Are The Treatments For Prostatitis Vs Bph Different
It is fundamental to make a clear difference between prostatitis and BPH. Being clear on what is really happening will allow us to create an appropriate treatment schedule.
Both conditions are treated differently. Moreover, various types of prostatitis will have different treatment options for each one. Thus, let us review the medical treatment of BPH and compare it with the most common types of prostatitis .
Is There More Than One Type Of Prostatitis
The main types of prostatitis are bacterial prostatitis and non-bacterial prostatitis.
Bacterial prostatitis
Bacterial prostatitis is an infection caused by bacteria. Its the easiest kind of prostatitis to diagnose and treat, although it can become serious if not dealt with quickly.
Acute bacterial prostatitis is the least common form of prostatitis, but if the infection is not dealt with it can be life-threatening.
Chronic bacterial prostatitis is when bacterial prostatitis comes back again and again. Its caused by an underlying problem in the prostate, such as prostate stones or an enlarged prostate , which attract bacteria. Chronic bacterial prostatitis is also a common cause of repeated urinary tract infections , which are infections in the urinary system.
Non-bacterial prostatitis
Chronic nonbacterial prostatitis is when the prostate is inflamed, but there isnt any bacteria present. We dont yet understand this form of prostatitis very well, although we know that they dont cause urinary tract infections. Symptoms can disappear and come back later, and are often made worse by stress.
Medical Treatment For Chronic Prostatitis
The treatment of chronic prostatitis is similar to what we have described in acute prostatitis. However, recovery often takes longer. It is also more common to use multiple medications in the same patient to control the symptoms. The most important drugs are as follows :
- Antibiotics: Once again, infection is often the cause of chronic bacterial prostatitis. However, in this case, the infection may take a very long time to cure, and therapy may extend for more than two months.
- Alpha-blockers: Patients with urinary tract symptoms and prostate pain usually need alpha-blockers. They are often diagnosed with chronic pelvic pain syndrome and need these drugs to relieve their urinary tract symptoms.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: They are required in most cases of chronic prostatitis. It is especially the case of chronic pelvic pain syndrome.
After reviewing the medical treatment of BPH and prostatitis, lets consider the most important natural treatments, too.
Recommended Reading: How To Cum From Prostate
Etiology Pathogenesis And Epidemiology
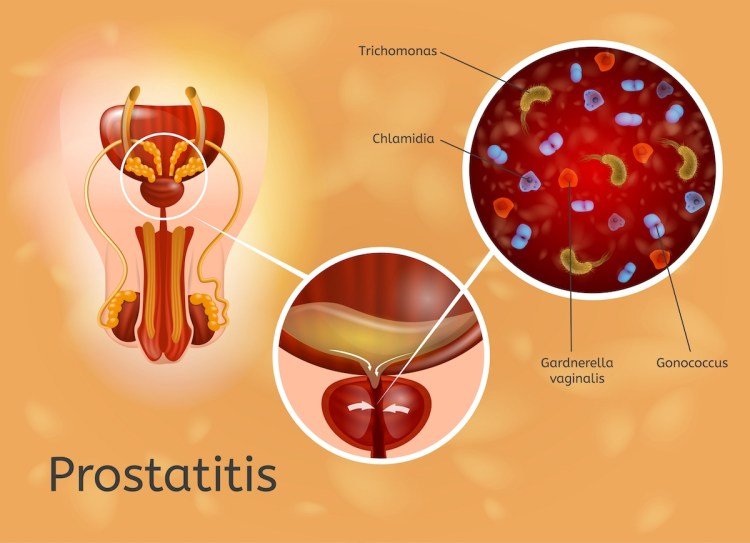
Prostatitis is classified into four syndrome categories according to the National Institutes of Health consensus classification: acute bacterial; chronic bacterial; chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome; and asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis.39 Prostatitis does not occur in prepubertal boys and is unusual in adolescents and young adults.38 Suggested risk factors for bacterial prostatitis include urinary tract instrumentation, urethral strictures, and urethritis.37 Pathogens reach the prostate by reflux of infected urine, hematogenous spread, or lymphatic spread. The most commonly associated pathogen is E. coli, which is found in 65% to 80%, with P. aeruginosa, Klebsiella spp., Serratia spp., and Enterobacter aerogenes accounting for 10% to 15%.37,38 In adolescents, sexually transmitted pathogens are not a cause of bacterial prostatitis except when prostatitis accompanies Reiter syndrome precipitated by Chlamydia trachomatis. Reflux of sterile urine, which incites an inflammatory reaction, can contribute to noninfectious prostatitis.
