Understanding Prostate Cancers Progression
To determine the appropriate treatment, doctors need to know how far the cancer has progressed, or its stage. A pathologist, the doctor trained in analyzing cells taken during a prostate biopsy, will provide two starting pointsthe cancers grade and Gleason score.
- Cancer grade: When the pathologist looks at prostate cancer cells, the most common type of cells will get a grade of 3 to 5. The area of cancer cells in the prostate will also be graded. The higher the grade, the more abnormal the cells.
- Gleason score: The two grades will be added together to get a Gleason score. This score tells doctors how likely the cancer is to grow and spread.
After a biopsy confirms prostate cancer, the patient may undergo additional tests to see whether it has spread through the blood or lymph nodes to other parts of the body. These tests are usually imaging studies and may include a bone scan, positron emission tomography scan or computed tomography scan.
Also Check:
Are Dogs With Prostate Cancer In Pain
No, dogs with prostate cancer are not in pain. Prostate cancer is painless and asymptomatic in the early stages. However, as the condition progresses and forms metastasis to distant body parts, the dog may start feeling pain and discomfort.
The pain may also be caused by the prostatic disease itself. For example, if the prostatic tumor overgrows and compresses the surrounding tissues, it can make the urination and defecation processes painful.
Stage 3 Prostate Cancer
In stage 3, cancer has now spread beyond the prostate and may have potentially spread into the nearby seminal vesicles.
- Stage IIIA The tumor may involve both lobes of the prostate or less than that . There is no regional lymph node metastasis and no distant metastasis. . The PSA level is below or equal to 20 ng/ml. The Grade Group is 1-4.
- Stage IIIB The tumor extended through the prostatic capsule to the seminal vesicles or the adjacent structures, such as the bladder, muscles or the pelvic floor . There is no regional lymph node metastasis and no distant metastasis. . There can be any PSA level. The Grade Group is 1-4.
- Stage IIIC The tumor may or may not be extended through the prostatic capsule but has not spread to the regional lymph nodes or to other distant areas . There can be any PSA level. The Grade Group is 5.
Don’t Miss: Can Drinking Alcohol Affect Your Prostate
Hormonal Therapy For Aggressive Prostate Cancer: How Long Is Enough
- By Charlie Schmidt, Editor, Harvard Medical School Annual Report on Prostate Diseases
Men weighing treatment options for intermediate- or high-risk cancer that is still localized to the prostate can face a tricky question. A standard approach in these cases is to give radiation to the prostate along with drugs that block testosterone, a hormone that makes the cancer cells grow faster. For how long should this hormone therapy last? Thats not entirely clear. The drugs have side effects, such as fatigue, impotence, and a loss of muscle mass. But radiation doesnt control prostate cancer effectively without them. Doctors therefore aim to give hormone therapy only for as long as it takes to help their patients, without causing any undue harm.
Now, newly published results from a phase 3 clinical trial are providing some needed guidance.
