How We Screen For Prostate Cancer Now
Most prostate cancers are first detected when a patient is found to have an elevated prostate-specific antigen , which is a blood test used for prostate cancer screening. The prostate is a walnut-sized gland that produces the fluid in semen. PSA is a protein made in the prostate, and elevated levels often are found in men with prostate cancer.
There has been some controversy about when men should get PSA tests, but we follow the guidelines of the American Urological Association, which recommend patients and their doctors discuss the test at age:
- 55-69 for men at average risk
- 40-54 for men at higher risk for prostate cancer, such as black men and men with a family history of prostate cancer
- 70 and older for men in excellent health with a 10- to 15-year life expectancy
While a PSA test can give us a clue that something may be wrong, it isnt fool-proof. For example, the test can be elevated in patients who have benign enlargement of their prostate or prostatic inflammation. In such cases, the abnormal PSA test can lead to an unnecessary biopsy.
If your PSA levels are elevated, well likely perform a transrectal ultrasound-guided prostate biopsy to gather small samples of the prostate to examine in the lab. We use a transrectal ultrasound to visualize the prostate. Then we insert a small needle into the gland to remove about 12 samples from different parts of the prostate.
How Is The Procedure Performed
MRI exams may be done on an outpatient basis.
You will be positioned on the moveable exam table. Straps and bolsters may be used to help you stay still and maintain your position.
Devices that contain coils capable of sending and receiving radio waves may be placed around or next to the area of the body being scanned.
MRI exams generally include multiple runs , some of which may last several minutes.
Your exam may use an endorectal coil. If so, a nurse or doctor will place a disposable cover over the coil. They will lubricate the assembly and insert the coil a short distance into your rectum. After insertion, the doctor inflates the circular balloon that sits around the coil and holds it in place during the exam. When the exam is complete, the doctor deflates the balloon and removes the coil.
If a contrast material is used, a doctor, nurse or technologist will insert an intravenous catheter into a vein in your hand or arm that will be used to inject the contrast material.
You will be placed into the magnet of the MRI unit. The technologist will perform the exam while working at a computer outside of the room.
If a contrast material is used during the exam, it will be injected into the intravenous line after an initial series of scans. More images will be taken during or following the injection.
When the exam is complete, you may be asked to wait while the radiologist checks the images in case more are needed.
Your IV line will be removed after the exam is over.
Use In Men Who Might Have Prostate Cancer
The PSA blood test is used mainly to screen for prostate cancer in men without symptoms. Its also one of the first tests done in men who have symptoms that might be caused by prostate cancer.
PSA in the blood is measured in units called nanograms per milliliter . The chance of having prostate cancer goes up as the PSA level goes up, but there is no set cutoff point that can tell for sure if a man does or doesnt have prostate cancer. Many doctors use a PSA cutoff point of 4 ng/mL or higher when deciding if a man might need further testing, while others might recommend it starting at a lower level, such as 2.5 or 3.
- Most men without prostate cancer have PSA levels under 4 ng/mL of blood. Still, a level below 4 is not a guarantee that a man doesnt have cancer.
- Men with a PSA level between 4 and 10 have about a 1 in 4 chance of having prostate cancer.
- If the PSA is more than 10, the chance of having prostate cancer is over 50%.
If your PSA level is high, you might need further tests to look for prostate cancer.
To learn more about how the PSA test is used to look for cancer, including factors that can affect PSA levels, special types of PSA tests, and what the next steps might be if you have an abnormal PSA level, see Screening Tests for Prostate Cancer.
Read Also: What Is The Definition Of Prostate
Radical Prostatectomy Histopathology Analysis
All patients underwent robotic-assisted laparoscopic RP by two urological surgeons. Histopathologic whole-mount specimens were prepared following the College of American Pathologists Protocol for the Examination of Radical Prostatectomy Specimens From Patients With Carcinoma of the Prostate Gland. Specimens were then assessed for presence of tumor and EPE by four experienced genitourinary pathologists, who were blinded to the results of mpMRI. Individual tumors were graded using the Gleason scoring system and their location was outlined onto Dickinson’s 27-sector map, thereby allocating a Gleason score to each sector. Gleason grade groups were defined as follows: Gleason 3 + 3 = GG1, Gleason 3 + 4 = GG2, Gleason 4 + 3 = GG3, Gleason 4 + 4 = GG4, and Gleason > 4+4 = GG5. csPCa is defined by Wolters et al. as Gleason 7-10 with > 5% grade 4 and 0.7 cc Gleason 6 and 1.3 cc pT stage 3a or greater and nodal metastasis. The present study considered Gleason score 6 in a given sector to indicate PCa in that sector, and Gleason score 7 in a given sector to indicate csPCa in that sector.
