What Causes An Enlarged Prostate
We still dont really know all the things that cause the prostate to grow. But we do know about two risk factors that can increase your risk of having an enlarged prostate.
Age
Your risk of having an enlarged prostate increases as you get older. Many men aged 50 or over have an enlarged prostate, but they dont all get symptoms. And some men have symptoms that don’t bother them.
Hormone levels
The balance of hormones in your body changes as you get older. This may cause your prostate to grow.
Other factors
Some studies show that obese men and men who have diabetes may be more likely to develop an enlarged prostate. Regular exercise may help to reduce your risk of urinary symptoms. But we still need more studies into the causes of enlarged prostate to know for certain if, and how, we can prevent it.
There is also some research that suggests you may be more at risk of developing an enlarged prostate if your father or brother has one. Again, further studies are needed to confirm this.
Understanding Your Prostate Pathology Report
At least initially, the pathology report is one of the most important factors in the management of your prostate health, especially if you have been diagnosed with cancer. For example, it can provide valuable information about the location and extent of the cancer, thus helping your physician decide whether to recommend active surveillance, hormone treatment, radiation therapy, or surgery.
With that in mind, you might think that preparing and reading a pathology report would be straightforward but unfortunately the opposite is true. Pathology reports are not prepared uniformly . In fact, they can vary considerably even within a single institution. They may not be labeled thoroughly or contain enough specifics for you and your doctor to make a good treatment decision.
At the same time, the information that is included in the report may be difficult to decipher. You may also get conflicting interpretations depending on how the report was prepared and who is reading it. It is entirely possible for two pathologists to look at the same biopsy slides and yet disagree about whether you have cancer!
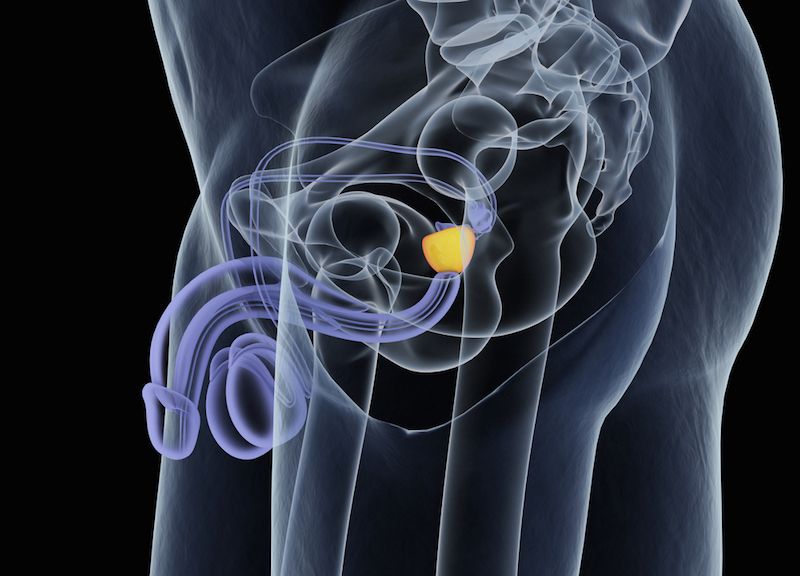
What Is Your Prostate And What Does It Do
Your prostate is a small gland that lives inside your body, just below your bladder. It sits around the urethra, which is the tube that carries pee from your bladder through your penis. Only men have a prostate.
Your prostate produces some of the fluids contained in your semen, the liquid that transports sperm. This liquid contains special enzymes and hormones that help your sperm cells function properly, which means the prostate plays a key part in your fertility. The muscles in your prostate also help push semen through your urethra when you ejaculate.
You May Like: Do Female Have Prostate
What Questions Should I Ask My Healthcare Provider
If you have prostate cancer, you may want to ask your healthcare provider:
- Why did I get prostate cancer?
- What is my Gleason score? What is my Grade Group? What do these numbers mean for me?
- Has the cancer spread outside of the prostate gland?
- What is the best treatment for the stage of prostate cancer I have?
- If I choose active surveillance, what can I expect? What signs of cancer should I look out for?
- What are the treatment risks and side effects?
