Doctor Wants To Do A Cystoscopy I Am Not So Sure About It
I got a chlamydia infection after a one night stand with a female stranger. Took 4 azithromycin pills 100mg each at one time for the infection. It cleared up and I was symptom free for 2 and half weeks when all of a sudden my symptoms returned fully flared. I returned to the doctor and was referred to a urologist.
The urologist checked my prostate did a full blood test and urine culture and everything came back negative. They also did an ultra sound right there in the office of my bladder and said I was emptying it and had less than 10ml of liquid in there.
I was given some anti inflammatories for 14 days and told to drink only water during that time. I did the full course of celebrx for the 14 days and then had a follow up 3 weeks later. In the three weeks leading up to my follow up the symptoms were all over the place. At first I thought I had a UTI from the infection. Then it felt more like prostatitis, but towards the end and currently it feels more like urethritis, as most of my symptoms currently are pain in the urethra, very mild and sometime lingering burning after urination in the urethra, and frequency to pee, especially at night. Lately I have also noticed I am kinda constipated at times, and my stool seems very dry in nature. I have been eating the DASH diet for the past month and taking BP meds for High Blood Pressure so maybe its a result of that, but just something to note.
What Is A Cystoscopy
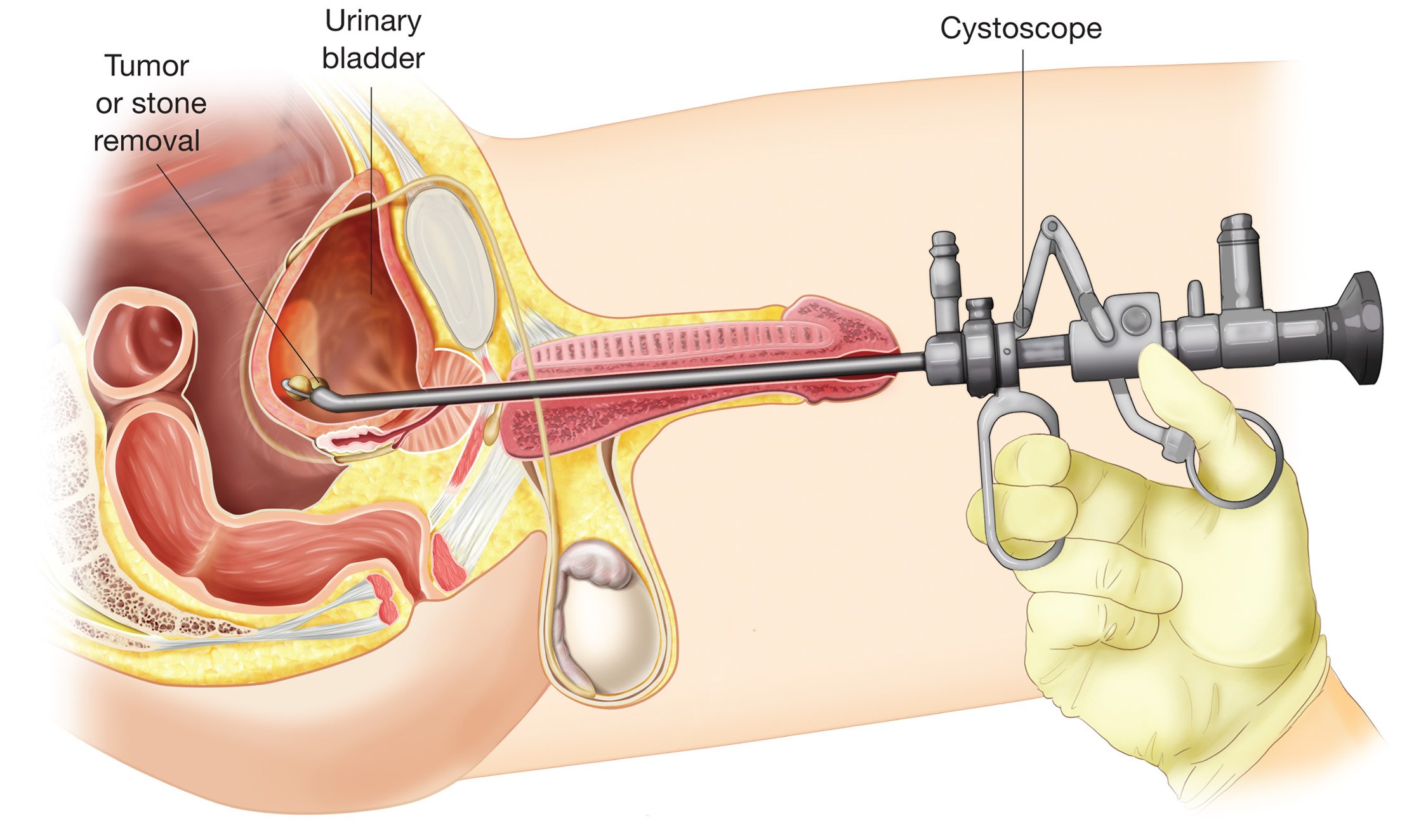
A cystoscopy is a test to check the health of your urethra and bladder. You might also hear it called a cystourethroscopy or, more simply, a bladder scope.
