Turp / Greenlight Pvp Laser / Thermotherapy
Transurethral resection of the prostate has long been the mainstay of enlarged prostate surgery, but less invasive alternatives are now available, with the potential for equal results. With TURP, the obstructing portion of the enlarged prostate tissue is removed. Although effective, TURP requires hospitalization and catheterization for 48 hours or more and comes with risks associated with anesthesia bleeding during and after the operation and, in rare cases, fluid absorption that can be life-threatening.
Prostate LaserOne alternative that has emerged is laser enlarged prostate surgery. Like TURP, the so-called GreenLight PVP Laser Therapy aims to create a channel in the urethra through which men can urinate more freely but the surgery is considerably less invasive. Instead of cutting tissue out, the newer technique creates the channel by vaporizing the tissue using laser energy. Thus far, almost every study has shown that when done by experienced urologists, the laser enlarged prostate surgery produces results that are equal to those with TURP, but without the severe side effects and risks. It is an outpatient procedure with minimal to no bleeding, no risk of fluid absorption, and catheterization only overnight, if at all.
Where To Get Treatment For Ed In Nyc
At New York Urology Specialists, we offer specialized treatment for ED for men. Same-day appointments are available.
or make an appointment online.
We treat sexual and erection problems and offer for infections. We treat penile problems in men, including phimosis, balanitis, penile irritation, and penile redness. We perform a no-scalpel vasectomy, vasectomy reversal, , , penile frenuloplasty. We offer confidential appointments.
Our prices are ED treatment prices are affordable with or without insurance. Low-cost Viagra and Cialis are available to our patients. We offer free insurance verification.
Symptoms Of Urinary Problems
Urinary symptoms commonly experienced with prostate problems include:
- the need to urinate frequently during the night
- urinating more often during the day
- urinary urgency the urge to urinate can be so strong and sudden that you may not reach the toilet in time
- the urine stream is slow to start
- urine dribbling for some time after finishing urination
- a sensation that the bladder isn’t fully emptied after urination
- lack of force to the urine flow, which makes directing the stream difficult
- the sensation of needing to go again soon after urinating.
Although these symptoms often do not need treatment, see your doctor if they are causing you difficulty, as they can be successfully treated.
You May Like: Is Black Pepper Bad For Prostate
Can Prostate Massage Really Help An Enlarged Prostate
Prostate milking, or prostate massage, has the ability to give men intense relief from prostate problems. The prostate, or the prostate gland is a major organ in the male reproductive system.
The primary function of this gland is to produce prostatic fluid. This is the fluid that helps the sperm survive after ejaculation.
Unfortunately, factors like aging and a poor lifestyle can make the prostate weak. This results in an impairment in urinary function, sexual function and prostate inflammation.
> > > Prostate Massage for Optimal Prostate Health
However, by massaging the prostate on a regular basis, blood flow increases in the area. The pain that is related to an inflamed prostate as well as discomfort in the area diminishes.
It is important to know that prostate massage is not a new practice. It is a treatment that has been utilized for thousands of years in Asian culture, and it is still a treatment that is used today.
In fact, many men have reported feeling much better after one prostate massage session.
Additional Types Of Therapy For Prostate Cancer
A few other treatments exist for advanced prostate cancer or prostate cancer that has stopped responding well to other forms of hormone therapy. They are usually taken with one of the therapies discussed above.
Chemotherapy. For cases of very aggressive prostate cancer, or when hormone therapy isnât effective, your doctor may recommend chemotherapy. This class of anti-cancer drug, taken by mouth or injected, fights cancers that have spread beyond the prostate to other parts of your body. The schedule of your treatment will depend on the specific drugs you require, but chemotherapy is typically given in cycles that last two to three weeks. Once you finish a cycle, the next cycle begins. The length of your treatment hinges on how well it works and whether you can cope with the side effects. Chemotherapy drugs are used to help you live longer. They rarely cure prostate cancer, according to the ACS, and can cause unpleasant side effects, including hair loss, nausea, and fatigue.
