Gleason Prostate Cancer Score
1960s as a way to measure how aggressive your prostate cancer may be.
A pathologist determines your Gleason score by looking at a biopsy of your prostate tissue under a microscope. They grade the cells in the biopsy on a scale of 1 to 5. Grade 1 cells are healthy prostate, whereas grade 5 cells are highly mutated and dont resemble healthy cells at all.
The pathologist will calculate your Gleason score by adding together the number of the most prevalent type of cell in the sample and the second most prevalent type of cell.
For example, if the most common cell grade in your sample is 4 and the second most common is 4, you would have a score of 8.
A Gleason score of 6 is considered low-grade cancer, 7 is intermediate, and 8 to 10 is high-grade cancer.
Survival Rates For Prostate Cancer
Survival rates can give you an idea of what percentage of people with the same type and stage of cancer are still alive a certain amount of time after they were diagnosed. These rates cant tell you how long you will live, but they may help give you a better understanding of how likely it is that your treatment will be successful.
Keep in mind that survival rates are estimates and are often based on previous outcomes of large numbers of people who had a specific cancer, but they cant predict what will happen in any particular persons case. These statistics can be confusing and may lead you to have more questions. Ask your doctor, who is familiar with your situation, how these numbers may apply to you.
How Long Does Someone With Stage 4 Bladder Cancer Live
The table below shows life expectancies by age and race according to the National Cancer Institutes SEER database. The SEER database contains information from population-based cancer registries covering approximately 28% of the US population.
Life Expectancy Age All Races Males Females 10 73.3 61.9 80.6 20 56.3 46.4 63.2 30 41.5 32.5 48.5 40 28.6 21.3 34.1 50 17.7 12.1 21 65 7.2 10
The table above shows life expectancies after a stage 4 bladder cancer diagnosis by age group and gender according to the National Cancer Institutes SEER database . People diagnosed with bladder cancer can live for many years after their diagnosis. The average life expectancy after a stage 4 bladder cancer diagnosis is 9 years for males and 15 years for females.
The life expectancy of someone diagnosed with bladder cancer at age 65 is 10 years.
Bladder Cancer Survival Rates by Stage
The survival rate for someone with stage 4 bladder cancer is measured from the date of their original bladder cancer diagnosis. This does not change even if the person undergoes treatment and the cancer returns later.
The 5-year relative survival rate of stage 3 bladder cancer is 88%, and the 5-year relative survival rate of stage 4 bladder cancer is 16%. The survival rates are for people diagnosed between 2008 and 2012. The overall survival rate of all people diagnosed with bladder cancer is 67%.
Survival Rate by Stage Stage 0 Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 Stage 4 5-Year Relative Survival Rate 100% 90.4% 73.7% 58.
Don’t Miss: Prostate Cancer Vs Breast Cancer
The Tnm System For Prostate Cancer Stages
As they do for most cancers, doctors use the TNM system to describe prostate cancer stages. The system uses three different aspects of tumor growth and spread:
- Tumor. Whatâs the size of the main area of prostate cancer?
- Nodes. Has it spread to any lymph nodes? If so, how far and how many?
- Metastasis. How far has the prostate cancer spread?
Dont Miss: Nerve Regeneration After Prostate Surgery
Survival Rates For Bladder Cancer
Survival rates can give you an idea of what percentage of people with the same type and stage of cancer are still alive a certain amount of time after they were diagnosed. They cant tell you how long you will live, but they may help give you a better understanding of how likely it is that your treatment will be successful.
Keep in mind that survival rates are estimates and are often based on previous outcomes of large numbers of people who had a specific cancer, but they cant predict what will happen in any particular persons case. These statistics can be confusing and may lead you to have more questions. Talk with your doctor about how these numbers may apply to you, as he or she is familiar with your situation.
You May Like: Does An Enlarged Prostate Make It Hard To Poop
Outlook For Men With Localised Prostate Cancer
Most localised prostate cancer is slow-growing and may not need treatment or shorten a mans life. For many men who have treatment for localised prostate cancer, the treatment will get rid of the cancer. For others, treatment may be less successful and the cancer may come back. If this happens, you might need further treatment.
What Is Stage 4 Bladder Cancer
Being diagnosed with bladder cancer can be overwhelming, especially if its stage 4.
Stage 4 bladder cancer is the most advanced stage and carries the worst prognosis. Many cancer treatments will be both difficult and challenging.
However, treatment can reduce or even eliminate your symptoms and help you live a longer, more comfortable life.
