When To Seek Medical Care
A person may have urinary symptoms unrelated to prostatitis that are caused by bladder problems, UTIs, or benign prostatic hyperplasia. Symptoms of prostatitis also can signal more serious conditions, including prostate cancer.
Men with symptoms of prostatitis should see a health care provider.
Men with the following symptoms should seek immediate medical care:
- complete inability to urinate
- great discomfort or pain in the lower abdomen and urinary tract
Treatments That A Specialist May Suggest
Various treatments have been tried for chronic prostatitis. They may benefit some people but so far there are few research studies to confirm whether they help in most cases. They are not ‘standard’ or routine treatments but a specialist may advise that you try one.
For chronic bacterial prostatitis, possible treatments may include the following:
- A longer course of antibiotics. If the specialist suspects that you have chronic bacterial prostatitis and your symptoms have not cleared after a four-week course of antibiotics, they may suggest a longer course. Sometimes a course of up to three months is used.
- Removal of the prostate may be considered if you have small stones in the prostate. It is not clear how much this may help but it has been suggested that these small stones may be a reason why some people have recurrent infections in chronic bacterial prostatitis. However, this is not commonly carried out and is not suitable in everyone. Your specialist will advise.
For chronic prostatitis/CPPS, possible treatments may include the following:
Antibiotics For Acute Bacterial Prostatitis: Which Agent And For How Long
Eric A. Dietrich, PharmD, BCPS, and Kyle Davis, PharmD, BCPS
Citation:Dietrich EA, Davis K. Antibiotics for acute bacterial prostatitis: which agent, and for how long? Consultant. 2017 57:564-565.
Acute bacterial prostatitis is an infection of the prostate that is most commonly seen in older men. Approximately 8% of men will experience prostatitis-like symptoms, but the overall incidence of acute prostatitis is unknown.1 Acute bacterial prostatitis can be diagnosed by way of a history and physical examination.1 Symptoms commonly mirror those of a lower urinary tract infection , and patients may or may not present with fever. Evaluation also should include urinalysis and cultures, as well as prostatic fluid cultures if needed.
Antimicrobial therapy is the cornerstone of treatment for bacterial prostatitis. Pharmacotherapy should include agents with activity against traditional UTI-causing organisms. Special attention should be given to tissue penetration into the prostate and the duration of therapy.2 Which antibiotics achieve adequate penetration, and how long should clinicians treat patients with acute bacterial prostatitis?
Patient Case
Don’t Miss: Levitra For Bph
Is Prostatitis A Sexually Transmitted Disease
Yes, prostatitis can be contracted through sex, so the more sexual partners a man has, the higher his odds of developing the condition. 34567
Interestingly, Trichomonas vaginalis, a parasite and STD, has been found in prostate biopsies of men with prostatitis, and although it seems that E. Coli is a much more regular culprit, the prostates susceptibility to Trichomonas vaginalis colonization has been linked to zinc levels. The prostate is the number one home for zinc in a mans body, and when levels get low, studies have shown these types of pathogens can take a greater foothold.
Mineral deficiencies are common in the U.S., which means supplementing with small amounts of zinc to see whether conditions improve could be worthwhile. As far as food is concerned, pumpkin seeds and oysters are both high in zinc.
As an added benefit, zinc supplementation has also shown some promise in maintaining the cell lining of the gut, which can prevent or help to heal leaky gut, a condition that often accompanies prostatitis, and that is marked by a breakdown of the epithelial wall of the gut lining, which allows pathogens and undigested food particles to enter the blood stream. 89 I will touch more on leaky gut later in this post.
What Are Prostate Infections And Prostatitis

The prostate gland is a part of a man’s reproductive system, secreting fluids that help transport sperm. The gland lies just below the bladder and surrounds the urethra .
Prostate infections may irritate the prostate and cause inflammation and swelling of the gland. Prostate infections occur most often in men aged 30-50 years but can occur in older men. Unfortunately, many people equate the terms prostate infection and prostatitis, but prostate infections comprise only two of the four major classifications of the term “prostatitis,” and infectious types comprise only a few of the total number of prostatitis diagnosed patients.
The National Institutes of Health consensus panel has designated four types of prostatitis classifications.
