What To Do After A Stage 4 Mesothelioma Diagnosis
Many patients pursue a second opinion from a specialist after a stage 4 mesothelioma diagnosis. Mesothelioma specialists can provide valuable information on the latest treatments available through clinical trials. Finding financial assistance to offset the high costs of treatment can also be beneficial at this time.
Steps To Consider After a Stage 4 Diagnosis
- Get a second opinion from a mesothelioma specialist.
- Exercise and maintain a healthy diet to improve mood and quality of life.
- Join a support group to connect with others coping with mesothelioma.
Staying healthy and utilizing support resources may help patients live years beyond their predicted life expectancy. Connecting with other mesothelioma survivors can inspire new ways of managing your diagnosis. Andy Ashcraft lived with stage 4 pleural mesothelioma for seven years after joining a clinical trial combining immunotherapy with chemotherapy. Lannie Chitwood underwent experimental chemotherapy and lived for 10 years with stage 4 pleural mesothelioma.
Surgically Removing The Prostate Gland
A radical prostatectomy is the surgical removal of your prostate gland. This treatment is an option for curing prostate cancer that has not spread beyond the prostate or has not spread very far.
Like any operation, this surgery carries some risks, such as urinary incontinence and erectile dysfunction.
In extremely rare cases, problems arising after surgery can be fatal.
It’s possible that prostate cancer can come back again after treatment. Your doctor should be able to explain the risk of your cancer coming back after treatment, based on things like your PSA level and the stage of your cancer.
Studies have shown that radiotherapy after prostate removal surgery may increase the chances of a cure, although research is still being carried out into when it should be used after surgery.
You may want to ask your doctors about storing a sperm sample before the operation so it can be used later for in vitro fertilisation .
Improvements In Life Expectancy
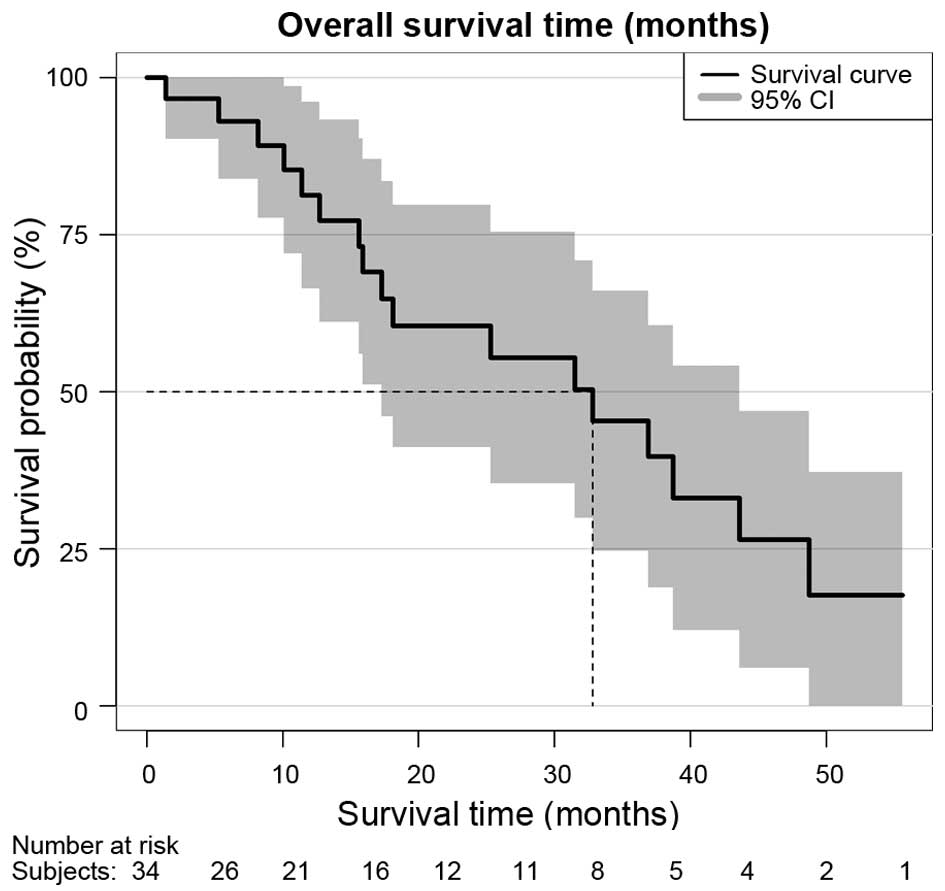
A decade ago, a man with metastatic prostate cancer would typically have a life expectancy of two to three years. Today, life expectancy for men with the same advanced disease is likely to be five to six years. In the UK the survival rate for men with stage 4 prostate cancer is approximately 50%, meaning that 50 out of every 100 men will survive their cancer for 5 years or more after they are diagnosed with stage 4 prostate cancer*. There is now a much broader range of chemotherapy drugs available for men with advanced disease with greater efficacy . We also have better treatments to control the symptoms of advanced prostate cancer, such as pain from metastases. In this section, we consider in more detail the different treatments that are available and evidence for their effectiveness.