Immunotherapy. This type of treatment harnesses the power of your immune system to fight cancer. While it has been used successfully in several types of cancer, it hasnt proved as effective in prostate canceryet. Researchers are working to discover the best ways to incorporate immune therapy into prostate cancer care, particularly for men whose cancer no longer responds to hormone treatment. In 2019, more than 100 such studies were underway.
Read Also: Erleada For Metastatic Prostate Cancer
You May Like: How To Reduce The Size Of The Prostate Naturally
Health Effects Of Prostate Enlargement
BPH is not associated with an increased risk of prostate cancer4.
While BPH may not directly threaten your health, its symptoms can have a significant effect on your wellbeing. The urinary symptoms of BPH can be inconvenient, limit daily activities, and cause considerable stress and anxiety.
The impact of lower urinary tract symptoms from BPH on mens quality of life is comparable to the effect of asthma5.
Since the prostate continues to grow as men age6, the symptoms of BPH may become more severe over time7, but sometimes symptoms stabilise or even improve over time.
Complications that can arise from BPH include:
- Urinary retention
Treating BPH can prevent these complications.
Latest Men’s Health News
At the start, prostate cancer does not cause symptoms. As the cancer grows, you may have trouble urinating. Some men need to urinate often, especially at night. Others have pain or burning during urination, blood in the urine or semen, pain in the back, hips, or pelvis, and painful ejaculation.
To find out if these symptoms are caused by prostate cancer, your doctor will ask about your past medical problems and your family’s medical history. He or she will perform a physical exam. During the exam, your doctor will put a gloved finger into your rectum to feel your prostate for hard or lumpy areas.
Your doctor may also do a blood test to check the prostate-specific antigen level. PSA levels can be high in men with an enlarged prostate gland or with prostate cancer. You may also need an ultrasound exam that takes computer pictures of the prostate.
If tests show that you might have cancer, your doctor will want to confirm this with a biopsy. He or she will take out tiny pieces of the prostate to look for cancer cells. Your doctor may want to do a biopsy again to re-check the results.
Treatment for prostate cancer depends on whether cancer is in part or all of the prostate or if it has spread to other parts of the body. It also depends on your age and overall health. Talk with your doctor about the best treatment choice for you. You may want to ask another doctor for a second opinion.
You May Like: Can Prostatitis Cause Elevated Psa Levels
> > > One Crazy Prostate Trick All Men Over 40 Should Try
Symptomatic treatment of an enlarged prostate usually involves a combination of medication and lifestyle changes. A diet rich in fruits and vegetables may be the best option if you suffer from chronic urination. It will help the body adjust to the increased size of the prostate. Also, taking regular urination intervals will help retrain the bladder to function properly. Inactivity also contributes to urine retention, and cold temperatures can increase the urge to urinate.
Invasive treatment of enlarged prostate includes medication that relieves the pressure on the urethra and bladder. However, if the condition is severe, it may require surgical intervention. If treatment is not successful, the enlarged prostate can become a potentially life-threatening disease. As the hormone levels in the body change, the enlarged prostate can lead to various complications, including urinary retention and even cancer. This is why it is critical to see a doctor for further evaluation.
A physician can recommend a number of treatments to address an enlarged prostate. An enlarged prostate will require surgery to relieve the symptoms. In most cases, surgical treatment for an enlargement of the penis is enough. Moreover, a doctor may recommend a course of treatment based on symptoms. A TURP procedure is not painful and requires less recovery time than open surgery. The recovery period will be shorter and less traumatic.
The 4 Causes Of An Enlarged Prostate
It is normal for a prostate to become enlarged as a man ages. The prostate is approximately the size of a walnut in younger men but can grow to be much larger as they get older. An enlarged prostate can cause no visible symptoms but will eventually impact urinary and erectile functions if not properly treated.
There are many reasons a prostate gets enlarged, and most of them arent cancerous. Here are the most common:
Read Also: What Does Prostate Cancer Do
Causes Of Prostate Enlargement
Men are more likely to have BPH as they age and if they have metabolic syndrome, diabetes, high blood pressure, obesity, or a diet thats low in fruit, vegetables and legumes1.
