Stage 2 Prostate Cancer
In stage 2, cancer can be detected during a digital rectal exam . Its still confined to the prostate, but the cells may be more abnormal and may grow faster.
- Stage IIA The tumor may involve more than one half of one lobe or even both lobes of the prostate but it is still organ-confined . There is no regional lymph node metastasis and no distant metastasis. . The PSA level is 10-20 ng/ml. The Grade Group is 1.
- Stage IIB The tumor may involve both lobes of the prostate or less than that . There is no regional lymph node metastasis and no distant metastasis. . The PSA level is below 20 ng/ml. The Grade Group is 2.
- Stage IIC The tumor may involve both lobes of the prostate or less than that . There is no regional lymph node metastasis and no distant metastasis. . The PSA level is below 20 ng/ml. The Grade Group is 3-4.
Dont Miss: Prostate Over The Counter Drugs
Stage I Prostate Cancer Treatment
In This Section
Vascular-targeted photodynamic therapy using a photosensitizing agent has been tested in men with low-risk prostate cancer. In the CLIN1001 PCM301 randomized trial, 413 men with low-risk cancer were randomly assigned in an open-label trial to receive either the photosensitizing agent, padeliporfin , or active surveillance. Median time to local disease progression was 28.3 months for patients receiving padeliporfin and 14.1 months for patients who were assigned to active surveillance . However, the appropriate population for photodynamic therapy may be quite narrow, as it may overtreat men with very low-risk disease and undertreat men with higher-risk disease.
Prognosis Of Men With High
Pan Song1#, Jiaxiang Wang2#, Mengxuan Shu2, Xiaoyu Di3, Yaxin Li3, Yuxin Qing3, Qiang Dong1
1 West China Hospital of Sichuan University , The First Clinical Medical College , The Second Clinical Medical College , , China
Contributions: Conception and design: Q Dong Administrative support: Q Dong Provision of study materials or patients: P Song, J Wang Collection and assembly of data: P Song, J Wang Data analysis and interpretation: P Song, J Wang, M Shu, X Di, Y Li, Y Qing Manuscript writing: All authors Final approval of manuscript: All authors.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Correspondence to:
Background: The aim was to evaluate the prognosis of men with all possible high-risk prostate cancers stratified by risk factors.
Methods: Within the Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results database from 2004 to 2015, men with non-metastasis high-risk PCa were identified. Kaplan-Meier analysis and Cox regressions were adopted to evaluate the overall survival and prostate cancer-specific survival . Nomograms were conducted to build a predictive model. Concordance index and calibration curves were used to validate the model.
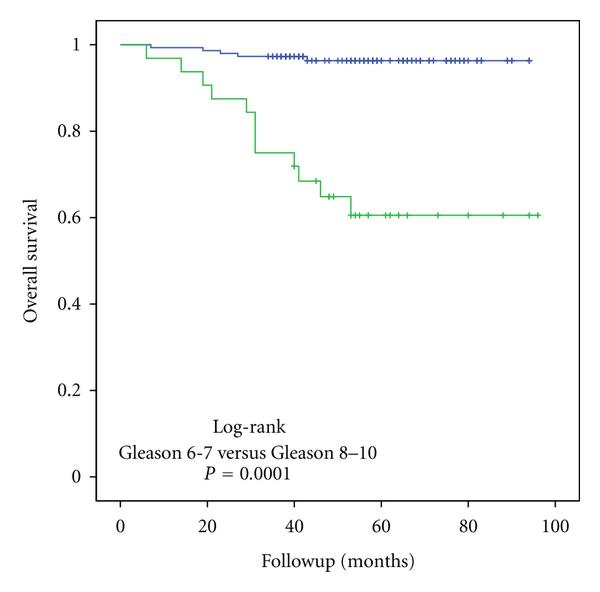
Men with the combination of PSA > 20 ng/mL and GS 810 had the worst PCSS among all patients. PCa with three high-risk factors was not more aggressive than that with two high-risk factors of GS 810 and PSA > 20 ng/mL.
