Screenings Can Lead To High Costs
The cost for a PSA test is fairly lowabout $40.
If your result is abnormal, the costs start adding up. Your doctor will usually refer you to a urologist for a biopsy. Costs may include:
- A consultation fee .
- An ultrasound fee .
- Additional professional fees .
- Biopsy fees .
If the biopsy causes problems, there are more costs. You might also have hospital costs.
How The Test Will Feel
During the procedure you may feel:
- Mild discomfort while the probe is inserted
- A brief sting when a sample is taken with the biopsy needle
After the procedure, you may have:
- Soreness in your rectum
- Small amounts of blood in your stools, urine, or semen, which may last for days to weeks
- Light bleeding from your rectum
To prevent infection after the biopsy, your provider may prescribe antibiotics to take for several days after the procedure. Be sure you take the full dose as directed.
Dont Miss: How Does Prostate Cancer Kill
What Is A Prostate Biopsy
The prostate gland is found only in males. It sits below the bladder andwraps around the urethra . Theprostate helps make semen.
A biopsy is a procedure used to remove a small piece of tissue or cellsfrom the body so it can be examined under a microscope.
In a prostate biopsy, prostate gland tissue is taken out with a biopsyneedle or during surgery. The tissue is checked to see if there are canceror other abnormal cells in the prostate gland.
A prostate biopsy may be done in several different ways:
-
Transrectal method. This is done through the rectum and is the most common.
-
Perineal method. This is done through the skin between the scrotum and the rectum.
-
Transurethral method. This is done through the urethra using a cystoscope .
Ultrasound is usually used to look at the prostate gland and guide thebiopsy needle.
Recommended Reading: What Happens After Prostate Surgery
What Does A Prostate Biopsy Involve
If you decide to have a biopsy, youll either be given an appointment to come back to the hospital at a later date or offered the biopsy straight away.
Before the biopsy you should tell your doctor or nurse if youre taking any medicines, particularly antibiotics or medicines that thin the blood.
You may be given some antibiotics to take before your biopsy, either as tablets or an injection, to help prevent infection. You might also be given some antibiotic tablets to take at home after your biopsy. Its important to take them all so that they work properly.;
A doctor, nurse or radiologist will do the biopsy. There are two main types of biopsy:
- a trans-rectal ultrasound guided biopsy, where the needle goes through the wall of the back passage
- a transperineal biopsy, where the needle goes through the skin between the testicles and the back passage .
Painful Prostate Biopsy Heres What You Need To Know
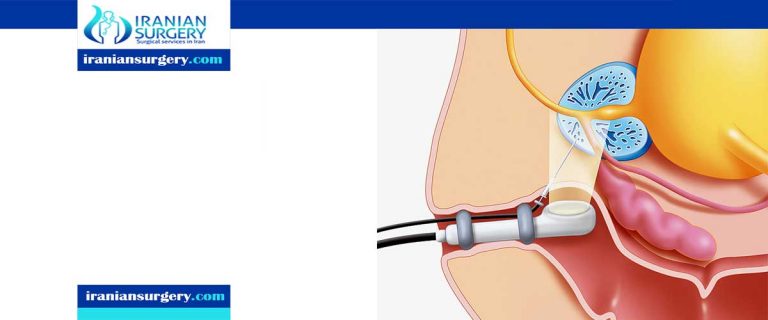
A standout amongst the most famous symptomatic tests performed to recognize Prostate Cancer is Biopsy. If you are experiencing pee issues, erectile brokenness, or any prostate-related indications and would look for medical counsel from a medical expert, the standard suggestion would either be for you to experience the PSA test first then Prostate Biopsy or the last quickly.
Don’t Miss: Can Prostate Issues Cause Erectile Dysfunction
Limitations Of The Study
This study did not account for the average number of prostate biopsy cores obtained or number of passes of the biopsy needle in the two groups. The study also did not explore the need for oral analgesia in the days following the prostate biopsy as this may have been a pointer to the sensation of post-procedural pain. However, most of the patients reported very low pain scores at 1 day after the procedure and this probably would not have affected the findings and conclusions of this study.
