What Are The Advantages Of An Mri
Research has shown that using an MRI image to guide a biopsy improves detection of prostate tumors that require treatment, while finding fewer tumors that are called biologically insignificant. This means that they do not need any immediate treatment and are not likely to pose a threat to the patient. Because using an MRI image gives doctors better information and reduces the chance that a serious tumor will be missed, it should also mean that patients with blood-test results that suggest possible prostate cancer are less likely to need repeat biopsies because the first one may have produced a false negative.
Comparative Effectiveness Of Magnetic Resonance Imaging
- Harvard Medical School, Boston, MADivision of Urologic Surgery, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, MA
- Harvard Medical School, Boston, MADivision of Urologic Surgery, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, MA
- Harvard Medical School, Boston, MADepartment of Radiology, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, MA
- Boris GershmanCorrespondenceAddress correspondence to: Boris Gershman, M.D., Division of Urologic Surgery, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, MA 02215Harvard Medical School, Boston, MADivision of Urologic Surgery, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, MA
How Does The Procedure Work
Ultrasound procedure:
Ultrasound imaging uses the same principles as the sonar that bats, ships, and fishermen use. When a sound wave strikes an object, it bounces back or echoes. By measuring these echo waves, it is possible to determine how far away the object is as well as its size, shape, and consistency. This includes whether the object is solid or filled with fluid.
Doctors use ultrasound to detect changes in the appearance of organs, tissues, and vessels and to detect abnormal masses, such as tumors.
In an ultrasound exam, a transducer both sends the sound waves and records the echoing waves. When the transducer is pressed against the skin, it sends small pulses of inaudible, high-frequency sound waves into the body. As the sound waves bounce off internal organs, fluids and tissues, the sensitive receiver in the transducer records tiny changes in the sound’s pitch and direction. A computer instantly measures these signature waves and displays them as real-time pictures on a monitor. The technologist typically captures one or more frames of the moving pictures as still images. They may also save short video loops of the images.
MRI procedure:
A computer processes the signals and creates a series of images, each of which shows a thin slice of the body. The radiologist can study these images from different angles.
MRI is often able to tell the difference between diseased tissue and normal tissue better than x-ray, CT, and ultrasound.
Don’t Miss: How To Find Prostate Gland Externally
What Are The Limitations Of Ultrasound
A biopsy can only show if there is cancer in the tissue samples. It is possible to miss cancer in unsampled areas of the prostate.
For MRI-guided biopsies, you must remain perfectly still to ensure the technologist captures high-quality images. If you are anxious, confused, or in severe pain, it may be hard to lie still. If so, the images may not be of high enough quality to be useful.
Likewise, the presence of an implant or other metallic object sometimes makes it difficult to obtain clear MR images. A person who is very large may not fit inside certain types of MRI machines.
Bleeding may sometimes occur in the prostate after a biopsy. MR imaging cannot always tell the difference between cancer, inflammation, or the presence of blood. To avoid confusing them, your doctor may perform a repeat MRI six to eight weeks after the biopsy to allow residual bleeding to resolve.
An MRI exam typically costs more and may take more time than other imaging exams. Talk to your insurance provider if you have concerns about the cost of MRI.
What Does The Equipment Look Like
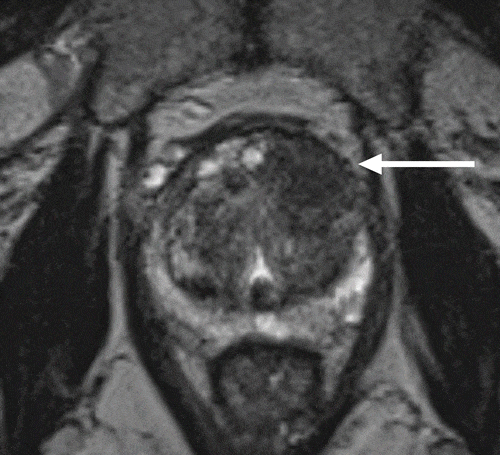
Ultrasound equipment:
Ultrasound scanners consist of an electronic console containing a computer, video monitor, and a handheld transducer . The transducer sends out inaudible high frequency sound waves into the body and listens for the returning echoes. The principle is similar to the sonar used by boats and submarines.
The computer displays the ultrasound image on a video monitor. This image is based on the amplitude and frequency of the signal. It is also based on signal travel time, tissue composition, and the type of body structure through which the sound travels.
The ultrasound probe for a prostate biopsy is about the size of a finger. Once the doctor inserts the probe into the rectum, they take tissue samples using a spring-driven needle core biopsy device . The handheld device includes a long but very thin needle. The needle opens inside the prostate, takes the sample, and then closes.