Keywords: Prostate cancer high-risk factors prognosis Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results
Also Check: Are You Sedated For A Prostate Biopsy
There Are 2 Types Of Staging For Prostate Cancer:
The Clinical Stage The clinical stage is based on the results of tests that can be done prior to the surgery. They include the DRE, biopsy, X-rays, CT and/or MRI scans and bone scans. X-rays, bone scans, CT scans and MRI scans may not always be needed. They are recommended based on the PSA level, the size of the cancer, which is determined by its grade and volume and the clinical stage of the cancer.
The Pathologic Stage The pathologic stage is based on information found during surgery, plus the laboratory results referred to as pathology, of the prostate tissue removed during surgery. The surgery often includes the removal of the entire prostate and some lymph nodes.One important part of the staging process is determining the grade of the cancer. The grading system is based on the microanalysis of the prostatic tissue. While the stage of the cancer is determined based on the macro appearance of the tumor, in connection with the nearby organs and tissues, the grade of cancer is usually determined after a biopsy, when the cells are analyzed under a microscope.
Using Survival Rate Statistics
Survival rate statistics can help you and your doctor understand your prognosis and develop a treatment plan, but they cannot precisely predict your survival or tell you which treatments to use.
Your individual prognosis will be affected by many factors, including:
- the type, stage, and grade of prostate cancer when diagnosed
- your response to treatment method being used
Statistics are estimates only and your outcome may be better or worse than the overall survival rate. The overall survival rate does not take into account the stage of the prostate cancer when diagnosed, does not tell you whether the cancer survivors were in remission , progression-free , or still undergoing treatment.
Survival rates cannot tell you which treatments to use or give you information about the newest treatments. The latest prostate cancer statistics are usually based on the information of patients who were diagnosed more than five years ago and the outcomes do not reflect the results seen with the most recent treatments.
Read Also: If You Get Your Prostate Removed Can You Still Ejaculate
Detecting Prostate Cancer Early
Thanks to advances in screening options for prostate cancer, it is very possible to detect this cancer early to improve a patients outlook. Prostate cancer screening is recommended for men ages 50 to 70, as well as younger men with risk factors, such as obesity or a family history of prostate cancer. The screening process typically involves a digital rectal examination , in which a physician inserts a gloved finger into the rectum, and a blood test called the prostate-specific antigen .
PSA is a protein produced by prostate tissue cancerous cells emit more PSA than noncancerous cells. Therefore, an elevated PSA level in a blood test may indicate prostate cancer. However, this screening test is not infallible, as there are other, less-serious reasons for an elevated PSA level, such as prostate inflammation, a urinary tract infection, benign prostatic hyperplasia or even the natural aging process. A physician will take other factors into account when evaluating a patients PSA levels and will recommend a biopsy if they suspect prostate cancer may be the cause.
Prostate Cancer Survival Rates Are Favorable Overall
Thinking about survival rates for prostate cancer takes a little mental stretching. Keep in mind that most men are around 70 when diagnosed with prostate cancer. Over, say, five years, many of these men will die from other medical problems unrelated to prostate cancer.
To determine the prostate cancer survival rate, these men are subtracted out of the calculations. Counting only the men who are left provides whats called the relative survival rate for prostate cancer.
Taking that into consideration, the relative survival rates for most kinds of prostate cancer are actually pretty good. Remember, were not counting men with prostate cancer who die of other causes:
- 92% of all prostate cancers are found when they are in the early stage, called local or regional. Almost 100% of men who have local or regional prostate cancer will survive more than five years after diagnosis.
- Fewer men have more advanced prostate cancer at the time of diagnosis. Once prostate cancer has spread beyond the prostate, survival rates fall. For men with distant spread of prostate cancer, about one-third will survive for five years after diagnosis.
Many men with prostate cancer actually will live much longer than five years after diagnosis. What about longer-term survival rates? According to the American Society of Clinical Oncology, for men with local or regional prostate cancer:
- the relative 10-year survival rate is 98%
- the relative 15-year survival rate is 95%
Also Check: What Is Your Prostate For
Outlook For Men With Localised Prostate Cancer
Most localised prostate cancer is slow-growing and may not need treatment or shorten a mans life. For many men who have treatment for localised prostate cancer, the treatment will get rid of the cancer. For others, treatment may be less successful and the cancer may come back. If this happens, you might need further treatment.