Types Of Prostate Biopsy
A prostate biopsy may be done in several different ways:
- Transrectal method
At the moment, most biopsies are done using a transrectal ultrasound-guided technique. A TRUS prostate biopsy is where the needle goes through the wall of the back passage .
- Perineal method
This is done through the skin between the scrotum and the rectum.
- Transurethral method
This is a type of biopsy done through the urethra using a cystoscope .
- Transperineal biopsy
Unlike the TRUS Guided Biopsy, this is where the doctor inserts a needle into the prostate through the skin between the testicles and the anus. This area is the perineum.
The needle is inserted through a template or grid. This is a targeted biopsy, which can be target a specific area of the prostate using MRI scans. An advantage of the TP biopsy is that it can now be performed under local anesthesia.
Also Check: How To Self Milk Prostate
How Long Does It Take To Recover From A Prostate Biopsy
A patient may take about four to six weeks or even more recover after a prostate biopsy. The recovery process after biopsy usually depends on the patient’s health and age. Doctors may recommend only light activities for 24-48 hours after a prostate biopsy. The doctor prescribes painkillers, vitamins, and antibiotics for a few days to speed up the healing process.
After the biopsy, it is normal to experience the following sensations or symptoms:
- Burning urination: It may start within 24 hours after the biopsy and may continue until three to seven days. This burning sensation is a side effect of the procedure and usually considered normal.;
- Frequent urination: It may gradually improve over the first 24-36 hours.
- Blood in the urine: It is considered normal to have slightly red-tinged urine or urine that resembles the color of a rose or red wine. This may last from 12 hours to 3 weeks after the biopsy.
- Blood in stool: A patient may notice red stains on the toilet tissue or see some bloody streaks in the stool. This may last for up to five days.
- Blood in the semen: This may persist for up to six weeks after the biopsy.
- Tiredness: A patient may feel tired for a month or two. It usually takes 30-45 days to regain full normal strength after the procedure; hence, sufficient rest is usually advised by the doctor.;
Post-biopsy restrictions and instructions:
Genetic Testing For Some Men With Prostate Cancer
Some doctors now recommend that some men with prostate cancer be tested to look for certain inherited gene changes. This includes men in whom a family cancer syndrome is suspected, as well as men with prostate cancer that has certain high-risk features or that has spread to other parts of the body. Talk to your doctor about the possible pros, cons, and limitations of such testing.;
Read Also: What Are The Manifestations Of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Mri/ultrasound Fusion Biopsy Of The Prostate
The MRI/Ultrasound fusion biopsy begins with an MRI of the prostate performed in the Department of Radiology. This initial exam will be done a few days or weeks prior to the scheduled prostate biopsy.; Both appointments will be made through the Department of Urology. A specially trained Radiologist will analyze the images and identify areas that appear suspicious for prostate cancer.
Read Also: How Likely Is It For Prostate Cancer To Spread
How Doctors Determine Whether To Recommend A Prostate Biopsy
No two patients are alike, and a urologist needs to take many variables into account before recommending a prostate biopsy, including a patients:
- Age and life expectancy
- Comorbidities
- Change in PSA values across time.
The decision of whether to undergo a prostate biopsy should be determined after an individual conversation with your doctor during which he or she presents you with the big picture of your situation.
Compare, for example, the case of two 50-year-old men: One of them has been diagnosed with heart failure and is in poor overall health. The other has no pre-existing health conditions. I probably wouldnt advise a prostate biopsy for the 50-year-old with heart failure because prostate cancer is unlikely to cause his death within the next five years.
But I would recommend that the healthy 50-year-old get a prostate biopsy, because even if his cancer isnt aggressive right now, missing a prostate cancer diagnosis may result in his death from the disease in 15 years. In his case, it would be better to risk the prostate biopsy to catch the cancer early and improve his chances of long-term survival.
Recommended Reading: Can You Really Milk A Prostate
Getting The Results Of The Biopsy
Your biopsy samples will be sent to a lab, where they will be looked at with a microscope to see if they contain cancer cells. Getting the results usually takes at least 1 to 3 days, but it can sometimes take longer. The results might be reported as:
- Positive for cancer: Cancer cells were seen in the biopsy samples.
- Negative for cancer: No cancer cells were seen in the biopsy samples.
- Suspicious: Something abnormal was seen, but it might not be cancer.