MRI equipment:
The traditional MRI unit is a large cylinder-shaped tube surrounded by a circular magnet. You will lie on a table that slides into a tunnel towards the center of the magnet.
You May Like: What Is The Function Of Prostate Gland In Human Body
Mr Guided Prostate Biopsy
We perform transperineal MRI-guided biopsies for prostate cancer at the wide-bore 3T MRI scanner in AMIGO. The wide-bore 3T MRI , combined with custom built software and hardware, was made possible through NIH grants, enabling us to launch this unique and clinically useful program from the inception of the AMIGO suite. Men with either recurrent prostate cancer post-surgeries or radiation treatments, or with consecutive negative ultrasound-guided biopsies but rising PSA are enrolled in our program.
Mri/trus Fusion Biopsy Vs In
We found only one published study which directly compared an MRI-ultrasound method with an in bore approach. This study, by Arsov et al. , compared in-bore and software-assisted fusion biopsies in men with prior negative biopsies. The Authors investigated 210 men and observed that detection rates for clinically significant prostate cancer and the highest percentage tumor involvement per biopsy core were similar between the arms.
Recommended Reading: New Blood Test For Prostate Cancer
Preparing For The Biopsy
For the biopsy, patients will be asked to wear metal-free clothing and remove any metallic objects, such as jewelry, watches, and hearing aids.
Busch Centers team members will walk through an MRI safety checklist with you, discussing your prior surgeries as well as metal implants, such as pacemakers, aneurysm clips, or joint replacements.
Prior to this procedure:
- Provide Dr. Busch with a list of the medications you are taking, including herbal supplements.
- Mention any allergies, especially to anesthesia and latex, as well as any recent illnesses or other medical conditions.
- You may be asked to stop or decrease blood thinning medications to prevent excessive bleeding during and after the biopsy.
- You may be instructed to take antibiotic pills for a day or two before the biopsy, to help prevent infection.
- Eat light meals on the day prior to and on the day of your exam. This will help make it easier to insert the ultrasound probe or endorectal coil.
- You may be asked to use an enema prior to your exam to help clear the bowel.
Research indicates that MRI In-bore Targeted Biopsies with ADC Mapping are far superior than other biopsy methods. Busch Center is proud to offer this best-in-class service at their Alpharetta, GA imaging center, providing our patients with the most superior diagnostic option available.
How Should I Prepare
Prior to a prostate biopsy, tell your doctor about all the medications you take, including herbal supplements. List any allergies , recent illnesses, and other medical conditions.
You may need to stop taking blood thinners for seven to 10 days before the procedure. This will help prevent excessive bleeding during and after the biopsy. The doctor may check your blood clotting on the day of the procedure. Ask your doctor and the hospital radiology clinic or department for more information.
You may need to take oral antibiotics a day before and the morning of the biopsy. This will help prevent infection.
If you are having an MRI-guided biopsy, you will need to wear metal-free clothing and remove any metallic objects, such as jewelry, watches, and hearing aids.
A technologist will walk through an MR imaging safety checklist with you. Tell your technologist about prior surgeries and metal implants, such as pacemakers, aneurysm clips, and joint replacements.
An MRI-guided procedure may use an injection of gadolinium contrast material. Because gadolinium does not contain iodine, it can be used safely in patients with contrast allergies.
Your MRI procedure may use an endorectal coil. This is a thin wire covered with a latex balloon. The doctor will lubricate this assembly and gently insert it into your rectum. Tell the doctor if you are allergic to latex so they may cover the coil with a latex-free balloon.
Read Also: What Does The Prostate Feel Like With Prostate Cancer
The Disadvantages Of Standard Prostate Biopsies
Other prostate cancer screening facilities still conduct standard prostate biopsies. This generally involves multiple needle sticks to take 12+ blind and random samples. Since these technicians are using ultrasound not MRI they arent able to detect tumors, and they cant differentiate between possible cancer and healthy tissue. Using this system, the physician cant see precisely where to aim their needle and, therefore, can only guess at where the cancer might be, capturing cells blindly or at random.
These standard biopsies have numerous disadvantages, including:
Significant inaccuracies.
Physicians misdiagnose cancer 30% of the time using this method because the blind needle biopsies often neglect to capture cancerous cells.
Errors in determining the cancers stage and aggression level.
This happens frequently when the blind samples miss the most dangerous cancer cells and instead capture cells on the fringes.
Unnecessary pain and discomfort for the patient.
This approach requires 12+ needle sticks that are done randomly and blindly. Whereas the Busch Center reduces this number to less than 4 with precise accuracy.
The need for repeat biopsies.
Often, patients PSA levels continue to rise, indicating that prostate cancer could be present, despite negative results, and they have to repeat this painful, stressful procedure.