Also Check: What Are The Effects Of Having A Prostate Removed
Radiation Therapy And Androgen Deprivation Therapy
A recent publication demonstrates an increasing trend of under treatment of high-risk prostate cancer, with many high-risk patients receiving ADT alone rather than curative treatment consisting of radiotherapy or radical prostatectomy.3 A Scandinavian randomised phase III trial, SPCG-7/SFUO-3 , showed that the addition of radiotherapy to total androgen blockade improved rates of survival and disease-free survival for high-risk patients .35 The National Cancer Institute of Canada and the United Kingdom Medical Research Council together randomized 1,057 patients with high-risk prostate cancer receiving lifelong ADT to pelvic radiotherapy or no further treatment . Similar to the results of the SPCG-7/SFUO-3 study, the addition of radiotherapy improved overall survival and prostate cancerspecific survival .36 This corresponds to very favorable number-needed-to-treat to prevent one prostate cancerspecific death .
Don’t Miss: How Many Stages Of Prostate Cancer Are There
Moffitt Cancer Centers Approach To Prostate Cancer Treatment
No matter the stage of your cancer, Moffitt Cancer Center can help you improve your prognosis and quality of life. Not only do we have a dedicated Genitourinary Oncology Program staffed by surgeons, medical oncologists, radiation oncologists and other support professionals who specialize in treating prostate cancer, but we also create individualized treatment plans for each of our patients. Our multispecialty team comes together in regular tumor board meetings to evaluate a number of different factors that can all affect a patients outcomeincluding the size, grade and location of tumors, along with any other treatments previously attemptedto develop the best possible plan for the patients unique situation.
At Moffitt, we welcome patients who have already received treatment elsewhere, as well as patients who are exploring their options for the very first time. Call , or submit a new patient registration form online a member of our team will tell you more about Moffitts prostate cancer survival rate and discuss your treatment options. We provide every new patient with rapid access to a cancer expert within a day, which is faster than any other cancer hospital in the nation.
Medically reviewed by Monica Chatwal, MD, medical oncologist, Genitourinary Oncology Program.
Stage Iv Prostate Cancer Prognosis
Prostate cancers detected at the distant stage have an average five-year survival rate of 28 percent, which is much lower than local and regional cancers of the prostate. This average survival rate represents stage IV prostate cancers that have metastasized beyond nearby areas to lymph nodes, organs or bones in other parts of the body.
Also Check: Does Prostate Cancer Treatment Make You Impotent
Hormonal Therapy And Its Complications
Several different hormonal approaches are used in the management of various stages of prostate cancer.
These approaches include the following:
- Abiraterone acetate .
- Aminoglutethimide.
Abiraterone acetate
Abiraterone acetate has been shown to improve OS when added to ADT in men with advanced prostate cancer who have castration-sensitive disease. Abiraterone acetate is generally well-tolerated however, it is associated with an increase in the mineralocorticoid effects of grade 3 or 4 hypertension and hypokalemia compared with ADT alone. It may also be associated with a small increase in respiratory disorders.
Bilateral orchiectomy
Benefits of bilateral orchiectomy include the following:
- Ease of the procedure.
- Immediacy in lowering testosterone levels.
- Low cost relative to the other forms of ADT.
Disadvantages of bilateral orchiectomy include the following:
- Psychological effects.
Bilateral orchiectomy has also been associated with an elevated risk of coronary heart disease and myocardial infarction.
Estrogen therapy
Estrogens at a dose of 3 mg qd ofdiethylstilbestrol will achieve castrate levels of testosterone. Likeorchiectomy, estrogens may cause loss of libido and impotence. Estrogens also cause gynecomastia, and prophylactic low-dose radiation therapy to the breasts is given to prevent this complication.
Luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone agonist therapy
Evidence :
Antiandrogen therapy
ADT
Evidence :
Antiadrenal therapy
Survival Rates For Prostate Cancer

Survival rates can give you an idea of what percentage of people with the same type and stage of cancer are still alive a certain amount of time after they were diagnosed. These rates cant tell you how long you will live, but they may help give you a better understanding of how likely it is that your treatment will be successful.
Keep in mind that survival rates are estimates and are often based on previous outcomes of large numbers of people who had a specific cancer, but they cant predict what will happen in any particular persons case. These statistics can be confusing and may lead you to have more questions. Ask your doctor, who is familiar with your situation, how these numbers may apply to you.