- Is my family at risk for developing prostate cancer? If so, should we get genetic tests?
- Am I at risk for other types of cancer?
- What type of follow-up care do I need after treatment?
- Should I look out for signs of complications?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Prostate cancer is a common cancer that affects males. Most prostate cancers grow slowly and remain in the prostate gland. For a small number, the disease can be aggressive and spread quickly to other parts of the body. Men with slow-growing prostate cancers may choose active surveillance. With this approach, you can postpone, and sometimes completely forego, treatments. Your healthcare provider can discuss the best treatment option for you based on your Gleason score and Group Grade.
How Common Is Prostate Cancer
About one in nine men will receive a prostate cancer diagnosis during his lifetime. Prostate cancer is second only to skin cancer as the most common cancer affecting males. Close to 200,000 American men receive a diagnosis of prostate cancer every year. There are many successful treatments and some men dont need treatment at all. Still, approximately 33,000 men die from the disease every year.
Also Check: Does Enlarged Prostate Affect Ejaculation
If My Biopsy Report Does Not Say That Prostate Cancer Was Found Can I Be Sure That I Dont Have Prostate Cancer
A biopsy only removes a small amount of the prostate tissue, so it is possible for a biopsy to miss a cancer. This is one of the reasons that doctors typically remove several cores from different parts of the prostate when they do a biopsy. But even when removing several cores, it is still possible for prostate cancer to be missed.
If a biopsy does not find cancer but your doctor still thinks that prostate cancer is likely , he or she may recommend that your prostate be biopsied again at some time in the future. Your doctor is the best person to discuss this with you.
Pain Around The Upper Thighs
Although the upper thighs are not an obvious location for symptoms of prostate cancer, pain in this region can indicate a problem. Soreness or sharp pain at the groin, where the thighs meet the pelvis, should be investigated by a doctor if the cause is not easily attributed to exercise or injury. As with the low back, people often describe this symptom as a consistent, deep ache.
Also Check: What Color Represents Prostate Cancer
Better Understanding Of Prostate Cancer
Were using the power of big data, working with partners to analyse and combine data from tens of thousands of men whove been diagnosed and treated for different types and stages of prostate cancer. The aim is to find patterns in when the cancers started, how they developed and how aggressive they are. In the future this could help doctors predict how particular prostate cancers are likely to develop so we can choose the most appropriate treatment for each man.
You May Like: Perineural Tumor
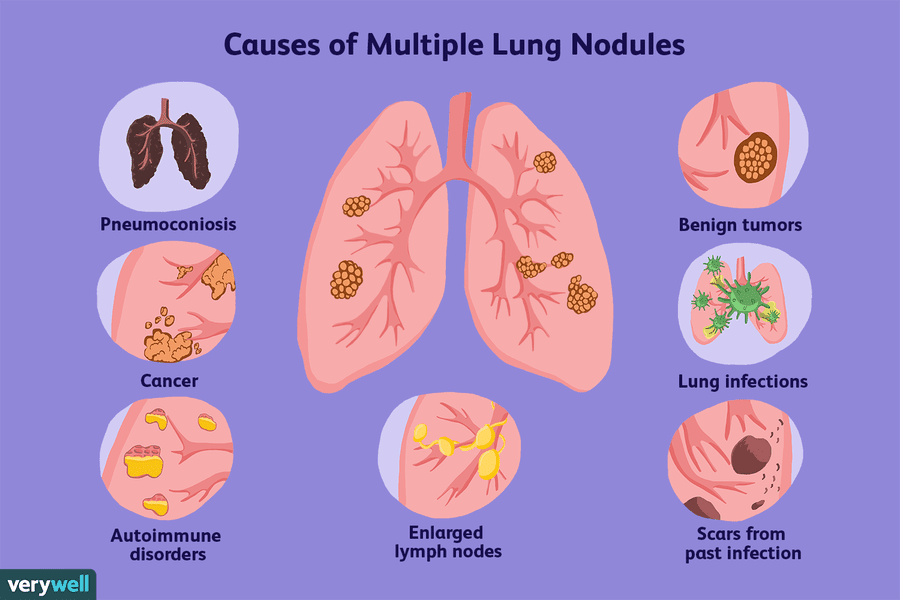
What Is A Lung Nodule
A lung nodule is an abnormal growth that forms in a lung. You may have one nodule on the lung or several nodules. Nodules may develop in one lung or both.