Read Also: Whatâs The Difference Between Colon Cancer And Prostate Cancer
Survival Of Prostate Cancer
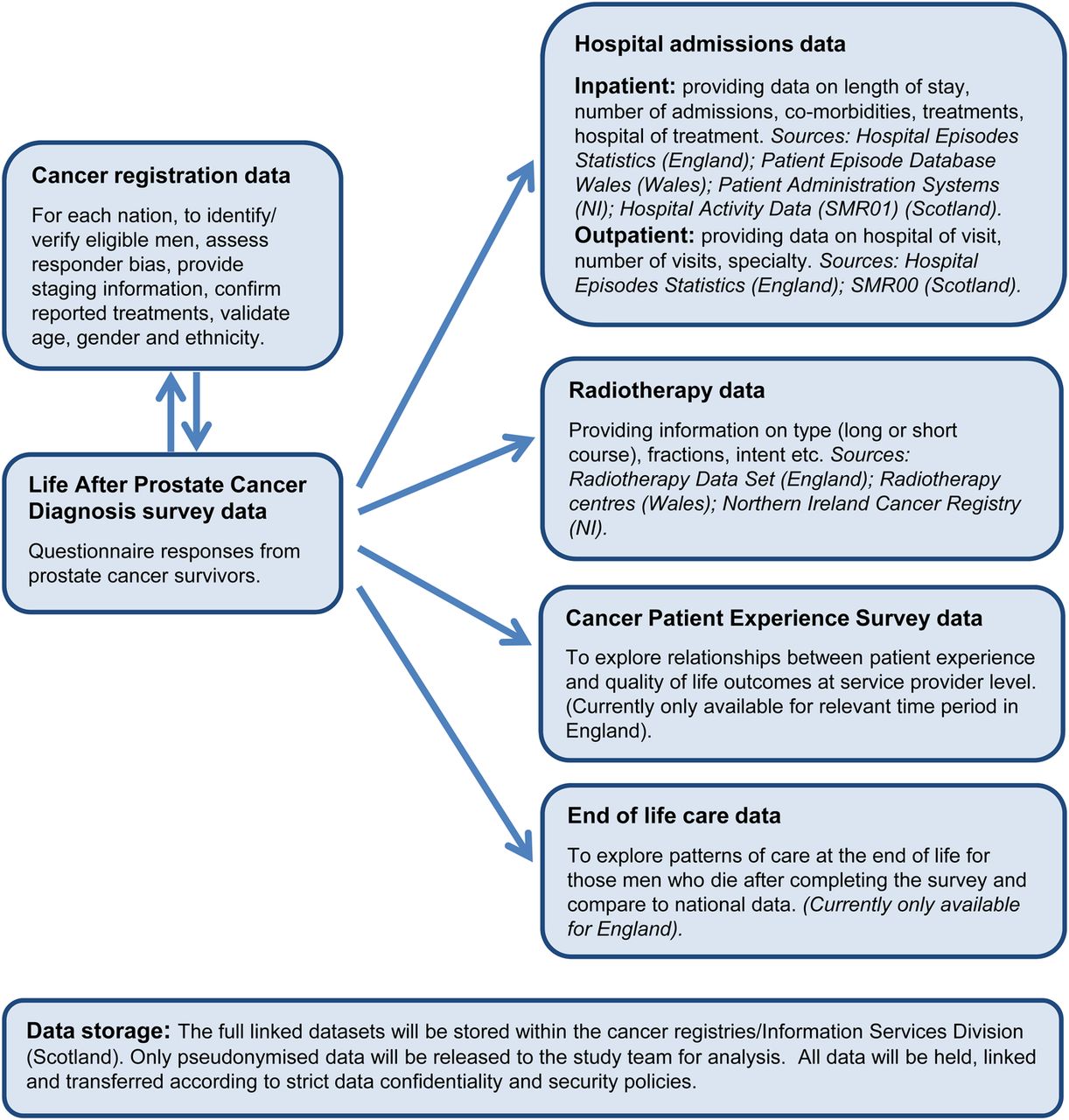
Survival depends on many factors. No one can tell you exactly how long you will live.
Below are general statistics based on large groups of people. Remember, they cant tell you what will happen in your individual case.
Survival for prostate cancer is generally good, particularly if you are diagnosed early.
Read Also: Prostate Cancer 4th Stage Treatment
Side Effects Of Radical Prostatectomy
The most common side effects of the procedure are incontinence and erectile dysfunction . The incontinence, though common early after surgery, usually goes away. Whether erectile function returns depends on whether the nerves surrounding the prostate can be spared at surgery, patient age and baseline function. Men who are older or already have erection problems are most likely to have erectile dysfunction afterward.
For more information on erectile dysfunction and treatment, see Managing Erectile Dysfunction A Patient Guide.
