Prostate Cancer Caregiver Podcast Series
We are proud to announce a new podcast series geared toward helping give support, hope and guidance to prostate cancer caregivers. The goal of this Prostate Cancer Caregiver Podcast Series is to help others connect with a diverse group of people who have felt the impact of prostate cancer in their lives and empower them on their journey.
Doctors Answer The Most Frequently Asked Questions:
Back to Prostate Cancer book
Cancer is characterized by uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells. After a while, groups of these cells form a detectable lump known as a tumour. Cancer can affect any type of cell in an organ, a gland, muscle tissue, blood or the lymphatic system. In the case of prostate cancer, the secretory cells are usually the ones that become cancerous. In theory, there are two types of prostate cancer: slow-growing and aggressive. In reality, most cases are somewhere between the two, growing at a moderate rate. For the moment, science does not have the tools to accurately predict the growth rate of a persons cancer once it has been diagnosed.
Over time, the malignant cells in cancerous tumours can invade neighbouring tissue or organs. They may even spread to the rest of the body through the blood or lymphatic system. The presence of prostate cancer cells anywhere outside of the prostate is called metastasis. The most common sites of metastasis in prostate cancer are the lymph nodes and the bones.
Yes. Prostate cancer is the most common cancer among Canadian men . According to the Canadian Cancer Society, in 2011, an estimated 25,500 Canadian men were diagnosed with prostate cancer and 4,100 died of it. Every day, on average, 70 Canadian men are diagnosed with prostate cancer and 11 die of it. One in seven men will develop prostate cancer during his lifetime and one in 28 will die of it.
Not in any significant manner.
Can Prostate Cancer Be Found Early
Screening tests are available to find prostate cancer early, but government guidelines don’t call for routine testing in men at any age. The tests may find cancers that are so slow-growing that medical treatments would offer no benefit. And the treatments themselves can have serious side effects. The American Cancer Society advises men to talk with a doctor about screening tests, beginning at:
- Age 50 for average-risk men who expect to live at least 10 more years
- Age 45 for men at high risk this includes African-Americans and those with a father, brother, or son diagnosed before age 65
- Age 40 for men with more than one first-degree relative diagnosed at an early age
The U.S.Preventive Services Task Force says that testing may be appropriate for some men age 55 â 69. They recommend that men talk to their doctor to discuss the potential risks and benefits of being tested.
8
Read Also: How Bad Is Stage 3 Prostate Cancer
How Do You Know If You Have Prostate Cancer
Theres no way of knowing if you have prostate cancer without visiting your doctor, as most men with early prostate cancer dont have any symptoms. And if you do have symptoms they can be caused by other things.
And you cant check for prostate cancer yourself.
You may want to speak to your GP if you’re over 50 , even if you don’t have any symptoms. These are all things that can increase your risk of prostate cancer. Your GP can give more information or tests if necessary.
If youre not sure about what to say to your GP, print and fill out this form and show it to them. This will help you have the conversation.
I thought I could be at risk after learning that African Caribbean men are more likely to get prostate cancer than white men.
What Do You Do Once Diagnosed With Prostate Cancer
If the biopsy shows the presence of prostate cancer, the next step is to determine how much cancer is present and to make sure that it has not spread. Our prostate cancer experts will expertly review your PSA blood tests, physical exam findings, and biopsy results. Some simple and painless tests such as a CT scan, bone scan, MRI,and possibly a PET scan can help make sure there is no cancer that has spread outside the prostate.
Using the above information, we can then calculate the likelihood of the cancer being completely confined to the prostate, having spread beyond the confines of the prostate, or having spread some distance to the lymph glands in the pelvis.
This information, as well as an evaluation of your overall medical condition and well-being, is critical in determining which treatment options will offer you the best chance for a cure.
Read Also: Can Prostate Cancer Go Away
Classification Of Prostatic Diseases
Common diseases of the prostate include acinar adenocarcinoma, BPH, chronic prostatitis, hemorrhage, cysts, calcifications, atrophy and fibrosis. Uncommon diseases of the prostate include tumors other than acinar adenocarcinoma, granulomatous prostatitis containing tuberculosis, abscesses and so on, and idiopathic disorders such as amyloidosis and exophytic BPH.
