Hormone Therapy For Prostate Cancer
Jump to a section
Hormone therapy is also called androgen suppression therapy. The goal of this treatment is to reduce levels of male hormones, called androgens, in the body, or to stop them from fueling prostate cancer cell growth.
Androgens stimulate prostate cancer cells to grow. The main androgens in the body are testosterone and dihydrotestosterone . Most androgens are made by the testicles, but the adrenal glands as well as the prostate cancer cells themselves, can also make androgens.
Lowering androgen levels or stopping them from getting into prostate cancer cells often makes prostate cancers shrink or grow more slowly for a time. But hormone therapy alone does not cure prostate cancer.
What Will I Learn By Reading This
You and your doctor may be talking about using hormone therapy to control your prostate cancer. It is important for you to learn about hormone therapy so that you will know what to expect and how best to take care of yourself before, during, and after treatment. You will learn:
It is important to think about how you will work these things into your everyday life if you and your doctor decide that hormone therapy is the best way for you to control your prostate cancer..
What Does Current Guidance Say On This Issue
NICE prostate cancer guidelines give recommendations for locally-advanced and metastatic prostate cancer, which fall under the advanced definition used in this review.
Radical radiotherapy plus androgen suppression therapy is recommended for high-risk localised cancer. NICE advises that suppression may be given before, during or after radiotherapy, but dont state a precise timing in relation to diagnosis. Chemotherapy plus androgen suppression is recommended for newly diagnosed metastatic prostate cancer.
Read Also: How Long Should You Take Lupron For Prostate Cancer
Secondary Treatment Following Relapse
Hormone therapy may also be used as a secondary or salvage treatment when PSA levels rise following initial prostate cancer treatment, indicating the cancer has returned. This situation is known as biochemical recurrence. The salient points to keep in mind are that hormone therapy is most often used as a salvage treatment when PSA doubling time is less than six months, indicating that the cancer is aggressive or may have already metastasized.
Kinds Of Hormone Therapy
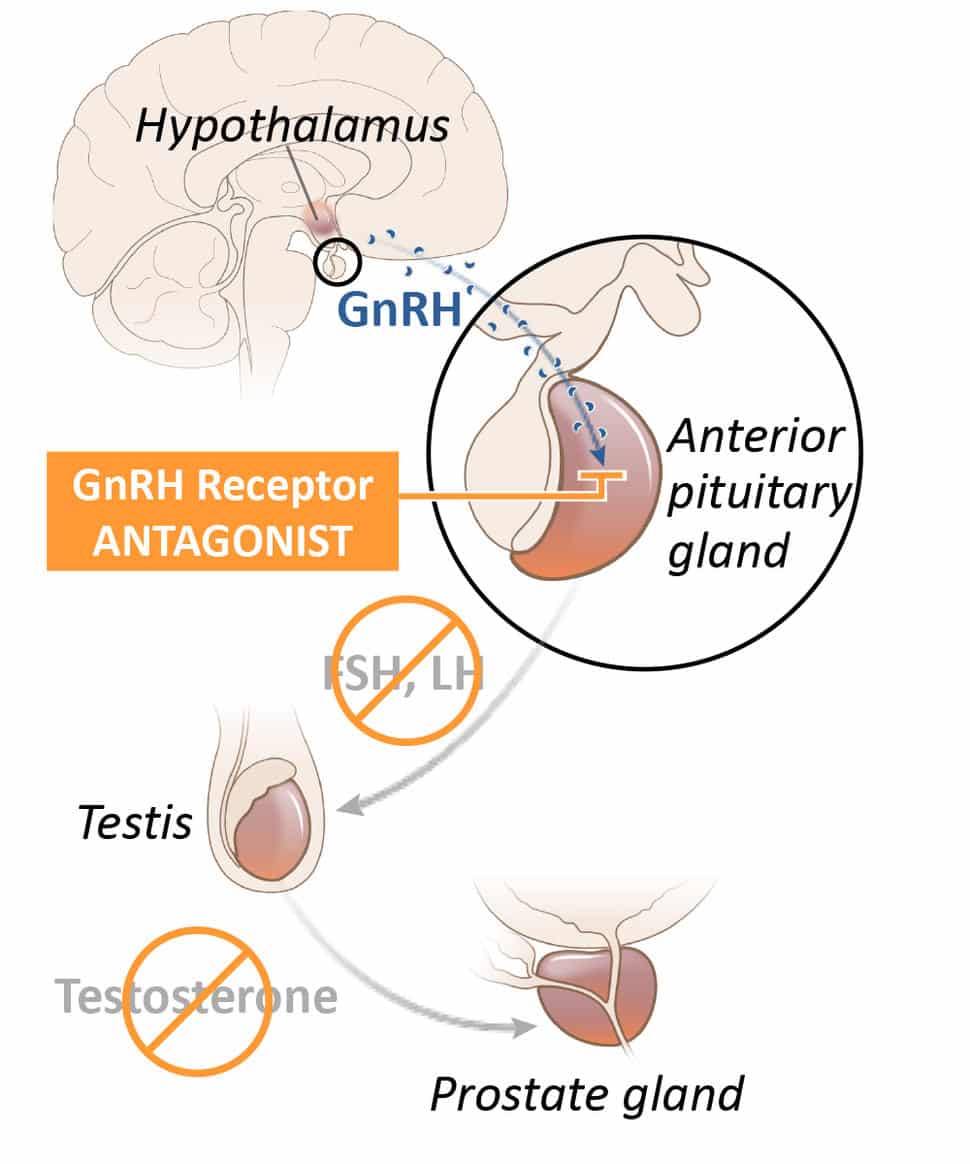