Read Also: How Much Does A Prostate Weigh
Stage 3 Prostate Cancer
In stage 3, cancer has now spread beyond the prostate and may have potentially spread into the nearby seminal vesicles.
- Stage IIIA The tumor may involve both lobes of the prostate or less than that . There is no regional lymph node metastasis and no distant metastasis. . The PSA level is below or equal to 20 ng/ml. The Grade Group is 1-4.
- Stage IIIB The tumor extended through the prostatic capsule to the seminal vesicles or the adjacent structures, such as the bladder, muscles or the pelvic floor . There is no regional lymph node metastasis and no distant metastasis. . There can be any PSA level. The Grade Group is 1-4.
- Stage IIIC The tumor may or may not be extended through the prostatic capsule but has not spread to the regional lymph nodes or to other distant areas . There can be any PSA level. The Grade Group is 5.
Radiation Therapy And Radiopharmaceutical Therapy
External-beam radiation therapy
Candidates for definitive radiation therapy must have a confirmed pathologic diagnosis of cancer that is clinically confined to the prostate and/or surrounding tissues . Staging laparotomy and lymph node dissection are not required.
Radiation therapy may be a good option for patients who are considered poor medical candidates for radical prostatectomy. These patients can be treated with an acceptably low complication rate if care is given to the delivery technique.
Long-term results with radiation therapy are dependent on stage and are associated with dosimetry of the radiation.
Evidence :
Evidence :
Brachytherapy
Don’t Miss: Can Prostate Cancer Cause Anemia
Learn More About Prostate Cancer Care At Rcca
If youve been diagnosed with prostate cancer or are concerned about potential symptoms, contact RCCA today. Our team of cancer care specialists will assess the stage of your cancer using the latest diagnostic methods and work with you to design a fully individualized care plan that includes advanced treatment options, the potential for clinical trials, and support that addresses physical and emotional well-being. To speak with a representative right away, please call .
Recommended Reading: Can Teenagers Get Prostate Cancer
What Is My Outlook
Many men will want to know how successful their treatment is likely to be. This is sometimes called your outlook or prognosis. No one can tell you exactly what will happen, as it will depend on many things, such as the stage of your cancer and how quickly it might grow, your age, and any other health problems.
Many men with locally advanced prostate cancer have treatment that aims to get rid of their cancer. For some men, treatment may be successful and they may live for many years without their cancer coming back or causing them any problems. For others, treatment may be less successful and the cancer may come back. If this happens, you might need further treatment.
Some men with locally advanced prostate cancer will have treatment that aims to help keep their cancer under control rather than get rid of it completely. For example, if you have hormone therapy on its own, it can help to keep the cancer under control. And there are other treatments available if your hormone therapy stops working so well.
For more information about the outlook for men with prostate cancer, visit Cancer Research UK. The figures they provide are a general guide and they cannot tell you exactly what will happen to you. Speak to your doctor or nurse about your own situation.
Recommended Reading: Do All Mammals Have Prostates
Data Acquisition And Definitions
RPs were conducted by several surgeons using open, laparoscopic, or robotic modality. All pathological specimens were evaluated by a staff pathologist with genitourinary expertise. The following variables were compared between the categorical groups: age body mass index pre-biopsy prostate-specific antigen level pathologic Gleason score pathologic characteristics including extracapsular extension , positive surgical margin , and lymph node invasion radiologic findings, including ECE and lymph node enlargement and BCR. BCR was defined as two consecutive rises in PSA, with the last PSA 0.2ng/ml or higher after the RP.
by University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center
Prostate cancer is the leading cause of cancer in men worldwide, and radiotherapy is one of the common forms of treatment. In a first-of-its kind meta-analysis, published today in The Lancet Oncology, researchers from University Hospitals and Case Western Reserve University show that there is consistent improvement in overall survival in men with intermediate- and high-risk prostate cancer with the addition of hormone therapy to radiotherapy treatments.
Throughout the past 40 years, randomized trials have been conducted on the impact of adding hormone therapy to prostate cancer treatments. While these trials individually show the benefit of hormone therapy, there are inconsistencies in timing and duration of treatment recommendations.
In this analysis, the team made three key discoveries:
Explore further