Many conditions that yield abnormal signals within the prostate, including hemorrhage, cysts, calcifications, atrophy and fibrosis, are benign and highly recognizable on mpMRI . In addition to these benign signal abnormalities and based on the applicability of PI-RADS assessment, we divide other focal signal abnormalities involving the prostate into two categories according to the patients age, serum PSA level, symptoms and mpMRI findings: category 1, diseases for which the PI-RADS assessment is suitable for use, and category 2, diseases for which the PI-RADS assessment is not suitable for use. Category 1 includes prostate cancer , typical BPH in the transitional zone , and some types of prostatitis/granulomatous prostatitis, which overlap in terms of clinical and mpMRI findings, while category 2 includes tumors except for PCa, exophytic BPH nodules, and some types of granulomatous prostatitis , for which PCa may be excluded according to the clinical and MRI findings.
Risk Factors For Prostate Cancer
Some risk factors have been linked to prostate cancer. A risk factor is something that can raise your chance of developing a disease. Having one or more risk factors doesn’t mean that you will get prostate cancer. It just means that your risk of the disease is greater.
- Age. Men who are 50 or older have a higher risk of prostate cancer.
- Race. African-American men have the highest risk of prostate cancerâthe disease tends to start at younger ages and grows faster than in men of other races. After African-American men, prostate cancer is most common among white men, followed by Hispanic and Native American men. Asian-American men have the lowest rates of prostate cancer.
- Family history. Men whose fathers or brothers have had prostate cancer have a 2 to 3 times higher risk of prostate cancer than men who do not have a family history of the disease. A man who has 3 immediate family members with prostate cancer has about 10 times the risk of a man who does not have a family history of prostate cancer. The younger a man’s relatives are when they have prostate cancer, the greater his risk for developing the disease. Prostate cancer risk also appears to be slightly higher for men from families with a history of breast cancer.
- Diet. The risk of prostate cancer may be higher for men who eat high-fat diets.
Don’t Miss: Expressed Prostatic Secretion
Individualized Prostate Cancer Screening
Coltman says that men and their doctors can no longer rely on PSA levels alone when deciding whether to have a prostate biopsy.
The situation now is that the individual man with his individual urologist will have to assess what the person feels are his risk factors, he says. In consultation with his doctor, the individual man must come to grips with the question of whether or not a biopsy should be done. It will become a more personalized interaction.
Whos at high risk? Men with the following factors have the highest risk of prostate cancer:
- Age. A mans risk of prostate cancer increases with age.
- Race.African American men have the highest incidence of prostate cancer and the highest death rate from prostate cancer of any men in the world, Coltman says.
- Family history. A mans risk increases if his brother or father has had prostate cancer.
What Is A Prostate Nodule
The prostate nodule is defined as a lump or area of hardness under the surface of a mans prostate.
In some instances, a patient can have prostate stone under the surface of the skin, and although it may seem like a nodule, its not the same thing as nodules are more like tissue masses.
While prostate stone is harmless, even though its uncomfortable, nodule represents an abnormal growth of cells, which may or may not be cancerous in nature.
Understanding there is a lump on the prostate is a primary source for concern among men, but you shouldnt panic. Instead, schedule an appointment to see your doctor who will perform specific diagnostic tests to see whats going on.
The best way to stay on top of everything is to go to regular checkups even if you have the normal prostate.
Also Check: How To Shrink Prostate Mayo Clinic Naturally
How Common Is Prostate Cancer
About one in nine men will receive a prostate cancer diagnosis during his lifetime. Prostate cancer is second only to skin cancer as the most common cancer affecting males. Close to 200,000 American men receive a diagnosis of prostate cancer every year. There are many successful treatments and some men dont need treatment at all. Still, approximately 33,000 men die from the disease every year.