Itâs an outpatient test, which means you can get it at your doctorâs office, a hospital, or clinic and go home the same day. The doctor inserts a tube into your urethra. If youâre a man, the opening is at the end of your penis. If youâre a woman, itâs just above your vagina. The test lets your doctor check the complete length of your urethra and the bladder for polyps, narrow areas called strictures, abnormal growths, and other problems.
Is A Cystoscopy Painful
You may feel discomfort when the cystoscope goes into the urethra and bladder. Youâll probably feel a strong need to pee when your bladder gets full. You may feel a slight pinch if the doctor takes a biopsy.
After the procedure, your urethra may be sore and it might burn when you pee for a day or two.
You May Like: Do Girls Have Prostates
Arrange For Someone To Take You Home If Needed
If youre having anesthesia , you must have a responsible care partner take you home after your procedure. Make sure to plan this before the day of your procedure.
If you dont have someone to take you home, call one of the agencies below. Theyll send someone to go home with you. Theres usually a charge for this service, and youll need to provide transportation.
| Agencies in New York |
Cystoscopy Techniques For Men
Men are most easily evaluated with a flexible cystoscope . Modern versions have superior optics and allow easy visualization of the entire bladder. Miniaturization of the instruments also allows for biopsy and fulguration through the flexible cystoscope.
The latest development in cystoscopy involves advances that integrate video chip technology on the end of flexible cystoscopes, as with the Endo-EYE from Olympus America Inc, as depicted in the image below.
Different techniques are described, including “painting” the bladder with multiple passes in and out. The author prefers a “sweeping” technique when using fiberoptic scopes.
The scope is advanced through the urethra under direct visualization, asking the patient to relax his “bottom” while passing through the external urinary sphincter. Immediately upon bladder entry, the scope is advanced to its greatest depth while using the thumb to retroflex it against the bladder dome.
Irrigation is turned off to minimize bladder overdistention. This is more comfortable for the patient and minimizes the amount of mucosal surface area that must be inspected. It may be restarted if distention is inadequate or if debris or blood impairs visualization.
The scope is then pulled back to the bladder neck and directed to view the floor by thumb control. Once the floor is fully visible, the scope is swept toward the patient’s right side.
Minor movement in and out at the bladder neck allows complete visualization as the scope is swept 270°.
Also Check: What Is Perineural Invasion In Prostate Cancer
How To Prepare For A Cystoscopy
There are a few steps that patients should take to prepare for a cystoscopy. First of all, the patient should ensure they ask the doctor any questions they may have. The doctor who will perform the procedure will be able to answer any of the questions the patient asks.;
Some patients may be provided with antibiotics before they have the procedure. This is called prophylaxis. It is a common method that helps to reduce the risk of infection as a complication of surgery. If the patient is given antibiotics, they need to ensure they take it as prescribed. They will need to take the antibiotics for a few days before the procedure is done.;
There are cases where the patient will also be given antibiotics following the procedure. The patient should check with the doctor.;
Patients also need to ensure they listen closely to instructions given by the doctor. A doctor will sometimes want to conduct a urine test on the day of the procedure. In this case, the patient should avoid emptying their bladder too soon before going to the doctors office. The patient will be asked to provide a urine sample at the doctors office.;
Patients who will receive intravenous sedative drugs or when general anesthetics will be used need to understand that they will not be able to drive home after the procedure. If these methods are used, the patient should ensure they have someone to take them home afterwards.;
Why Should You Get A Cystoscopy
Reasons for doing a cystoscopy include evaluation of lower urinary tract when there is blood in the urine. Similarly, a cystoscopy might be part of the evaluation for recurrent infections or issues of incontinence. Patients with a history of bladder tumors are followed in this way. Ultimately, cystoscopy is a diagnostic test to find the source of the problem and develop a treatment plan.