Hormone therapy is a category encompassing a number of treatments. In some conditions or diseases, certain hormones are prescribed in order to increase their levels. This is frequently referred to as hormone replacement therapy . Hormones can be natural or synthetic, meaning produced commercially . Patients who do not have prostate cancer but have symptoms from low testosterone levels, such as fatigue, may be prescribed testosterone as a type of HRT. In certain cases, patients with prostate cancer under control may receive this type of hormone therapy however, because of the risk of activating the cancer, some doctors advise against it. Male children or adults with hypogonadism are prescribed testosterone as HRT.
As mentioned previously, HT in prostate cancer aims to reduce production of the hormone testosterone, rather than increase it, thereby interfering with cancer cells ability to use it to grow.
The hormone therapies that have become standard prostate cancer treatments are the ones we discuss in detail in this guide. All decisions regarding these treatments should be carefully made by the patient and doctor together.
Read Also: Car-t For Prostate Cancer
Therapies That Interfere With Androgen Function
Taken daily as pills, antiandrogens bind to the androgen receptor proteins in the prostate cells, preventing the androgens from functioning. In addition to preventing a flare reaction, antiandrogens may be added to your treatment plan if an orchiectomy, LHRH agonist or LHRH antagonist is no longer working by itself. Commonly prescribed antiandrogens include flutamide and bicalutamide .
Enzalutamide is a newer type of antiandrogen that blocks the signal that the receptor normally sends to the cells control center to trigger growth and division. This antiandrogen may be used to treat castration-resistant prostate cancer.
What Is The Most Effective Treatment For Prostate Cancer
The good news is that there are many effective treatments that can result in positive outcomes for prostate cancer patients. For example, for localized prostate cancer, external beam radiation therapy can have an up to 95% efficacy. Radical prostatectomy has also been found to achieve an over 90% efficacy against prostate cancer. The decision of which treatment plan or plans to follow is ultimately a personal decision that should be based on the recommendations of your doctor.