Most lung nodules are benign . Rarely, pulmonary nodules are a sign of lung cancer.
Lung nodules show up on imaging scans like X-rays or CT scans. Your healthcare provider may refer to the growth as a spot on the lung, coin lesion or shadow.
Also Check: Is Cranberry Juice Good For The Prostate
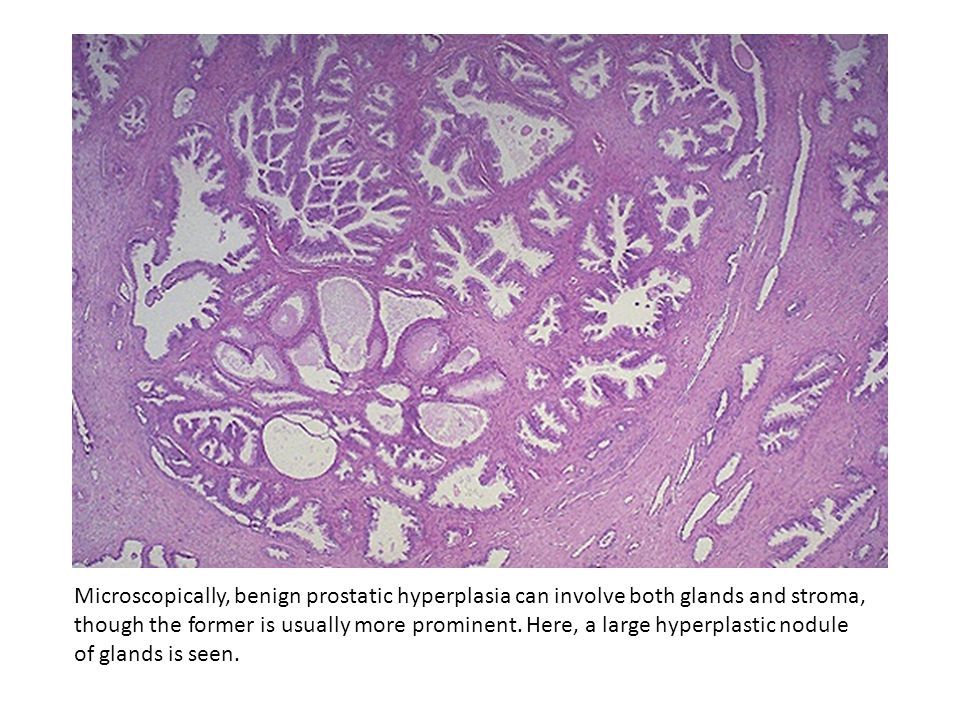
What Does It Mean If Under The Word Diagnosis My Biopsy Report Says Benign Prostate Tissue Benign Prostate Glands Or Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
These are terms that mean there is no cancer present. Benign prostatic hyperplasia is also a term used to describe a common, benign type of prostate enlargement caused by an increase number of normal prostate cells. This condition is more common as men get older and is not linked to cancer. When this term is used in a biopsy report, though, it doesnt mean anything about the size of the prostate. It just means that no cancer was found.
Prostate Cancer Caregiver Podcast Series
We are proud to announce a new podcast series geared toward helping give support, hope and guidance to prostate cancer caregivers. The goal of this Prostate Cancer Caregiver Podcast Series is to help others connect with a diverse group of people who have felt the impact of prostate cancer in their lives and empower them on their journey.
Recommended Reading: Is Zinc Good For Prostate
What Exactly Is Psa
PSA stands for Prostate Specific Antigen. It is a chemical produced only by prostate cells, both normal and cancerous. It can be measured easily in the blood. Your physician must carefully review your PSA results. Traditionally, it had been thought in the past that a PSA of 4 was normal. We now know that a normal PSA depends on your age and the size of your prostate, amongst other factors. What is a normal PSA for one man, may, in fact, be very abnormal for another.