Get The Optimal Diagnosis
| Soteria Medical BVs goal is to improve MR-guided biopsies of the prostate. Soteria has developed a unique new system for MR-guided interventions – based on a novel, patented motor principle.We are enabling the Physician to perform a targeted prostate biopsy using the best possible imaging modality with the same image quality for diagnostic imaging and biopsy guidance to further improve prostate cancer diagnosis. Our unique robot makes it able to detect and target the most aggressive part of the lesions and therefore improved and accurate MRgBx will help advance diagnostic results,followed by the best possible treatment for the patient. |
The RCM allows us to achieve high precision biopsies in a time-efficient manner and with that it is greatly appreciated by our patients, clinicians and radiologists alike. Confident high precision biopsies reduces the number of unnecessary cores to a minimum and maximizes the chances of retrieving tissue representative of the patients disease. At the same time it generates reliable feedback to the radiologist which we consider of paramount importance for optimizing the performance of the MR-diagnostics. Moreover, the efficiency of the procedure enables us to apply it whenever we expect it to outperform TRUS-biopsies, that is in most of our patients. With this, the system has revolutionized our practice and propelled us into a new era in the quest for stratifying prognosis.
You May Like: Can Prostate Cancer Cause Blood In Stool
Mri Analysis And Biopsy Technique
The referring institutions had carried out the mpMRI studies by means of 1.5 T or 3 T MRI scanners, and some of them had applied an endorectal coil and a variety of imaging protocols. All of those studies included multiplanar high-resolution T2, diffusion-weighted and dynamic contrast enhancement series. All of the scans and original readings were reviewed by a single expert radiologist who had more than 8 years experience in prostate mpMRI reading. Only patients with lesions suspected as clinically significant cancer were sent to IB-MRGpB. The same radiologist attended all subsequent biopsy procedures, and reviewed the previous diagnostic and MRI images taken real-time during guided biopsy. The IB-MRGpBs were carried out with 3 T MRI scanners and external coil application.
The IB-MRGpB patients were placed in a prone position and administered general anesthesia. A transrectal probe containing an MR visible gel was positioned against the apex of the prostate and attached externally to a manual biopsy device . Axial and sagittal T2-weighted images were obtained to visualize the prostate and identify the target lesion. Diffusion-weighted series were used at the radiologists discretion. A dedicated software package was used for device tracking and target localization as described elsewhere . Suspected clinically significant target lesions that were detected by MRI were sampled first, followed by 12-core template systematic prostate sampling when applicable.
Visual Registration Compared To Standard Biopsy
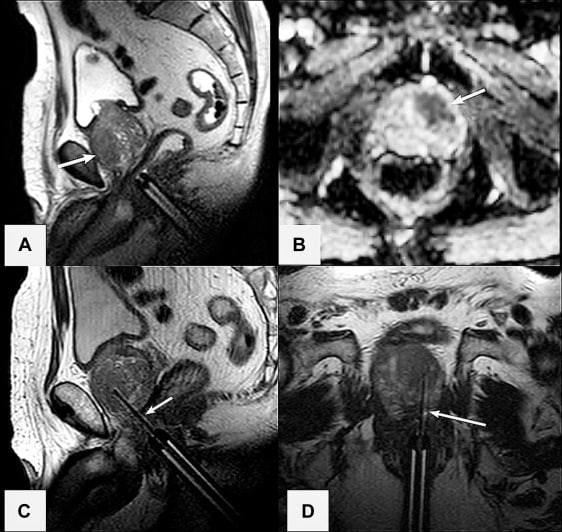
In a study by Park et al. of biopsy-naïve men randomized to standard TRUS or mpMRI-targeted biopsies , prostate cancer was detected in 30% of the mpMRI-targeted group compared with 10% of the standard TRUS biopsy group. The Authors concluded that in men with rising PSA and no previous biopsy, the use of mpMRI before TRUS-GB contributed to the detection of prostate cancer.
Haffner et al. compared MRI-targeted biopsy with systematic biopsy in 555 men, and reported that the detection accuracy of significant prostate cancer by targeted biopsies is significantly higher than that by extended systematic biopsies. Moreover, 13% of clinically insignificant cancers would have been avoided with the use of targeted biopsy alone.
Watanabe et al. have reported interesting results on the use of DW-MRI from mpMRI to guide MRI-targeted biopsies. The population comprised 1,448 men suspected of having prostate cancer based on PSA level, and was split into two groups. Group A underwent both targeted and systematic biopsies, whereas group B underwent systematic biopsies. Overall prostate cancer detection was 70.1% for group A compared with 13.1% for group B . Interestingly, the use of ADC maps resulted in the significantly greater cancer detection rates observed in group A.