What Are Prostate Cancer Treatment Side Effects
Some prostate cancer treatments can affect the bladder, erectile nerves and sphincter muscle, which controls urination. Potential problems include:
- Incontinence: Some men experience urinary incontinence. You may leak urine when you cough or laugh, or you may feel an urgent need to use the bathroom even when your bladder isnt full. This problem can improve over the first six to 12 months without treatment.
- Erectile dysfunction : Surgery, radiation and other treatments can damage the erectile nerves and affect your ability to get or maintain an erection. Some men regain erectile function within a year or two . In the meantime, medications like sildenafil or tadalafil can help by increasing blood flow to the penis.
- Infertility: Treatments can affect your ability to produce or ejaculate sperm, resulting in male infertility. If you think you might want children in the future, you can preserve sperm in a sperm bank before you start treatments. After treatments, you may undergo sperm extraction. This procedure involves removing sperm directly from testicular tissue and implanting it into a womans uterus.
Also Check: What Are The Symptoms Of Perineural Invasion
What Are Other Local Treatment Options For Prostate Cancer
Besides radical prostatectomy, external beam radiation and/or brachytherapy, cryosurgical ablation of the prostate and high-intensity focused ultrasound have emerged as alternative therapeutic options in patients with clinically localized prostate cancer.
Cryotherapy and high-intensity focused ultrasound has been used to destroy tissue, either by freezing or by generating local thermal energy. These techniques can be applied focally, sub-totally, or to the entire prostate gland. However, the role of these techniques remains uncertain. Potential advantages in men with the localized disease include the ability to destroy cancer cells using a relatively noninvasive procedure. As such, these procedures are associated with minimal blood loss and pain. There is also faster post-treatment convalescence.
Cryotherapy
This technique involves inserting a probe through a small skin incision and freezing areas of cancer in the prostate.
HIFU
- HIFU was first developed as a treatment for benign prostatic hyperplasia and is now also being used as a procedure for the killing of prostate cancer cells. This procedure utilizes transrectal ultrasound that is highly focused into a small area, creating intense heat of 80° C to 100° C, which is lethal to prostate cancer tissue.
- The published clinical experience with HIFU for this application is limited and the procedure is not yet approved by the FDA for use in the U.S.
Hope For Advanced Cancer

Your doctor will continue to monitor your PSA levels and may perform other tests after treatment for prostate cancer. If it recurs or spreads to other parts of the body, additional treatment may be recommended. Lifestyle choices may matter, too. One study found that prostate cancer survivors who exercised regularly had a lower risk of dying, for example.
23
You May Like: Is Cranberry Juice Good For Prostate Infection
How Does The Doctor Know I Have Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer tends to grow slowly over many years. Most men with early prostate cancer dont have changes that they notice. Signs of prostate cancer most often show up later, as the cancer grows.
Some signs of prostate cancer are trouble peeing, blood in the pee , trouble getting an erection, and pain in the back, hips, ribs, or other bones.
If signs are pointing to prostate cancer, tests will be done. Most men will not need all of them, but here are some of the tests you may need:
PSA blood test: PSA is a protein thats made by the prostate gland and can be found in the blood. Prostate cancer can make PSA levels go up. Blood tests will be done to see what your PSA level is and how it changes over time.
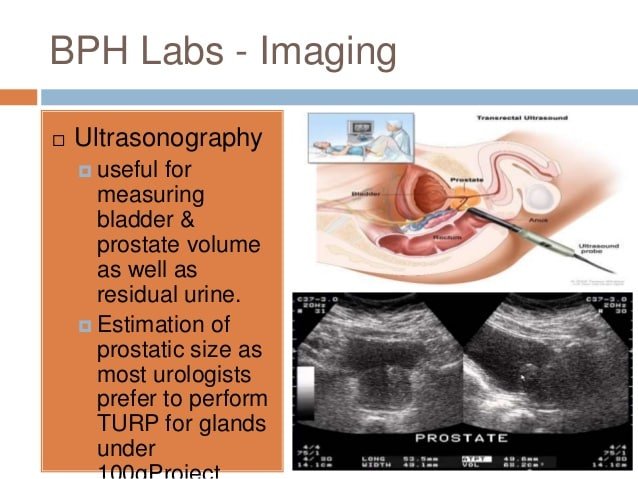
Transrectal ultrasound : For this test, a small wand is put into your rectum. It gives off sound waves and picks up the echoes as they bounce off the prostate gland. The echoes are made into a picture on a computer screen.