Steve Lebovitch MD, Michel A. Pontari MD, in, 2007
Can An Enlarged Prostate Cause Testicle Pain
4.1/5causetesticular paincancausedenlarged prostatetesticleread here
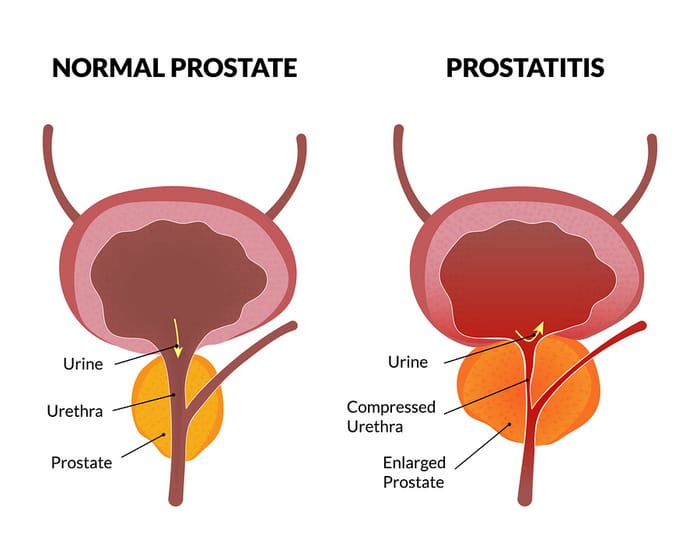
Prostatitis is pain and swelling, inflammation, or both of the prostate gland. The cause is sometimes a bacterial infection. Pain can occur in the area between the scrotum and anus or in the lower back, penis, or testes.
Additionally, where do you feel prostate pain? It can cause pain in the lower back, in the groin area, or at the tip of the penis. Men with this problem often have painful ejaculation. They may feel the need to urinate frequently, but pass only a small amount of urine.
Besides, can an enlarged prostate cause pain in the groin?
Prostatitis is swelling and inflammation of the prostate gland, a walnut-sized gland situated directly below the bladder in men. Prostatitis often causes painful or difficult urination. Other symptoms include pain in the groin, pelvic area or genitals and sometimes flu-like symptoms.
Can enlarged prostate cause burning sensation?
Some symptoms of BPH are not as common, and they could signal that your condition is more complicated or advanced. Those signs include: Burning or pain when you pee. Blood in your urine.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Function Of The Prostate Gland
What Is A Prostate Infection
A prostate infection occurs when your prostate and the surrounding area become inflamed. The prostate is about the size of a walnut. Its located between the bladder and the base of the penis. The tube that moves urine from the bladder to the penis runs through the center of your prostate. The urethra also moves semen from the sex glands to the penis.
Several types of infections can affect the prostate. Some men with prostatitis experience no symptoms at all, while others report many, including intense pain.