Diagnosis Of Prostate Cancer
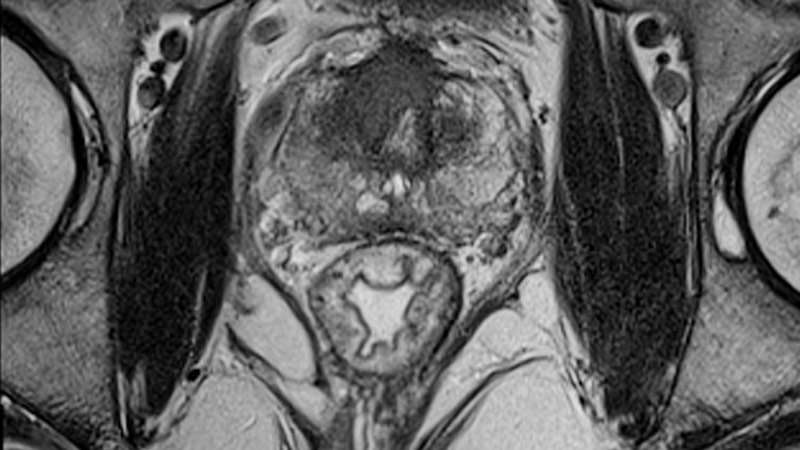
Check out this factsheet for a summary of the video.
Diagnosis is the process of finding out the cause of a health problem. Diagnosing prostate cancer usually begins with a visit to your family doctor. Your doctor will ask you about any symptoms you have and do a physical exam. Based on this information, your doctor may refer you to a specialist called a urologist or order tests to check for prostate cancer or other health problems. A urologist is a doctor who specializes in treating conditions of the genital and urinary tracts, including the prostate.
The process of diagnosis may seem long and frustrating. It’s normal to worry, but try to remember that other health conditions can cause similar symptoms as prostate cancer. It’s important for the healthcare team to rule out other reasons for a health problem before making a diagnosis of prostate cancer.
The following tests are usually used to rule out or diagnose prostate cancer. Many of the same tests used to diagnose cancer are used to find out the stage . Your doctor may also order other tests to check your general health and to help plan your treatment.
Read Also: Finding The Prostate Externally
Summary Comparison Of Pathways
There was no statistically significant difference in significant prostate cancer detected by cognitive targeted TRUS and MRGB or the combination of MRGB and cognitive targeted TRUS . Furthermore, there was no significant difference in diagnosed insignificant prostate cancer between cognitive targeted TRUS and MRGB or the combination of MRGB and cognitive targeted TRUS . The overall performance of each biopsy method stratified by PI-RADS is detailed in Table 5.
Figure 3 Detection rates of prostate cancer for MRGB, combined biopsy, and cognitive targeted TRUS. MRGB, MR-guided in-bore biopsy. CB, combined biopsy scTRUS, cognitive targeted transrectal ultrasound-guided biopsy with additional systematic biopsy cores sPCa, significant prostate cancer insPCa, insignificant prostate cancer.
Table 5 Cancer detection rates for biopsy methods stratified by PI-RADS.
Multiparametric Mri May Miss Or Underestimate Prostate Cancer Lesions
Multiparametric MRI may not show all prostate cancer lesions or may underestimate their size.
Multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging may miss clinically important lesions in prostate cancer, according to a study published in Radiology.
Researchers from the National Institutes of Health in Bethesda, MD, performed a retrospective single-center study to characterize clinically important prostate cancers missed at MP MR imaging. The study included 100 consecutive patients who had undergone MP MR imaging and subsequent radical prostatectomy. A genitourinary pathologist blinded to MP MR findings outlined prostate cancers on whole-mount pathology slices.
The MP MR images were correlated by two readers who were blinded to histopathology results during prospective reading. Eighty clinically unimportant lesions were excluded from the study. The same two readers then retrospectively reviewed cancers missed at MP MR imaging and assigned a Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System version 2 score to better understand false-negative lesion characteristics.
The results showed that of the 162 lesions found, 26 were missed and 136 were correctly identified with MP MR imaging. Eight lesions were underestimated for size.
The Gleason scores for the 26 missed lesions were:
3+4 in 17 4+4 in 7 4+5 in 1
Retrospective PI-RADS version 2 scores were:
PI-RADS 1, n = 8
You May Like: How To Shrink Prostate Mayo Clinic
Locations Where This Service Is Available
- 260 Leach Highway Booragoon
Weekday evening MRI appointments available*Please note: not all services are performed on Saturdays.