You May Like: What Is Cystic Hormonal Acne
Also Check: How Often Should You Be Tested For Prostate Cancer
How Does Hormone Therapy Work Against Prostate Cancer
Early in their development, prostate cancers need androgens to grow. Hormone therapies, which are treatments that decrease androgen levels or block androgen action, can inhibit the growth of such prostate cancers, which are therefore called castration sensitive, androgen dependent, or androgen sensitive.
Most prostate cancers eventually stop responding to hormone therapy and become castration resistant. That is, they continue to grow even when androgen levels in the body are extremely low or undetectable. In the past, these tumors were also called hormone resistant, androgen independent, or hormone refractory however, these terms are rarely used now because the tumors are not truly independent of androgens for their growth. In fact, some newer hormone therapies have become available that can be used to treat tumors that have become castration resistant.
Neoadjuvant And Adjuvant Hormone Therapy For Early
Hormone therapy is sometimes given in conjunction with a definitive prostate cancer treatment, such as radiation therapy, in order to improve health outcomes. When hormone therapy is given in advance of a primary treatment, its known as neoadjuvant therapy when its given during or after a primary treatment, its known as adjuvant therapy.
Recommended Reading: Is It Ok To Ejaculate After Prostate Biopsy
Questions To Ask Your Doctor Or Nurse
- What is the aim of treatment?
- What type of hormone therapy are you recommending for me and why?
- How often will I have my injections or implants?
- How will my treatment be monitored?
- How long will it be before we know if the hormone therapy is working?
- What are the possible side effects, and how long will they last?
- What will happen if I decide to stop my treatment?
- Are there any clinical trials that I could take part in?
Hormone Therapy With Radiation
Hormone therapy is often given together with radiation therapy for localized disease .
Hormone therapy usually consists of a shot that lowers your testosterone, given every 1 to 6 months, depending on the formulation. Sometimes, it is prescribed as a daily pill that blocks testosterone from reaching the cancer cells. Clinical trials show a benefit in patients who receive hormonal treatment in combination with external beam radiation. Hormone therapy has been shown to improve cure rates of prostate cancer for men receiving radiation therapy and is part of the standard of care for men with certain types of intermediate-risk prostate cancer and nearly all high-risk prostate cancer. It is often given for intermediate-risk cancer for 4 to 6 months , and for 2 to 3 years in men with high-risk localized prostate cancer, although some doctors may recommend as little as 18 months of hormone therapy.
Hormone therapy should not be given to men with low-risk prostate cancer and is not a standalone treatment for localized prostate cancer in any risk category.
Want more information about a prostate cancer diagnosis and treatment options? Download or order a print copy of the Prostate Cancer Patient Guide.
You May Like: Prostate Cancer Stage 3 Treatment
Types Of Hormone Therapy
The table at the right provides an overview of three commonly used types of hormone therapy. These and others are discussed below. While hormone therapy is commonly used, side effects of the treatment are reported as well. They range from erectile dysfunction, hot flashes, weight gain and loss of bone density.
What Are The Stages Of Prostate Cancer
Cancer staging is first described using what is called a TNM system. The T refers to a description of the size or extent of the primary, or original, tumor. N describes the presence or absence of, and extent of spread of the cancer to lymph nodes that may be nearby or further from the original tumor. M describes the presence or absence of metastases usually distant areas elsewhere in the body other than regional lymph nodes to which the cancer has spread. Cancers with specific TNM characteristics are then grouped into stages, and the stages are then assigned Roman numerals with the numerals used in increasing order as the extent of the cancer being staged increases or the cancer prognosis worsens. Prognosis is finally reflected by considering the patients PSA score at presentation as well as their Gleason score in assigning a final stage designation.
The American Joint Commission on Cancer system for prostate cancer staging is as follows:
Traditionally, advanced prostate cancer was defined as disease that had widely metastasized beyond the prostate, the surrounding tissue, and the pelvic lymph nodes and was incurable. However, a more contemporary definition includes patients with lower grade disease with an increased risk of progression and/or death from prostate cancer in addition to those with widely metastatic disease.