If the biopsy is negative
If the prostate biopsy results are negative , and the chance that you have prostate cancer isnt very high based on your PSA level and other tests, you might not need any more tests, other than repeat PSA tests sometime later.
But even if many samples are taken, biopsies can still sometimes miss a cancer if none of the biopsy needles pass through it. This is known as a false-negative result. If your doctor still strongly suspects you have prostate cancer , your doctor might suggest:
- Getting other lab tests to help get a better idea of whether or not you might have prostate cancer. Examples of such tests include the Prostate Health Index , 4Kscore test, PCA3 tests , and ConfirmMDx. These tests are discussed in Whats New in Prostate Cancer Research?
- Getting a repeat prostate biopsy. This might include getting additional samples of parts of the prostate not biopsied the first time, or using imaging tests such as MRI to look more closely for abnormal areas to target.
Prostate cancer grade
Gleason score
Comparison Of Pain Scores Between Groups

Our study showed that patients reported a higher pain score at insertion of the TRUS probe in the PPNB group compared to the CB group, though this was not statistically significant. Similarly, Urabe et al. reported a statistically significant higher average pain score at the point of probe insertion for PPNB+IRLA group compared to the CB+IRLA group. This is probably due to the fact that insertion of the TRUS probe precedes the administration of the PPNB in the PPNB group, while the administration of CB preceded probe insertion which also had the effect of relaxing the anal sphincter. This point may confer an advantage on CB over PPNB as analgesia for prostate biopsy.
There was no significant difference in the experience of pain at administration of block in our study. However, Urabe et al. reported a significantly higher average pain score of 2.9±2.1 in the CB+IRLA group than in the PPNB+IRLA group at the moment of administering the analgesia. This could have been as a result of the fact that in their study, IRLA was instilled prior to the administration of PPNB.
Table 4 Protocols, findings and conclusions of studies that compared CB with PPNB
Recommended Reading: How To Stop Leaking After Prostate Surgery
Set To Experience Biopsy
The little reproductive organs behind the prostate will be assessed and the area amongst it and the prostate will be infused one on every side with anesthesia, to numb it. The biopsy will be performed then, by taking specimens of your prostate tissues and putting these examples under the magnifying instrument to search for tumor cells.
Comparison Of Satisfaction With Procedure And Willingness To Repeat Biopsy Procedure And Incidence Of Complications Between Groups
The results of this study revealed that there was no statistical difference in the level of satisfaction experienced by the participants of either groups. This was in contrast to the report by Na Wang and colleagues . In their study of 190 men, over half in the CB group while only 24.2% of the men in PPNB+IRLA group reported excellent satisfaction with the procedure . However, the difference in proportion was less pronounced when the sum of men who reported either excellent or good levels of satisfaction were compared between the groups: 84.7% versus 75.8% for CB and PPNB+IRLA, respectively.
The willingness to repeat the prostate biopsy using the same method of analgesia was similar across the groups. Obi et al. reported similar proportions of men willing to have a repeat biopsy; 72% of the men who had PPNB and 88% men who had saddle block were willing to have a repeat prostate biopsy .
The results showed a low incidence of complications, with no significant difference between the groups. This was similar to the findings by Na Wang et al. where out of 95 persons per group, one man, 2 men and 6 men had hematuria, fever and urinary retention, respectively in the CB group, while 3 men, 4 men and 4 men with similar complications, respectively, in the PPNB+IRLA group. Similarly, there was no significant difference in the incidence of complications between the groups in the study by Urabe et al. .
You May Like: Can The Prostate Grow Back After Surgery
Benefits Of Getting A Prostate Biopsy
A prostate biopsy is the only way to definitively determine whether you have prostate cancer and, if you do, how aggressive it is.
While prostate biopsies arent always conclusive, in general, a biopsy gives men the reassurance of knowing whether they have cancer or not. If you know you have prostate cancer, youre more likely to be appropriately treated.
Appropriate prostate cancer treatment options depend on several factors, including the stage of the cancer, your age, your general health and which risk category your cancer falls into.
Localized prostate cancer is categorized into six risk categories, which range from very low-risk to very high-risk. The risk group is determined by the stage of your cancer, your PSA levels and the Gleason score obtained from the biopsy pathology report.
