How Is Prostatitis Treated
Treatment depends on the type of prostatitis.
Chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome. Treatment for chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome aims to decrease pain, discomfort, and inflammation. A wide range of symptoms exists and no single treatment works for every man. Although antibiotics will not help treat nonbacterial prostatitis, a urologist may prescribe them, at least initially, until the urologist can rule out a bacterial infection. A urologist may prescribe other medications:
- silodo
- 5-alpha reductase inhibitors such as finasteride and dutasteride
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugsalso called NSAIDssuch as aspirin, ibuprofen, and naproxen sodium
- glycosaminogly
- cans such as chondroitin sulfate
- muscle relaxants such as cyclobenzaprine and clonazepam
- neuromodulators such as amitriptyline, nortriptyline , and pregabalin
Alternative treatments may include
- warm baths, called sitz baths
- local heat therapy with hot water bottles or heating pads
- physical therapy, such as
- Kegel exercisestightening and relaxing the muscles that hold urine in the bladder and hold the bladder in its proper position. Also called pelvic muscle exercises.
- myofascial releasepressing and stretching, sometimes with cooling and warming, of the muscles and soft tissues in the lower back, pelvic region, and upper legs. Also known as myofascial trigger point release.
Ejaculation Is A Potential Cause Of Mildly Elevated Psa
“Ejaculation can cause a mild elevation of your PSA level, and so can having a digital rectal exam,” says Milner. “These types of PSA elevations are usually not enough to make a significant difference unless your PSA is borderline. PSA should return to normal in two to three days.”
To avoid this type of elevation, doctors will usually draw blood for a person’s PSA level before doing a rectal exam. Ask your doctor if you should avoid ejaculation for a few days before a PSA test.
What Is Chronic Prostatitis
The prostate is a walnut-sized gland that sits below the bladder in men. This gland makes fluid that mixes with sperm to form semen.
Prostatitis is inflammation or swelling of the prostate gland. When symptoms start gradually and linger for more than a couple of weeks, the condition is called chronic prostatitis.
Three major types of chronic prostatitis are:
Chronic prostatitis is common and affects adult men of all ages and from all backgrounds. About five percent of men experience symptoms of chronic prostatitis at some point in their lives. Chronic prostatitis is the reason for up to 25% of office visits to urologists. Urologists are doctors who specialize in diseases of the urinary tract.
Some men develop a chronic infection in the prostate that does not cause any symptoms. Men with this problem may be diagnosed during an evaluation for other urological conditions, such as enlarged prostate or infertility. Doctors often treat the infection with the same antibiotics used for chronic bacterial prostatitis.
Bacterial infection of the prostate gland also can cause acute prostatitis, which starts suddenly and usually causes fever and more serious symptoms. Acute prostatitis is less common than chronic prostatitis.
Read Also: Can You Give Yourself A Prostate Massage
Chronic Prostatitis And Asymptomatic Inflammatory Prostatitis
Non-infectious prostatitis may be inflammatory or non-inflammatory. Despite the fact that prostatitis means prostate inflammation, the non-inflammatory cases are termed as such due to the absence of inflammatory cells in the urine or semen.
Non-infectious prostatitis is often chronic and may appear repeatedly and resolve, often without treatment. Infections of the prostate gland frequently arise in these cases. Non-inefctious prostatitis is often associated with pain and even in instances where the prostate gland is not inflamed, pain may still be present possibly as a result of nerve injury . Some cases of non-infectious prostatitis may be silent despite the presence of inflammatory cells in the urine and semen.