There is a genetic component to BPH, so some men inherit an increased risk of prostate enlargement2.
Testosterone stimulates cell division in the gland, causing prostate growth. Molecules involved in inflammation can also stimulate prostate gland cell division1.
When Is Bph Treatment Necessary
The course of BPH in any individual is not predictable. Symptoms, as well as objective measurements of urethral obstruction, can remain stable for many years and may even improve over time for as many as one-third of men, according to some studies. In a study from the Mayo Clinic, urinary symptoms did not worsen over a 3.5-year period in 73% of men with mild BPH. A progressive decrease in the size and force of the urinary stream and the feeling of incomplete bladder emptying are the symptoms most correlated with the eventual need for treatment. Although nocturia is one of the most annoying BPH symptoms, it does not predict the need for future intervention.
If worsening urethral obstruction is left untreated, possible complications are a thickened, irritable bladder with reduced capacity for urine infected residual urine or bladder stones and a backup of pressure that damages the kidneys.
- Inadequate bladder emptying resulting in damage to the kidneys
- Complete inability to urinate after acute urinary retention
- Incontinence due to overfilling or increased sensitivity of the bladder
- Bladder stones
- Recurrent severe hematuria
- Symptoms that trouble the patient enough to diminish his quality of life
Read Also: What Happens To The Prostate Later In Life
Possible Cancer Protection From Prostate Drugs
Early research suggested that 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors , a class of drugs used to treat prostate enlargement, might increase the risk of developing more aggressive prostate cancer. However, newer studies have found that not only do the drugs appear to pose no extra risk, they may even protect against prostate cancer.
For instance, research from the Prostate Cancer Prevention Trial study in 2013 showed that taking the 5-ARI finasteride for seven years could lower the chance of getting low-grade prostate cancer by 25% among men ages 55 and older. A follow-up study of almost 9,500 men, published in the Nov. 1, 2018, issue of the Journal of the National Cancer Institute, also showed that finasteride lowered the risk by a similar amount , and found the protective effect lasted for at least 16 years.