The National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines outline appropriate treatment options based on risk categories and whether the cancer has already metastasized.
Patients whose cancer is confined to the prostate and falls into the very low-risk and low-risk categories tend to have slow-growing cancers. Treatment options for these patients often include active surveillance, radiation therapy or surgery. Similar treatment options may be recommended to patients in the low-risk and favorable intermediate prostate cancer risk categories.
The NCCN guidelines recommend immediate treatment for patients with high-risk disease or those patients whose cancer has metastasized.
Technique And Anesthetic Agents Used For The Periprostatic Nerve Block
The technique for the periprostatic nerve block is based on the original method described by Nash et al. in 1996 for basal injections. The procedure can be performed in an out-patient setting, but resuscitation facilities should be available. The same protocol used for pre-procedure preparation of TRUS-guided prostate biopsy is followed. The bladder is emptied before the procedure to prevent urinary retention .
The optimal patient position for performing the periprostatic nerve block is the left lateral decubitus position with buttocks at or slightly beyond the side of the table, the left leg in a straight position, and the right leg flexed so as to touch the abdomen. The lithotomy position is an alternative, but it is associated with more discomfort .
Optimal position of ultrasound transrectal transducer with biopsy-guide attachment for periprostatic nerve block. Tip of ultrasound transducer is pressed against prostate and anterior rectal mucosa. Transducer is manipulated to direct needle towards neurovascular bundles at base and apex of prostate and local anesthetic drug is injected around bundles.
Also Check: Is Masturbation Good For Your Prostate
Why You Should Not Have A Prostate Biopsy
Prostate biopsy risks There are risks associated with prostate biopsies, but physicians can take steps to reduce those risks. Risks and ways to manage them include: Infection: The most serious risk of a prostate biopsy is the risk of infection, including urinary tract infections and, less commonly, sepsis.
Can Prostate Biopsy Cause Erectile Dysfunction
If are recommended by your doctor to undergo prostate biopsy procedure for the detection of cancer, you must have a lot of questions and reservations. One of the most common question that people usually have is, can prostate biopsy cause erectile dysfunction or alter the quality of sex life at all?
The answer is yes; erectile dysfunction may occur after prostate biopsy in some susceptible individuals; but it is usually transient and self-limiting.
Accorded to a study published in the Journal of Urology, men who undergo prostate biopsy are at risk of temporary erectile dysfunction due to anxiety or pain; however, in most men, symptoms improve within a couple of weeks.
Recommended Reading: How To Get To A Man’s Prostate
What Kind Of Anesthesia Is Used For Prostate Biopsy
The procedure may be done;under;a local or;general anesthetic. . Local anesthesia Just the area that is being operated on is numbed, given as an injection and may also be given with a sedative.;General anesthetic;means medicines are;used;to put you into a deep sleep during the procedure.) ;General anesthesia Blocks;pain;and keeps you asleep through the surgery.
Should I Get A Prostate Biopsy An In
Rising or elevated prostate-specific antigen; levels, an abnormal digital rectal exam , or both, may indicate the presence of prostate cancer, and having those conditions may lead your doctor to recommend a prostate biopsy. But controversy surrounding the PSA blood test and concerns about prostate biopsies cause many patients to ask:
- Should I get a prostate biopsy?
- Are the risks of a prostate biopsy worth it?
- Are there alternatives to a prostate biopsy?
- If I have prostate cancer, is treatment necessary if Im not experiencing symptoms?;
If youre looking for answers to these questions, you may find conflicting and confusing information across the medical field, in the news and on prostate cancer websites. Some dispute the necessity of prostate cancer screening and discourage men from getting a PSA test to begin with. Others suggest that prostate cancer is overtreated and that the risks associated with biopsies and treatment arent worth the potential benefit.
While the 10-year survival rate of men with a diagnosis of prostate cancer is approximately 98 percent, prostate cancer remains the second leading cause of cancer deaths in American men. The American Cancer Society estimates that 248,530 new cases of prostate cancer will be diagnosed in the United States in 2021 and that one in every 41 men diagnosed will die from the disease.
To help you better understand this topic and whether you should get a prostate biopsy, this article will cover:
You May Like: How Do You Check For Prostate Cancer