What Are The Causes Of Prostate Infection
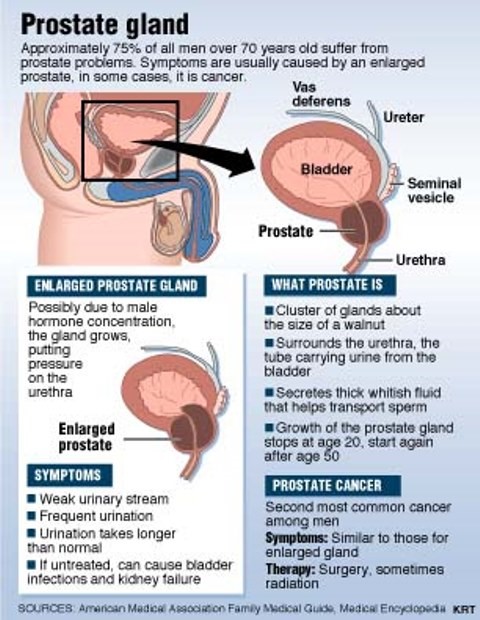
If the prostate gland becomes swollen and tender, it is called prostatitis or prostate infection. The prostate gland is a walnut-shaped organ that lies just below a man’s urinary bladder. The prostate produces a fluid that goes into the semen. An inflamed or infected prostate gland may be seen in men of all ages. While the exact cause of prostate infection isnt known, some cases of prostatitis are clearly related to bacterial infections. Bacterial prostatitis isnt contagious and isnt a sexually transmitted disease. Below are a few common causes of prostate infection:
- Severe injury to the groin
- Recurrent use of a urinary catheter
- Prostate biopsy
Also Check: Perineural Invasion Prostate Cancer Prognosis
Does Prostatitis Cause Cancer
Although prostatitis can cause you trouble, it does not cause cancer. There is a blood test some doctors use for prostate cancer called the prostate-specific antigen test . If you have prostatitis, your PSA level might go up. This does not mean you have cancer. Your doctor will treat your prostatitis and may check your PSA level again.
Read the full article.
- Get immediate access, anytime, anywhere.
- Choose a single article, issue, or full-access subscription.
- Earn up to 6 CME credits per issue.
Causes Of Prostate Gland Infection
Most prostate gland infections are due to bacteria. Rarely, viral and fungal prostatitis may occur although it is more often associated with immunocompromised states. Bacterial prostatitis is less common than other non-infectious causes. In acute prostatitis, usually the same bacteria that are involved in urinary tract infections may also infect the prostate. This includes E.coli, enterococci and staphylococci. With chronic prostatitis, however, the are a host of microorganisms that may also play a role in infection, including Klebsiella spp, Enterobacter spp, staphylococci, Pseudomonas spp and enterococci.
The microorganisms gain entry into the prostatic tissue through multiple routes. The most common is when microorganisms enter through the penile urethra and spread up the urinary tract. This is known as an ascending urethral infection. Microorganisms in the urine may also enter the prostatitic ducts, against the regular flow of urine. This is known as reflux of infected urine. In acute prostatitis, these routes of transmission are usually responsible.
Bacterial prostatitis may also arise through direct infiltration of the rectal bacteria. Lymphatic spread of the rectal bacteria and hematogenous spread of bacteria through the blood stream from distant sites may also be responsible.
Recommended Reading: Zinc For Prostate
Medical Procedures Can Cause Psa To Rise
“Anything that traumatically interferes with the architecture around the prostate gland can make PSA go up,” says Dr. Milner. “One of the most common causes of significantly high PSA from this type of trauma is the placing of a catheter into the bladder.”
Another cause is a prostate or bladder exam that involves passing a scope or taking a biopsy.
“Since it takes about two to three days for PSA to go down by half, you should wait two to three weeks after this type of trauma to do a PSA test,” Milner says.
What Is A Prostate Infection
A prostate infection occurs when your prostate and the surrounding area become inflamed. The prostate is about the size of a walnut. Its located between the bladder and the base of the penis. The tube that moves urine from the bladder to the penis runs through the center of your prostate. The urethra also moves semen from the sex glands to the penis.
Several types of infections can affect the prostate. Some men with prostatitis experience no symptoms at all, while others report many, including intense pain.