The National Cancer Institute and the National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines on prostate cancer version 2.2017 indicate the following:
You May Like: Prostate Massage And Prostate Cancer
How Effective Is Hormone Therapy For Prostate Cancer
In the initial years of diagnosis, hormone therapy for prostate cancer can help patients with their symptoms and add years to their lives.
For men who need hormone therapy, such as men whose prostate-specific antigen levels are rising after surgery or radiation or men with advanced prostate cancer who dont yet have symptoms, its not always clear when the best time is to start hormone treatment:
- Some doctors think that hormone therapy works better if its started as soon as possible, even if the patient feels well and is not exhibiting any symptoms. Studies have shown that hormone treatment may slow down the disease and perhaps even help men live longer.
- Some doctors, however, don’t agree with this approach. Because of the side effects and the risk of the cancer becoming resistant to therapy sooner, some doctors feel that treatment should not be started until cancer symptoms appear.
Watchful Waiting Or Active Surveillance
Prostate cancer treatments can have side effects. If you’re worried about these risks, you can decide to hold off on these treatments and see if your tumor grows. Waiting is also an option if youâre older, your cancer is growing slowly, or you don’t have symptoms that bother you.
Waiting does not mean that you do nothing about your cancer. Your doctor will keep a close eye on the tumor and watch for any signs that itâs getting worse.