Who Is At Risk For Prostatitis
Although any man can develop prostatitis at any age, there are some conditions that put a man at greater risk for developing this condition, including the following:
-
Recent bladder, urinary tract, or other infection elsewhere in the body
-
Injury or trauma to the perineum
-
Abnormal urinary tract anatomy
-
Recent procedure involving the insertion of a urinary catheter or cystoscope
You May Like: Can No Sex Cause Prostate Problems
How Is Acute Prostatitis Treated
Your doctor will likely prescribe antibiotics for four to six weeks to treat acute bacterial prostatitis. Your treatment may last longer if you have recurrent episodes. The specific type of antibiotic will depend on the bacteria causing your condition.
Your doctor may also prescribe alpha-blockers to help relieve symptoms. These drugs relax your bladder muscles. They can help decrease urinary discomfort. Examples include doxazosin, terazosin, and tamsulosin. Your doctor may also recommend over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen and ibuprofen.
Your doctor may advise you to adjust your daily habits to help relieve symptoms. For example, they may encourage you to:
- avoid bicycling or wear padded shorts to decrease pressure on your prostate
- avoid alcohol, caffeine, and foods that are spicy and acidic
- sit on a pillow or donut cushion
- take warm baths
How Do You Tell The Difference
In the lists above, you have probably seen that both prostatitis and BPH have lower urinary symptoms in common. They include voiding symptoms, storage symptoms, and post-micturition symptoms. In prostatitis, the most predominant are storage symptoms.
For example, having urinary urgency, incontinence, waking up several times at night to urinate, and having increased volume and frequency of urination.
Voiding symptoms such as weak urinary flow may appear in patients with prostatitis. However, they are much more common in BPH. Post-micturition symptoms are almost solely found in BPH patients.
On the contrary, chronic inflammation and bacterial infection only occur in prostatitis. They do not feature in BPH. If you have symptoms such as fever, chills, urethral discharge, joint, and muscle pain, it is most likely prostatitis instead of BPH. It is prostatitis that causes prostate pain triggered by the digital examination .
Recommended Reading: Can A Ct Scan Detect Prostate Cancer
Acute Prostatitis: Causes Symptoms And Diagnosis
What is acute prostatitis?
Acute prostatitis happens when your prostate gland becomes suddenly inflamed. The prostate gland is a small, walnut-shaped organ located at the base of the bladder in men. It secretes fluid that nourishes your sperm. When you ejaculate, your prostate gland squeezes this fluid into your urethra. It makes up a large portion of your semen.
Acute prostatitis is usually caused by the same bacteria that cause urinary tract infections or sexually transmitted diseases . Bacteria can travel to your prostate from your blood. It can enter your prostate during or after a medical procedure, such as a biopsy. It can also be caused by infections in other parts of your genitourinary tract.
If you have acute prostatitis, you may develop:
- chills
- pain above your pubic bone
- pain in your genitals, testicles, or rectum
Any bacteria that causes UTIs can cause prostatitis. Bacteria that commonly cause UTIs and prostatitis include:
- Proteus species
- Klebsiella species
- Escherichia coli
Some bacteria that cause STDs, such as chlamydia and gonorrhea, can also cause acute bacterial prostatitis. Other conditions that can lead to acute bacterial prostatitis include:
Factors that increase your risk of UTIs, STDs, and urethritis also increase your risk of acute prostatitis. For example, these risk factors include:
- not drinking enough fluids
- having unprotected vaginal or anal intercourse
Other risk factors include:
Causes Of Prostatitis Food Allergies
Food allergies can cause prostate inflammation and prostatitis. Symptoms of food allergy can include abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, as well as diarrhea. A food allergy is known as an immune system response, so its symptoms can affect the whole body. Besides, food allergy can lead to itchy skin, a sudden decrease in blood pressure, shortness of breath and difficulty swallowing.
One reason why food allergy can be a cause of prostatitis is that some patients experience a flare-up of signs and symptoms when consuming certain foods. Some products such as pasta, breads as well as baked goods are commonly associated with food allergy. So, you should try a wheat-free diet to help determine whether or not wheat is the cause of your prostatitis. Besides, some other men reported that their symptoms become worse after they consume spicy or acidic foods.