You May Like: Does An Enlarged Prostate Affect A Man Sexually
Prostatitis And Prostatic Abscess
Prostatitis is defined as inflammation of the prostate gland, which can be caused by infectious agents or may be aseptic. In dogs, approximately one-third of prostatitis cases result from bacterial infection.7 The primary route of infection is ascending , but bacteria can also colonize the prostate by hematogenous spread.1,22 On DRE, the prostate may appear normal to enlarged and is typically painful. Abdominal ultrasonography often reveals changes in the echodensity of the prostate.
If bacterial prostatitis is suspected, ejaculation or prostatic wash may be a preferred method for sample collection to prevent complications that might occur from FNA. However, bacterial contamination from the lower urinary and genital tracts could lead to misdiagnosis. Should FNA be performed, care should be taken to maintain continual negative pressure until the needle is fully extracted from the tissue to avoid leakage of material. Cytological evaluation of samples obtained via ultrasound-guided FNA may be more sensitive than histology for the diagnosis of sepsis, because the thickness of the histological sections can impede visualization of bacteria.8 Sample material obtained from cases of suspected prostatitis should be submitted for bacterial culture and susceptibility testing. Treatment of prostatitis involves medical management in conjunction with castration, which will help control the infection more quickly.
Takeshi Sasaki, … Simon W. Hayward, in, 2018
How Is Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome Managed Or Treated
Prostatitis treatments vary depending on the cause and type. Asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis doesnt require treatment.
For chronic pelvic pain syndrome , your healthcare provider may use a system called UPOINT to classify symptoms into six categories. Your provider uses multiple treatments at the same time to treat only the symptoms youre experiencing.
Approximately 80% of men with CPPS improve with the UPOINT system. The system focuses on these symptoms and treatments:
- Urinary: Medications, such as tamsulosin and alfuzosin , relax muscles around the prostate and bladder to improve urine flow.
- Psychosocial: Stress management can help. Some men benefit from counseling or medications for anxiety, depression and catastrophizing .
- Organ: Quercetin and bee pollen supplements may relieve a swollen, inflamed prostate gland.
- Infection:Antibiotics kill infection-causing bacteria.
- Neurologic: Prescription pain medicines, such as amitriptyline and gabapentin , relieve neurogenic pain. This pain can include fibromyalgia or pain that extends into the legs, arms or back.
- Tenderness: Pelvic floor physical therapy may include myofascial release . This therapy can reduce or eliminate muscle spasms.
Also Check: Carboplatin Prostate Cancer
What Are Prostate Infections And Prostatitis
The prostate gland is a part of a man’s reproductive system, secreting fluids that help transport sperm. The gland lies just below the bladder and surrounds the urethra .
Prostate infections may irritate the prostate and cause inflammation and swelling of the gland. Prostate infections occur most often in men aged 30-50 years but can occur in older men. Unfortunately, many people equate the terms prostate infection and prostatitis, but prostate infections comprise only two of the four major classifications of the term “prostatitis,” and infectious types comprise only a few of the total number of prostatitis diagnosed patients.
The National Institutes of Health consensus panel has designated four types of prostatitis classifications.
The NIH has established extensive criteria for chronic pelvic pain syndrome that excludes infection and other problems and is as follows:
Inclusion Criteria
- male, at least age 18
- pain or discomfort in the pelvic area for at least 3 months
Exclusion Criteria
This classification system is important to understand because about 90% of men with prostatitis symptoms are diagnosed with chronic pelvic pain syndrome and, by definition, do not have infectious prostatitis.
Stress and depression are common in men with chronic infectious prostatitis.
