Where Do These Numbers Come From
The American Cancer Society relies on information from the SEER database, maintained by the National Cancer Institute , to provide survival statistics for different types of cancer.
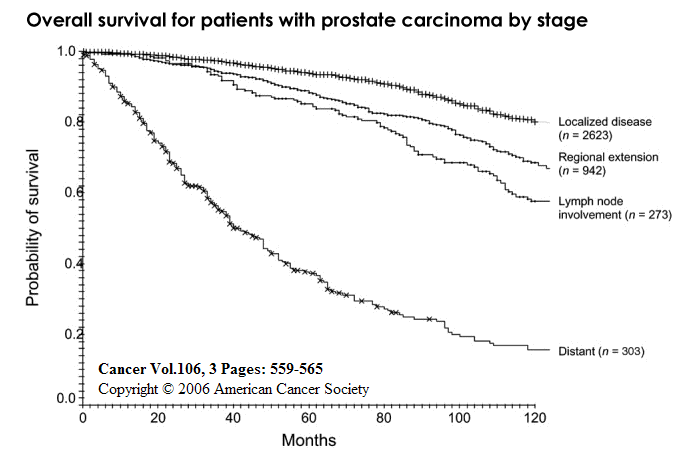
The SEER database tracks 5-year relative survival rates for prostate cancer in the United States, based on how far the cancer has spread. The SEER database, however, does not group cancers by AJCC TNM stages . Instead it groups cancers into localized, regional, and distant stages.
- Localized: There is no sign that the cancer has spread outside the prostate.
- Regional: The cancer has spread outside the prostate to nearby structures or lymph nodes.
- Distant: The cancer has spread to parts of the body farther from the prostate, such as the lungs, liver, or bones.
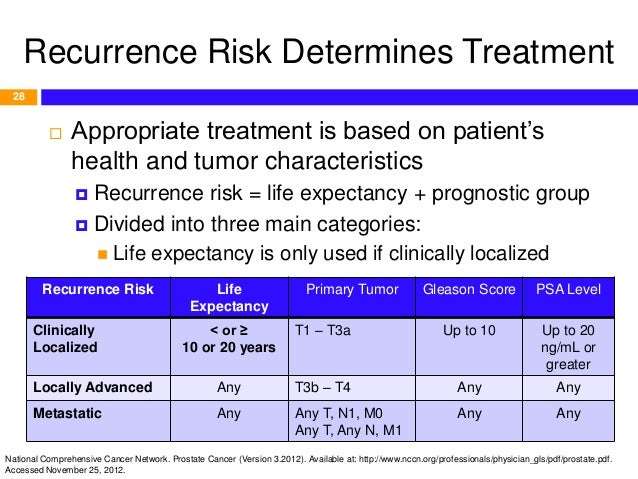
Recurrence Of Prostate Cancer Life Expectancy
According to the table above, when the prostate cancer recurrence rate is low, then life expectancy generally is 10 years or higher. When calculating life expectancy to a prostate expectancy too.
Meanwhile, if the recurrence rate is high, then most probably the tumor will involve the adjacent areas. And often the recurrence seems to occur after 6-8 years of radical prostatectomy.
In cases of metastastasis, it is difficult to assess the period of relapse. This is actually considered as very high risk zone.
Sometimes, the actual cause is not the prostate cancer, but some other associated problems. Thats why, it is highly recommended regular annual check-ups not only to tackle prostate cancer, but also a scheduled check-up to detect its recurrence and related problems too.
Variables And Main Outcomes
The general characteristics, tumor information, and survival outcomes were collected.
Variables included age, race, marital status, T staging, PSA, GS, treatment, survival time, living state , and PCa-specific living state . The survival time was defined as the time from the patients first diagnosis to the patients death or the last follow-up time .
According to the definition of high-risk PCa, the included patients were divided into seven groups. Patients with one high-risk factor were in A1 , A2 , and A3 . Men with two risk factors were in B1 , B2 , and B3 . The group with three high-risk factors was C .
The main outcomes in this study were overall survival and prostate cancer-specific survival . The survival time was defined as the time from the patients first diagnosis to the patients death or the last follow-up time .
Also Check: Can You Check For Prostate Cancer Yourself
Searches And Article Selection
A research librarian conducted searches in Ovid MEDLINE , Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials , and Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews . An updated search was conducted prior to publication through January 20, 2020. The methodology team supplemented searches of electronic databases with the studies included in the prior AUA review and by reviewing reference lists of relevant articles.