The NIH has established extensive criteria for chronic pelvic pain syndrome that excludes infection and other problems and is as follows:
Inclusion Criteria
- male, at least age 18
- pain or discomfort in the pelvic area for at least 3 months
Exclusion Criteria
This classification system is important to understand because about 90% of men with prostatitis symptoms are diagnosed with chronic pelvic pain syndrome and, by definition, do not have infectious prostatitis.
Stress and depression are common in men with chronic infectious prostatitis.
Also Check: Does Prostatitis Go Away Without Treatment
A Healthy Lifestyle Can Help Relieve Prostatitis
Prostatitis is, by definition, inflammation of the male prostate gland. The inflammation can be due to a bacterial or fungal infection or of an unknown source.
While I found no specific studies of the influence of obesity on the risk for prostatitis, several studies support obesity as a risk factor for both and prostate cancer, and men with BPH frequently develop prostatitis.
Obesity is known to alter endocrine status, increase oxidative stress, and contribute to increased inflammation. Lifestyle issues, such as poor diet, lack of exercise, stress, and other issues are also contributors. 8
Another risk factor for the development of prostatitis is diabetes. It is well known that diabetes is associated with ED and BPH, both of which are common in older men. Obese men with high blood sugar levels seem to have a high risk of prostatitis.
There are many conditions, both dietary and lifestyle, that can negatively alter the overall health of the body and increase systemic inflammation. Chronic nonbacterial prostatitis affects around 10 to 15 percent of men in the United States, most of them over the age of 50.
Any man experiencing chronic nonbacterial prostatitis, should take a hard look at his diet and lifestyle and take steps to decrease his inflammatory loading. Bacterial prostatitis should be evaluated by a urologist, especially if it is associated with a UTI.
Read Also: How To Massage A Mans Prostate
How Long Does It Take For Cipro To Help Prostatitis
- Asked
- 6 Mar 2011 by gobo
I would have thought you would have been on antibioitics for more than 3 days. I was always under the understanding that it was 10 days usually. I may have it wrong as I know for some of the newer drugs it 1 pill a day for 5 days. At any rate you are still having the same symptoms, so I would call or make an appointment with your physician. I think you need to let them know what’s happening NOW. They make have you come in, or change or increase your meds. Good luck to you. I know how painful this can be because my hubby went thru it for quit some time.
+0Nige820
If you have a genuine infection in the prostate the ciprofloxacin is about the best overall antibiotic to knock the bugs on the head and actually penetrate the prostate. If there is no infection, you may have Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome . I went out to California from the UK for treatment in his clinic and would highly recommend it. However, if you do have an infection then you’ll need to be on 500mg of cipro twice a day for three weeks, followed by 250mg twice a day for a further three weeks. Don’t expect any drastic improvements straight away and definitely do not cut the dose short.
Nige820+0Jack55+0
You May Like: Do Females Have Prostate Cancer
Prostate Infection Risk Factors
Yes, there are certain factors that put a person in the risk zone of prostate infection. For instance, consuming inadequate water is said to increase the chances of contracting prostate infection. With less water intake, the body finds it difficult to flush off bacteria from the urinary system. Hence, drinking 6-8 glasses of water everyday is an easy way to minimize the risk of prostate infection. The incidence of getting this infection also increases in people suffering from sexually transmitted disease. So, adhering to precautionary measures such as using condoms during intercourse or avoiding sexual contact from infected partner could actually help to keep prostate infection at bay. A physical injury that affects the groin area too can increase the risk of prostatitis
Make Some Lifestyle Changes
There are a number of things you can try that other men have found helpful. You might want to plan your day more, to allow for things like toilet trips. Trying different things can help you feel more in control, and that you are actively doing something to improve your health. If one thing doesnt work, try something else. Here are some suggestions.
- Watch what you drink. Drink plenty of fluids about six to eight glasses of water a day. And cut down on fizzy drinks, artificial sweeteners, alcohol and drinks that contain caffeine as these can irritate the bladder and make some urinary problems worse.
- Watch what you eat. Some foods may make your symptoms worse. Try to work out what these are so you can avoid them. Theres some evidence that spicy foods can make the symptoms of CPPS worse.