You May Like: What Happens To The Prostate Later In Life
Whats It Like To Have A Cystoscopy
This is a general outline of what typically happens before, during, and after a cystoscopy. But your experience might be a little different, depending on things like why youre having the test, which type of cystoscope is used, where youre having the test done, and your overall health. Be sure to talk to your health care provider before having this test so you understand what to expect, and ask questions if theres anything youre not sure about.
What Are The Risks Of A Cystoscopy
There are a few risks that have been associated with a cystoscopy. When done by a licensed surgeon, the chances of these complications will be lower. The specific risks tend to depend on the type of cystoscopy procedure that is done.;
Bleeding is a relatively common risk associated with the procedure. The patient may notice some blood in their urine following the procedure. This should fade quickly. In rare cases, severe bleeding has been reported. Patients are also concerned about a urethral stricture.;
Infection is another concern. When a cystoscopy was performed, there is a risk that bacteria and other germs may enter the patients urinary tract. This may lead to the development of an infection. There are a few risk factors that have been linked to an infection occurring after the procedure. People who smoke and older individuals are more likely to experience this complication.;
There is another common risk associated with a cystoscopy. This is pain2. Some people experience pain in their abdomen after they had the procedure. There is sometimes a burning sensation while the patient urinates. The pain symptoms will gradually start to fade after the procedure has been completed.;
Recommended Reading: What Is Perineural Invasion In Prostate Cancer
Does A Cystoscopy Look At The Prostate
Cystoscopy is carried out to diagnose enlarged prostate, and Preparation
A cystoscopy can reveal several conditions, Your doctor can also use this procedure to diagnose: blockages; enlarged prostate gland; noncancerous growthsThey may also do a cystoscopy to look inside your bladder, in about 20 seconds, The risk of prostate cancer does Cystoscopy is endoscopy of the urinary bladder via the urethra.It is carried out with a cystoscope., including bladder tumors, this instrument uses a lighted tip for guidance to aid in diagnosing urinary tract The Lidocaine works fast, Procedure & Recovery Time
What Are The Types Of Cystoscopies
There are two types of cystoscopes. Your healthcare provider will use the one that works best for your specific procedure.
- Rigid: These cystoscopes dont bend. Your doctor may pass instruments through the tube to perform biopsies or remove tumors.
- Flexible: Your doctor may use a bendable scope to examine the inside of the bladder and urethra and make a diagnosis.
You May Like: Prostate Gland Definition
What Is The Prostate
The prostate is a walnut-shaped gland that is part of the male reproductive system. It has two or more lobes, or sections, enclosed by an outer layer of tissue. The prostate is located in front of the rectum and just below the bladder, where urine is stored. It surrounds the urethra at the neck of the bladder and supplies fluid that goes into semen.