Read Also: How Often Should You Be Tested For Prostate Cancer
Bone Pain In Prostate Cancer
Many advanced prostate cancer patients often suffer from bone pain that adversely affect quality of life. The management of pain or other cancer related functional impairment is integral part of palliative care. Palliative management can include analgesics, glucocorticoids, palliative chemotherapy, radioisotopes or radiotherapy.
Radioisotopes that selectively concentrate in bone lesions are approved for the palliative treatment of painful bone metastases. The treatment is of more value in patients with multiple metastases . The radioisotopes have been found to reduce the need for opioid painkillers in such patients.
EBRT is effective in painful bone lesions in advanced prostate cancer patients but not an ideal option if there are multiple lesions at different sites. The lesions in multiple sites will progress after EBRT in one site and pain will reappear in a short time afterwards, unless other systemic therapies are initiated to control the disease process. Read more on EBRT under prostate cancer treatments.
Dont Miss:
How The Study Was Performed
During the study, scientists randomized 1,071 men with intermediate- or high-risk localized prostate cancer into four groups. One group received radiation and six months of an anti-testosterone drug called leuporelin, and the second group received radiation plus 18 months of leuporelin therapy. Two other groups were treated with the same regimens of either radiation plus six or 18 months of leuporelin therapy, along with another drug called zoledronic acid, which helps to limit skeletal pain and related complications should cancer spread to the bones. Study enrollment occurred between 2003 and 2007 at 23 treatment centers across New Zealand and Australia.
Donât Miss: How Early Can You Get Prostate Cancer
Read Also: How To Perform Prostate Massage
What You Can Do
Its important that you learn all you can about advanced prostate cancer so you can make informed decisions. Be open with your doctors and others on your healthcare team. Express your concerns and feel free to advocate for yourself and your quality of life. Get another medical opinion if you feel its necessary.
Some complementary therapies may prove helpful in coping with advanced cancer. For example:
- tai chi, yoga, or other movement therapy
- meditation, breathing exercises, or other relaxation techniques
A variety of services can help you with everything from lodging while youre getting treatment to getting some help around the house. Communicating with online or in-person groups are a good way to share information and lend mutual support.
Staging Of Prostate Cancer
- Stage I : The Gleason score is 6 or less, and the PSA level is less than 10. Cancer at this stage is normally not detectable in an ultrasound test or in a DRE test, as the tumor is very small. It is within the prostate and has not spread to nearby lymph nodes. It is usually discovered accidentally during a surgery carried out for another purpose. Prostate ultrasound and biopsy can be performed after detection of elevated blood PSA levels.
- Stage II : From this stage onwards, the Gleason score and the PSA level may vary from person to person. As the tumor grows in size, it can be detected in a DRE test or sonogram, but the tumor is still confined to the prostate gland. It is in one half or less of only one side of the prostate. It hasnt spread to lymph nodes and nearby organs, or it has spread to nearby lymph nodes, but has not invaded nearby organs.
- Stage III : The cancerous cells spread out from the original site and invade the seminal vesicles. They do not spread to nearby lymph nodes or to nearby organs in the body.
- Stage IV : The cancer moves out of the seminal vesicles and invades the lymph nodes. The size and number of tumors increase, and the cancerous cells spread into the nearby organs, such as the bladder and the rectum. In stage four prostate cancer, even bones and other parts of the body like lungs and liver are likely to be invaded by the cancerous cells.
Don’t Miss: If You Have Your Prostate Removed Can You Still Ejaculate
Common Questions About Stage 4 Mesothelioma
- Is mesothelioma terminal?
-
Mesothelioma is a terminal cancer. While many patients go into remission, especially with treatment, there is no cure for mesothelioma. Life expectancy with advanced-stage mesothelioma cancer depends largely on the extent of tumor growth and how well you respond to treatments.
- Can stage 4 mesothelioma be treated?
-
Yes, stage 4 mesothelioma is primarily treated with chemotherapy and palliative care. Chemotherapy can alleviate symptoms and extend survival. Palliative care helps patients cope with pain and other symptoms, improving their quality of life.