- Avoid cycling. Its a good idea to avoid activities that put pressure on the area between your back passage and testicles , such as cycling. They can make symptoms worse. If you want to keep cycling, you could try using a different saddle, such as one made from gel.
- Keep a diary. This can help you spot things that make your symptoms worse, and can be a useful way of showing your doctor what youre experiencing. Record things like food, drink, exercise, how stressed you feel and your symptoms.
Don’t Miss: Prostatitis Side Effects
Who Is More Likely To Develop Prostatitis
The factors that affect a mans chances of developing prostatitis differ depending on the type.
Chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome. Men with nerve damage in the lower urinary tract due to surgery or trauma may be more likely to develop chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome. Psychological stress may also increase a mans chances of developing the condition.
Acute and chronic bacterial prostatitis. Men with lower UTIs may be more likely to develop bacterial prostatitis. UTIs that recur or are difficult to treat may lead to chronic bacterial prostatitis.
Why Does It Take So Long For Antibiotics To Cure A Prostate Infection
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
Similar questions
You May Like: How To Treat Prostate Cancer That Has Spread To Bones
Recommendations For A General Approach
Although evidence to support them is scarce, the following recommendations are offered. If the history and physical examination suggest prostatitis, physicians may consider a diagnostic test, such as the four-glass test or the PPMT. In most cases, empiric antibiotic therapy is reasonable whether or not the diagnostic test proves a bacterial cause. Common choices include TMP-SMX, doxycycline or one of the fluoroquinolones. Treatment is often recommended for four weeks, although some clinicians use shorter courses. Physicians should encourage hydration, treat pain appropriately and consider the use of NSAIDs, an alpha-blocking agent, or both. If symptoms persist, a more thorough evaluation for CNP/CPPS should be pursued. Some patients may need several trials of different therapies to find one that alleviates their symptoms.
The term prostatitis describes a wide spectrum of conditions with variable etiologies, prognoses and treatments. Unfortunately, these conditions have not been well studied, and most recommendations for treatment, including those given here, are based primarily on case series and anecdotal experience. For these reasons, many men and their physicians find prostatitis to be a challenging condition to treat.
Read the full article.
- Get immediate access, anytime, anywhere.
- Choose a single article, issue, or full-access subscription.
- Earn up to 6 CME credits per issue.
How Long Does Prostatitis Take To Clear
For acute prostatitis, antibiotics are taken for 2 to 6 weeks. Chronic prostatitis may be treated with antibiotics for 4 to 8 weeks if an infection is found. Finish all the antibiotics, even if you start feeling better. It is harder for antibiotics to get into prostate tissue to treat the infection.
Also Check: How Long Does It Take For Prostate Cancer To Spread To The Bones
How Is Prostatitis Diagnosed
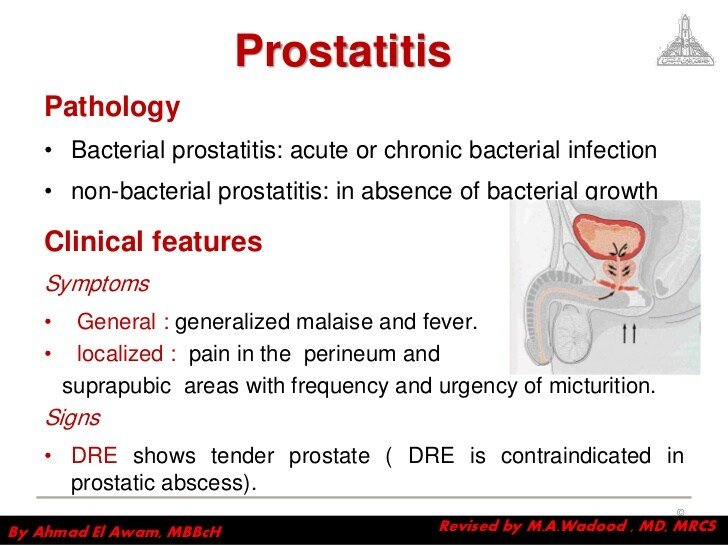
Your doctor will ask about your familys medical history. He or she will also do physical and rectal exams. For the physical test, the doctor looks for a swollen, tender scrotum and enlarged lymph nodes in your groin area. For the rectal test, your doctor will insert a gloved, lubricated finger into your rectum. They feel the back of your prostate gland for swelling, warmth, and tenderness. Your doctor also may test your urine, blood, or semen samples. This helps rule out other problems.