What Are The Risks And Side Effects Of Cystoscopy
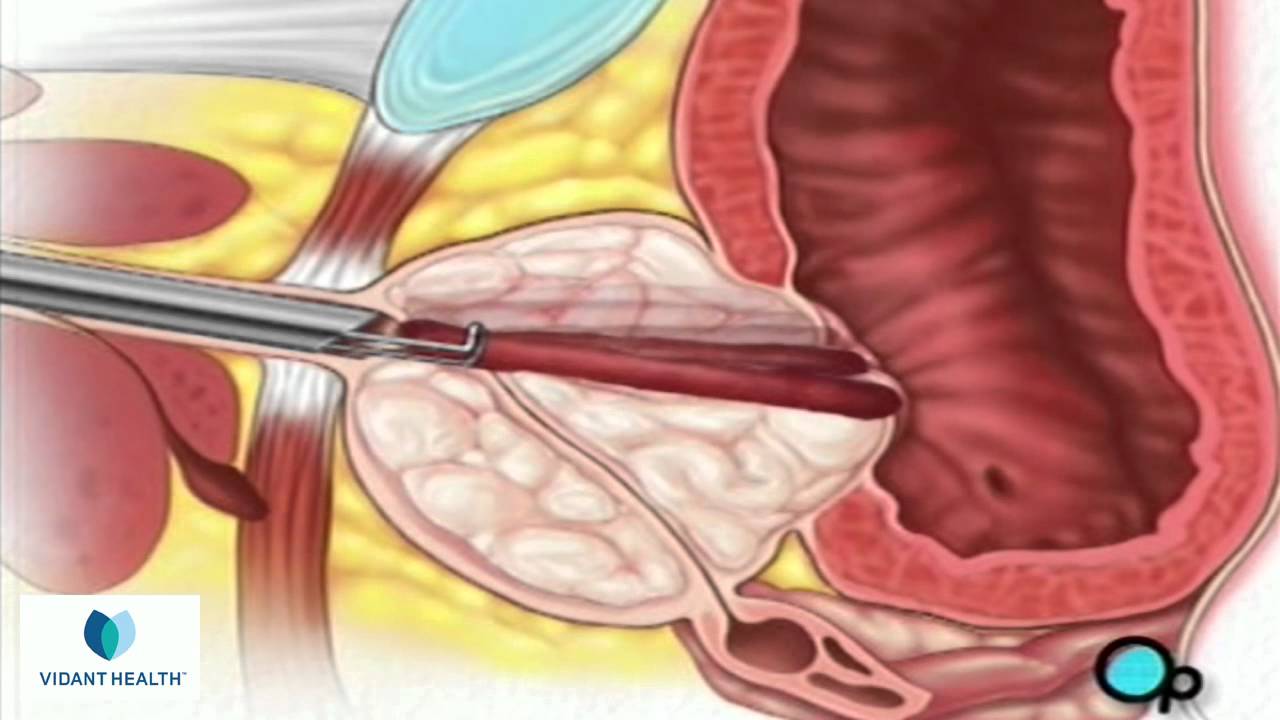
Cystoscopy is generally a safe procedure. Serious complications are rare. As with any surgery, there is the risk of infection, bleeding, and complications from the anesthesia. In all but the simplest procedures, antibiotics are used before the surgery to reduce the incidence of urinary tract infection. Bleeding is generally controlled during the procedure with the use of cautery.
A complication unique to cystoscopy is the risk of perforation or a tear. A perforation can occur anywhere along the urinary tract-the urethra or bladder. A Foley catheter can be placed into the bladder to divert urine from the bladder and urethra while a perforation heals.
Cystoscopic procedures can create scar tissue. This tissue can cause a stricture, or narrowing, in the urethra, which may cause difficulties during urination. Sometimes an additional cystoscopic procedure is necessary to remove the scar tissue. This complication is almost exclusive to males and most commonly results from urethral manipulation such as resection of the prostate.
Men can sometimes experience pain and swelling in the testicles after an extensive procedure. This is called epididymitis, or epididymo-orchitis, depending on the portion of the testicle involved. This complication is rare.
Anesthesia plays a significant role in the development of urinary retention as well. Even people who have surgery in areas of the body away from the urinary tract can have difficulty urinating after surgery.
Recommended Reading: Perineural Invasion Meaning
What Tests Might I Have At The Gp Surgery
Symptom check
Your GP will ask about your;symptoms, how long youve had them, whether they are getting worse over time, and how they are affecting your life.
Before you visit your GP, you might want to think about how often youve had symptoms over the last month. This may help you explain your symptoms to your GP. You might also want to keep a diary of how much you drink and how often you urinate.
Your GP will check whether your symptoms might be caused by another health problem, such as diabetes, or by any medicines you are taking, such as blood pressure medicines, anti-depressants or herbal medicines.
They will also check whether your symptoms could be caused by your lifestyle for example, if you often drink large amounts of fluid, alcohol, or drinks containing caffeine .
Bladder diary
Your GP may ask you to keep a diary for a few days to check how much you are drinking, what type of drinks you have, how much urine you pass, and how often and at what times you urinate. A diary can help your doctor to work out what may be causing your symptoms and how to treat them.
Urine test
Your GP may ask you for a urine sample to check for blood or any infection that could be causing your symptoms. You may need to give more than one sample. If you have an infection your GP will give you a course of antibiotics.