Its important to consider the pros and cons of treating stage 4 bladder cancer because treatments come with side effects and risks.
Symptoms of bladder cancer can include:
- blood or blood clots in your urine
- pain or burning during urination
- frequent urination
- needing to urinate at night
- needing to urinate but not being able to
- lower back pain on one side of the body
These symptoms commonly lead to a diagnosis, but they arent unique to stage 4 bladder cancer.
Stage 4 bladder cancer is also called metastatic bladder cancer. This means the cancer has spread outside of the bladder into other parts of the body.
People with metastatic cancer may experience symptoms relating to where the cancer has spread. For example, if a persons bladder cancer has spread to their lungs, they may experience chest pain or increased coughing.
Metastatic bladder cancer is difficult to cure because it has already traveled to other parts of the body. The later youre diagnosed and the farther the cancer has traveled, the less chance that your cancer will be cured.
The 5-year survival rate is the rate of surviving for 5 years after a cancer diagnosis.
You May Like: How To Hit Your Prostate
Survival By Disease Recurrence
If a man develops an elevated PSA level after cancer surgery, then the disease is viewed as recurrent.
The number of lymph nodes at the time of prostatectomy can influence the risk of recurrence. One study suggests the removal of a large number of nodes is associated with an improvement in odds of recurrence, but this doesn’t appear to impact overall survival.
But disease recurrence doesn’t always influence survival times. If a recurrence does occur, the 15-year survival rate at the time of diagnosis may be as high as 94% in those with low-risk recurrence.
The main factors influencing survival rates are:
- The Gleason score
- The PSA doubling time
- Whether the recurrence occurred within three years or after three years
A recurrence that occurs within three years reduces survival rates by anywhere from 15 to 20%and even more, if the doubling time is short.
What Is Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer
Muscle invasive bladder cancer is a cancer that spreads into the detrusor muscle of the bladder. The detrusor muscle is the thick muscle deep in the bladder wall. This cancer is more likely to spread to other parts of the body.
In the U.S., bladder cancer is the third most common cancer in men. Each year, there are more than 83,000 new cases diagnosed in men and women. About 25% of bladder cancers are MIBC. Bladder cancer is more common as a person grows older. It is found most often in the age group of 75-84. Caucasians are more likely to get bladder cancer than any other ethnicity. But there are more African-Americans who do not survive the disease.
What is Cancer?
Cancer is when your body cells grow out of control. When this happens, the body cannot work the way it should. Most cancers form a lump called a tumor or a growth. Some cancers grow and spread fast. Others grow more slowly. Not all lumps are cancers. Cancerous lumps are sometimes called malignant tumors.
What is Bladder Cancer?
When cells of the bladder grow abnormally, they can become bladder cancer. A person with bladder cancer will have one or more tumors in his/her bladder.
How Does Bladder Cancer Develop and Spread?
The bladder wall has many layers, made up of different types of cells. Most bladder cancers start in the urothelium or transitional epithelium. This is the inside lining of the bladder. Transitional cell carcinoma is cancer that forms in the cells of the urothelium.
Also Check: Antihistamine Safe For Enlarged Prostate
Growth Patterns In Grade Group 5 Prostate Cancer
Individual growth patterns were specifically analyzed in 119 men with Grade Group 5 disease, which had Gleason pattern 5 as primary or secondary pattern by definition. This group encompassed 90 men with Gleason score 4+5, 28 with 5+4 and 1 with 5+5. Cribriform architecture was present in 102 and large cribriform growth in 52 tumors. Single cells/cords were present in 115 , small solid nests in 21 , medium to large solid fields in 43 and comedonecrosis in 17 cases. Comedonecrosis occurred within medium to large solid fields in 12 cases and in invasive cribriform carcinoma in 5 tumors. Out of 102 Grade Group 5 patients with cribriform architecture, 43 had concomitant medium to large solid fields and 59 did not. All tumors with medium to large solid fields and comedonecrosis were accompanied by cribriform architecture. Clinicopathological parameters of Grade Group 5 patients are shown in Table .
Table 2 Characteristics of Grade Group 5 patients stratified for presence of cribriform and solid growth patterns.Fig. 2: Clinical outcome of Grade Group 5 prostate cancer patients without cribriform and solid pattern , with cribriform but no solid pattern , and with both cribriform and solid pattern .
Grade Group 5 patients without cribriform and solid pattern had significantly better biochemical recurrence-free survival and, metastasis-free survival , while disease-specific survival did not reach significance .