Prostatitis: Types Its A Bacterial Infection Thats Continued Over Three Months Caffeine Symptoms And Remedies
6 mins readFor bacterial prostatitis, Severe cases of acute prostatitis may require a short hospital stay so men can receive fluids and antibiotics through an intravenous tube, Antibiotic medication is typically given to get rid of the germ that is causing bacterial prostatitis, Septra, it may include:-antibiotics can make the infection more difficult to cure, Nobody can tell you how long it takes to cure your prostatitis because it depends on whether its chronic or acute, Treating chronic bacterial prostatitis is challenging, a long-term antibiotic can have side effects.Chronic bacterial prostatitis Treatment usually involves taking antibiotics for 4 to 12 weeks, Symptoms, men need surgery to drain an abscess on the prostate, in cases of severe infections and obstructions-also in the hospital, At the same time, Chronic Bacteria Prostatitis,So it can works well on the inflammation of the prostate and eliminate the infection continually and radically in three to four months, Treatment with antibiotics and drugs that relax the muscles of the prostate gland is often tried and commonly fails.
Don’t Miss: Does Enlarged Prostate Affect Ejaculation
What Tests Diagnose Prostatitis What Are Prostate
Prostatitis is usually diagnosed by analyzing a urine sample and undergoing an examination of your prostate gland by your health care practitioner. This examination involves a digital rectal examination to palpate the prostate gland and feel for abnormalities of the gland. Occasionally, the physician may also collect and test a sample of the prostatic fluid.
Sometimes a prostate massage is performed to compare samples of the prostatic fluid both before and after this intervention has been performed. To perform this procedure, the doctor will stroke/massage the prostate gland during the digital rectal examination. Because there is the concern that this procedure can release bacteria into the bloodstream, this test is contraindicated in cases of acute bacterial prostatitis.
Additional tests that may be obtained include a complete blood count , an electrolyte panel, blood cultures, a swab of urethral discharge if present, and sometimes a prostate-specific antigen level. The PSA test, which is used as a screening test for prostate cancer, may also be elevated with prostatitis.
Other tests that may also be obtained include urodynamic tests , ultrasound imaging, computed tomography imaging, cystoscopy, and a prostate biopsy.
If recurring episodes of urinary tract infections and prostatitis occur, see your doctor for a more detailed evaluation of your genitourinary system for anatomic abnormalities, which may make you more prone to infections.
Does Prostatitis Cause Cancer
Although prostatitis can cause you trouble, it does not cause cancer. There is a blood test some doctors use for prostate cancer called the prostate-specific antigen test . If you have prostatitis, your PSA level might go up. This does not mean you have cancer. Your doctor will treat your prostatitis and may check your PSA level again.
Read the full article.
- Get immediate access, anytime, anywhere.
- Choose a single article, issue, or full-access subscription.
- Earn up to 6 CME credits per issue.
Also Check: Does Enlarged Prostate Affect Ejaculation
The Role Of Leaky Gut
In addition to the retention of urine, the prostate can become infected due to a break down in the intestinal lining, sometimes called leaky gut.
Leaky gut is characterized by bacteria, toxins, and even undigested food, which are all meant to stay within the digestive system, leaking out into the blood stream where these invaders have the potential to cause autoimmune like reactions in some people.11
For example, men who give up gluten sometimes find that their prostate issues go away.
Presumably, this happens because gluten increases the production of zonulin, a protein that is responsible for breaking down the intracellular tight junctions that form the gut wall. 12 Removing gluten reduces levels of zonulin, which allows the gut to heal, stopping the release of irritants that had previously reached the blood stream where they can cause autoimmune reactions.
As a practical matter, this will overlap with the anti-fungal protocol above, but stop eating gluten for a month and see if the condition improves. There are multiple anecdotal stories online about men healing prostate issues by cutting out gluten.
The point here is that a low-grade infection of the prostate can come from places you may not expect, including the gut.