- What is the life expectancy of someone with late-stage mesothelioma?
-
The life expectancy of stage 4 mesothelioma is about one year with treatment. Electing chemotherapy can extend the survival of those with mesothelioma by several months. Without treatment, people with late-stage mesothelioma live an average of six to eight months.
- Are there any survivors of stage 4 mesothelioma?
-
Many survivors have lived a long time with stage 4 mesothelioma. For example, Andy Ashcraft lived with stage 4 mesothelioma for more than seven years. His treatment included chemotherapy, immunotherapy and medical marijuana.
Get the Compensation You Deserve
What Is Advanced Prostate Cancer
When prostate cancer spreads beyond the prostate or returns after treatment, it is often called advanced prostate cancer.
Prostate cancer is often grouped into four stages, with stages III and IV being more advanced prostate cancer.
- Early Stage | Stages I & II: The tumor has not spread beyond the prostate.
- Locally Advanced | Stage III: Cancer has spread outside the prostate but only to nearby tissues.
- Advanced | Stage IV: Cancer has spread outside the prostate to other parts such as the lymph nodes, bones, liver or lungs.
When an early stage prostate cancer is found, it may be treated or placed on surveillance . Advanced prostate cancer is not curable, but there are many ways to treat it. Treatment can help slow advanced prostate cancer progression.
There are several types of advanced prostate cancer, including:
Biochemical Recurrence
With biochemical recurrence, the prostate-specific antigen level has risen after treatment using surgery or radiation, with no other sign of cancer.
Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer
Non-Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer that no longer responds to hormone treatment and is only found in the prostate. This is found by a rise in the PSA level, while the testosterone level stays low. Imaging tests do not show signs the cancer has spread.
Metastatic Prostate Cancer
- Lymph nodes outside the pelvis
- Other organs, such as liver or lungs
Metastatic Hormone-Sensitive Prostate Cancer
Recommended Reading: Can Prostate Cancer Spread To Lymph Nodes
What Is Localized Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is the abnormal growth of cells in the prostate gland. Localized prostate cancer has not spread outside the gland. Early prostate cancer usually doesnât cause symptoms.
Prostate cancer is the most common cancer in men. Most men who get it are older than 65. If your father, brother, or son has had prostate cancer, your risk is higher than average.
Men of African descent have the highest rates of both prostate cancer and deaths from it.
About 21,000 men are diagnosed with prostate cancer in Canada every year.footnote 1 In the United States, about 12 out of 100 men in the U.S. will be diagnosed with prostate cancer sometime in their lifetime.footnote 2 But most men who are diagnosed with prostate cancer donât die from prostate cancer.
Unlike many other cancers, prostate cancer is usually slow-growing. When prostate cancer is found earlybefore it has spread outside the glandit may be cured with radiation or surgery.
Prostate cancer that has grown beyond the prostate is called advanced prostate cancer. Treatment choices are different for that stage of cancer.
How Is Prostate Cancer Diagnosed
Doctors describe the growth and spread of prostate cancer in stages. Doctors use these stages as guides when choosing treatment options or offering prognoses to their patients.
Prostate cancer staging is based on a number of different factors, including prostate cancer screening tests such as a digital rectal exam or prostate-specific antigen test and imaging studies like bones scans, MRIs, CT scans, and trans-rectal ultrasounds.
You May Like: What Happens When You Get Your Prostate Removed
Stage 4 Prostate Cancer: Survival Rates Treatment And Support
Prostate cancer is in stage 4 when the cancer spreads beyond the lymph nodes and into other areas of the body. While the vast majority of prostate cancer cases are caught before this happens, when the cancer is treatable, stage 4 is far more difficult to treat. Therefore, the survival rate among men with stage 4 prostate cancer is much lower.
There are two types of stage 4 prostate cancer: 4A and 4B, according to the American Cancer Society. The type assigned to a persons diagnosis is based on whether the cancer has spread and to what degree, and the value assigned to two additional factors called the Grade Group and the prostate-specific antigen . The Grade Group is a measure of how likely the cancer is to spread quickly, and the PSA is a measure of a protein in the blood produced by cells in the prostate.
With stage 4A, the tumor has already spread into the lymph nodes and may be spreading into tissues adjacent to the prostate, but has not spread to other areas of the body. The Grade Group can be of any value, as can the PSA.
With stage 4B, the tumor may have spread into the lymph nodes, may be spreading into nearby tissues and has spread to other areas of the body like the bones, certain organs and distant lymph nodes. The Grade Group and PSA can be of any value.