- 57 Shenton Avenue Joondalup
Weekday evening MRI appointments available.*Please note: not all services are performed on Saturdays.
- 217 Wanneroo Road Balcatta
Weekday evening MRI appointments available.*Please note: not all services are performed on Saturdays.
The Diagnostic Accuracy Of Multiparametric Mri For Detection And Localization Of Prostate Cancer Depends On The Affected Region
Swiss International Prostate Center, Geneva, Switzerland
ImageRive, Institut de Radiologie Spécialisée, Geneva, Switzerland
Swiss International Prostate Center, Geneva, Switzerland
Clinique Générale Beaulieu, Geneva, Switzerland
Swiss International Prostate Center, Geneva, Switzerland
Clinique Générale Beaulieu, Geneva, Switzerland
Swiss International Prostate Center, Geneva, Switzerland
Clinique Générale Beaulieu, Geneva, Switzerland
Swiss International Prostate Center, Geneva, Switzerland
ImageRive, Institut de Radiologie Spécialisée, Geneva, Switzerland
Swiss International Prostate Center, Geneva, Switzerland
Clinique Générale Beaulieu, Geneva, Switzerland
Swiss International Prostate Center, Geneva, Switzerland
Clinique Générale Beaulieu, Geneva, Switzerland
Swiss International Prostate Center, Geneva, Switzerland
Clinique Générale Beaulieu, Geneva, Switzerland
Read Also: How To Shrink Prostate Mayo Clinic Naturally
Mri Twice As Likely As Biopsy To Spot Prostate Cancer Research Shows
Finding could bring about change of practice in NHS with potential to save many lives, says charity
Every man with suspected prostate cancer should have an MRI scan, which is twice as likely to identify the presence of dangerous tumours as the invasive biopsy used currently, say doctors.
A major trial, which could influence a change of practice in the NHS, will amount to the biggest leap forward in prostate cancer diagnosis in decades, with the potential to save many lives, Prostate Cancer UK said.
Researchers publishing in the Lancet medical journal have shown that an MRI picks up 93% of aggressive cancers, compared with 48% for a biopsy. The biopsy, which removes a sample of tissue for lab testing, often misses the tumour altogether.
The Prostate MRI Imaging Study , led by researchers at University College London , also showed that more than a quarter of all men with suspected cancer could avoid a biopsy altogether.
MRI scans were shown to be better at ruling out cancer, as well as identifying tumours that are not dangerous because they are slow growing and do not need to be treated. In the trial, the number wrongly diagnosed with a cancer that needed treatment was reduced by 5%.
Some men suffer a life-threatening sepsis a bloodstream infection as a result of the standard transrectal ultrasound-guided biopsy.
Extrapolation To The Screening Cohort
In the ProScreen trial approximately 16,700 men are randomized to the screening arm. A power calculation determined that roughly 11,690 men would be expected to participate in screening and of these, 1520 men would have PSA3.0 g/l and subsequently 1000 men would have a 4KScore of 7.5% and would therefore have the indication for prostate MRI .
Assuming a 30% prevalence of csPCa in the screen-positive subcohort with 1000 men, the mean sensitivity and specificity of radiologists would entail 639 men being referred to biopsy of which 244 men would be true positive and 395 false positive. Of the 361 men who would not be referred to biopsy, 305 would be true negatives and 56 would harbor a cancer that would be missed, i.e., false negative.
If the sensitivity and specificity of the evaluations done by the most sensitive radiologist is assumed in a similar subcohort of 1000 men, 846 men would be biopsied and 154 men would not be biopsied .
Conversely, if the sensitivity and specificity of the evaluations carried out by the least sensitive radiologist is extrapolated into the same subcohort of 1000 men, 376 men would be biopsied and 624 men would not be biopsied .
Recommended Reading: Chemo Drug For Prostate Cancer
What Does An Mri Scan Involve
Before the scan the doctor or nurse will ask questions about your health. As the scan uses magnets, they will ask whether you have any implants that could be attracted to the magnet. For example, if you have a pacemaker for your heart you may not be able to have an MRI scan. Youll also need to take off any jewellery or metal items.
You will lie very still on a table, which will move slowly into the scanner. MRI scanners are shaped like a doughnut or a long tunnel. If you dont like closed or small spaces , tell your radiographer .
The radiographer might give you an injection of a dye during the scan. The dye helps them see the prostate and other organs more clearly on the scan. It is usually safe, but can sometimes cause problems if you have kidney problems or asthma. So let the radiographer know if you have either of these, or if you know youre allergic to the dye or have any other allergies.