Generally speaking, as men age and their prostates enlarge, the normal level for PSA increases. Likewise, for men with prostate cancer, as the amount of prostate cancer increases, the PSA level typically increases. Your physician will typically be alerted when your PSA is above what is expected for your age or if it shows a significant rise from the previous year. Because not all cancers can be found by an elevated PSA, it is critical that you also have regular physical exams to feel for abnormal growths of the prostate.
How Are Lung Nodules Managed Or Treated
Small, noncancerous lung nodules dont usually require treatment. You may need treatments, such as antibiotics or antifungal medications, if you have an infection.
If the nodule grows, causes problems or is cancerous, you may need surgery. Surgical procedures to remove noncancerous and cancerous pulmonary nodules include:
- Video-assisted thoracic surgery : During VATS, your provider inserts a thoracoscope and tiny surgical instruments through several small chest incisions. Your provider refers to images from the camera to remove the nodule.
- Thoracotomy: Your provider removes the lung nodule through a larger incision between your ribs, below your shoulder blade. For several days after the surgery, a tube drains excess fluid from your chest.
Don’t Miss: Does Enlarged Prostate Affect Ejaculation
The Basics Of Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer occurs when the cells in the prostate, a male reproductive gland, begin to grow out of control and develop into cancerous cells.
The prostate gland is only found in males and is the gland that creates some of the fluid that is in semen. It is a walnut-sized gland located below the bladder and in front of the rectum. The urethra the tube that carries urine and semen to the penis travels through the center of the prostate.
Nearly all prostate cancers are adenocarcinomas, which grow from the gland cells and grow slowly.
When Is Bph Treatment Necessary
The course of BPH in any individual is not predictable. Symptoms, as well as objective measurements of urethral obstruction, can remain stable for many years and may even improve over time for as many as one-third of men, according to some studies. In a study from the Mayo Clinic, urinary symptoms did not worsen over a 3.5-year period in 73% of men with mild BPH. A progressive decrease in the size and force of the urinary stream and the feeling of incomplete bladder emptying are the symptoms most correlated with the eventual need for treatment. Although nocturia is one of the most annoying BPH symptoms, it does not predict the need for future intervention.
If worsening urethral obstruction is left untreated, possible complications are a thickened, irritable bladder with reduced capacity for urine infected residual urine or bladder stones and a backup of pressure that damages the kidneys.
- Inadequate bladder emptying resulting in damage to the kidneys
- Complete inability to urinate after acute urinary retention
- Incontinence due to overfilling or increased sensitivity of the bladder
- Bladder stones
- Recurrent severe hematuria
- Symptoms that trouble the patient enough to diminish his quality of life
Find a Location
Currently, the main options to address BPH are:
- Watchful waiting
- Medication
- Surgery
Read Also: How To Find The Prostate Gland Externally
How Do You Know If You Have Prostate Cancer
Theres no way of knowing if you have prostate cancer without visiting your doctor, as most men with early prostate cancer dont have any symptoms. And if you do have symptoms they can be caused by other things.
And you cant check for prostate cancer yourself.
You may want to speak to your GP if youre over 50 , even if you dont have any symptoms. These are all things that can increase your risk of prostate cancer. Your GP can give more information or tests if necessary.
If youre not sure about what to say to your GP, print and fill out this form and show it to them. This will help you have the conversation.
I thought I could be at risk after learning that African Caribbean men are more likely to get prostate cancer than white men.
Treatment: Prostate Cancer Vaccine
This vaccine is designed to treat, not prevent, prostate cancer by spurring your body’s immune system to attack prostate cancer cells. Immune cells are removed from your blood, activated to fight cancer, and infused back into the blood. Three cycles occur in one month. It’s used for advanced prostate cancer that no longer responds to hormone therapy. Mild side effects can occur such as fatigue, nausea, and fever.
22
You May Like: Characteristics Of Prostate Cancer
How The Prostate Changes As You Age
Because the prostate gland tends to grow larger with age, it may squeeze the urethra and cause problems in passing urine. Sometimes men in their 30s and 40s may begin to have these urinary symptoms and need medical attention. For others, symptoms aren’t noticed until much later in life. An infection or a tumor can also make the prostate larger. Be sure to tell your doctor if you have any of the urinary symptoms listed below.
