When To See A Doctor
If you don’t see a reduction in symptoms or if your symptoms worsen, you may need to undergo a different treatment plan.Â
Prescription Medications
The first higher-level treatment is to begin taking prescription drugs for an enlarged prostate. One class of medication is an alpha blocker. These medications, such as Flomax, Rapaflo, and Cardura, work by relaxing the affected muscles around the prostate to encourage urine flow.Â
Another type of medication is a 5-alpha reductase inhibitor. Examples of these medications include Proscar and Avodart, which are long-term medications that help to block the production of dihydrotestosterone and shrink the size of the prostate.
Surgery and Minimally Invasive Procedures
For moderate to severe BPH, you may need a medical procedure to relieve your symptoms. There are a variety of procedures, including laser therapy, microwave heat, or prostate tissue compression. Partial prostate removal and full removal are more invasive but may be necessary for extremely large prostate glands.
What Causes Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
The cause of benign prostatic hyperplasia is not well understood; however, it occurs mainly in older men. Benign prostatic hyperplasia does not develop in men whose testicles were removed before puberty. For this reason, some researchers believe factors related to aging and the testicles may cause benign prostatic hyperplasia.
Throughout their lives, men produce testosterone, a male hormone, and small amounts of estrogen, a female hormone. As men age, the amount of active testosterone in their blood decreases, which leaves a higher proportion of estrogen. Scientific studies have suggested that benign prostatic hyperplasia may occur because the higher proportion of estrogen within the prostate increases the activity of substances that promote prostate cell growth.
Another theory focuses on dihydrotestosterone , a male hormone that plays a role in prostate development and growth. Some research has indicated that even with a drop in blood testosterone levels, older men continue to produce and accumulate high levels of DHT in the prostate. This accumulation of DHT may encourage prostate cells to continue to grow. Scientists have noted that men who do not produce DHT do not develop benign prostatic hyperplasia.
How To Get Rid Of Enlarged Prostate
The prostate gland is a male reproductive organ that secretes the fluid that semen needs to transport sperm. Located underneath the bladder, the prostate surrounds the urethra, which is the duct through which urine passes. The prostate does naturally enlarge somewhat as a result of aging; however, problems occur when it grows to the extent that it chokes off this passageway, making urination difficult to impossible. That said, an enlarged prostate-known medically as benign prostatic hypertrophy – is an extremely common male malady, affecting 50 percent of men over 50, and 80 percent of men over 70.
Signs and Symptoms
- Frequent need to urinate, often with an inability to sleep through the night without frequent trips to the bathroom
- Difficulty urinating
- Diminished force of urine stream
- Dribbling after the end of urination
- Recurrent urinary tract infection
- Complete inability to urinate, even though the urge is present
Conventional Medical Treatment
To diagnose an enlarged prostate, your physician examines your prostate by inserting a gloved finger into the rectum and feeling the gland. You also may undergo a urine test, an ultrasound of the prostate gland, and/or a bladder cystoscope test. A cytoscope is passed through the urethra into the bladder and allows your doctor to visualize the inside of the bladder.
Complementary and Alternative Treatments
Nutrition and Supplementation
Most Important
Also Recommended
The Most Common Prostate Problem Among Men Over Age 50 This Condition Can Cause Embarrassing Urination Issues
While BPH does not increase your risk of getting prostate cancer or having sexual problems, it can affect quality of life, specifically by causing annoying and embarrassing urination problems.
“Since prostate enlargement happens gradually, men often think more frequent trips to the bathroom are a natural part of aging,” says Dr. Howard LeWine, chief medical editor at Harvard Health Publishing and an assistant professor of medicine at Harvard-affiliated Brigham and Women’s Hospital. “But a little medication can help relieve symptoms, meaning less urinary urgency and fewer nighttime awakenings to use the bathroom.”
How Is Enlarged Prostate Treated
Treatments for enlarged prostate include:
Lifestyle changes: These can include reducing liquid intake, bladder training , abstaining from alcohol and caffeinated beverages and regularly exercising the pelvic muscles.
Medication: A class of medication called Alpha Blockers works to relax muscle fibers in the prostate and bladder. This relaxation allows for increased urine flow and less frequent urination. A second class of medication, called Alpha Reductase Inhibitors, works to block the hormones that cause the prostate to swell. Many patients will take a combination of these two types of medication.
Minimally invasive procedures: Our specialists are trained in two minimally invasive procedures that can help remove or reduce the obstructing prostate tissue:
Surgery: For severe cases of a very enlarged prostate, surgical removal of the prostatecalled transurethral resection of the prostate may be the recommended course of action. Patients will decide with their doctor if aggressive treatment is warranted, depending on the size of the prostate and severity of symptoms.