The scan takes 30 to 40 minutes. The machine wont touch you but it is very noisy and you might feel warm. The radiographer will leave the room but youll be able to speak to them through an intercom, and you might be able to listen to music through headphones.
Performance Interpretation And Reporting Of Prostate Mri Following A Negative Biopsy
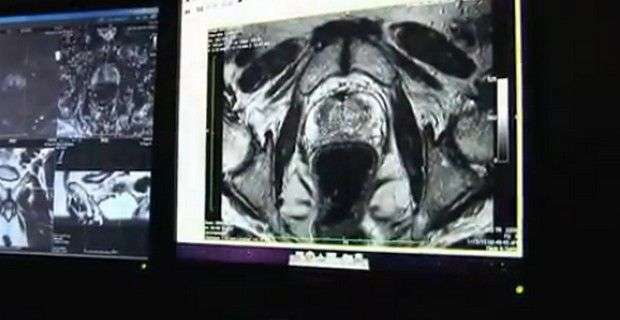
The Prostate Imaging and Reporting Data System Version 2 was released in December 2014,15 representing the work of an international panel of leaders in the field of prostate MRI. PI-RADS is a comprehensive, publicly available online document that provides guidelines for the acquisition, interpretation, and reporting of prostate MRI. PI-RADS seeks to standardize the technique and interpretation of prostate MRI, reducing variability among readers and centers. The content of PI-RADS reflects the best evidence available at the time of its development, in combination with the expert opinion. It represents an expanded version of a more focused initial version published in 2012.16 While PI-RADS provides guidelines for standardizing prostate MRI, performing consistent state-of-the-art prostate MRI remains challenging. Moreover, it is important for radiology practices performing prostate MRI to engage in continual quality improvement of their imaging and interpretation though adherence to standards and routine correlations of imaging results with histologic findings.
Recommended Reading: Household Items For Prostate Massage
Has The Radiologist Who Will Read The Study Undergone Pi
The Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System, or PI-RADS®, refers to standards that have been developed by several organizations to improve early diagnosis and treatment of prostate cancer.
Prostate cancer is the most commonly diagnosed cancer in men, with one out of nine men diagnosed in their lifetime. And while many cases dont require treatment, it is a leading cause of cancer death among men, second only to lung cancer. The broad range between cancer that does not require treatment and life-threatening prostate cancer means that proper diagnosis is key to determining next steps.
Prostate Mri With And Without Contrast
gary37907
Has anyone here had experience with the a Prostate MRI with and without contrast for prostate cancer screening? My internist suggested that I have this rather than biopsy due to possible side effects of needle biopsy. He said that MRI has become pretty accurate in detecting tumors and when it is positive for tumors it can be used as a guide for directing needle biopsy. Mine showed no masses but BPH with medial lobe involvement intruding into the blaldder neck. This all came about because my BPH symptoms got so bad that I was retaining urine in my bladder. MY urologist wanted me to have a biopsy before any BPH surgical procedures because of a history of 3 brothers with prostate cancer. My last PSA was 2.9 but it has gotten up to the low 3’s on several occasions. I don’t know what my Uro will do with these results tho I would assume it would mean a go for any procedure I decide to have. Now the hard part is deciding which procedure to get. I am an otherwise healthy 67 year old. I would appreciate some input from those who have knowledge and or experience with the prostate MRI. Thanks Gary
0 likes, 14 replies
Read Also: Fiducial Marker Placement For Prostate Cancer
Potential Disadvantages Of Mri
The primary disadvantage of adoption of an mpMRI-based approach for prostate cancer screening is the associated cost which is considerably higher than a serum PSA test at a population-based level. However, the per-individual costs for a prostate MRI are similar to those for colonoscopy, the recommended screening test for colorectal cancer . In addition, in many jurisdictions, the cost of mpMRI is equivalent or marginally higher than genomic tests with the added advantage of providing biopsy guidance. Further, compared to ongoing PSA-based screening, mpMRI-based prostate cancer screening offers the opportunity to significantly reduce the cost and morbidity of prostate cancer screening by reducing the number of biopsies performed and reducing the diagnosis of clinically insignificant prostate cancer, thus reducing overtreatment. In addition, compared to abandoning prostate cancer screening entirely, mpMRI-based prostate cancer screening offers the opportunity to diagnose clinically significant disease while it is localized and amenable to prostate-directed treatments. Such treatment has been shown to decrease progression to metastatic disease , which carries significant cost and morbidity . Should mpMRI be proven to be a better screening instrument than serum PSA from further studies, comprehensive cost-related studies will be required to determine the feasibility of mpMRI screening for prostate cancer.
Donât Miss: How To Stimulate Prostate Gland
