How We Treat Prostate Cancer
The prognosis for metastatic prostate cancer can be discouraging, but some treatment centerslike the Johns Hopkins Precision Medicine Center of Excellence for Prostate Cancerspecialize in innovative, individualized therapy with the potential to improve outcomes.
What Is My Outlook
If youre diagnosed with advanced prostate cancer, you may want to know how well your treatment is likely to control your cancer and for how long it will control it. This is sometimes called your outlook or prognosis. But not all men will want to know this.
While it isnt possible to cure advanced prostate cancer, treatments can help keep it under control, often for several years. Treatments will also help manage any symptoms, such as pain.
No one can tell you exactly what your outlook will be, as it will depend on many things such as where the cancer has spread to, how quickly it has spread, and how well you respond to treatment. Some men may not respond well to one treatment, but may respond better to another. And when your first treatment stops working, there are other treatments available to help keep the cancer under control for longer. Speak to your doctor about your own situation and any questions or concerns you have.
Making Sense Of Your Diagnosis
When you were diagnosed with advanced prostate cancer, you may have heard your doctor say it was recurrent, locally advanced, or metastatic. These are types of advanced prostate cancer.
When prostate cancer has returnedâfollowing initial treatment such as radiation therapy or surgeryâas detected by a rising PSA* level, biopsy, or scan
*PSA stands for prostate-specific antigen.
When prostate cancer has spread to tissues near the prostate
When prostate cancer has spread far from the prostate to other parts of the body, such as the bones, liver, or lungs
*PSA stands for prostate-specific antigen.
Don’t Miss: Surgery Options For Enlarged Prostate
Fast Facts On Prostate Cancer
- Prostate cancer rarely reaches an advanced stage.
- People with the condition normally have a very good outlook when they receive an early diagnosis and treatment.
- Hormone therapy is a treatment option for advanced prostate cancer, as are chemotherapy and immunotherapy.
- Prostate cancer can spread to the bones, brain, and lungs.
Prostate cancer occurs when cells in the prostate gland mutate and start to develop abnormally, multiplying at an uncontrolled rate. In some instances, the cancerous cells can spread to other body parts through tissue, the blood, or the lymphatic system.
After a doctor diagnoses prostate cancer, they will test to see if the cancer has spread to other areas of the body, or how much of the body is affected.
The doctor will assign a stage of prostate cancer from 1 to 4. Stage 4 is the most advanced form.
Stage 4 prostate cancer has spread to pelvic lymph nodes or is blocking the ureters. The ureters are the tubes that connect the kidneys to the bladder. Stage 4 prostate cancer may also have spread to the bladder, the rectum, the bones, or distant lymph nodes.
Doctors will test any cancerous cells in the body to determine if the additional cells came from the prostate. Even if they detect cancer in the bones, doctors still consider this prostate cancer if that is where the cancer originated.
There are two types of stage 4 prostate cancer:
Metastatic Stage Iv Or D2 Prostate Cancer
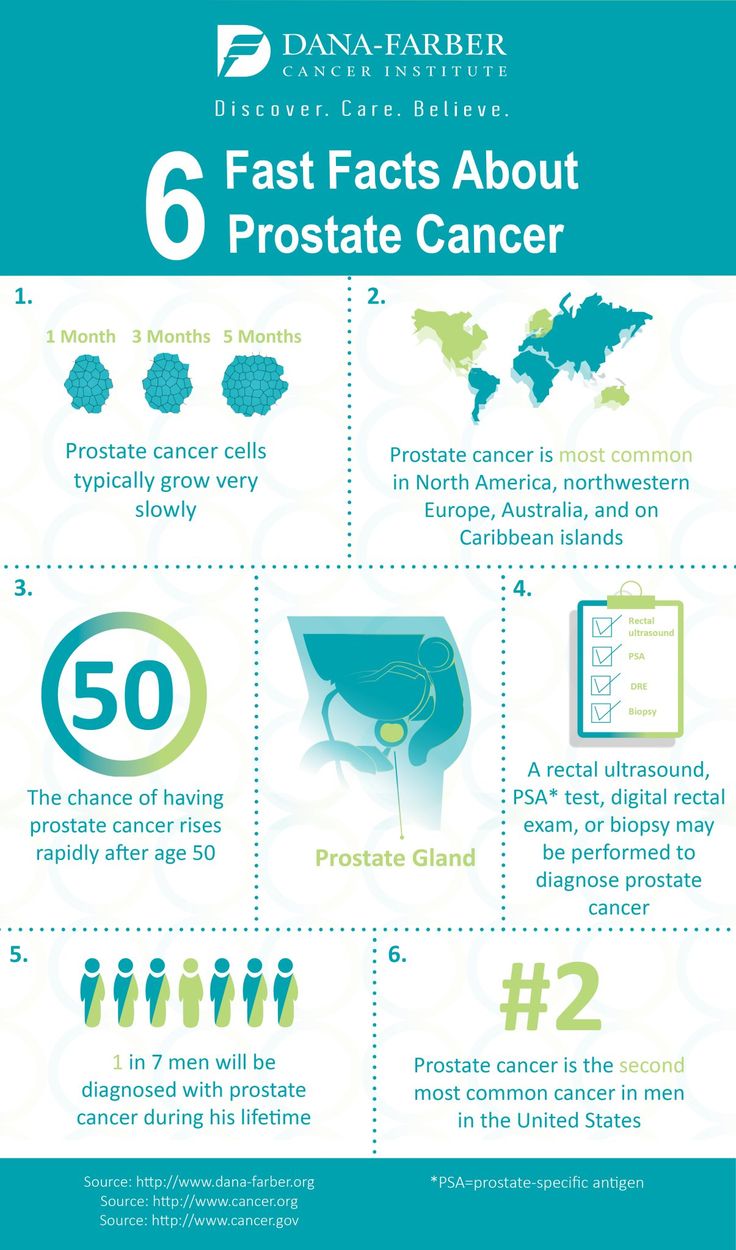
Prostate cancer that has spread to distant organs and bones is treatable, but not usually curable with current standard therapies. Treatment has evolved significantly over the past decade from hormone or androgen deprivation therapy alone to newer combination treatment regimens incorporating ADT plus chemotherapy and targeted therapies.1,20
Don’t Miss: What Age Should You Get Your Prostate Checked
Treatment By Stage Of Prostate Cancer
