Can I Survive Advanced Prostate Cancer Whats The Prognosis
Prostate cancer is the second leading cause of death from cancer in men, according to the National Cancer Institute. While theres no cure, men can live with it for years if they get the right treatment. Each man with advanced prostate cancer is different, of course. You and your cancer have unique qualities that your doctor takes into consideration when planning the best treatment strategy for you.
According to Harvard Medical School, the prognosis for men with advanced prostate cancer is improving because of newer medications that help them get past a resistance to androgen-deprivation therapy that typically develops after a few years of treatment. With these medications, many men are living longer, and a number of men diagnosed with advanced prostate cancer are dying with the cancer, not from it.
Promptly treating prostate cancer bone metastases with the newest medication can help change a mans prognosis dramatically, Tagawa says. There are men who do well for decades, he says. Some men can even stop treatment, go on to live many years, and actually die of something unrelated.
Tagawa says that cancer specialists who use sophisticated imaging technologies, like positron-emission tomography scans, have gotten very good at finding even tiny bone metastases, which is valuable in diagnosing and removing early stage metastases.
When Prostate Cancer Spreads Where It Goes Matters A Lot
And if the cancer progresses or spreads beyond his prostate? We can treat it then, Callaghan said.
The study shows that you have no business treating low-grade prostate cancer in someone with a life expectancy of less than 15 years because the side effects outweigh any benefits, said urological surgeon Dr. Peter Albertsen of the University of Connecticut Health. The Oxford scientists reported that 46 percent of men who had their prostate removed were using adult diapers six months later . Similarly, only 12 percent of men who got surgery and 22 percent who had radiation could sustain an erection, compared to 52 percent of the monitoring group.
An estimated 180,890 men in the US will be diagnosed with prostate cancer this year, according to the American Cancer Society. Some 26,120 will die of it in 2016, almost always because it has spread to a vital organ.
In an editorial accompanying the study, radiation oncologist Dr. Anthony DAmico of Brigham and Womens Hospital focused on the finding that men who opted for monitoring were more than twice as likely to develop metastatic prostate cancer. That is, malignant cells reached the bones, lung, liver, or brain.
Garnick agreed: The intermediate-risk men we would never assign to active monitoring. If the increased metastases came from these patients, it would explain those differences and even more strongly encourage the role of active management in truly low-risk prostate cancer.
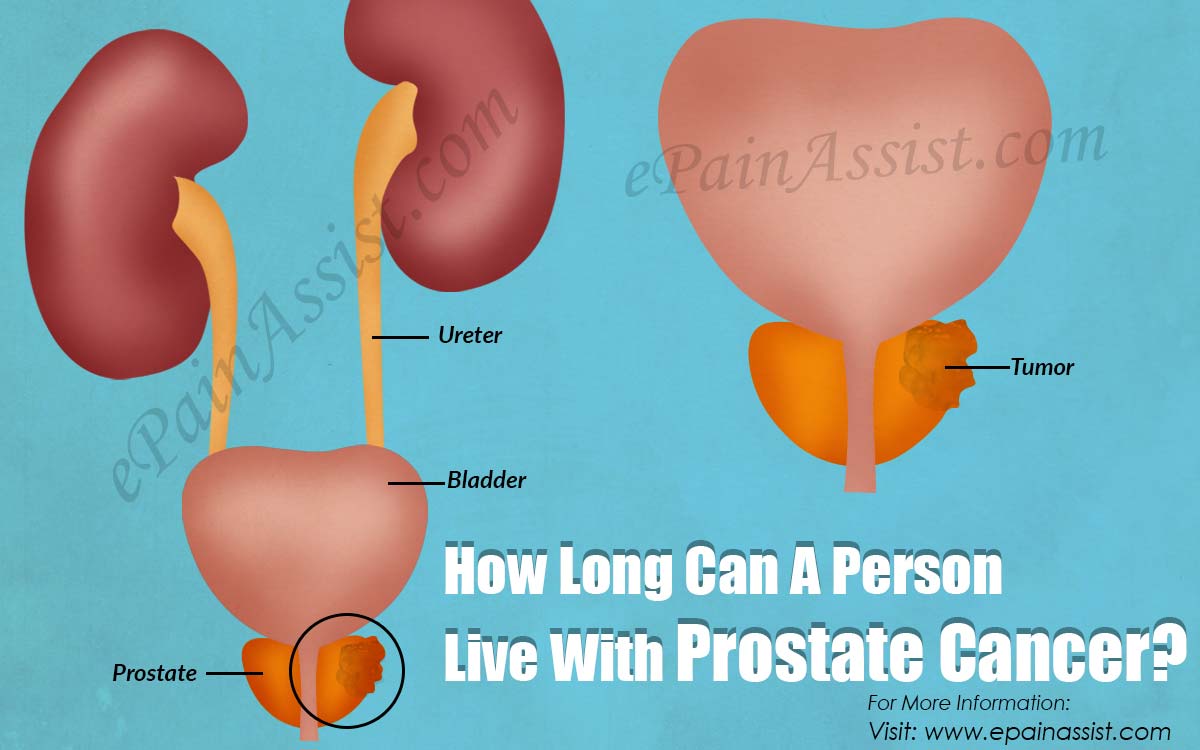
Where Prostate Cancer Spreads
If left untreated, diagnosed prostate cancer can grow and possibly spread outside of the prostate to local tissues or distantly to other sites in the body. The first sites of spread are typically to the nearby tissues.
The cancer can spread down the blood vessels, lymphatic channels, or nerves that enter and exit the prostate, or cancer could erode directly through the capsule that surrounds the prostate.
The seminal vesicles are a site of particularly common early spread. More extensive local spread can occur with cancer invading the nearby bladder or rectum.