Symptoms Of Prostate Cancer
- Frequent urge to pass urine, especially at night
- Weak or interrupted urine stream
- Pain or burning when passing urine
- Blood in the urine or semen
- Painful ejaculation
- Nagging pain in the back, hips, or pelvis
Prostate cancer can spread to the lymph nodes of the pelvis. Or it may spread throughout the body. It tends to spread to the bones. So bone pain, especially in the back, can be a symptom of advanced prostate cancer.
Read Also: Can You Detect Prostate Cancer With A Blood Test
How Common Is Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Benign prostatic hyperplasia is the most common prostate problem for men older than age 50. In 2010, as many as 14 million men in the United States had lower urinary tract symptoms suggestive of benign prostatic hyperplasia.1 Although benign prostatic hyperplasia rarely causes symptoms before age 40, the occurrence and symptoms increase with age. Benign prostatic hyperplasia affects about 50 percent of men between the ages of 51 and 60 and up to 90 percent of men older than 80.2
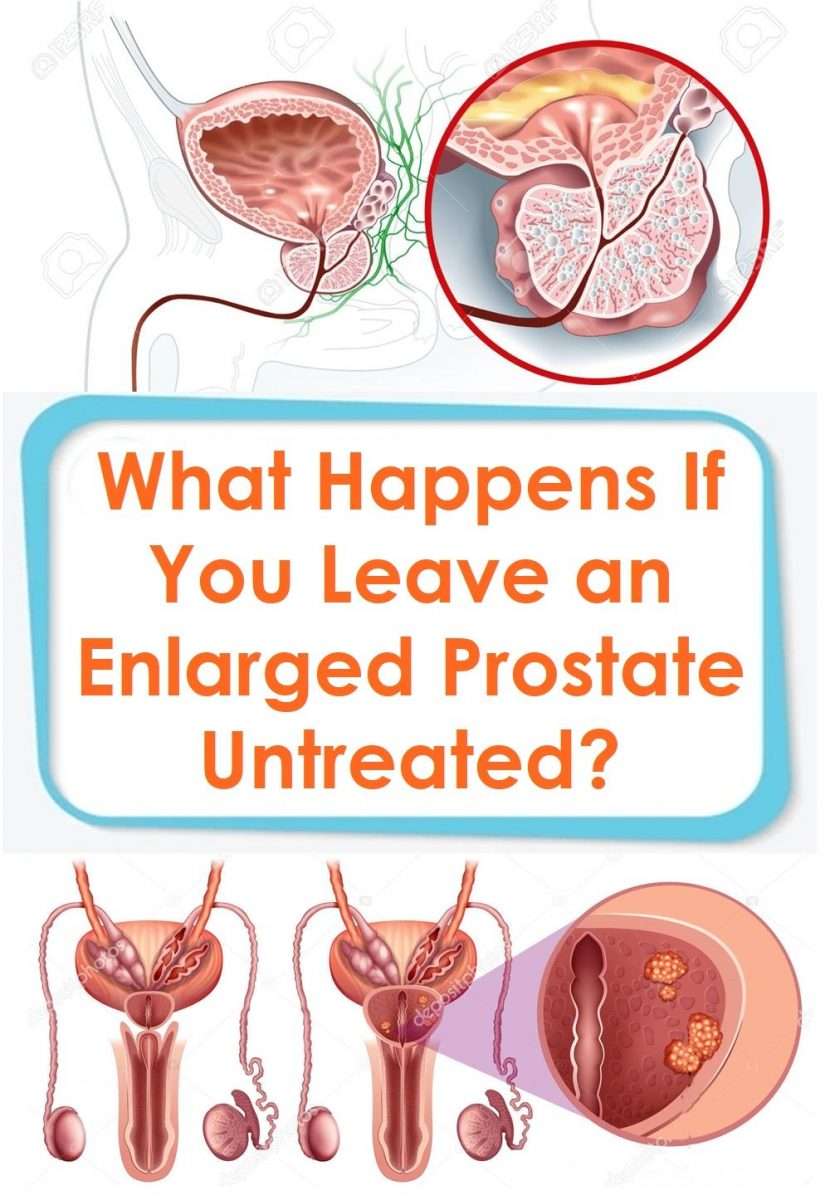
What Is An Enlarged Prostate
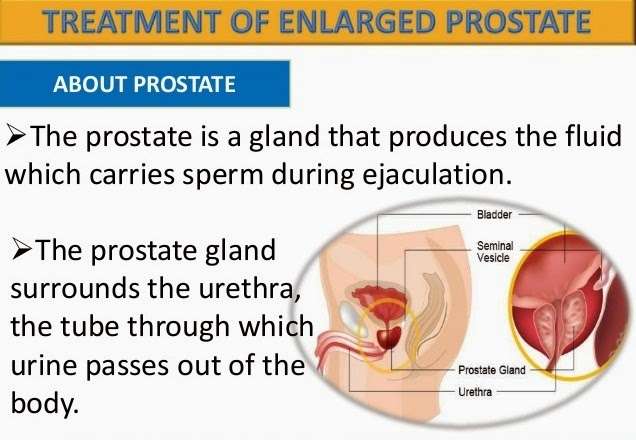
The prostate is an essential gland in the male reproductive system. It contributes to the semen volume and synthesizes a substance that supports sperm cells.
This gland is below the urinary bladder, surrounding the urethra. In the bladder neck. Thus, as it grows, it can put pressure over the urethra or the urinary bladder. However, what is an enlarged prostate? Is it the same as prostate cancer?
An enlarged prostate is simply a gland that increased in size. It is not caused by cancer. Another medical term is benign prostatic enlargement, where benign means theres no cancer. Another name is benign prostatic hyperplasia .
When we talk about hyperplasia, we refer to an increase in number and not size. Thus, in prostatic hyperplasia, there are more prostate cells . However, they remain the same size as normal prostate tissue. Such an increase in the number of cells causes an enlarged prostate. It usually starts in men after the age of 40. But they typically find out when they are near their 50s .