Quality Of Life With Advanced Stage Prostate Cancer
Since Huggins and Hodges won a Nobel Prize in 1966 for their work describing the relationship between testosterone and prostate cancer, androgen deprivation has continued to be an important component in the treatment of advanced prostate cancer. It is associated, however, with significant cost in terms of morbidity as well as economics. Side effects of androgen deprivation therapy include hot flashes, osteoporosis, loss of libido or impotence, and psychological effects such as depression, memory difficulties, or emotional lability. Recently Harle and colleagues55 reported insulin resistance, hyperglycemia, metabolic syndrome, and metabolic complications being associated with castration and thus being responsible for increased cardiovascular mortality in this population.
Because of the palliative nature of androgen ablation, quality of life is an important component of evaluating competing therapies. Intermittent androgen deprivation is one approach to hormonal therapy that has been developed with the aim of minimizing the negative effects of therapy while maximizing clinical benefits and the patients quality of life. It can be used in any clinical situation where continuous androgen deprivation treatment could be applied.56
Recommended Reading: How Is The Prostate Checked
How Are Hormone Therapies For Prostate Cancer Administered
LHRH agonists, the most commonly used drug class for hormone therapy, are given in the form of regular shots: once a month, once every three months, once every four or six months, or once per year. These long-acting drugs are injected under the skin and release the drug slowly over time. LHRH antagonists include degarelix and relugolix, an oral form.
Staging Of Prostate Cancer
- Stage I : The Gleason score is 6 or less, and the PSA level is less than 10. Cancer at this stage is normally not detectable in an ultrasound test or in a DRE test, as the tumor is very small. It is within the prostate and has not spread to nearby lymph nodes. It is usually discovered accidentally during a surgery carried out for another purpose. Prostate ultrasound and biopsy can be performed after detection of elevated blood PSA levels.
- Stage II : From this stage onwards, the Gleason score and the PSA level may vary from person to person. As the tumor grows in size, it can be detected in a DRE test or sonogram, but the tumor is still confined to the prostate gland. It is in one half or less of only one side of the prostate. It hasnt spread to lymph nodes and nearby organs, or it has spread to nearby lymph nodes, but has not invaded nearby organs.
- Stage III : The cancerous cells spread out from the original site and invade the seminal vesicles. They do not spread to nearby lymph nodes or to nearby organs in the body.
- Stage IV : The cancer moves out of the seminal vesicles and invades the lymph nodes. The size and number of tumors increase, and the cancerous cells spread into the nearby organs, such as the bladder and the rectum. In stage four prostate cancer, even bones and other parts of the body like lungs and liver are likely to be invaded by the cancerous cells.
Also Check: Side Effects Of Prostate Surgery
What Happens Without Treatment
Physicians will sometimes talk about a particular diseases natural history or typical progression if it is left untreated indefinitely.
With regard to prostate cancer, most cases of the disease are discovered while the cancer is still confined to the prostate itself. This is called local disease or localized disease.
The disease is easiest to treat while it is confined to the prostate. At this stage, surgery and radiation are most likely to be curative and completely kill or remove whatever cancer cells are present.
If left untreated, however, prostate cancer can proceed on a number of different paths.
Improvements In Life Expectancy
A decade ago, a man with metastatic prostate cancer would typically have a life expectancy of two to three years. Today, life expectancy for men with the same advanced disease is likely to be five to six years. There is now a much broader range of chemotherapy drugs available for men with advanced disease with greater efficacy . We also have better treatments to control the symptoms of advanced prostate cancer, such as pain from metastases. In this section, we consider in more detail the different treatments that are available and evidence for their effectiveness.
You May Like: How To Pleasure A Woman After Prostate Surgery
Treatments To Control And Prevent Symptoms Caused By The Spread Of Prostate Cancer To The Bones
Palliative External beam radiotherapy
Radiopharmaceuticals: Strontium-89 , samarium-153
Radium-223 dichloride is now licensed and called Xofigo. This is not widely available in the UK but BPC is one of a relatively small number of specialist centres using this treatment.