The methodology team developed criteria for inclusion and exclusion of studies based on the Key Questions and the populations, interventions, comparators, outcomes, and settings of interest. The population was patients with advanced prostate cancer as described in Table 3. Treatments included first and second line antiandrogens, immunotherapy, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, surgery, radiopharmaceuticals, and surveillance strategies. Comparisons were against placebo, no therapy, or another active intervention and intermittent versus continuous therapy. Outcomes included overall survival , prostate cancer mortality, progression-free survival , prostate-specific antigen progression-free survival , failure-free survival, metastases-free survival, time to metastases, time to progression, skeletal events, and adverse events.
Differences Among Risk Groups
Men with PCa have been classified into low-, intermediate- and high-risk Groups for tumor recurrence and disease specific mortality, based on PSA level, clinical or pathological staging and GS. High-risk patients have PSA level 20ng/mL or GS 8 or clinical/pathological stage T2c . Lymph-node positive and PSM have also been reported as poor prognosis factors.
Risk Group classification predicts biochemical and clinical progression as well as PCa specific mortality and overall survival. The risk of disease progression in these groups has been validated for patients submited to RP in many studies. In patients from Mayo Clinic, BCR rates were 2.3 and 3.3-fold greater in high and intermediate-risk in comparison with low-risk patients, respectively. In those patients, mortality rates in high and intermediate-risk patients were greater than 11 and 6-fold over low-risk men .
Therefore, it is crutial to understand the role of each clinical and pathologic feature in PCa BCR and disease progression.
Dont Miss: Can You Be Asleep During A Prostate Biopsy
Read Also: How Long Do You Bleed After A Prostate Biopsy
What Are Prostate Cancer Survival Rates By Stage
Staging evaluation is essential for the planning of treatment for prostate cancer.
- A basic staging evaluation includes the patient examination, blood tests, and the prostate biopsy including ultrasound images of the prostate.
- Further testing and calculations may be performed to best estimate a patient’s prognosis and help the doctor and patient decide upon treatment options.
Prognosis refers to the likelihood that cancer can be cured by treatment, and what the patient’s life expectancy is likely to be as a consequence of having had a prostate cancer diagnosis.
If cancer is cured, your life expectancy is what it would have been had you never been diagnosed with prostate cancer. If cancer cannot be cured due to it recurring in distant locations as metastases, or recurs either locally or in an area no longer able to be treated in a curative manner, then estimates can be made of what is likely to be your survival-based again on group statistics for people who have been in the same situation.
Nomograms are charts or computer-based tools that use complex math from the analysis of many patients’ treatment results.
The prognosis for prostate cancer varies widely and depends on many factors, including the age and health of the patient, the stage of the tumor when it was diagnosed, the aggressiveness of the tumor, and cancer’s responsiveness to treatment, among other factors.
The 5 and 10-year survival rate of prostate cancer chart
| Stage and 5-Year Survival |
|---|
When Prostate Cancer Comes Back: What You Need To Know
If youve been treated for prostate cancer successfully in the past, recurrence of your cancer is probably your worst nightmare. But you should know that prostate cancer recurrence is far from a death sentence. Most men with prostate cancer dont die of it even when the cancer is recurrent.
Twenty to 30 percent of men who have been successfully treated for prostate cancer will experience a relapse more than five years after treatment, even if they have received a prostatectomy. But you dont need to rush into aggressive treatment just because your cancer has come back. The speed with which your PSA levels return and the rate at which they rise will help your doctor determine whether you should pursue aggressive treatment, or adopt a wait-and-see approach.
Don’t Miss: Can A Man Have Intercourse After Prostate Removal
Survival For All Stages Of Prostate Cancer
Generally for men with prostate cancer in England:
- more than 95 out of 100 will survive their cancer for 1 year or more
- more than 85 out of 100 will survive their cancer for 5 years or more
- almost 80 out of 100 will survive their cancer for 10 years or more
Survival of prostate cancer is also reported in Scotland and Northern Ireland. But it is difficult to compare survival between these countries because of differences in the way the information is collected.
Cancer survival by stage at diagnosis for England, 2019Office for National Statistics
These statistics are for net survival. Net survival estimates the number of people who survive their cancer rather than calculating the number of people diagnosed with cancer who are still alive. In other words, it is the survival of cancer patients after taking into account the background mortality that they would have experienced if they had not had cancer.
What Types Of Hormone Therapy Are Used For Prostate Cancer
Hormone therapy for prostate cancer can block the production or use of androgens . Currently available treatments can do so in several ways:
- reducing androgen production by the testicles
- blocking the action of androgens throughout the body
- block androgen production throughout the body
Treatments that reduce androgen production by the testicles are the most commonly used hormone therapies for prostate cancer and the first type of hormone therapy that most men with prostate cancer receive. This form of hormone therapy includes:
Treatments that block the action of androgens in the body are typically used when ADT stops working. Such treatments include:
Treatments that block the production of androgens throughout the body include:
Also Check: What Age Do You Get A Prostate Exam
Survival By Disease Recurrence
If a man develops an elevated PSA level after cancer surgery, then the disease is viewed as recurrent.
The number of lymph nodes at the time of prostatectomy can influence the risk of recurrence. One study suggests the removal of a large number of nodes is associated with an improvement in odds of recurrence, but this doesn’t appear to impact overall survival.
But disease recurrence doesn’t always influence survival times. If a recurrence does occur, the 15-year survival rate at the time of diagnosis may be as high as 94% in those with low-risk recurrence.
The main factors influencing survival rates are:
- The Gleason score
- The PSA doubling time
- Whether the recurrence occurred within three years or after three years
A recurrence that occurs within three years reduces survival rates by anywhere from 15 to 20%and even more, if the doubling time is short.
Prognosis And Survival For Prostate Cancer
If you have prostate cancer, you may have questions about your prognosis. A prognosis is the doctor’s best estimate of how cancer will affect someone and how it will respond to treatment. Prognosis and survival depend on many factors. Only a doctor familiar with your medical history, the type and stage and other features of the cancer, the treatments chosen and the response to treatment can put all of this information together with survival statistics to arrive at a prognosis.
A prognostic factor is an aspect of the cancer or a characteristic of the person that the doctor will consider when making a prognosis. A predictive factor influences how a cancer will respond to a certain treatment. Prognostic and predictive factors are often discussed together. They both play a part in deciding on a treatment plan and a prognosis.
The following are prognostic and predictive factors for prostate cancer.
Don’t Miss: Can Prostate Cancer Kill If Not Treated
Staging Spread And Survival Rates
As with all cancers, doctors use the term stage to describe the characteristics of the primary tumor itself, such as its size and how far prostate cancer has spread when it is found.
Staging systems are complicated. The staging system for most cancers, including prostate cancer, uses three different aspects of tumor growth and spread. It’s called the TNM system, for tumor, nodes, and metastasis:
- T, for tumor describes the size of the main area of prostate cancer.
- N, for nodes, describes whether prostate cancer has spread to any lymph nodes, and how many and in what locations.
- M, for metastasis, means distant spread of prostate cancer, for example, to the bones or liver.
Using the TNM system, each man’s prostate cancer can be described in detail and compared to other men’s prostate cancer. Doctors use this information for studies and to decide on treatments.
As far as survival rates for prostate cancer go, however, the staging system is pretty simple. As we’ve mentioned, in terms of survival rates, men with prostate cancer can be divided into two groups:
Show Sources
How Is Prostate Cancer Staged
Prostate cancer is one of the most common types of cancer that develops in men and is the second leading cause of cancer deaths in American men, behind lung cancer and just ahead of colorectal cancer. The prognosis for prostate cancer, as with any cancer, depends on how advanced the cancer has become, according to established stage designations.
The prostate gland is a walnut-sized gland present only in men, found in the pelvis below the bladder. The prostate gland wraps around the urethra and lies in front of the rectum. The prostate gland secretes part of the liquid portion of the semen, or seminal fluid, which carries sperm made by the testes. The fluid is essential to reproduction.
The term to stage a cancer means to describe the evident extent of the cancer in the body at the time that the cancer is first diagnosed.
- Clinical staging of prostate cancer is based on the pathology results, physical examination, PSA, and if appropriate, radiologic studies.
- The stage of a cancer helps doctors understand the extent of the cancer and plan cancer treatment.
- Knowing the overall results of the different treatments of similarly staged prostate cancers can help the doctor and patient make important decisions about choices of treatment to recommend or to accept.
You May Like: How Long To Recover From Prostate Surgery
Additional Treatment After Surgery
Additional treatment can come with one of two approaches: treatment given as adjuvant therapy , or as salvage therapy . In the modern era, most additional treatment is given as salvage therapy because firstly this spares unnecessary treatment for men who would never experience recurrence, and secondly because the success rates of the two approaches appear to be the same.
Regardless of whether an adjuvant or salvage therapy approach is taken, the main treatment options following biochemical recurrence are:
- Radiotherapy this is the commonest approach. Because scans dont show metastatic deposits until the PSA is more than 0.5 ng/ml and because radiotherapy is more effective when given before this level is reached, the radiotherapy energy is delivered to the prostate bed. This is because we know that this is the commonest site of recurrence in most men, and that 80% of men treated in this way will be cured.
- Active surveillance this is appropriate for a very slowly-rising PSA in an elderly patient who has no symptoms.
- Hormonal therapy in many ways this is the least appealing option as it causes symptoms but does not cure anyone, although it does control the recurrence and lower the PSA.
Multidisciplinary Nature Of Treatment In Todays Advanced Prostate Cancer Care Paradigm
As the therapeutic landscape evolves to include increasingly complex combinations of systemic therapies with or without local therapies, advances in imaging, and germline and somatic genetic testing, treating men with advanced prostate cancer is increasingly one that must embrace multidisciplinary management approaches. Team members should include urologists, medical oncologists, and radiation oncologists at a minimum when supporting treatment decisions for advanced disease. Additional specialists may also include genitourinary pathology, genetic counseling, palliative care, and holistic specialists, as appropriate, in addition to primary care. Best practices must also include clinicians comfortable describing the use of germline and somatic genetic testing, and when advanced imaging techniques could be optimally used or avoided. Radiologists and nuclear medicine specialists are valuable in helping to accurately interpret scans. Palliative care team members may also play a key role when treating men with symptomatic metastatic disease. Palliative care itself is an interdisciplinary, holistic approach to managing an advanced disease such as prostate cancer with a guarded prognosis. It can include controlling symptoms that are physical, psychological, spiritual, and social. The goal of palliation is to prevent and relieve suffering and to support the best possible QOL for the patient and family.
Dont Miss: What Is The Best Over The Counter Prostate Supplement
You May Like: Does Sex Improve Prostate Health
What Is A 5
A relative survival rate compares people with the same type and stage of cancer to people in the overall population. For example, if the 5-year relative survival rate for a specific stage of prostate cancer is 90%, it means that men who have that cancer are, on average, about 90% as likely as men who dont have that cancer to live for at least 5 years after being diagnosed.
How Is A Recurrence Detected
After prostate cancer treatment, you will go for medical check-ups every few months as determined by your doctor. At each follow-up appointment, your doctor will order a blood test to measure PSA levels. This test helps your doctor detect a cancer recurrence. You will also be examined. New symptoms should be reported to the doctor, as these may prompt other testing.
When PSA test results suggest that the cancer has come back or continued to spread, X-rays or other imaging tests may be done, depending on your situation and symptoms. Your doctor may use a radioactive tracer called Axumin with a PET scan to help detect and localize any recurrent cancer so that it could be biopsied or treated.
Your doctor may also use a new drug called Ga 68 PSMA-11 in the scan which binds to PSMA-positive prostate cancer lesions in the tissues of the body so they can be targeted for treatment.
You May Like: What To Expect From Radiation Therapy For Prostate Cancer
Assessing Metastases And Local Recurrence
Once BCR has been detected, it is important to try to establish whether this represents local recurrence or disseminated disease, or both, in order to guide subsequent treatment decisions. Importantly, metastatic disease must be acceptably ruled out before subjecting patients to local salvage treatment, owing to the significant morbidity associated with such treatments. Regardless of whether BCR is detected post-RP or post-RT, the same principles of imaging apply.
Justification For A New Guideline
Clinicians treating men with advanced prostate cancer are challenged with the rapidly evolving prostate cancer landscape given the approval of new classes of agents for use in various prostate cancer disease states. The increasing complexity of advanced prostate cancer management underscores the need for the current clinical practice guideline, developed to provide a rational basis for treatment of patients with advanced disease, based on currently available published data. To assist in clinical decision-making, guideline recommendations are furnished according to disease state across the entire continuum of advanced prostate cancer.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Check For Prostate Cancer