In some cases, an enlarged prostate grows evenly. In other instances, prostate growth is more irregular. When the overgrowth is near the center, it presses the urethra on the outside.
As a result, the urethra becomes narrow, compromising the urine flow. As a result, 1 out of 3 men over 50 years old report urinary symptoms. In the majority of cases, they are caused by an enlarged prostate gland .
Also Check: What Is A Prostate Biopsy
Enlarged Prostate This Treatment Can Help You Avoid Sexual Side Effects
Benign prostatic hyperplasia , or enlarged prostate, is a common condition in men older than age 50. BPH occurs when the prostate gland becomes enlarged and begins to press on the urethra the tube that carries urine out of the body.
When the prostate continues to grow, it can lead to urinary symptoms that include:
- Leaking or dribbling of urine
- Frequent nighttime awakenings to urinate
- Urinary retention or urgency
- A weak urine stream
BPH is not prostate cancer and it doesnt lead to cancer. However, the two conditions may have similar symptoms in the early stages
So its important that men who experience these symptoms be evaluated by a mens health specialist to rule out cancer and determine the best treatment options to relieve their symptoms.
Without treatment, BPH can lead to serious complications in some men, including incontinence, kidney or bladder damage, urinary tract infections and bladder stones. In some extreme cases, BPH can cause a total inability to urinate and require emergency catheterization.
> > > All Natural Technique Fixes Enlarged Prostate Watch Here< <
Surgical procedures to remove the diseased prostate are usually necessary. Surgical procedures are not always necessary. If the disease is caused by bacterial infections, a doctor can treat the symptoms using alpha-blockers or surgery. Physical therapy, relaxation exercises, and warm baths are all recommended. A physician may also prescribe antibiotics to cure the infection. A bacterial infection can also cause a recurrence of the condition.
An enlarged prostate can be uncomfortable for both men and women. Some of the symptoms of an enlarged male reproductive organ include a weakened urine stream, urgent need to urinate, and urinary tract infections. BPH can also cause damage to the kidneys. A sudden inability to urinate can be life-threatening, as it can lead to bladder and kidney damage. Unfortunately, most men with enlarged prostrates put up with the symptoms for years before they seek treatment. However, many of the men with symptoms finally decide to go to a doctor for proper gynecological evaluation and to begin enlarged prostatic therapy.
Also Check: What Antibiotics Are Good For Prostatitis
Symptoms Of An Enlarged Prostate
As mentioned above, the most common symptoms of an enlarged prostate are urination problems. Its because the prostate portion surrounding the urethra narrows the normal passage of urine. These problems become worse as the patient gets older.
The progression prolongs which some patients may not even realize. They learn to live with the symptoms and sometimes wont even report them. However, it is crucial to recognize the symptoms of an enlarged prostate and consult your doctor.
Heres a list of the most important symptoms .
Can An Enlarged Prostate Keep You From Ejaculating
Enlarged prostate, or BPH, is one of the most common urological conditions that a man can encounter as he gets older. It can cause uncomfortable urinary symptoms, such as blocking the flow of urine out of the bladder and other urinary tract, bladder, or kidney problems. Statistics show that 50% of men over the age of 50 will have BPH, then 60% over 60, and so forth, increasing by 10% with every decade of life. Accordingly, as men get older, they’re also more prone to have sexual dysfunction.
There is no evidence that having BPH leads immediately to erectile dysfunction, yet there are relationships between BPH and erectile dysfunction. In general, these relationships are due to patients with BPH who may have other numerous medical conditions that are also associated with erectile dysfunction like hypertension, lipid abnormalities, diabetes, heart disease, etc.
When the pills don’t work, treatments go to surgery such as TURP, where you basically carve out a part of the prostate to make the passageway of the urine bigger. These surgeries may have irreversible side effects that cause erectile dysfunction as well as ejaculatory dysfunction after surgery, retrograde ejaculation, sexual issues, bleeding, and can sometimes require catheters to be placed again. Additionally, they can cause incontinence in up to 1% of people, which can be quite disconcerting to a lot of patients.
Read Also: Are You Sedated For A Prostate Biopsy