Diagnosis Of Prostate Disease
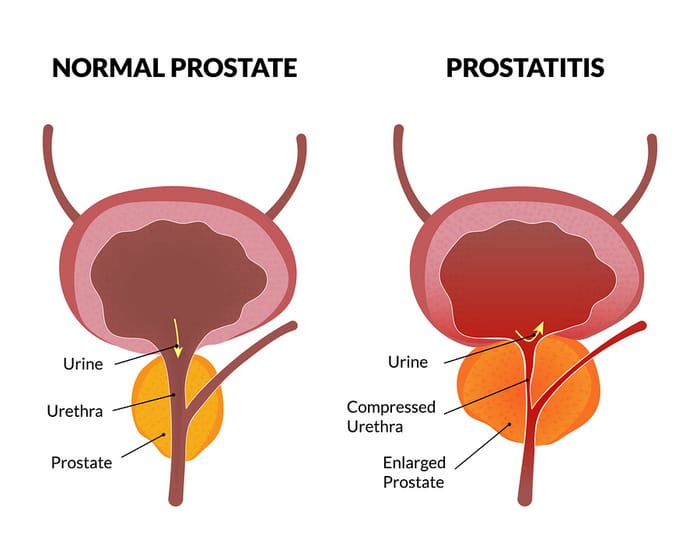
Prostate disease is diagnosed using a variety of tests, including:
- physical examination, including digital rectal examination , where the doctor inserts a gloved finger into your rectum to check the size of your prostate
- blood test for prostate specific antigen
- mid-stream urine tests to look for infection or blood in the urine
- ultrasound scans and urinary flow studies
- biopsies of the prostate.
Don’t Miss: Is Zinc Good For Prostate
What Are The Complications Of Prostatitis
Men with acute bacterial prostatitis may develop . This widespread inflammation can be life-threatening. It requires immediate medical treatment.
Antibiotics can cause an upset stomach. Men with chronic bacterial prostatitis may need lots of antibiotics to treat recurring infections. Some people develop antibiotic resistance, making treatment ineffective.
Asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis can lower sperm count, affecting fertility.
The Risk Factors And Causes Of Prostatitis
Theres no denying it prostatitis is uncomfortable. The pain, frequent urination and flu-like symptoms associated with prostatitis make it almost unbearable at times. The worst part? Trying to figure out why you are living with prostatitis in the first place.
Prostatitis is a non-cancerous condition in which the prostate gland is inflamed. While the causes can be different for every individual, some causes of prostatitis are simply not known. However, there are few potential causes that have been found to encourage prostatitis.
Below, youll learn about the different types of prostatitis, the most common potential causes of prostatitis and the risk factors associated with prostatitis to further protect yourself against this condition in the future.
You May Like: Cialis For Prostatitis
Preventing Or Controlling Symptoms
Doctors cant always identify what causes prostatitis, which makes it difficult to avoid prostatitis completely. However, men can take steps to try to reduce the likelihood of experiencing the condition. The same actions can help control symptoms of chronic prostatitis.
- Stay hydrated. Drinking plenty of water helps men to urinate frequently, which flushes out the urethra .
- Avoid irritating the urethra. Avoiding or limiting caffeine, spicy foods and alcohol can help to avoid prostatitis.
- Reduce prostate pressure. Men who ride a bicycle frequently might consider wearing padded shorts and using a split seat to reduce pressure on the prostate region.
- Stay sexually active. Some physicians advise that men ejaculate regularly as another way to flush the urethra.
Request an Appointment
What Causes Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis
Chronic bacterial prostatitis is a type of infective prostatitis. It is caused by a persistent infection with a germ of the prostate gland. A man with chronic bacterial prostatitis will usually have had recurring urine infections. Chronic bacterial prostatitis is usually caused by the same type of germs that causes the urine infections. The prostate gland can harbour infection and therefore recurring infections can occur. Chronic bacterial prostatitis is not a sexually transmitted infection.
Recommended Reading: Define Prostate
Prostatitis: A Common Problem In Men Under 50
“The PSA test is a good screening tool for prostate cancer, but it is not very specific,” says Erik P. Castle, MD, a urologist and researcher at the Mayo Clinic in Phoenix, Arizona. “Common causes of inflammation in the gland, called prostatitis, can cause high PSA levels.”
Prostatitis is the most common prostate problem for men younger than 50.
Prostatitis caused by bacteria can be treated with antibiotics. Another, more common type of prostatitis, called nonbacterial prostatitis, can be harder to treat and may last a long time.