Causes Of Benign Prostate Enlargement
The exact cause of benign prostate enlargement is unknown, but research suggests that hormones probably play an important role in the condition’s development.
Hormones are powerful chemicals that can have a wide range of effects on the cells of the body.
One theory is that as some men get older, the levels of a type of hormone called dihydrotestosterone increases, which may stimulate the growth of the prostate.
Another theory suggests that two hormones, testosterone and oestrogen, play a role. Younger men produce high levels of testosterone and much smaller levels of oestrogen. But as men get older, their levels of testosterone decrease, which means they then have a higher proportion of oestrogen in their body. It’s been suggested that the relative increase in oestrogen may stimulate prostate growth.
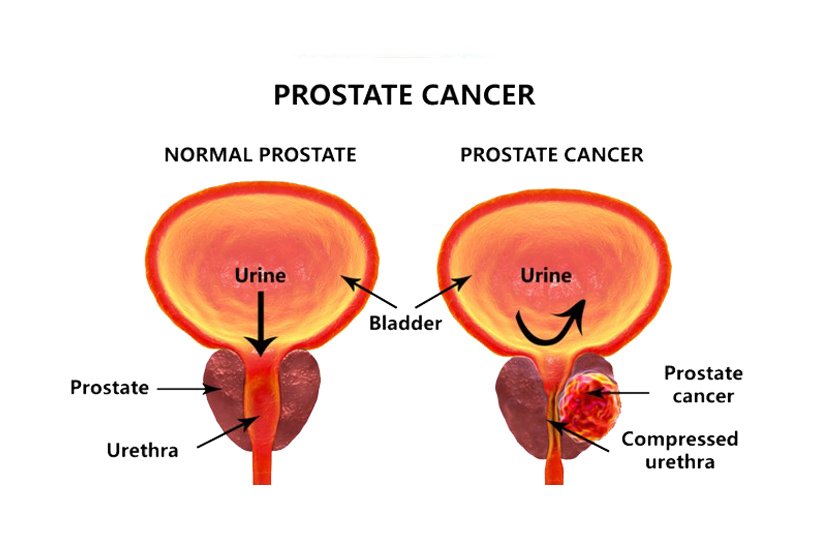
Symptoms Of Prostate Cancer
- Frequent urge to pass urine, especially at night
- Weak or interrupted urine stream
- Pain or burning when passing urine
- Blood in the urine or semen
- Painful ejaculation
- Nagging pain in the back, hips, or pelvis
Prostate cancer can spread to the lymph nodes of the pelvis. Or it may spread throughout the body. It tends to spread to the bones. So bone pain, especially in the back, can be a symptom of advanced prostate cancer.
Enlarged Prostate Treatments In The Pipeline
Researchers continue to investigate new therapies for enlarged prostates. “Another category of drugs is under development,” says Slawin. “We’ve come a long way in treating BPH. It’s no longer the life-threatening disease it once was. Now, in treatment, we’re working on quality of life issuesââ¬Â¦ reducing side effects of treatment.”
Also being studied is a procedure called water-induced thermotherapy , an experimental procedure that involves destroying excess prostate tissue utilizing heated water and an air-filled balloon, which protects normal prostate tissue. The procedure is performed with only local anesthesia. Results may not be fully apparent for three to four months. However, preliminary studies examining WIT have shown positive results, with a near doubling in urine flow. However, the American Urological Association has not thus far endorsed WIT as a viable treatment option for symptoms of BPH.
How Is Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Treated
Treatment options for benign prostatic hyperplasia may include
- lifestyle changes
- minimally invasive procedures
- surgery
A health care provider treats benign prostatic hyperplasia based on the severity of symptoms, how much the symptoms affect a mans daily life, and a mans preferences.
Men may not need treatment for a mildly enlarged prostate unless their symptoms are bothersome and affecting their quality of life. In these cases, instead of treatment, a urologist may recommend regular checkups. If benign prostatic hyperplasia symptoms become bothersome or present a health risk, a urologist most often recommends treatment.
Tips For Coping With An Enlarged Prostate
When a man reaches about age 25, his prostate begins to grow. This natural growth is called benign prostatic hyperplasia and it is the most common cause of prostate enlargement. BPH is a benign condition that does not lead to prostate cancer, though the two problems can coexist.
Although 50% to 60% of men with BPH may never develop any symptoms, others find that BPH can make life miserable. The symptoms of BPH include:
- a hesitant, interrupted, weak urine stream
- urgency, leaking, or dribbling
- a sense of incomplete emptying
- more frequent urination, especially at night.