Zolidronic acid a bisphosphonate given by a 15 minute intravenous infusion every 34 weeks. It reduces the risk of bone complications, including pain and fractures.
Xgeva : this is a newly licensed drug available at BPC.
Pain medications
Surgery may be undertaken to treat bone fractures or to relief the pressure on the spinal cord by bone metastases.
My Tips For Men Family And Friends
- Ask how long someone has left to live if you want to know. The doctor may not always be able to give you an answer. And if they can give you an answer, it wont be exact. And it might not be the answer you want. But if youre ok with that, then you should ask.
- Try to explain why you want to know to the doctor or nurse. It might be that you want to be able to plan care at home, plan a trip, get time off work, or organise some quality time with your family. They might be able to help you work out those things, even if they cant give you exact timings.
Also Check: Laser Ablation For Prostate Cancer
You May Like: How Is Prostate Specific Antigen Test Done
How Long Can You Live With Lung Metastasis
A lung metastasis is life threatening. Few patients survive more than five years after their diagnosis. The anxiety and stress that accompany this illness can often be lessened by joining a support group. The health care providers and fellow patients who participate can help make a difficult situation a bit less so.
What Is Localized Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is the abnormal growth of cells in the prostate gland. Localized prostate cancer has not spread outside the gland. Early prostate cancer usually doesnât cause symptoms.
Prostate cancer is the most common cancer in men. Most men who get it are older than 65. If your father, brother, or son has had prostate cancer, your risk is higher than average.
Men of African descent have the highest rates of both prostate cancer and deaths from it.
About 21,000 men are diagnosed with prostate cancer in Canada every year.footnote 1 In the United States, about 12 out of 100 men in the U.S. will be diagnosed with prostate cancer sometime in their lifetime.footnote 2 But most men who are diagnosed with prostate cancer donât die from prostate cancer.
Unlike many other cancers, prostate cancer is usually slow-growing. When prostate cancer is found earlybefore it has spread outside the glandit may be cured with radiation or surgery.
Prostate cancer that has grown beyond the prostate is called advanced prostate cancer. Treatment choices are different for that stage of cancer.
Don’t Miss: Prostate Cancer Scale 6-10
Castrate Refractory Prostate Cancer: A Wider Range Of Options
In this section, we explain the treatments available at Birmingham Prostate Clinic for patients once their disease becomes resistant to hormone treatment, called castrate refractory prostate cancer. Two types of treatments are needed to:
- Control the cancer and preventing further spread of cancer
- Control or prevent the symptoms caused by the spread of prostate cancer to the bones
Donât Miss: How Do They Treat An Enlarged Prostate
Stages Of Prostate Cancer
In order to determine the stage of a patients prostate cancer, most doctors start by using the TNM staging system, which helps describe different aspects of the cancers growth.
- T the T category measures the size and extent of the Tumor
- N the N category measures whether and how far the cancer has spread to the Lymph Nodes
- M the M category whether the cancer has spread to other organs in the body (a process called Metastasis
The score for each of these categories is determined based on a pre-determined set of criteria. Your doctor cannot feel or see the tumor with a score of T1. A score of T3 means that the tumor has begun to grow outside of the prostate.
After calculating the TNM categories, doctors will combine the TNM score with the patients Gleason score and PSA levels assigning of a specific stage to the patients cancer.
Prostate cancer prognosis and survival rates can help give patients an idea of their chances of surviving the disease based on the stage and time of diagnosis. While some patients may find this information helpful, others may not want to know.
Donât Miss: Does Prostatitis Go Away Without Treatment
Read Also: How To Do Prostate Exam At Home
Can The Gleason Score On My Biopsy Really Tell What The Cancer Grade Is In The Entire Prostate
Because prostate biopsies are tissue samples from different areas of the prostate, the Gleason score on biopsy usually reflects your cancers true grade. However, in about 1 out of 5 cases the biopsy grade is lower than the true grade because the biopsy misses a higher grade area of the cancer. It can work the other way, too, with the true grade of the tumor being lower than what is seen on the biopsy.