Different treatments may be recommended for each stage of prostate cancer. Your doctor will work with you to develop a specific treatment plan based on the cancers stage and other factors. Detailed descriptions of each type of treatment are provided earlier on this same page. Clinical trials may also be a treatment option for each stage.
Early-stage prostate cancer
Early-stage prostate cancer usually grows very slowly and may take years to cause any symptoms or other health problems, if it ever does at all. As a result, active surveillance or watchful waiting may be recommended. Radiation therapy or surgery may also be suggested, as well as treatment in clinical trials. For those with a higher Gleason score, the cancer may be faster growing, so radical prostatectomy and radiation therapy are often recommended. Your doctor will consider your age and general health before recommending a treatment plan.
ASCO, the American Urological Association, American Society of Radiation Oncology, and the Society of Urologic Oncology recommend that patients with high-risk early-stage prostate cancer that has not spread to other areas of the body should receive radical prostatectomy or radiation therapy with hormonal therapy as standard treatment options.
Locally advanced prostate cancer
Watchful waiting may be considered for older adults who are not expected to live for a long time and whose cancer is not causing symptoms or for those who have another, more serious illness.
Castrate Refractory Prostate Cancer: A Wider Range Of Options
In this section, we explain the treatments available at Birmingham Prostate Clinic for patients once their disease becomes resistant to hormone treatment, called castrate refractory prostate cancer. Two types of treatments are needed to:
- Control the cancer and prevent further spread of cancer
- Control or prevent the symptoms caused by the spread of prostate cancer to the bones
Don’t Miss: Is Ginger Good For Prostate Cancer
What Are Some New Diagnostic Methods For Prostate Cancer
Diagnosing prostate cancer isnt easy. Thats because the major tools the prostate-specific antigen test and prostate biopsy arent perfect. PSA levels can be high for reasons other than cancer, and they can be low even when someone has cancer. This makes it hard to know when someone needs a prostate biopsy. Some people end up getting prostate biopsies they dont need, while others can get biopsies too late. Even when done perfectly, the biopsy can miss the cancer cells and delay a diagnosis.
Once someone has a diagnosis of prostate cancer, theyll get a risk class. This risk class tries to predict how the cancer will behave over time. Teams usually pick treatments based on these risk classes. But the tools that help to assign a risk class arent perfect either.
Scientists are working to improve methods for diagnosis to overcome these limitations. The FDA hasnt approved some of these methods yet, and your insurance may not cover them. But even so, they might be right for you:
What Is The Best Treatment For Stage Iv Breast Cancer
Although systemic drugs are the main treatment for stage IV breast cancer, local and regional treatments such as surgery, radiation therapy, or regional chemotherapy are sometimes used as well. These can help treat breast cancer in a specific part of the body, but they are very unlikely to get rid of all of the cancer.
Also Check: Axumin Pet Scan For Prostate Cancer
Prostate Cancer Survival Rates
Answering the question of how curable is prostate cancer? first requires understanding what doctors mean when they refer to curability. Regardless of the type of cancer, doctors consider cancer cured when a patient remains cancer-free for a specified period after treatment. The higher the number of patients who stay cancer-free for five years or longer, the higher the curability of that particular disease.