As a result, many men seek treatment. The good news is that treatments are constantly being improved. Patients and their physicians now have more medications to choose from, so if one doesn’t do the trick, another can be prescribed. And thanks to some refinements, surgical treatments are more effective and have fewer side effects than ever before.
But there are some things men dealing with BPH can do on their own. When symptoms are not particularly bothersome, watchful waiting may be the best way to proceed. This involves regular monitoring to make sure complications aren’t developing, but no treatment. For more troubling symptoms, most doctors begin by recommending a combination of lifestyle changes and medication. Often this will be enough to relieve the worst symptoms and prevent the need for surgery
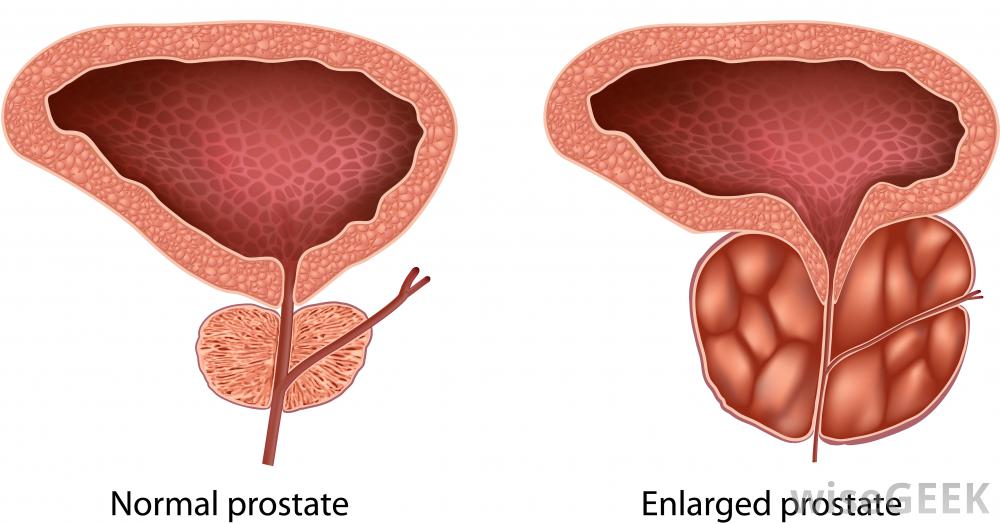
What Is Enlarged Prostate
Enlarged prostate refers to the state in which the prostate is enlarged but not cancerous.
Hormonal changes and cell growth resulting from the aging process may cause the prostate to swell, often impinging upon and compressing the urethra. This causes the bladder walls to become thicker and can prevent the bladder from emptying completely.
Symptoms Of Benign Prostate Enlargement
The prostate is a small gland, located in the pelvis, between the penis and bladder.
If the prostate becomes enlarged, it can place pressure on the bladder and the urethra, which is the tube that urine passes through.
This can affect how you pee and may cause:
- difficulty starting to pee
- a frequent need to pee
- difficulty fully emptying your bladder
In some men, the symptoms are mild and do not need treatment. In others, they can be very troublesome.
When Is A Big Prostate A Big Deal

If symptoms of BPH are affecting your daily life, your doctor may prescribe alpha-blockers, which relax the muscles near the prostate and help urine flow more freely, or 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors, which help shrink the prostate to relieve symptoms.
If your prostate is so enlarged that it is causing other health problems, you might need surgery. Surgery is an option when medications stop working or for those who can no longer urinate at all.
If you have an enlarged prostate, visiting a urologist who specializes in this condition can help prevent worsening symptoms and lead to dramatic improvement through minor interventions.
When Is Bph Treatment Necessary
The course of BPH in any individual is not predictable. Symptoms, as well as objective measurements of urethral obstruction, can remain stable for many years and may even improve over time for as many as one-third of men, according to some studies. In a study from the Mayo Clinic, urinary symptoms did not worsen over a 3.5-year period in 73% of men with mild BPH. A progressive decrease in the size and force of the urinary stream and the feeling of incomplete bladder emptying are the symptoms most correlated with the eventual need for treatment. Although nocturia is one of the most annoying BPH symptoms, it does not predict the need for future intervention.
If worsening urethral obstruction is left untreated, possible complications are a thickened, irritable bladder with reduced capacity for urine; infected residual urine or bladder stones; and a backup of pressure that damages the kidneys.