Watchful waiting means you and your doctor will look out for symptoms. The doctor may do tests from time to time to make sure the cancer hasn’t grown.
Active surveillance means your doctor will do tests, including PSA blood tests and rectal exams, usually about every 3-6 months to check on it. You may also have a biopsy, when a doctor takes a small piece of tissue from your prostate and checks it for cancer.
You May Like: Does Prostate Cancer Cause Weight Loss
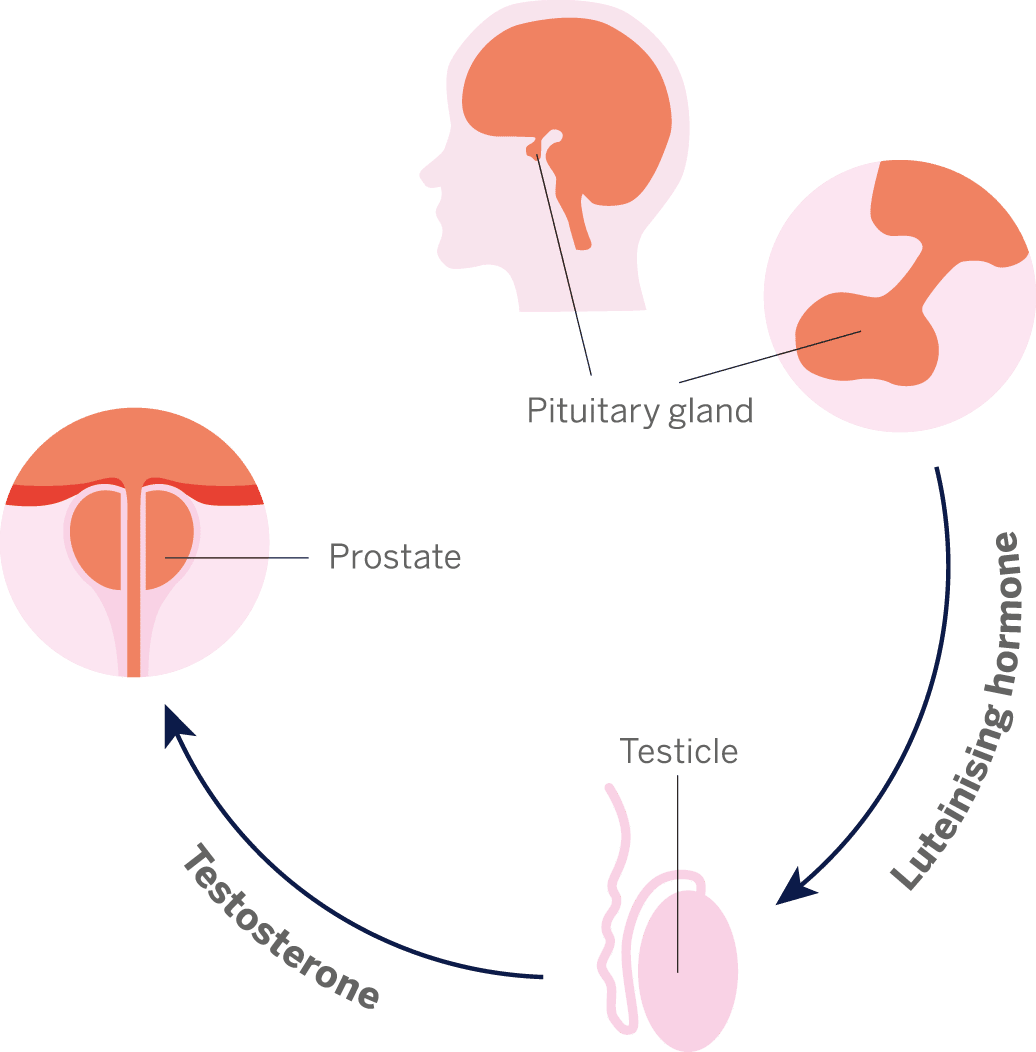
Male Hormones And Prostate Cancer
Androgens are male sex hormones. Testosterone is one main type of androgen. Most testosterone is made by the testicles. The adrenal glands also produce a small amount.
Androgens cause prostate cancer cells to grow. Hormone therapy for prostate cancer lowers the effect level of androgens in the body. It can do this by:
- Stopping the testicles from making androgens using surgery or medicines
- Blocking the action of androgens in the body
- Stopping the body from making androgens
Does Equelle Increase Estrogen Levels
Taking Equelle does not impact estrogen levels. Although Equelles active ingredient, S-equol, mimics some of the same activities of estrogen by preferentially binding to estrogen receptor beta, Equelle is a hormone free dietary supplement and clinical research shows S-equol supplementation reduces the frequency of hot flashes, supports the quality of sleep, reduces bothersome vaginal symptoms like irritation, soreness and itching, and alleviates mood swings.
Read Also: Pain In Prostate After Ejaculation
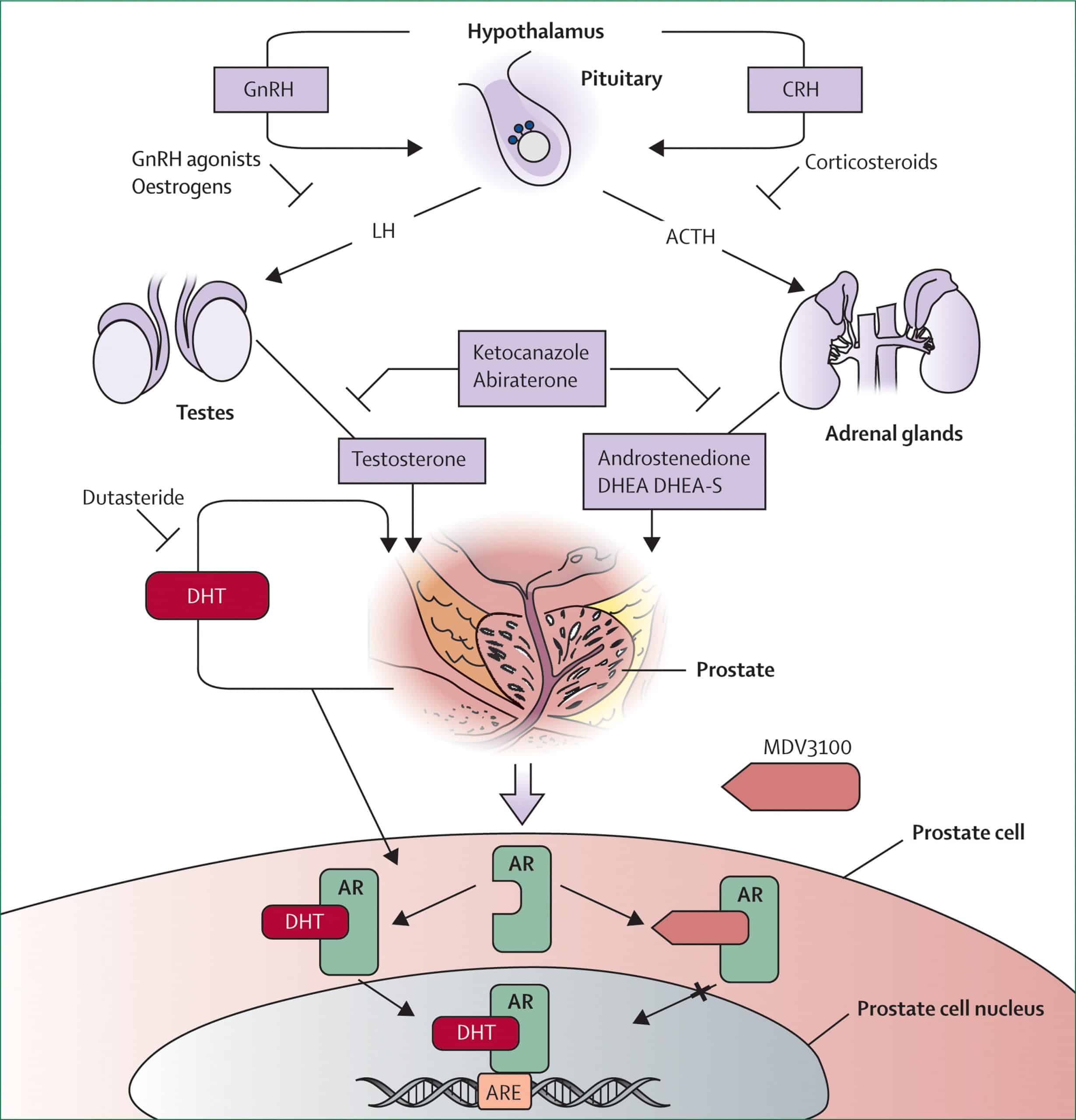
Treatment To Lower Androgen Levels From Other Parts Of The Body