Ask Your Doctor For A Survivorship Care Plan
Talk with your doctor about developing a survivorship care plan for you. This plan might include:
- A summary of the treatment you received
- A suggested schedule for follow-up exams and tests
- A schedule for other tests you might need in the future, such as early detection tests for other types of cancer, or tests to look for long-term health effects from your cancer or its treatment
- A list of possible late- or long-term side effects from your treatment, including what to watch for and when you should contact your doctor
- Suggestions for things you can do that might improve your health, including possibly lowering your chances of the cancer coming back
Read Also: Prostate Cancer In Lymph Nodes
Prevalence Of Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer in U.S. men and is the second leading cause of cancer death in men. One in nine men born in the U.S. today will be diagnosed with prostate cancer during his lifetime. The risk of dying from prostate cancer, however, is much lower, at one in 41. Your individual risk depends on your risk factors. Continue reading this document to better understand your particular risk.
The American Cancer Society has estimated that more than 248,000 new cases of prostate cancer will be diagnosed each year in the United States and more than 33,000 men will die from the disease. The death rate for prostate cancer is twice as high for African American men as for the general population.
Most cases are diagnosed when men are in their 60s and 70s , although prostate cancer is sometimes detected in men in their 50s or younger. The good news is that the five-year survival rate for all stages of prostate cancer has increased from 69% to almost 99% over the past 20 years. These rates vary depending on the extent of disease. Reasons for this improvement include increased public awareness, earlier detection though screening with prostate specific antigen blood tests, and advances in the treatments for this cancer.
Your Cancer Care Team

People with cancer should be cared for by a multidisciplinary team . This is a team of specialists who work together to provide the best care and treatment.
The team often consists of specialist cancer surgeons, oncologists , radiologists, pathologists, radiographers and specialist nurses.
Other members may include physiotherapists, dietitians and occupational therapists. You may also have access to clinical psychology support.
When deciding what treatment is best for you, your doctors will consider:
- the type and size of the cancer
- what grade it is
- whether the cancer has spread to other parts of your body
Don’t Miss: Focal Laser Ablation Prostate Cancer Results
What Is Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is cancer that affects the prostate gland in men. Prostate cancer is the second-leading cause of cancer deaths for men in the US.
Growth in the prostate can be of two types
Prostate cancer starts in the prostate gland and may spread to the nearby areas: lymph nodes, organs, or bones in other parts of the body.
You May Like: Elevated Prostate Specific Antigen Icd 10
First Line Treatment For Advanced Prostate Cancer
The established first line approach is to control the progression of the disease by reducing levels of testosterone in the body. This is because testosterone increases the speed at which prostate cancer cells reproduce.
There are two different ways to lower testosterone levels. Hormone therapy lowers the levels of testosterone in the body by taking tablets or having injections. It is sometimes referred to as medical castration. The surgical option involves removing the testicles, known as surgical castration or orchidectomy, although this is now rarely used.
Another approach is called anti-androgen treatment. Androgens have to bind to a protein in the cell called an androgen receptor to work. Anti-androgens are drugs that bind to these receptors so the androgens cant, effectively blocking them. The main side-effects are gynaecomastia breast enlargement and breast pain, although a single radiotherapy dose to the breasts can help this side-effect.
Combining anti-androgens with testosterone reduction is known as Maximum Androgen Blockade and may be used if hormone treatment alone is not working sufficiently.
Treating with chemotherapy at the same time as the start of hormone deprivation was found to increase survival by 13 months in all patients and 17 months in men with high-volume disease.
Dont Miss: Whats Good For An Enlarged Prostate
Recommended Reading: What Is Advanced Prostate Cancer