MRI: This test uses radio waves and strong magnets to make detailed pictures of the body. MRI scans can be used to look at the prostate and can show if the cancer has spread outside the prostate to nearby organs.
Prostate biopsy: For a prostate biopsy, the doctor uses a long, hollow needle to take out small pieces of the prostate where the cancer might be. This is often done while using TRUS or MRI to look at the prostate. The prostate pieces are then checked for cancer cells. Ask the doctor what kind of biopsy you need and how its done.
Risk Factors You Can Control
Diet seems to play a role in the development of prostate cancer, which is much more common in countries where meat and high-fat dairy are mainstays. The reason for this link is unclear. Dietary fat, particularly animal fat from red meat, may boost male hormone levels. And this may fuel the growth of cancerous prostate cells. A diet too low in fruits and vegetables may also play a role.
6
You May Like: What Is Perineural Invasion In Prostate Cancer
Enlarged Prostate Or Prostate Cancer
The prostate can grow larger as men age, sometimes pressing on the bladder or urethra and causing symptoms similar to prostate cancer. This is called benign prostatic hyperplasia . It’s not cancer and can be treated if symptoms become bothersome. A third problem that can cause urinary symptoms is prostatitis. This inflammation or infection may also cause a fever and in many cases is treated with medication.
4
What Is The Prostate
The prostate is a small gland in the pelvis, found only in men.
About the size of a satsuma, it’s located between the penis and the bladder, and surrounds the urethra.
The main function of the prostate is to produce a thick white fluid that creates semen when mixed with the sperm produced by the testicles.
Read Also: Does Enlarged Prostate Affect Ejaculation
Men With Prostate Cancer May Experience Unintended And Significant Weight Loss There Are Five Reasons Why This Can Happen
The first reason is rather obvious: anxiety and/or depression over the illness. Both anxiety and depression suppress appetite.
Another well-known explanation is the sick feeling that chemotherapy often causes. The drugs can also alter the patients perception of how foods taste.
But there are less obvious reasons why prostate cancer can cause a man to lose weight even if he doesnt have any pre-existing excess body fat.
If You Have A Lung Nodule
Most often the next step is to get a repeat CT scan to see if the nodule is growing over time. The time between scans might range anywhere from a few months to a year, depending on how likely your doctor thinks that the nodule could be cancer. This is based on the size, shape, and location of the nodule, as well as whether it appears to be solid or filled with fluid. If a repeat scan shows that the nodule has grown, your doctor might also want to get another type of imaging test called a positron emission tomography scan, which can often help tell if it is cancer.
If later scans show that the nodule has grown, or if the nodule has other concerning features, your doctor will want to get a sample of it to check it for cancer cells. This is called a biopsy. This can be done in different ways:
- The doctor might pass a long, thin tube down your throat and into the airways of your lung to reach the nodule. A small tweezer on the end of the bronchoscope can be used to get a sample of the nodule.
- If the nodule is in the outer part of the lung, the doctor might pass a thin, hollow needle through the skin of the chest wall and into the nodule to get a sample.
- If there is a higher chance that the nodule is cancer , surgery might be done to remove the nodule and some surrounding lung tissue. Sometimes larger parts of the lung might be removed as well.
These types of tests, biopsies, and surgeries are described in more detail in Tests for Lung Cancer.
You May Like: Perineuronal Net
What Causes Prostate Cancer
Doctors dont know exactly what causes prostate cancer. However, they do know that certain risk factors may increase your risk for the disease. Those risk factors include:
- Older age. Men of any age can get prostate cancer. However, its most common in men older than 65 years of age.
- African-American men are more likely to develop prostate cancer than Caucasian men.
- Family history. Men who have had a father or brother with prostate cancer are at increased risk of developing the disease.
- Obesity. Obese men who are diagnosed with prostate cancer are more likely to have an advanced or aggressive cancer.
