formula of 5 natural ingredients that outperformed all others in terms of safety and effectiveness,” Dr. Jamison states. “Following the results of the placebo-controlled clinical study, we decided to release the formula to the public.”
Read Also: Do Prostate Massages Help Prevent Cancer
What Is Chronic Prostatitis/chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome
There are different types of prostatitis, one of which is chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome . This is the most common type. Young and middle-aged men are more likely to develop CP/CPPS, but it can happen at any age.
CP/CPPS may be classified as inflammatory or non-inflammatory.
When CP/CPPS is non-inflammatory, no infection-fighting cells and no bacteria are found in the fluid.
Symptoms
- Men with CP/CPPS can experience chronic discomfort or pain in the groin, genitals, perineum , or bladder.
But symptoms dont happen to every man with CP/CPPS. Also, symptoms may come and go on their own.
Diagnosis
TreatmentCP/CPPS can also be difficult to treat and, unfortunately, it cannot always be cured. It can also take some time to find what best relieves a mans symptoms. Some strategies for treating CP/CPPS symptoms include the following:
Men with severe CP/CPPS may require surgery.
Sometimes, CP/CPPS gets better on its own.
Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis And Pelvic Pain
A 4- to 6-week trial of antibiotic therapy is indicated in chronic bacterial prostatitis and chronic pelvic pain syndrome with inflammation, but no consensus exists regarding its use in chronic pelvic pain syndrome without inflammation and asymptomatic prostatitis. Recurrences of chronic bacterial prostatitis are common, possibly in part because few antibacterial agents distribute well into the prostatic tissue and achieve sufficient concentrations to eradicate infections. Preferred antimicrobial agents include fluoroquinolones, macrolides, tetracyclines, and trimethoprim. Fluoroquinolones provide relief in about 50% of patients, and treatment is more effective if treatment starts earlier in the course of symptoms. The course of antibiotics can be repeated if the first course provides some relief. A Cochrane review of 18 studies that compared the various fluoroquinolone antibiotics suggested that there were no differences in clinical efficacy or adverse events among them in treating chronic bacterial prostatitis. Fosfomycin has been used to effectively treat multidrug-resistant gram-negative prostatitis.
Supportive measures such as analgesics , alpha-blocking agents, hydration, stool softeners, and sitz baths are often used. Alpha-blockers reduce bladder outlet obstruction and thus improve voiding dysfunction that may be associated with prostatic swelling that is common with prostatitis.
Don’t Miss: Is Milk Bad For The Prostate
Imaging And Other Investigations
Uroflowmetry is done to measure the rate of urine flow and total volume of urine voided when the subject is peeing.
Abdominal ultrasound examination of the prostate and is often performed to rule out and hydroureter. Incidentally, cysts, tumours, and stones may be found on ultrasound. of more than 100 ml may indicate significant obstruction. Prostate size of 30 cc or more indicates enlargement of the prostate.
Prostatic calcification can be detected through transrectal ultrasound . Calcification is due to solidification of prostatic secretions or calcified . Calcification is also found in a variety of other conditions such as prostatitis, , and prostate cancer. For those with elevated levels of PSA, TRUS guided biopsy is performed to take a sample of the prostate for investigation. Although MRI is more accurate than TRUS in determining prostate volume, TRUS is less expensive and almost as accurate as MRI. Therefore, TRUS is still preferred to measure prostate volume.
Medical conditions
Medications
Certain medications can increase urination difficulties by increasing bladder outlet resistance due to increased tone at the prostate or bladder neck and contribute to LUTS. medications, such as with can increase bladder outlet resistance. In contrast, and medications can worsen urinary retention by promoting bladder muscle relaxation. Diuretic medications such as or can cause or worsen urinary frequency and nighttime awakenings to urinate.
The Pharmacists Role In Managing Chronic Prostatitis/chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome
Mena Alrais Dellarocca, PharmD, RPhAdjunct Instructor of Pharmacy Practice University of Southern California, School of PharmacyLos Angeles, California
US Pharm. 2020 45:HS-11-HS-16.
ABSTRACT: Prostatitis, an inflammation of the prostate gland, is a common condition, with prevalence peaking in middle-aged men. Chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome is characterized by pelvic pain, variable urinary symptoms, and sexual dysfunction. Focused multimodal therapy appears to be more successful than empiric monotherapy, which may add complexity to the drug regimen and calls for collaboration with a pharmacist for an effective continuum of care, management of pain, and antibiotic stewardship.
Chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome is a common condition worldwide, affecting approximately 2% to 10% of men. The prevalence seems to peak in the fifth decade and decline thereafter and shows no apparent racial predisposition. The symptomatic, chronic forms of prostatitis as defined by the National Institutes of Health , are chronic bacterial prostatitis and CP/CPPS . Most men diagnosed with prostatitis have CP/CPPS rather than acute or chronic bacterial prostatitis. Despite having a significant negative impact on patients quality of life and presenting diagnostic and therapeutic challenges for physicians, CP/CPPS has received relatively little attention in the literature, in comparison with other urologic conditions.1-8
Recommended Reading: Does Super Beta Prostate Work
Treatment For Acute And Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis
Antibiotics treat both acute and chronic bacterial prostatitis. The most commonly used antibiotics for these conditions are:
-
Ciprofloxacin , at a dosage of 500 mg twice a day
-
Levofloxacin , at a dosage of 500 mg once a day
-
Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole , at 1 tablet twice a day
Youll take these antibiotics for 4 to 12 weeks, depending on whether you have acute or chronic bacterial prostatitis.
A Deficient Antioxidant Defense
Our bodies possess a biological mechanism to absorb and break down these irritants. However, after age 50, our antioxidant defense grows less effective in preventing free radical damage. This results in chronic inflammation, to which the prostate is particularly susceptible, and commonly causes frequent urination, discomfort, bloating, and a feeling of fullness. But with a little help, you can restore your body’s natural defense against free radicals and stop living life around the bathroom.
That’s where Prostacor comes in…
Prostacor’s unique formulation of earth-grown herbs and natural biological compounds is designed to restore your body’s natural antioxidant defense and help control prostate inflammation. This relieves your overactive bladder and ensures proper protection for healthy prostate function as you grow older.
Don’t Miss: Are Almonds Good For Enlarged Prostate
What Is The Return Policy For Prostacor
We are so confident that Prostacor will work for you that every bottle comes with our 30 Day Money Back Guarantee. If you are not satisfied with your purchase, we don’t want you paying for it… even if you have taken the entire bottle! Simply contact us within 30 days of your original purchase, and we will immediately arrange for a refund.
Check out ourReturn Policy page for more details.