What Is The Prostate Gland
The prostate is a gland that lies just below a man’s urinary bladder. It surrounds the urethra like a donut and is in front of the rectum. The urethra is the tube that carries urine out of the bladder, through the penis and out of the body. Your doctor may check your prostate by putting a finger into your rectum to feel the back of your prostate gland.
The prostate gland makes a fluid that provides nutrients for sperm. This fluid makes up most of the ejaculate fluid. We do not yet know all of the ways the prostate gland works.
Read Also: Finding The Prostate Externally
What Are The Remedies For Prostate Infection
The common remedies of prostate infection include:
Warm baths called sitz baths
Local heat therapy with hot water bottles or heating pads
Physical therapy:
- Kegel exercises: Tightening and relaxing the muscles that hold urine in the bladder and hold the bladder in its proper position. These are also called pelvic muscle exercises.
- Myofascial release: Pressing and stretching, sometimes with cooling and warming, of the muscles and soft tissues in the lower back, pelvic region, and upper legs. It is also known as myofascial trigger point release.
Phytotherapy: Plant extracts such as quercetin, bee pollen, and saw palmetto may help in relieve symptoms.
Avoiding food that triggers symptoms such as caffeine, spicy foods, and alcohol
Using a cushion if you will be sitting for a long time
Pathologic Definition Of Prostatitis
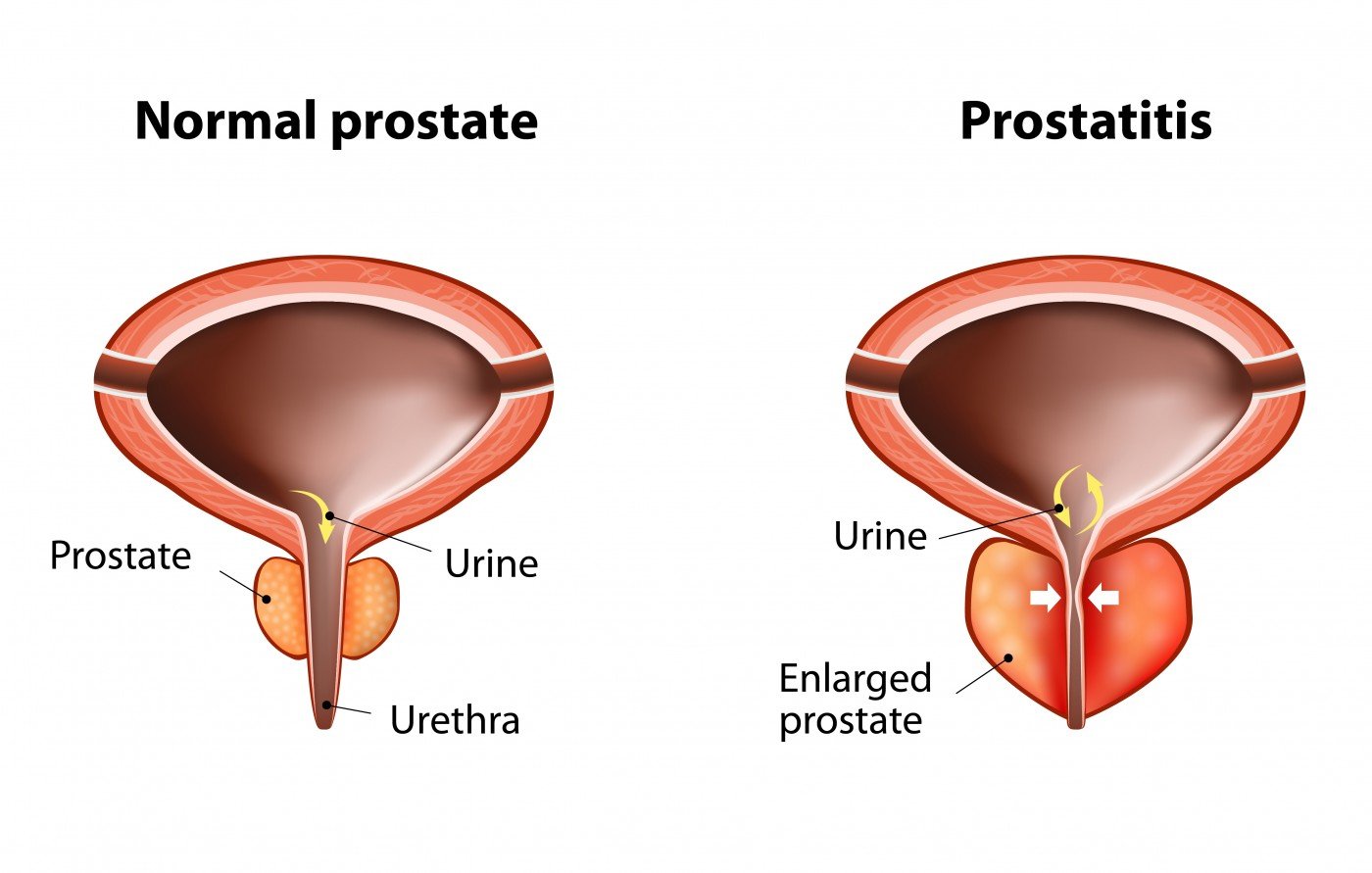
Pathologically, prostatitis is defined as an increased number of inflammatory cells within the prostate gland. The inflammatory process may be infectious or inflammatory in origin. The most common histologic pattern is a lymphocytic infiltrate in the stroma immediately adjacent to the prostatic acini .
Prostatitis occurs in distinct forms that have separate causes, clinical features, and outcomes. Four clinical entities have been described: acute bacterial prostatitis, chronic bacterial prostatitis, nonbacterial or abacterial prostatitis, and prostatodynia.
You May Like: How To Treat Prostate Cancer That Has Spread To Bones
Causes Of Prostatitis Prostate Pain Syndrome