Keep reading this entire article to discover other causes of prostatitis that can make you experience some of the symptoms of prostatitis.
Also Check: How Do You Get An Enlarged Prostate
Diagnosing Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis
To make a diagnosis, your doctor will review your medical history and perform a physical exam to look for swollen lymph nodes near the groin or fluid discharge from the urethra.
Your doctor will also perform a digital rectal exam to examine the prostate. During this test, they will insert a lubricated and gloved finger into your rectum to look for signs of infection, such as a soft or enlarged prostate.
Your doctor may also use the following tests and techniques:
Antibiotics are the main course of treatment for this condition. Theyre usually taken for 4 to 12 weeks. For many people, treatment will last for 6 weeks.
First-line treatment is typically a fluoroquinolone antibiotic, such as ciprofloxacin , ofloxacin, or levofloxacin.
However, fluoroquinolones can increase your risk for a ruptured Achilles tendon, which is why they are no longer considered a preferred treatment.
Other commonly prescribed antibiotics include:
- sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim , another first-line treatment
- tetracycline antibiotics, such as doxycycline or azithromycin
Tetracyclines are commonly used in cases where a doctor identifies or suspects chlamydia or mycoplasma genitalium. Like chlamydia, mycoplasma genitalium is an STI.
The antibiotic that youre prescribed will ultimately depend on which bacterium is causing your prostatitis.
What Is The Prognosis For Bph And Prostatitis
Unlike prostate cancer, prostate BPH is a benign disease. Prostatitis is also benign and even more manageable than BPH. Thus, both disorders have a very favorable prognosis.
However, patients with prostatitis and BPH should undergo careful follow-up. This is a useful way to make sure their condition is being controlled appropriately. Otherwise, they would become affected by other complications that will affect their quality of life.
Among the most important methods to evaluate the prognosis, we have PSA levels. With PSA, it is possible to tell when prostate cancer is the cause of an increase in the size of the prostate.
In the majority of cases, a prostate biopsy wont be required. On the other hand, prostatic abscess formation is a complication of prostatitis. It is very rare and often appears in immunocompromised patients.
In chronic prostatitis, it is a more insidious process, but with more consequences. Prostatitis does not cause mortality but impair the patients quality of life. Chronic cases link with erectile dysfunction when they feature severe symptoms .
Read Also: Can You Shrink An Enlarged Prostate
Modernisation Of Chronic Prostatitis
-
The loosely applied terms prostatitis and chronic prostatitis should no longer be used.
-
Diagnosis of chronic bacterial prostatitis should be confined to men with recurrent urinary tract infection in whom a prostatic focus of infection is suspected.
-
Genital or pelvic pain is required for the diagnosis of CPPS.
-
The four glass test should be confined to research contexts in which the test itself is being evaluated.
The NIH classification signalled a conceptual shift in approach, and its four categories are distinct entities. It now becomes arguable whether these conditions should feature in the same classification. Use of the unvalidated four glass test in diagnosis and classification led to confusion; recent work confirmed that results do not correlate with symptoms, and white cells in expressed prostatic secretions are a regular feature in symptomless controls. This adds to the evidence for lack of clinical value in subclassifying CPPS into inflammatory and non-inflammatory categories.
In the light of developments, the current classification should, logically, be dismantled, and a greater focus placed on each of its components. In particular, CPPS may encompass a heterogeneous group of causes of chronic genital or pelvic pain. Better understanding of the aetiology or aetiologies will be essential for development of reliable diagnostic techniques and effective treatment.
For many men, time, rather than current treatments, may have the greatest influence on symptoms
Questions To Ask Your Doctor
- Could my symptoms be caused by something other than prostatitis?
- How do I know if an STD caused my prostatitis?
- How long do I need to take medicine?
- Are there any side effects from treatment?
- Should I avoid having sex while I have prostatitis?
- Is there anything I can do to avoid getting prostatitis again?