LHRH agonists and antagonists can stop the testicles from making androgens, but cells in other parts of the body, such as the adrenal glands, and prostate cancer cells themselves, can still make male hormones, which can fuel cancer growth. Some drugs can block the formation of androgens made by these cells.
Abiraterone blocks an enzyme called CYP17, which helps stop these cells from making androgens.
Abiraterone can be used in men with advanced prostate cancer that is either:
- Castration-resistant
This drug is taken as pills every day. It doesnt stop the testicles from making testosterone, so men who havent had an orchiectomy need to continue treatment with an LHRH agonist or antagonist. Because abiraterone also lowers the level of some other hormones in the body, prednisone needs to be taken during treatment as well to avoid certain side effects.
Ketoconazole , first used for treating fungal infections, also blocks production of androgens made in the adrenal glands, much like abiraterone. It’s most often used to treat men just diagnosed with advanced prostate cancer who have a lot of cancer in the body, as it offers a quick way to lower testosterone levels. It can also be tried if other forms of hormone therapy are no longer working.
Ketoconazole also can block the production of cortisol, an important steroid hormone in the body, so men treated with this drug often need to take a corticosteroid .
Treating Prostate Cancer With Combined Hormonal
Androgens, the family of male sex hormones that includes testosterone, function as a fuel for growth in normal development. However, in some men they can also drive the progression of prostate cancer. Hormonal therapy treats prostate cancer by dramatically reducing levels of testosterone and other androgens.