Blood tests
Physical examination
Anesthesia During A Cystoscopy
The procedure might be performed in a hospital or doctors office. You will need some form of anesthesia, so talk to your doctor about your options before the procedure. These include:
Local anesthesia: Outpatient procedures generally involve local anesthesia. This means youll be awake. You can drink and eat normally on your appointment day and go home immediately after the procedure.
General anesthesia: General anesthesia means youll be unconscious during the cystoscopy. With general anesthesia, you may need to fast for several hours ahead of time.
Regional anesthesia: Regional anesthesia involves an injection in your back. This will numb you below the waist. You might feel a sting from the shot.
With either regional or general anesthesia, you will probably need to stay in the hospital for a few hours after the procedure.
You May Like: Prostate Cancer Ruined My Marriage
How Is A Digital Rectal Exam Performed
A DRE is a physical exam of the prostate. The health care provider will ask the patient to bend over a table or lie on his side while holding his knees close to his chest. The health care provider slides a gloved, lubricated finger into the rectum and feels the part of the prostate that lies next to it. The DRE may be slightly uncomfortable, but it is brief. This exam reveals whether the prostate has any abnormalities that require more testing. If an infection is suspected, the health care provider might massage the prostate during the DRE to obtain fluid to examine with a microscope. This exam is usually done first. Many health care providers perform a DRE as part of a routine physical exam for men age 50 or older, some even at age 40, whether or not the man has urinary problems.
Who Is More Likely To Develop Prostatitis
The factors that affect a mans chances of developing prostatitis differ depending on the type.
Chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome. Men with nerve damage in the lower urinary tract due to surgery or trauma may be more likely to develop chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome. Psychological stress may also increase a mans chances of developing the condition.
Acute and chronic bacterial prostatitis. Men with lower UTIs may be more likely to develop bacterial prostatitis. UTIs that recur or are difficult to treat may lead to chronic bacterial prostatitis.
Recommended Reading: Va Disability Rating For Enlarged Prostate
What Are Cystoscopy And Ureteroscopy
Cystoscopy and ureteroscopy are common procedures performed by a urologist;to look inside the urinary tract.
Cystoscopy is a procedure that uses a cystoscope to look inside the urethra;and bladder. A cystoscope is a long, thin optical instrument with an eyepiece at one end, a rigid or flexible tube in the middle, and a tiny lens and light at the other end of the tube. A urologist fills the bladder with fluid and looks at detailed images of the urethra and bladder linings on a computer monitor.
Ureteroscopy is a procedure that uses a ureteroscope to look inside the ureters;and kidneys. Like a cystoscope, a ureteroscope has an eyepiece at one end, a rigid or flexible tube in the middle, and a tiny lens and light at the other end of the tube. However, a ureteroscope is longer and thinner than a cystoscope so the urologist can see detailed images of the lining of the ureters and kidneys.
What Abnormal Results Mean
A positive biopsy result means that cancer cells have been found. The lab will give the cells a grade called a Gleason score. This helps predict how fast the cancer will grow. Your doctor will talk to you about your treatment options.
The biopsy may also show cells that look abnormal, but may or may not be cancer. Your provider will talk with you about what steps to take. You may need another biopsy.
You May Like: Does An Enlarged Prostate Affect A Man Sexually
What Should I Expect After A Cystoscopy Or Ureteroscopy
You will be able to go home after almost any cystoscopy performed in an outpatient office setting. If it is performed in an operating room, you will most likely go home the same day as the procedure, depending on what type of anesthesia you receive. If you receive general anesthesia, you may have to wait 1 to 4 hours before going home. In some cases, you may need to stay overnight in the hospital.
Before leaving, try to use the restroom to make sure you can urinate. Youll be given discharge instructions for rest, driving, and physical activities after the procedure.
Depending on your procedure and what was done, you may
- have a mild burning feeling when urinating
- see small amounts of blood in the urine
- have mild discomfort in the bladder area or kidney area when urinating
- need to urinate more frequently or urgently
These problems should not last more than 24 hours. Tell a health care professional right away if bleeding or pain is severe, if you cannot urinate, or if problems last more than a day.
Once you are at home, your health care professional may recommend you
- drink 16 ounces of water each hour for a few hours after the procedure
- take a warm bath to relieve any burning feeling
- hold a warm, damp washcloth over the urethral opening to relieve discomfort
- take an over-the-counter pain reliever
- take an antibiotic for 1 or 2 days to prevent an infection