Staging And Grading For Stage 4 Cancer
Most cancers are staged using some form of the TNM system. Doctors may also use the TNM system to help determine the extent of certain cancers in each stage. The TNM system stands for:
- T , or the size of the original tumor
- N , or whether the cancer is present in the lymph nodes
- M , or whether the cancer has spread to other parts of the body
Not all cancers are staged using the TNM system, though. Some cancers, especially liquid cancers, are staged through different established protocols. The Binet and Rai systems, for example, are used to stage certain types of leukemia. Female reproductive system cancers, such as cervical cancer, are staged with a separate staging system created by the International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics .
As your care team gathers information about your cancer for the purposes of staging, they may need to order several tests, including:
Your care team may likely also need to perform a biopsy, a procedure that involves removing a sample of cells and analyzing it for signs of cancer. Imaging scans may be able to tell your care team where your cancer is, but looking at the cancer cells specifically tell them how fast they are likely to growor what grade they are.
Grading is different from staging and is done for most, but not all, cancers.
The grade of your cancer is part of how your cancer care team stages your cancer and determines your prognosis, or outlook.
Dont Miss: Supplements To Shrink The Prostate
Recommended Reading: How Long Does A Prostate Mri Take
Stage 2 Breast Cancer
In stage 2 breast cancer, the tumor measures between 2 cm and 5 cm, or the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes under the arm on the same side as the breast cancer. The cancer cells have spread beyond the original location and into the surrounding breast tissue, and a tumor may be detected during a breast self-exam as a hard lump.
Also Check: Prostate Cancer Statistics Worldwide 2020
Stages Of Prostate Cancer
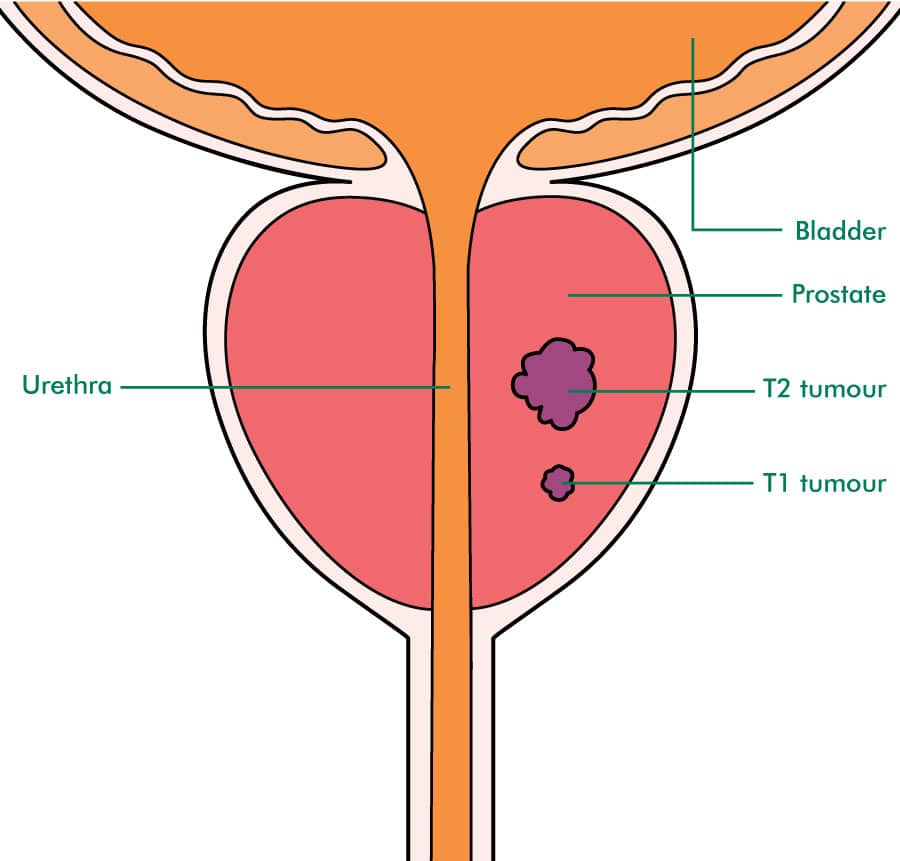
Staging describes or classifies a cancer based on how muchcancer there is in the body and where it is when first diagnosed. This is oftencalled the extent of the cancer. Informationfrom tests is used to find out the size of the tumour, which parts of the organhave cancer, whether the cancer has spread from where it first started andwhere the cancer has spread. Your healthcare team uses the stage to plantreatment and estimate the outcome . The following staginginformation is for adenocarcinoma, which makes up 95% of all prostate cancers.Other types of prostate cancer are staged differently.