Prostate cancer, therefore, has one of the highest curability rates of all types of cancer, thanks in large part to early detection standards and advances in treatment, such as the stereotactic body radiation therapy offered by Pasadena CyberKnife. When the cancer is detected in the early local or regional stages that is, before the cancer has spread or when it has only spread to limited areas in the pelvic regions the five-year survival rate is nearly 100 percent.
Survival rates decline significantly when cancer is detected at later stages however, the good news is that only about five percent of men are diagnosed after the cancer has become widespread throughout the body. In short, more than 90 percent of men who are diagnosed with prostate cancer live for five years or longer after treatment, making it one of the most curable forms of cancer.
Recommended Reading: What Is Level 7 Prostate Cancer
Watchful Waiting Or Active Surveillance/active Monitoring
Asymptomatic patients of advanced age or with concomitant illness may warrantconsideration of careful observation without immediate active treatment. Watch and wait, observation, expectant management, and active surveillance/active monitoring are terms indicating a strategy that does not employ immediate therapy with curative intent.
Watchful waiting and active surveillance/active monitoring are the most commonly used terms, and the literature does not always clearly distinguish them, making the interpretation of results difficult. The general concept of watchful waiting is patient follow-up with the application of palliative care as needed to alleviate symptoms of tumor progression. There is no planned attempt at curative therapy at any point in follow-up. For example, transurethral resection of the prostate or hormonal therapy may be used to alleviate tumor-related urethral obstruction should there be local tumor growth hormonal therapy or bone radiation might be used to alleviate pain from metastases. Radical prostatectomy has been compared with watchful waiting or active surveillance/active monitoring in men with early-stage disease .
- Regular patient visits.
- Transrectal ultrasound .
- Transrectal needle biopsies .
Patient selection, testing intervals, and specific tests, as well as criteria for intervention, are arbitrary and not established in controlled trials.
Also Check: How To Get Tested For Prostate Cancer
Are There Side Effects Of The Combination Approach To Prostate Cancer Radiation Therapy
When it comes to early stages of disease, patients very frequently do well with either brachytherapy or external beam radiation. Success rates of around 90% or higher can be achieved with either approach. When the disease is somewhat more advanced based on the PSA level, Gleason score, extent of visible disease on magnetic resonance imaging we have learned over the years that higher doses of radiation are critical to achieving better results. Some evidence, including a large trial, suggests that for patients with intermediate- or high-risk prostate cancer, a combined approach using brachytherapy along with external beam radiation may be best compared to standard dose external beam radiation therapy alone.
Read Also: Beginning Signs Of Prostate Cancer
Strategies To Improve Treatment
The progress that has been made in the treatment of prostate cancer has resulted from development of better treatments that were evaluated in clinical studies. Future progress in the treatment of prostate cancer will result from patients continued participation in appropriate clinical trials. Developing novel precision cancer medicines and immunotherapies is the main area of active current investigation.
Cabazitaxel : Cabazitaxel is administered intravenously and has been demonstrated to improve time to cancer progression and overall survival in men with HRPC previously treated with docetaxel. Cabazitaxels primary side effect is neutropenia, and it is recommended that patients receive a white blood cell growth factor if they are at high risk of this complication.
Sipuleucel-T: Sipuleucel-T is an immunotherapy that prompts the bodys immune system to respond against the cancer. A Phase III clinical trial that contributed to the FDA approval of sipuleucel-T was a study known as IMPACT which demonstrated an improvement in overall survival for men treated with sipuleucel-T. The main side effects reported were chills, fever, and headache.
References:
Don’t Miss: How To Give A Prostate Massage
What You Can Do
Its important that you learn all you can about advanced prostate cancer so you can make informed decisions. Be open with your doctors and others on your healthcare team. Express your concerns and feel free to advocate for yourself and your quality of life. Get another medical opinion if you feel its necessary.
Some complementary therapies may prove helpful in coping with advanced cancer. For example:
- tai chi, yoga, or other movement therapy
- meditation, breathing exercises, or other relaxation techniques
A variety of services can help you with everything from lodging while youre getting treatment to getting some help around the house. Communicating with online or in-person groups are a good way to share information and lend mutual support.
The Stages Of Treatment
Because the stage of your cancer is the most influential factor in how your treatment will progress, weve divided the rest of this article into segments based on the stage of your cancer:
Stage 1 prostate cancer is the least advanced stage. This means your cancer is small and hasnt advanced past your prostate.
In this stage, PSA and Grade Group levels are low. Over 99% of people with prostate cancer caught in this stage survive the effects of cancer for at least 5 years. This means that you can still die of other causes, but you have a less than 1% chance of dying of prostate cancer complications.
for stage 1 prostate cancer usually consists of some combination of active surveillance, surgery, or radiation therapy. You may also be eligible for clinical trials that offer newer treatment techniques.