The exact cause of chronic prostatitis can be caused by pelvic pain that occurs for more than 3 months with urinary tract infection. The pain can range from mild to severe and some possible risk factors for this condition are:
- Earlier episode of the infection of prostate gland
- Inflammation of the nerves that are around the prostate gland
- Backflow of urine into your prostate
- Nerve damages causing pain
- Weak pelvic floor muscles
- Irritable bowel syndrome and chronic fatigue syndrome
Continue reading this entire article to discover other common causes of prostatitis and then try to treat this syndrome as soon as possible.
Learn More: How To Cure A Urinary Tract Infection Naturally 8 Tips
Acute Prostatitis: Causes Symptoms And Diagnosis
What is acute prostatitis?
Acute prostatitis happens when your prostate gland becomes suddenly inflamed. The prostate gland is a small, walnut-shaped organ located at the base of the bladder in men. It secretes fluid that nourishes your sperm. When you ejaculate, your prostate gland squeezes this fluid into your urethra. It makes up a large portion of your semen.
Acute prostatitis is usually caused by the same bacteria that cause urinary tract infections or sexually transmitted diseases . Bacteria can travel to your prostate from your blood. It can enter your prostate during or after a medical procedure, such as a biopsy. It can also be caused by infections in other parts of your genitourinary tract.
If you have acute prostatitis, you may develop:
- chills
- pain above your pubic bone
- pain in your genitals, testicles, or rectum
Any bacteria that causes UTIs can cause prostatitis. Bacteria that commonly cause UTIs and prostatitis include:
- Proteus species
- Klebsiella species
- Escherichia coli
Some bacteria that cause STDs, such as chlamydia and gonorrhea, can also cause acute bacterial prostatitis. Other conditions that can lead to acute bacterial prostatitis include:
Factors that increase your risk of UTIs, STDs, and urethritis also increase your risk of acute prostatitis. For example, these risk factors include:
- not drinking enough fluids
- having unprotected vaginal or anal intercourse
Other risk factors include:
Read Also: Do Female Have Prostate