Decisions regarding treatment are based on the severity of symptoms , the extent of urinary tract damage and the mans overall health. In general, no treatment is indicated in those who have only a few symptoms and are not bothered by them. Intervention usually surgical is required in the following situations:
Find a Location
Currently, the main options to address BPH are:
- Watchful waiting
- Medication
- Surgery
Does Having Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Increase The Risk Of Prostate Cancer
Based on research to date, having BPH does not seem to increase the risk of developing prostate cancer. However, BPH and prostate cancer have similar symptoms, and a man who has BPH may have undetected cancer at the same time.
To help detect prostate cancer in its early stages, the American Urological Association and the American Cancer Society recommend a prostate screening every year for men ages 55 to 69. They also recommend that men who are at high risk such as African-American men and men who have a family history of prostate cancer begin screening at age 40. Screening tests for prostate cancer include a blood test for a substance called prostate-specific antigen and the digital rectal exam .
Questions You May Want To Consider Asking Your Doctor Include:
- What type of prostate problem do I have?
- Is more testing needed and what will it tell me?
- If I decide on watchful waiting, what changes in my symptoms should I look for and how often should I be tested?
- What type of treatment do you recommend for my prostate problem?
- For men like me, has this treatment worked?
- How soon would I need to start treatment and how long would it last?
- Do I need medicine and how long would I need to take it before seeing improvement in my symptoms?
- What are the side effects of the medicine?
- Are there other medicines that could interfere with this medication?
- If I need surgery, what are the benefits and risks?
- Would I have any side effects from surgery that could affect my quality of life?
- Are these side effects temporary or permanent?
- How long is recovery time after surgery?
- Will I be able to fully return to normal?
- How will this affect my sex life?
- How often should I visit the doctor to monitor my condition?
Related Resources
How Do You Give A Prostate Massage With Your Fingers
If, after talking through a few specifics, youre still not sure where to start, Brown-James has some techniques. Bring your pointer, middle, and ring fingers together, then push up into , Brown-James explains. Stimulating this area with gentle but firm strokes also stimulates the prostate. It’s basically a playground down thereBrown-James recommends techniques like rubbing clockwise for 810 strokes, then going counterclockwise, stroking toward the scrotum or touching the penis while you massage your partners perineum. Even though youve hopefully discussed what youd both like beforehand, you and your partner should talk about what you think you might each like to do and feel and then, if you agree to test things out, try that next, making sure youre each being open about what feels good and what doesnt feel so good in the moment.
What Are The Symptoms Of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Lower urinary tract symptoms suggestive of benign prostatic hyperplasia may include
- urinary frequencyurination eight or more times a day
- urinary urgencythe inability to delay urination
- trouble starting a urine stream
- a weak or an interrupted urine stream
- dribbling at the end of urination
- nocturiafrequent urination during periods of sleep
- urinary incontinencethe accidental loss of urine
- pain after ejaculation or during urination
- urine that has an unusual color or smell
Symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia most often come from
- a blocked urethra
- a bladder that is overworked from trying to pass urine through the blockage
The size of the prostate does not always determine the severity of the blockage or symptoms. Some men with greatly enlarged prostates have little blockage and few symptoms, while other men who have minimally enlarged prostates have greater blockage and more symptoms. Less than half of all men with benign prostatic hyperplasia have lower urinary tract symptoms.3
What Is Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
BPH is an age-related enlargement of the prostate gland. BPH is one of the most frequent medical problems in elderly males. In humans, it can result in urinary tract problems, obstruction of the urethra, sexual dysfunction, and blood in the urine. One of the most frequent symptoms is having to get up to use the bathroom multiple times during the night.
BPH results from urogenital aging, although the etiology is not precisely known. Traditional treatment options for men with BPH include medications such as alpha-blockers or surgical interventions. Side effects of treatments may include the inability to ejaculate, retrograde ejaculation , erectile dysfunction, and even loss of bladder control. Some men affected have reported that taking saw palmetto, an herbal supplement, gives them relief but clinical evidence for its effectiveness is not conclusive. Clearly, effective and less invasive treatments for this common disease are needed.
What Other Problems Might An Enlarged Prostate Cause
A small number of men may find it difficult to empty their bladder properly this is called urine retention. If youve been diagnosed with an enlarged prostate, your doctor will look at your test results to see if youre at risk of urine retention. You may be more likely to get urine retention if:
- youre aged 70 or over
- your prostate is very large
- you have a raised prostate specific antigen level
- you have severe urinary symptoms and a very slow flow.
Chronic urine retention
This is where you cant empty your bladder fully, but can still urinate a little. It usually develops slowly over time. Chronic means long-lasting. The first signs often include a weak flow when you urinate, or leaking urine at night. You may feel that your abdomen is swollen, or that youre not emptying your bladder fully.