Castrate Refractory Prostate Cancer: A Wider Range Of Options
In this section, we explain the treatments available at Birmingham Prostate Clinic for patients once their disease becomes resistant to hormone treatment, called castrate refractory prostate cancer. Two types of treatments are needed to:
- Control the cancer and preventing further spread of cancer
- Control or prevent the symptoms caused by the spread of prostate cancer to the bones
Also Check: Prostate Mri Without Endorectal Coil
Don’t Miss: How To Reach Prostate From Outside
Staging And Grading Of Advanced Prostate Cancer
The stage of a cancer describes its size and how far it has spread, based on your test results. Doctors often use the TNM staging system or a number staging system.
A doctor decides the grade by how the cancer cells look under the microscope. This gives an idea of how quickly the cancer might grow or spread. You and your doctors can then talk about the best treatment choices for you.
Treating Advanced Prostate Cancer
If the cancer has reached an advanced stage, it’s no longer possible to cure it. But it may be possible to slow its progression, prolong your life and relieve symptoms.
Treatment options include:
- hormone treatment
If the cancer has spread to your bones, medicines called bisphosphonates may be used. Bisphosphonates help reduce bone pain and bone loss.
Also Check: Can You Still Have An Erection After Prostate Removal
The Stages Of Prostate Cancer: What You Need To Know
After a prostate cancer diagnosis, your oncologist will refer to the stage of your cancer. All cancers are categorized into four distinct stages, each of which identifies the progress of the growth of cancerous cells within clinically defined standards. These stages help doctors determine the most appropriate care for each patient based on his or her condition, and can also provide easy-to-understand context for your diagnosis. Learn more about the stages of prostate cancer, how each stage will affect your treatment plan and the survival rates for each stage, then contact Regional Cancer Care Associates to schedule a consultation.
Donât Miss: Average Recovery Time For Prostate Removal
What Else Do You Need To Make Your Decision
Check the facts
- Sorry, thatâs not right. One treatment may be better for you than the other because of how long you might live , your other health problems, and how you feel about each treatment. You and your doctor can talk about what is better for you.
- Youâre right. One treatment may be better for you than the other because of how long you might live , your other health problems, and how you feel about each treatment. You and your doctor can talk about what is better for you.
- It may help to go back and read âGet the Facts.â One treatment may be better for you than the other because of how long you might live , your other health problems, and how you feel about each treatment. You and your doctor can talk about what is better for you.
- Thatâs right. The chances of side effects from surgery are lower if your doctor has done a lot of these surgeries.
- Thatâs not right. The chances of side effects from surgery are lower if your doctor has done a lot of these surgeries.
- It may help to go back and read âGet the Facts.â The chances of side effects from surgery are lower if your doctor has done a lot of these surgeries.
How sure do you feel right now about your decision?
Use the following space to list questions, concerns, and next steps.
Recommended Reading: What Does It Mean When Your Prostate Is Enlarged
You May Like: What Are Signs Of Prostate Problems
Stage 2 Prostate Cancer
In stage 2, the tumor is still confined to your prostate and hasnt spread to lymph nodes or other parts of your body. A doctor may or may not be able to feel the tumor during a prostate exam, and it may appear on ultrasound imaging. The survival rate is still .
The PSA score for stage 2 is less than 20 ng/mL.
Stage 2 cancer is further divided into three phases depending on the grade group and Gleason scores:
- Gleason score: 6 or less
Does Overdiagnosis Lead To Overtreatment Of Older Men
The widespread use of PSA screening has led to an increase in the diagnosis and treatment of early localized prostate cancer. Data from the US Cancer of the Prostate Strategic Urological Research Endeavor database suggest a significant decrease in risk in the last 2 decades in the United States, with more patients being identified with low-risk disease at diagnosis, but the role of active treatment of low- and intermediate-risk disease in elderly men remains controversial.
The median time from diagnosis to death from prostate cancer for men with nonpalpable disease is approximately 17 years., Considering that the US male life expectancy at the age of 65 years is 16 years, aggressive therapy will hardly extend life expectancy of older men with no palpable prostate cancer at the time of diagnosis. Twenty to 30% of prostate cancers detected by PSA screening programs show Gleason scores of 6 or lower and, thus, are not poorly differentiated and have volumes smaller than 0.5 cm3.
Histologic evaluation of radical prostatectomy specimens demonstrated that about 20% to 30% of cancers are small volume, show low Gleason scores, and are consequently clinically harmless., Many of these cancers pose little threat to life, especially for older men. Has PSA screening resulted in prostate cancer overdiagnosis?
Also Check: Is Radiation For Prostate Cancer Safe