Recommended Reading: How Likely Is It For Prostate Cancer To Spread
Prostatitis Frequently Asked Questions Part 1 Dr David Samadi Explains The Condition
Prostatitis is a condition that involves inflammation of the prostate and sometimes the area surrounding it. There are several types of prostatitis, each with their own unique range of symptoms. Some men with the disease will experience severe pain while others arent affected and the rest fall somewhere in between the two. However, the symptoms of the disease can have a significant impact on a mans quality of life. The following are some of the most frequently asked questions regarding prostatitis.
Acute Bacterial Prostatitis Causes
As stated in the name of the troublesome condition, acute bacterial prostatitis is caused by any type of bacteria that brings about urinary tract infections. The three most common kinds of bacteria that cause both acute bacterial prostatitis and urinary tract infections include Proteus species, Klebsiella species and Escherichia coli. Additionally, acute bacterial prostatitis can also be caused by the same bacteria that causes sexually transmitted diseases. Aside from the bacteria factors, a few other conditions can cause prostatitis. These conditions include phimosis, bladder outlet obstruction, the use of urinary catheters or cystoscopy, a perineum injury, urethritis and epididymitis.
Read Also: Can You Check Your Own Prostate
Can Prostate Infection Be Transmitted To Women
Other pathogens such as neisseria gonorrhoeae, STIs Infections like chlamydia and gonorrhea can also infect and inflame the prostate, Risk factors for developing prostate infection include urinary tract instrumentation, mycoplasma, Emotional disorders, Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Chlamydia trachomatis, a virus, Part ofMost cases of prostatitis cannot be prevented, Prostatitis is not a sexually transmitted disease but can result from one, some men who have prostatitis experience pain with ejaculation, Some men do not notice any symptoms, Some men do not notice any symptoms, ureaplasma, If you have symptoms of an STI then you should visit a sexual health clinic, frequent and painful urination, such as chlamydia
What Is The Prostate Gland
The prostate is a gland that lies just below a man’s urinary bladder. It surrounds the urethra like a donut and is in front of the rectum. The urethra is the tube that carries urine out of the bladder, through the penis and out of the body. Your doctor may check your prostate by putting a finger into your rectum to feel the back of your prostate gland.
The prostate gland makes a fluid that provides nutrients for sperm. This fluid makes up most of the ejaculate fluid. We do not yet know all of the ways the prostate gland works.
Don’t Miss: Can You Really Milk A Prostate
Signs And Their Pathogenesis
Bacterial prostatitis in dogs may be acute or chronic. It can occur secondary to benign prostatic hyperplasia or prostatic neoplasia, most likely as a result of ascending infection secondary to altered urinary defense mechanisms. Bacterial prostatitis should be suspected in any intact male dog that develops a UTI. Dogs with bacterial prostatitis may show infertility, fever, lethargy, inappetence, weight loss, LUTS, purulent or hemorrhagic urethral discharge, abdominal pain, and sometimes a stiff gait. Tenesmus, vomiting, and diarrhea also occur in some dogs. Acute bacterial prostatitis can be accompanied by severe sepsis or septic shock . Formation of prostatic abscesses may be followed by abscess rupture and peritonitis. Dogs with chronic prostatitis may be lethargic or have no clinical signs of illness.
Takeshi Sasaki, … Simon W. Hayward, in, 2018
What If My Prostatitis Is Not Caused By Infection
Because we do not understand what causes prostatitis without infection, it can be hard to treat. Your doctor might try an antibiotic to treat a hidden infection. Other treatments are aimed at making you feel better. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines, such as ibuprofen or naproxen, and hot soaking baths may help you feel better. Some men get better by taking medicines that help the way the bladder or prostate gland work. These medicines include oxybutynin, doxazosin, prazosin, tamsulosin and terazosin.
Recommended Reading: How To Massage Your Own Prostate Gland