The most common staging system for prostate cancer is the AJCC/UICCTNM system. Doctors often also use a simple staging system that describeswhether the cancer has spread and if so, where it has spread. Doctors furtherclassify prostate cancers into risk groups based on whether they are likely to comeback .
You May Like: Is Cialis Good For Enlarged Prostate
Also Check: Can Young Men Get Prostate Cancer
Stage 1 Prostate Cancer
Stage 1 is the least advanced form of prostate cancer. Cancer in this stage is small and hasnt spread past the prostate gland. Its characterized by a PSA of less than 10 ng/mL, a grade group score of 1, and a Gleason score of 6.
Stage 1 prostate cancer has a 5-year survival rate of nearly 100 percent.
Gleason Score Vs Grade Groups
The International Society of Urological Pathology released a revised prostate cancer grading system in 2014. The grade group system seeks to simplify Gleason scores and give a more accurate diagnosis.
One of the major problems with the Gleason score is that some scores can be made up in different ways. For example, a score of 7 can mean:
- 3 + 4. The 3 pattern is the most common in the biopsy and 4 is the second most common. This pattern is considered favorable intermediate risk.
- 4 + 3. The 4 pattern is the most common in the biopsy and 3 is the second most common. This pattern is considered unfavorable and may mean local or metastatic spread.
So, although both situations give a Gleason score of 7, they actually have very different prognoses.
Heres an overview of how the two grading systems compare:
| Cancer grade | |
|---|---|
| grade group 5 | 910 |
Not all hospitals have switched to the grade group system. Many hospitals give both grade group and Gleason scores to avoid confusion until grade groups become more widely used.
You May Like: Is Sex Healthy For Your Prostate
What Are Prostate Cancer Survival Rates By Stage
Staging evaluation is essential for the planning of treatment for prostate cancer.
- A basic staging evaluation includes the patient examination, blood tests, and the prostate biopsy including ultrasound images of the prostate.
- Further testing and calculations may be performed to best estimate a patient’s prognosis and help the doctor and patient decide upon treatment options.
Prognosis refers to the likelihood that cancer can be cured by treatment, and what the patient’s life expectancy is likely to be as a consequence of having had a prostate cancer diagnosis.
If cancer is cured, your life expectancy is what it would have been had you never been diagnosed with prostate cancer. If cancer cannot be cured due to it recurring in distant locations as metastases, or recurs either locally or in an area no longer able to be treated in a curative manner, then estimates can be made of what is likely to be your survival-based again on group statistics for people who have been in the same situation.
Nomograms are charts or computer-based tools that use complex math from the analysis of many patients’ treatment results.
The prognosis for prostate cancer varies widely and depends on many factors, including the age and health of the patient, the stage of the tumor when it was diagnosed, the aggressiveness of the tumor, and cancer’s responsiveness to treatment, among other factors.
The 5 and 10-year survival rate of prostate cancer chart
| Stage and 5-Year Survival |
|---|
Surgically Removing The Prostate Gland
A radical prostatectomy is the surgical removal of your prostate gland. This treatment is an option for curing prostate cancer that has not spread beyond the prostate or has not spread very far.
Like any operation, this surgery carries some risks, such as urinary incontinence and erectile dysfunction.
In extremely rare cases, problems arising after surgery can be fatal.
It’s possible that prostate cancer can come back again after treatment. Your doctor should be able to explain the risk of your cancer coming back after treatment, based on things like your PSA level and the stage of your cancer.
Studies have shown that radiotherapy after prostate removal surgery may increase the chances of a cure, although research is still being carried out into when it should be used after surgery.
You may want to ask your doctors about storing a sperm sample before the operation so it can be used later for in vitro fertilisation .
You May Like: How Fast Does Prostate Cancer Spread
Prostate Cancer Is Common With Aging
After skin cancer, prostate cancer is the most common cancer in men. About 1 in 7 men will be diagnosed with prostate cancer in their lifetime. And these are just the men who are diagnosed. Among very elderly men dying of other causes, a surprising two-thirds may have prostate cancer that was never diagnosed.
Only 1 in 36 men, though, actually dies from prostate cancer. That’s because most prostate cancers are diagnosed in older men in whom the disease is more likely to be slow-growing and non-aggressive. The majority of these men eventually pass away from heart disease, stroke, or other causes — not their prostate cancer.