Tell your doctor if you have these urinary symptoms:
- Are passing urine more during the day
- Have an urgent need to pass urine
- Have less urine flow
- Feel burning when you pass urine
- Need to get up many times during the night to pass urine
Growing older raises your risk of prostate problems. The three most common prostate problems are inflammation , enlarged prostate , and prostate cancer.
One change does not lead to another. For example, having prostatitis or an enlarged prostate does not increase your risk of prostate cancer. It is also possible for you to have more than one condition at the same time.
A Note On Suspicious Results
A suspicious result indicates that the biopsy sample contained some abnormalities but no cancer was found. There are a couple of potential explanations for a suspicious prostate biopsy result, including:
- Prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia refers to changes within prostate cells that are abnormal, but not indicative of cancer. This condition is low-grade or high-grade, depending on how abnormal the cells are. Low-grade PIN is very common and isn’t associated with prostate cancer. High-grade PIN, however, is associated with a higher risk of prostate cancer. If you have high-grade PIN after a prostate biopsy, your doctor may recommend that biomarker tests be performed on the sample to learn more about the cells. Alternatively, another prostate biopsy may be suggested.
- Atypical small acinar proliferation indicates that the biopsy sample contains some cells that appear to be cancerous, but not enough to confirm the diagnosis. In most cases, this finding suggests that another prostate biopsy is needed.
- Proliferative inflammatory atrophy describes a prostate biopsy that reveals inflammation in the prostate and abnormally small prostate cells. While these cells arent cancerous, having PIA may be associated with an increased risk of developing prostate cancer.
Don’t Miss: Veterans Disability Compensation For Prostate Cancer Rates
Setting Your Browser To Accept Cookies
There are many reasons why a cookie could not be set correctly. Below are the most common reasons:
- You have cookies disabled in your browser. You need to reset your browser to accept cookies or to ask you if you want to accept cookies.
- Your browser asks you whether you want to accept cookies and you declined. To accept cookies from this site, use the Back button and accept the cookie.
- Your browser does not support cookies. Try a different browser if you suspect this.
- The date on your computer is in the past. If your computers clock shows a date before 1 Jan 1970, the browser will automatically forget the cookie. To fix this, set the correct time and date on your computer.
- You have installed an application that monitors or blocks cookies from being set. You must disable the application while logging in or check with your system administrator.
Monitoring And Pharmacologic Therapy
Ordinarily, in patients in whom only a single focus of PIN, particularly HGPIN, has been identified, therapy may not be necessary. In patients with multiple areas of HGPIN or ASAP on the initial biopsy or on subsequent biopsies, therapy may be considered, as the risk of cancer in these patients is 15 times that in patients without these entities. Prostate cancerprevention studies indicate that 5-alpha reductase inhibitors, antiandrogens, and selective estrogen receptor modulators are usually not effective in eliminating HGPIN and ASAP,. .
Read Also: Perineural Invasion Present
Figure : Zones Of The Prostate
To help your doctor more precisely determine the location of prostate cancer or another condition, such as high-grade PIN, your pathology report may name specific areas. For example, it may refer to the apex, located at the bottom of the prostate the base, at the top or the mid zone, the area between the apex and base. Alternatively, it may note three zones: the peripheral zone , the central zone , and the transition zone . Seventy percent of prostate cancers arise in the peripheral zone. Few arise in the anterior prostate.
What Is Radical Prostatectomy For Prostate Cancer
Radical prostatectomy is the surgical removal of the entire prostate. This operation is indicated for cancer that is limited to the prostate and has not invaded the capsule of the prostate, any other nearby structures or lymph nodes, or distant organs.
Transurethral resection of the prostate is an alternative to radical prostatectomy.
- Only part of the prostate is removed by an instrument inserted through the urethra.
- An electric current passes through a small wire loop at the end of the instrument. The electrical current cuts away a piece of the prostate.
- This procedure is used to remove tissue that is blocking urine flow in patients with extensive disease or those that are not fit enough to undergo radical prostatectomy. It is not considered a procedure for cure.
You May Like: Can Prostatitis Heal On Its Own