Hormonal therapy is sometimes given in conjunction with external beam radiation to boost the effectiveness of treatment. Hormonal therapy may also be used to shrink the size of large prostate glands before brachytherapy takes place, to enable proper placement of the radioactive seeds.
Combination hormonal/radiation therapy is now a standard option for men with cancer that has extended beyond the prostate or whose cancer is considered high-risk based on other clinical findings, with studies showing that it reduces the risk of dying from prostate cancer and other causes more than with either treatment given alone..
Combination therapy can also be considered for men with localized prostate cancer in the intermediate-risk category. Whether men with low-risk prostate cancer would benefit from a hormonal therapyradiation combination is uncertain.
Image: sturti/Getty Images
Also Check: Can Prostate Cancer Cause Back Pain
Treating Advanced Prostate Cancer
If the cancer has reached an advanced stage, its no longer possible to cure it. But it may be possible to slow its progression, prolong your life and relieve symptoms.
Treatment options include:
- hormone treatment
If the cancer has spread to your bones, medicines called bisphosphonates may be used. Bisphosphonates help reduce bone pain and bone loss.
When Is Hormone Therapy Used
Hormone therapy may be used:
- If the cancer has spread too far to be cured by surgery or radiation, or if you cant have these treatments for some other reason
- If the cancer remains or comes back after treatment with surgery or radiation therapy
- Along with radiation therapy as the initial treatment, if you are at higher risk of the cancer coming back after treatment
- Before radiation to try to shrink the cancer to make treatment more effective
Don’t Miss: Prostate Bed Radiation Side Effects
When Hormone Therapy Is Recommended
Hormone therapy is typically given to patients with intermediate- or high-risk prostate cancer. It may be used in the following ways:
- In combination with radiation, mostly for patients with high Gleason scores or other high-risk factors.
- After radiation or surgery when PSA rises, indicating a recurrence.
- As therapy for patients unsuitable for radiation or surgery.
- As therapy for metastatic prostate cancer . It may be given instead of or in combination with chemotherapy.
HT is usually not prescribed for:
- Patients choosing a localized treatment for low-risk prostate cancer
- Low-risk patients preferring to monitor their cancer on an active surveillance program
HT may be an option for patients who are not candidates for surgery, radiation or other localized treatment because of age, pre-existing health conditions or concerns about potential side effects of localized treatments.
How Third Stage Prostate Cancer Manifests Itself
At this stage the tumour has already grown outside the prostate gland. There are no distant metastases and no pain associated with them yet, but the patient may experience symptoms of obstruction, that is, compression of the urinary tract:
- frequent and difficult urination
- the need to push yourself when you go to the bathroom
- imperative, i.e. very intense, almost unbearable urges
- nighttime urge to pee, or nocturia
- a feeling of incomplete bladder emptying.
If the tumour has grown into the bladder neck, you may develop urinary incontinence or haematuria blood in the urine. Sometimes the patient experiences pain because the tumour is compressing the surrounding tissues. Due to the obstruction, some patients may develop renal failure or hydronephrosis enlargement of the renal pelvis.
Recommended Reading: What Is Stage 5 Prostate Cancer
Outlook For Locally Advanced Prostate Cancer
Many men with locally advanced prostate cancer have treatment that aims to get rid of their cancer. For some men, this treatment can be very successful and they may live for many years without their cancer coming back or causing them any problems. For others, treatment may be less successful and the cancer may come back. If this happens, you might need further treatment. Read more about the risk of your cancer coming back.
Some men with locally advanced prostate cancer will have treatment that aims to help keep their cancer under control rather than get rid of it completely. For example, if you have hormone therapy on its own, it can help to keep the cancer under control, usually for several years. And there are other treatments available if your hormone therapy stops working.
You May Like: What Age To Get Checked For Prostate Cancer