Read Also: Bone Density Test For Prostate Cancer
What Happens During An Mri
These are done in the outpatient procedure area. Antibiotics will be given to reduce the risk of infection from the biopsy. Your doctor will be using the MRI and ultrasound images to watch where the biopsy needles are going. You may feel some discomfort or mild pain when the ultrasound probe is inserted into the rectum. Local anesthesia is used to ease the discomfort.
Mri Targeted Prostate Biopsy
DOI:Dr Joachim FegerRevisions:see full revision historySystems:
- MRI-guided prostate biopsy
MRI targeted prostate biopsy refers to an imaging targeted technique rather than the traditional systematic approach of a prostate biopsy after respective imaging with multiparametric MRI of the prostate.
As a consequence of the recent advances of multiparametric MRI of the prostate in the detection and characterization of prostate cancer 1,2, three different targeted MRI-guided biopsy techniques have been established and are in use 3: cognitive fusion biopsy, ultrasound-MRI fusion biopsy and MRI-guided in-bore biopsy 3,8-10.
MRI-targeted prostate biopsy has been shown to detect more clinically significant prostate cancer and less clinically insignificant cancer when compared with systematic biopsies, requiring fewer cores 4-7.
Don’t Miss: How Do Prostate Massagers Work
Studies Comparing Multiple Mri
Eleven studies were identified which compared two different MRI-targeting techniques. One study was a simulation study, and two studies selected men for one technique or another in a non-randomised fashion, and are described below. The eight remaining studies are summarized in Table 1 and Table S1. Only two studies investigated a totally biopsy-naïve cohort of men . All mpMRI scans were performed on either a 1.5T or 3T scanner and had T2-weighted scans, DWI and DCE. In the study by Lee et al. 12% of men did not have a DCE study. Standard TRUS biopsy was used as an additional comparator in 6 studies.
Table 1
Two studies compared biopsy techniques across different men biopsied at different time periods in the same institution, rather than comparing techniques in the same men, or randomizing men to one approach or another. With a sequential design, it is possible that the selection criteria for men having an MRI or biopsy may differ between groups, or that there may be a learning curve effect both in terms of MRI and biopsy, over time.
Patient Demographics And Clinical Data
Multiparametric MRI followed by in-bore MRI-guided biopsy was performed in 283 consecutive patients from 2007 to 2020.
Prostate carcinoma was detected in 173 patients, 110 patients did not show malignancy.
The retrospectively standardized PI-RADS score according to version 2.1 was 5 in 68 patients, 4 in 120 patients, 3 in 58 patients, and 2 in 34 patients three patients had missing diagnostic data for retrospective PI-RADS evaluation .
Figure 1
The mean prostate volume in our patients measured in MRI was 49.7 ml , mean prostate-specific antigen PSA was 9.63 ng/ml , mean PSA density was 0.22 ng/ccm .
Don’t Miss: Does Prostate Cancer Cause Back Pain
Study Method And Population
From July 2015 to April 2018, a series of 142 consecutive patients undergoing MRI-GB were prospectively enrolled. Indications for MRI-GB included patients with an elevated prostate-specific antigen serum level and/or abnormal digital rectal examination findings and 1 suspicious area on the mpMRI scan. We included both patient biopsy naïve and patient with previous TRUS-GB. According to the European Society of Urogenital Radiology guidelines, the presence of clinically significant PCa on mpMRI is defined as equivocal, likely, or highly likely according to a PI-RADS v2, score of 3, 4, or 5, respectively . The local institutional review board approved the present study.
Potential Methodological Differences Between Studies
During MRI-targeted prostate biopsies the operator is privy both to mpMRI and ultrasound findings and has a real-time image of the lesion during the biopsy process. This has shown significant advantages over systematic TRUS-GB . However, there is considerable heterogeneity in the study designs reported in the literature. This is due to a number of differences that range from the definition of clinically significant disease to the mpMRI protocols used.
The definition of clinically significant prostate cancer is often based on the Epstein criteria or the dAmico classification . These were defined in the setting of a systematic biopsy. Of note, these classifications were derived from a previous analysis by Stamey et al. where the tumor volume threshold of 0.5 cm3 for insignificant prostate cancer was obtained from 139 consecutively sampled radical cystoprostatectomy specimens. The Authors found that 55/139 men had incidental prostate cancer andbasing on epidemiological datasuggested that tumors measuring < 0.5 cm3 were unlikely to reach a clinically significant size within a mans life.
Due to the introduction of MRI-targeted biopsies, the definition of clinically significant prostate cancer has been changing and a number of new definitions have been proposed, though none have been widely recognized so far .
Don’t Miss: Can Prostatitis Cause Low Sperm Count