Also Check: How Do They Check Your Prostate
The Stages Of Prostate Cancer: What You Need To Know
After a prostate cancer diagnosis, your oncologist will refer to the stage of your cancer. All cancers are categorized into four distinct stages, each of which identifies the progress of the growth of cancerous cells within clinically defined standards. These stages help doctors determine the most appropriate care for each patient based on his or her condition, and can also provide easy-to-understand context for your diagnosis. Learn more about the stages of prostate cancer, how each stage will affect your treatment plan and the survival rates for each stage, then contact Regional Cancer Care Associates to schedule a consultation.
Donât Miss: Average Recovery Time For Prostate Removal
About Half Of Men Older Than 50 Have An Enlarged Prostate Here Are Some Of The Basic Facts You Need To Know About This Common Condition
As men age, many experience prostate gland enlargement. This condition is known as benign prostatic hyperplasia .
The prostate gland surrounds the urethra, the hollow tube that carries urine out of the body. When the prostate gets bigger, it can squeeze or partially block the urethra, which leads to problems urinating.
BPH is quite common in older men. In fact, the condition impacts about 50% of men between the ages of 51 and 60. For men 80 and older, the prevalence of BPH is approximately 90%, according to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases.
You May Like: Survival Rate Prostate Cancer Stage 4
Read Also: How Big Is The Prostate
What Is Intermittent Adt
Researchers have investigated whether a technique called intermittent androgen deprivation can delay the development of hormone resistance. With intermittent androgen deprivation, hormone therapy is given in cycles with breaks between drug administrations, rather than continuously. An additional potential benefit of this approach is that the temporary break from the side effects of hormone therapy may improve a mans quality of life.
Randomized clinical trials have shown similar overall survival with continuous ADT or intermittent ADT among men with metastatic or recurrent prostate cancer, with a reduction in some side effects for intermittent ADT .
Also Check: What Are The Chances Of Getting Prostate Cancer
What Treatments Are Available
If you have advanced prostate cancer, treatment wont cure your cancer. But it can help keep it under control and manage any symptoms.
If youve just been diagnosed with advanced prostate cancer, you may be offered the following treatments:
- chemotherapy with hormone therapy
- clinical trials.
Research has found that having radiotherapy together with one of the main treatments listed above can help some men with advanced prostate cancer to live longer. But radiotherapy isnt suitable for all men with advanced prostate cancer.
If you live in Scotland, you may also be offered a type of hormone therapy called abiraterone acetate together with standard hormone therapy. In the rest of the UK, abiraterone is currently only given to men with advanced prostate cancer that has stopped responding to other types of hormone therapy. The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence is currently deciding whether to make it available for men who have just been diagnosed with advanced prostate cancer.
Before you start treatment
Before you start any treatment, make sure you have all the information you need. Its important to think about how you would cope with the possible side effects. Speak to your doctor or nurse about this.
It can help to write down any questions you want to ask at your next appointment. It may also help to take someone with you, such as your partner, a family member or friend.
If you have any questions, speak to our Specialist Nurses.
Also Check: What Happens When You Have A Prostate Removed
Ajcc Stage Groupings And Tnm Definitions
The AJCC has designated staging by TNM classification.
| Grade Group | Gleason Score | Gleason Pattern |
|---|---|---|
| aAdapted from AJCC: Prostate. In: Amin MB, Edge SB, Greene FL, et al., eds.: AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 8th ed. New York, NY: Springer, 2017, pp. 71526. | ||
| 1 | ||
| 4+4, 3+5, or 5+3 | ||
| 5 | 4+5, 5+4, or 5+5 |
| Stage | Gleason Score Gleason Pattern g | Illustration | |
|---|---|---|---|
| T = primary tumor N = regional lymph nodes M = distant metastasis cT = clinical T PSA = prostate-specific antigen pT = pathological T. | |||
| aAdapted from AJCC: Prostate. In: Amin MB, Edge SB, Greene FL, et al., eds.: AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 8th ed. New York, NY: Springer, 2017, pp. 71526. | |||
| The explanations for superscripts b through g are at the end of Table 5. | |||
| I | cT1ac, cT2a, N0, M0 | cT1 = Clinically inapparent tumor that is not palpable. | < 10 |
| cT1a = Tumor incidental histologic finding in 5% of tissue resected. | |||
| cT1b = Tumor incidental histologic finding in > 5% of tissue resected. | |||
| cT1c = Tumor identified by needle biopsy found in one or both sides, but not palpable. | |||
| cT2 = Tumor is palpable and confined within prostate. | |||
| cT2a = Tumor involves ½ of one side or less. | |||
| N0 = No positive regional nodes. | |||
| M0 = No distant metastasis. | |||
| Gleason Score, 6 Gleason Pattern, 3+3 . | |||
| N0 = No positive regional nodes. | |||
| M0 = No distant metastasis. |
References