Chronic urine retention is usually painless. But the pressure of the urine can slowly stretch your bladder muscle and make it weaker. This can cause urine to be left behind in the bladder when you urinate. If you dont empty your bladder fully, you might get a urine infection, need to urinate more often, leak urine at night, or get painful bladder stones. You might also see some blood in your urine. Chronic urine retention can damage your bladder and kidneys if it isnt treated.
There are treatments for chronic urine retention, including:
- passing a thin, flexible tube called a catheter to drain urine from your bladder
- surgery to widen the urethra.
Acute urine retention
Natural Ways To Shrink The Prostate
, Prostate
If you are one of the 14 million men who suffer from an enlarged prostate due to benign prostatic hyperplasia , it is understandable that you would like to find a way to shrink your prostate or at least reduce its symptoms. You may wonder how to take the prostate back to a younger, more normal size that doesnt keep you running to the bathroom all night long.
When enlarged, the prostate gland can put pressure on the urethra and cause symptoms such as frequent urination and nighttime urination. The growing prostate can also keep the bladder from completely emptying and can affect the flow of urine, making for a weaker flow, starting and stopping of the flow, and urinary tract infections. More severe cases of BPH can make it difficult to urinate.
Even though BPH is not cancerous, it does affect a man and his familys quality of life. If you are waking up several times a night to urinate, chances are you are waking up your family members at least some of the time. Having to stop activities due to urinary urgency can have an effect and cause stress and annoyance for everyone involved.
Growth of the prostate with age is normal. One-third of men experience symptoms of an enlarged prostate by age 50. By age 70, 70 percent of men are affected, according to Johns Hopkins. So what can you do about it? Actually, there is a lot you can do.
Diagnosing An Enlarged Prostate
As with all incontinence conditions, a thorough diagnosis must be developed before action can be taken. You may have heard of some of these exams. And if you havent, now is a good time to familiarize yourself with them. Not only is knowledge power, but it also eliminates surprises.
Because those with BPH can experience symptoms from mild to severe, the treatment options featured here are organized from least invasive to more intense.
Diagnosing Benign Prostate Enlargement
You might have several different tests to find out if you have an enlarged prostate.
A GP may do some of these tests, such as a urine test, but others might need to be done at a hospital.
Some tests may be needed to rule out other conditions that cause similar symptoms to BPE, such as prostate cancer.
Medications For Enlarged Prostate
There are two main classes of pharmaceuticals that work to alleviate enlarged prostate symptoms: alpha blockers and alpha reductase inhibitors
-
Alpha Blockers. Alpha blockers relax the smooth muscle around the bladder neck and within the urethra.
-
Inhibitors. Inhibitors stop the conversion of the male hormone testosterone to DHT to reduce the prostate’s size, eliminating blockage.
Dont be surprised if your physician prescribes a combination of the two medications, as they have been shown to work more effectively together than alone. The downside is that combination therapy may increase the likelihood of experiencing side effects from the medications. Be sure to work with your doctor to assess the benefits and costs before starting on combination therapy.
Part 2 Of 3:using Medication To Reduce Symptoms
No 5: Try Supplements
There are many prostate supplements that can benefit an aging prostate and support normal urinary health. When shopping for supplements, look for formulations that include ingredients that can help with overall prostate health. As already mentioned, there are several supplements that help support hormone regulation. One of them, pygeum, has also been found in studies to be useful in reducing BPH symptoms. While studies have not found that pygeum actually shrinks the prostate, it does help offer relief of urinary symptoms. Curcumin is another supplement that can help regulate the inflammatory processes that support health of the prostate. Saw palmetto is a well-researched supplement that studies have found as effective as popular drugs for BPH without causing the scary side effects of prostate drugs.
Should I Be Concerned About An Enlarged Prostate
Posted on by McIver Clinicin , Enlarged Prostate
Benign prostatic hyperplasia or BPH is what is known as an enlarged prostate. It may sound scary, but should you be concerned about an enlarged prostate? This depends on your age, whether you are symptomatic, and how severe those symptoms are. Heres a bit more detail!
Maintain A Healthy Weight
Being overweight can cause and worsen BPH symptoms so if necessary take some steps to reduce your weight. You can do this by incorporating moderate exercise and good dietary choices into your daily routine. This might seem easier said than done but it can make a big difference.
If youd like more advice on good nutrition Id recommend you have a look at our food hub. Also, our get active hub is a good place to find information and advice on incorporating more exercise into your routine. Some of my favourite blogs here include:
