What Is The Risk Of Prostate Cancer In Patients With Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis
There is concern that clinical chronic prostatitis may be a risk factor for prostate cancer. Two separate meta-analyses and other large case-control studies have estimated a 60% increased risk of prostate cancer in patients with symptomatic prostatitis in white men. However, African Americans have been shown in one study to actually have a slightly decreased risk of prostate cancer with symptomatic prostatitis.
Some studies report that men with prostate cancer have histological prostatic inflammation 4-5 times more often than men without prostate cancer. Other studies have suggested that histological prostatic inflammation in benign prostate tissue specimens from asymptomatic men are associated with decreased future prostate cancer risk. As mentioned previously, prostatic inflammation is a nonspecific finding, and its relation to prostate cancer is also unclear.
Identifying Potential Prostate Problems
Lower Urinary Tract Localization Studies
The lower urinary tract localization technique, Meares-Stamey four-glass test consists of collection of initial voided urine , mid stream or second voided urine representing urethral and bladder specimens, respectively. Expressed prostatic secretions are collected during prostatic massage. Voided bladder sample is then collected after prostatic massage. All the specimens are cultured along with microscopic examination of the sediment in VB1, VB2 and VB3 and EPS is subjected to a wet mount microscopy. The test, however, is largely abandoned by urologists in North America since it is expensive, cumbersone, does not predict response to therapy and may lead to false-positive and false-negative results., Nickel suggested a more simple and less expensive screening technique . In this, urine specimens are collected before and after a vigorous prostatic massage. Increased number of uropathogenic bacteria and leukocytes in the post-massage specimen compared to the pre-massage sample indicate NIH category II prostatitis, whereas leukocytosis alone indicates NIH category IIIA. Category IIIB is suggested by an absence of bacteria or leukocytes in the post-massage specimen. While using this test, urethritis can be ruled out by a repeat VB1 collection. The positive predictive value and false-negative rate of PPMT are similar to the Meares-Stamey test.
Also Check: Chemo Pill For Prostate Cancer
Risk Factors For Prostate Cancer
Some risk factors have been linked to prostate cancer. A risk factor is something that can raise your chance of developing a disease. Having one or more risk factors doesn’t mean that you will get prostate cancer. It just means that your risk of the disease is greater.
- Age. Men who are 50 or older have a higher risk of prostate cancer.
- Race. African-American men have the highest risk of prostate cancerâthe disease tends to start at younger ages and grows faster than in men of other races. After African-American men, prostate cancer is most common among white men, followed by Hispanic and Native American men. Asian-American men have the lowest rates of prostate cancer.
- Family history. Men whose fathers or brothers have had prostate cancer have a 2 to 3 times higher risk of prostate cancer than men who do not have a family history of the disease. A man who has 3 immediate family members with prostate cancer has about 10 times the risk of a man who does not have a family history of prostate cancer. The younger a man’s relatives are when they have prostate cancer, the greater his risk for developing the disease. Prostate cancer risk also appears to be slightly higher for men from families with a history of breast cancer.
- Diet. The risk of prostate cancer may be higher for men who eat high-fat diets.
Pathophysiology Of Prostate Pain
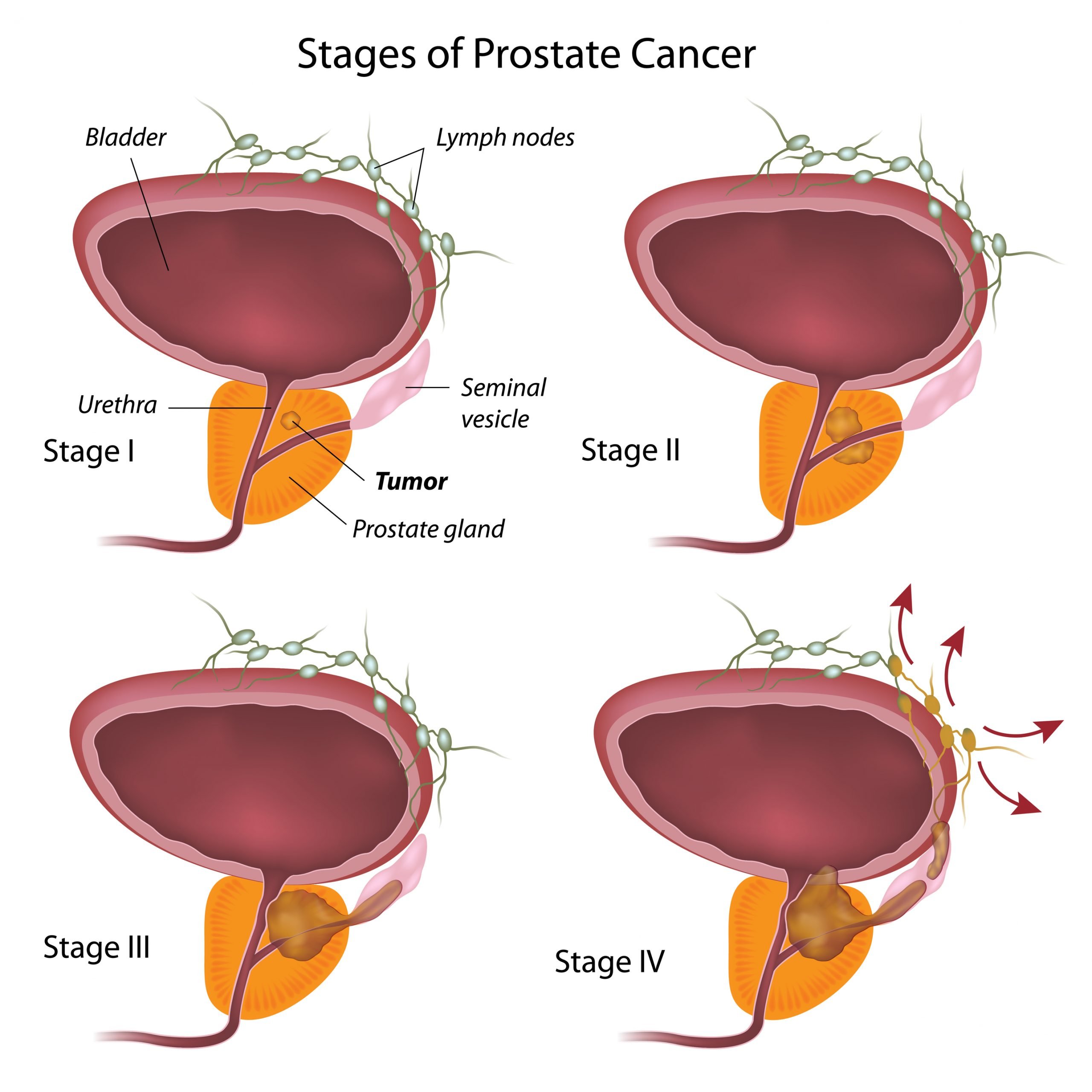
Most commonly men who are affected with enlarged prostate donât exhibit particular symptoms. One important symptom of enlarged prostate is urine incontinence. Patient cannot sit for a long of period of time, especially without voiding. If we go through the anatomy of male, the flow of urine is from bladder through urethra. In case of prostate enlargement, extreme pressure will be on urethra. In this case, to overcome the situation of narrowing of urethra, the bladder tries to contract with more strength in order for it to push the urine out of the body. The bladder muscles will become sensitive, stronger and thicker. This will lead to altered function of the bladder in which condition it will void small quantity of urine.
You May Like: Chemo Drug For Prostate Cancer
Prostatitis Vs Prostate Cancer
The prostate gland is an integral part of the male reproductive system. The gland secretes prostate fluid, which nourishes sperm. The gland sits around the urethra, which forms part of the urinary tract.
A prostate problem can result in complications with the functioning of this gland. In some cases, prostate conditions can also lead to urinary symptoms.
Multiple conditions can affect the prostate gland. Prostatitis vs prostate cancer is a common comparison, particularly due to the common symptoms in many cases.
Understanding the signs that signal a prostate condition is important. Men should also understand the difference between these two conditions. In this post, we take a look at how they differ and the available treatments.
What Is The Difference Between Kidney Stones And Prostate Stones
Kidney stones are solid stones made of minerals that form within the kidneys when your body is having difficulty filtering excess water and waste. Kidney stones affect both men and women and can result in sudden, severe pain in the abdomen, side, or lower back, a burning sensation when you urinate, and problems with urination.
Prostate stones are poppy seed-sized stones that form within the prostate. Only men can have prostate stones. Some men may experience lower back pain or pain in the penis or perineum. Typically, prostate stones do not cause any problems or symptoms. However, if prostate stones become infected, it can lead to urinary tract infections or prostatitis.
You May Like: Is Viagra Good For Enlarged Prostate
You May Like: Is Zinc Good For Prostate
Publication Bias And Small Study Effect
reports Eggers publication bias results, with p-value=0.82> 0.05, and the intercept is 0.91. This insignificant p-value indicates that bias is not significantly different from 0, thus, there is not enough evidence to conclude that there is publication bias in this study.
Eggers publication bias plot.
In , most studies are at the top of funnel, with a large sample size. Some studies with smaller sample sizes were spread across the bottom of funnel. However, most studies are at the dashed bonds, which represent a lack of bias and heterogeneity, 95% of studies are expected to lie in this triangle area. The funnel is symmetric to the middle line, which is from the top of the triangle also indicate no evidence of small study effects.
Funnel plot of standard error of log OR over log OR.
What Are The Types Of Prostatitis
Types of prostatitis include:
- Acute bacterial prostatitis : A UTI causes an infection in the prostate gland. Symptoms include fever and chills. You may experience painful and frequent urination or have trouble urinating. Acute bacterial prostatitis requires immediate medical treatment.
- Chronic bacterial prostatitis : Bacteria become trapped in the prostate gland, causing recurrent UTIs that are difficult to treat.
- Chronic pelvic pain syndrome, or CPPS : CPPS is the most common prostatitis type. Prostate gland inflammation occurs in approximately 1 out of 3 men. As the name implies, this type causes chronic pain in the pelvis, perineum and genitals.
- Asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis : This condition causes prostate gland inflammation but no symptoms. You may learn you have this condition after getting tests to find the cause of other problems. For example, a semen analysis for infertility may detect asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis. This type doesnt need treatment.
Recommended Reading: How Are Fiducial Markers Placed In The Prostate
The Initial Causes Prostatitis Jelly In Semen
One of the first symptoms of prostate issues is pain or tenderness in the groin or lower back. This can be the result of a noncancerous condition called enlarged prostatic tissue, or it could be an infection of the bladder. In either case, its important to see a doctor as soon as possible. If youre suffering from prostate pain, you may want to consider reducing your caffeine intake.
Another symptom of a potentially enlarged prostate is difficulty starting a stream of urine, leaking, or dribbling. These symptoms are not serious, but theyre still alarming. Most men put up with an enlarged prostate for years before seeking medical attention, but they typically seek treatment as soon as they notice symptoms. Even if you dont have symptoms, its worth getting checked to determine if you have any prostate issues.
If you experience nightly bathroom runs, you may be experiencing an enlarged prostate. You may be having difficulty starting a stream of urine, or you may even be dribbling or leaking during the day. These problems arent life-threatening, but can become a nuisance. You should not ignore these signs and seek treatment as soon as you notice them. If you feel any of these symptoms, you should consult a doctor.
Symptoms Of Prostate Cancer
- Frequent urge to pass urine, especially at night
- Weak or interrupted urine stream
- Pain or burning when passing urine
- Blood in the urine or semen
- Painful ejaculation
- Nagging pain in the back, hips, or pelvis
Prostate cancer can spread to the lymph nodes of the pelvis. Or it may spread throughout the body. It tends to spread to the bones. So bone pain, especially in the back, can be a symptom of advanced prostate cancer.
Recommended Reading: Fiducial Marker Placement For Prostate Cancer
Prevention Of Prostate Cancer
To avoid such dangerous diseases as cancer or inflammation of the prostate, men need to adhere to a healthy lifestyle and be sure to visit a urologist annually. For representatives of the stronger sex after 50 years, it is recommended to do this even more often, because due to age-related changes, the chances of getting ailments are higher. Prevention should be started as early as possible, this will significantly reduce the likelihood of oncology or inflammation.
Also, to avoid pathologies, it is important to get enough sleep and rest, to avoid stress. In order not to get a stagnant type of prostatitis, you need to have a regular sex life, preferably with a regular partner. This and physical activity are especially important for those men who have a sedentary job. If you find symptoms of cancer or prostatitis, immediately contact a specialist and get tested. Even if it is a false alarm, it is better to play it safe than to put your health and life in danger. If a man has already recovered, prevention is still a must for him.
Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome
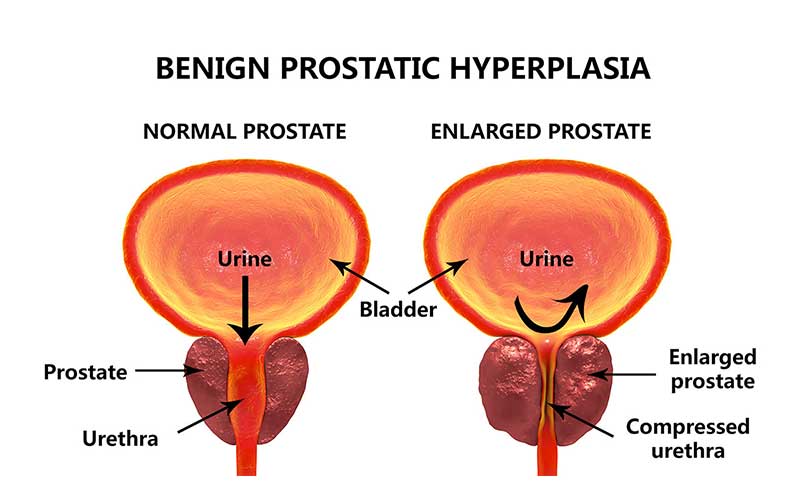
CPPS is the most common type of prostatitis around 19 out of every 20 men with prostatitis have it. You might also hear it called chronic non-bacterial prostatitis, chronic abacterial prostatitis or prostate pain syndrome. Chronic means long-lasting.
Men with CPPS usually have symptoms for three months or longer. Even after treatment, you may still have prostatitis for a long time. It might come and go, causing occasional episodes of severe pain, sometimes known as flare-ups.
What causes it?
Nobody knows for certain what causes CPPS. Unlike other types of prostatitis it isnt usually caused by a bacterial infection. There could be a number of causes, which makes it difficult to diagnose and treat.
There are also a number of things that might trigger it, including:
- urine getting into the prostate
- previous infections in or around the prostate
- an infection that doesnt show up in tests
- problems with nerves, so that they send pain signals to the brain even when theres nothing physically wrong
- stress, anxiety or depression
- problems with the pelvic floor muscles .
Some research shows a link between stress, anxiety and depression and CPPS. But this doesnt mean that CPPS is all in your head. If youre feeling stressed or depressed, this may cause physical symptoms that trigger CPPS, or make symptoms worse.
Read Also: Finding The Prostate Externally
What Are Symptoms Of Prostatitis
How you feel will help your doctor diagnose the type of prostatitis you have. Chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome is an inflammation of the prostate and the nerves to this area. Pain from CP/CPPS can last for weeks to months. This is NOT an infection. Symptoms are:
- Trouble passing urine
- Pain in and around the bladder, testicles, penis and/or anus
- Pain with ejaculation
Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis is from bacteria and is less common. It is known to come and go over a long period of time at least three months. Symptoms can be:
- A burning feeling while passing urine
- The need to pass urine often
- Pain in and around the bladder, testicles, penis and/or anus
- Pain with ejaculation
Acute Bacterial Prostatitis is also from bacteria and is less common. Symptoms for this problem can begin suddenly and can be very painful. Men should get medical care right away. Symptoms include:
- Chills
- Very painful burning while passing urine
- Trouble draining the bladder
Nonbacterial Prostatitis may be from stress, nerve irritation, injuries or past urinary tract infections. This form of prostatitis has no signs of bacteria in the urine or semen.
What Causes Prostatitis Vs Bph
The cause of BPH or enlarged prostate is by benign growth that enlarges the prostate gland. Researchers do not know exactly what causes the gland to enlarge, but they have speculated that it might be related to hormonal changes as men age.
In men under the age of 35, the most common type of prostatitis is acute bacterial prostatitis, while in older patients non-bacterial prostatitis is the most common type. There are four types or syndromes of prostatitis.
- Type I – Acute bacterial prostatitis
- Type II – Chronic bacterial prostatitis
- Type III Chronic prostatitis and chronic pelvic pain syndrome
- Type IV is asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis.
The cause of acute bacterial prostatitis is by bacteria that may be present in the urethra and then infect the prostate gland. Chronic bacterial prostatitis occurs because of inadequate treatment or because of a structural/functional problem in the urinary tract. Researchers and doctors do not completely understand the cause of chronic prostatitis, but it is speculated that the cause may be initiated by neurological injury and/or related to infection.
You May Like: Pseudoephedrine And Prostate
Are The Treatments For Prostatitis And Bph Different
The treatment for an enlarged prostate and prostatitis are very different.
BPH treatment may include an interactive questionnaire to determine the extent of your symptoms. The results of the questionnaire may influence what medications or other treatments you may need. Drugs used to treat BPH include:
- Alpha receptor blockers
- Phosphodiesterase inhibitors
- Anticholinergic agents
Some patients with more severe prostatic enlargement may need surgery. A transurethral resection of the prostate is the usual procedure to reduce pressure on the urethra by reducing the size of the prostate.
Treatment for prostatitis depends on the type.
- Bacteria acute and chronic prostatitis are typically treated and cured with antibiotics like fluoroquinolones or trimethoprim. These infections typically take longer to cure so you may have to take antibiotics for as long as 4-8 weeks. Some infections of the prostate gland are resistant or unresponsive to treatment so antibiotics like gentamicin or doxycycline may need to be injected directly into the gland.
- Type III, chronic bacterial prostatitis and pelvic pain syndrome, is treated similarly with antibiotics, however, alpha-blockers and NSAIDs , for example, aspirin, ibuprofen , naproxen also are used.
- Type IV, asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis, in most patients requires no treatment. However, some doctors prescribe antibiotics and NSAIDs for this condition.
How Is Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome Managed Or Treated
Prostatitis treatments vary depending on the cause and type. Asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis doesnt require treatment.
For chronic pelvic pain syndrome , your healthcare provider may use a system called UPOINT to classify symptoms into six categories. Your provider uses multiple treatments at the same time to treat only the symptoms youre experiencing.
Approximately 80% of men with CPPS improve with the UPOINT system. The system focuses on these symptoms and treatments:
- Urinary: Medications, such as tamsulosin and alfuzosin , relax muscles around the prostate and bladder to improve urine flow.
- Psychosocial: Stress management can help. Some men benefit from counseling or medications for anxiety, depression and catastrophizing .
- Organ: Quercetin and bee pollen supplements may relieve a swollen, inflamed prostate gland.
- Infection:Antibiotics kill infection-causing bacteria.
- Neurologic: Prescription pain medicines, such as amitriptyline and gabapentin , relieve neurogenic pain. This pain can include fibromyalgia or pain that extends into the legs, arms or back.
- Tenderness: Pelvic floor physical therapy may include myofascial release . This therapy can reduce or eliminate muscle spasms.
Read Also: Household Items For Prostate Massage
How Are Bacterial Forms Of Prostatitis Managed Or Treated
Antibiotics can kill bacteria that cause bacterial types of prostatitis. Men with acute bacterial prostatitis may need 14 to 30 days of antibiotics, starting with IV antibiotics in the hospital. Rarely, men need surgery to drain an abscess on the prostate.
Treating chronic bacterial prostatitis is challenging. You may need up to three months of antibiotics to sterilize the prostate. If the prostate cant be sterilized, low-dose antibiotics can be used long term to prevent recurrences. Some men need surgery to remove prostate stones or scar tissue in the urethra. Rarely, surgeons remove part or all of the prostate gland .
If Youre The Receiving Partner
Youll want to be as relaxed and aroused as possible, because itll make the experience easier and more enjoyable.
The whole poop-comes-out-of-the-butt thing gives some people a case of the heebie-jeebies even when its their own butt.
Remedy this by taking a shower and paying a little extra attention back there to get it squeaky clean. Some people like to use an enema before engaging in butt play, but it isnt necessary.
Use the bathroom before getting started. Prostate stimulation can make you feel like you need to pee, and anal penetration can cause the sensation of needing to poop.
Even though you wont actually do either, worrying that you might can interfere with your ability to let go and enjoy yourself. Knowing your bladder and bowels are empty can help.
Getting used to the sensation of having your prostate touched can help, too. Practice with an anal sex toy, like a butt plug, or your fingers.
Be sure to set the mood so that youre turned on and primed for action. Light candles, watch porn, or engage in some good old-fashioned masturbation or foreplay to get there.
Finally, be sure to lube up real good. Applying a water-based lubricant will allow for easier penetration and make for some easy gliding if stimulating your prostate externally.
You May Like: What Is The Female Version Of A Prostate