Further advancement of cancer can occur when cancer cells enter the blood vessels and lymphatic channels. Once cancer has entered into these vessels, prostate cancer cells can seed into virtually any other part of the body.
Prostate cancer is known to have a particular affinity for spreading or metastasizing to the bones especially the lower spine, pelvis, and femur. Other organs such as the liver, brain, or lungs can also be the sites of spread, but these are much rarer.
You May Like: Prostatic Neoplasms
What Questions Should I Ask My Healthcare Provider
If you have prostate cancer, you may want to ask your healthcare provider:
- Why did I get prostate cancer?
- What is my Gleason score? What is my Grade Group? What do these numbers mean for me?
- Has the cancer spread outside of the prostate gland?
- What is the best treatment for the stage of prostate cancer I have?
- If I choose active surveillance, what can I expect? What signs of cancer should I look out for?
- What are the treatment risks and side effects?
- Is my family at risk for developing prostate cancer? If so, should we get genetic tests?
- Am I at risk for other types of cancer?
- What type of follow-up care do I need after treatment?
- Should I look out for signs of complications?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Prostate cancer is a common cancer that affects males. Most prostate cancers grow slowly and remain in the prostate gland. For a small number, the disease can be aggressive and spread quickly to other parts of the body. Men with slow-growing prostate cancers may choose active surveillance. With this approach, you can postpone, and sometimes completely forego, treatments. Your healthcare provider can discuss the best treatment option for you based on your Gleason score and Group Grade.
Patients Near Death May Not Respond To Others
Patients may withdraw and spend more time sleeping. They may answer questions slowly or not at all, seem confused, and may not be interested in what’s going on around them. Most patients are still able to hear after they are no longer able to speak. It may give some comfort if family members continue to touch and talk to the patient, even if the patient does not respond.
You May Like: Tamsulosin Ejaculation
What Is Advanced Prostate Cancer
When prostate cancer spreads beyond the prostate or returns after treatment, it is often called advanced prostate cancer.
Prostate cancer is often grouped into four stages, with stages III and IV being more advanced prostate cancer.
- Early Stage | Stages I & II: The tumor has not spread beyond the prostate.
- Locally Advanced | Stage III: Cancer has spread outside the prostate but only to nearby tissues.
- Advanced | Stage IV: Cancer has spread outside the prostate to other parts such as the lymph nodes, bones, liver or lungs.
When an early stage prostate cancer is found, it may be treated or placed on surveillance . Advanced prostate cancer is not curable, but there are many ways to treat it. Treatment can help slow advanced prostate cancer progression.
There are several types of advanced prostate cancer, including:
Biochemical Recurrence
With biochemical recurrence, the prostate-specific antigen level has risen after treatment using surgery or radiation, with no other sign of cancer.
Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer
Non-Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer that no longer responds to hormone treatment and is only found in the prostate. This is found by a rise in the PSA level, while the testosterone level stays low. Imaging tests do not show signs the cancer has spread.
Metastatic Prostate Cancer
- Lymph nodes outside the pelvis
- Bones
- Other organs, such as liver or lungs
Metastatic Hormone-Sensitive Prostate Cancer
In The Last Days Of Life Patients And Family Members Are Faced With Making Decisions About Treatments To Keep The Patient Alive
Decisions about whether to use life-sustaining treatments that may extend life in the final weeks or days cause a great deal of confusion and anxiety. Some of these treatments are ventilator use, parenteral nutrition, and dialysis.
Patients may be guided by their oncologist, but have the right to make their own choices about life-sustaining treatments. The following are some of the questions to discuss:
- What are the patients goals of care?
- How would the possible benefits of life-sustaining treatments help reach the patient’s goals of care, and how likely would this be?
- How would the possible harms of life-sustaining treatments affect the patient’s goals of care? Is the possible benefit worth the possible harm?
- Besides possible benefits and harms of life-sustaining treatments, what else can affect the decision?
- Are there other professionals, such as a chaplain or medical ethicist, who could help the patient or family decide about life-sustaining treatments?
Also Check: Fiducial Marker Placement For Prostate Cancer
What Are The Symptoms Of Advanced Prostate Cancer And Bone Metastases
When cancer cells spread to the bones, the condition weakens the very frame on which the body rests. The cells interfere with the strength and hardness of the bones structure, interrupting its normal cycle of building up and dissolving.
Theres no cure for advanced prostate cancer, but theres a lot that doctors can do to help with the symptoms that might develop. This includes managing pain. A common misconception is that if theres cancer in the bone, there must be pain, Tagawa says. Thats not true. Cancer can be in the bone without pain. However, if there is pain, he says, it can be controlled with anticancer therapies and pain medication, and good quality of life can be maintained.
In addition to pain, some men with bone metastases develop a condition called hypercalcemia, in which, because of the damage to bones from the cancer cells, too much calcium builds up in the blood. Hypercalcemia can make you feel constipated, thirsty, sleepy, or sluggish, and it can increase the urge to urinate, according to the ACS. Over time, hypercalcemia can cause muscle and joint achiness, as well as weakness in the muscles. In advanced stages, it can cause the kidneys to shut down.
There are treatments for hypercalcemia as well as for other complications from advanced prostate cancer, such as bones that become weak and break or fracture, and for growths in the spine that can press on the spinal cord and damage nerves.
Signs Vs Symptoms Of Cancer
Signs and symptoms of disease can be two different things:
- A sign is something that can be observed by another person, such as a change in skin color or wheezing.
- A symptom is something you feel, such as fatigue or pain, that isnt obvious to others.
The nature of cancer signs and symptoms differ greatly, depending on where the cancer is located.
Bladder cancer, for instance, causes blood in the urine, while brain cancer triggers terrible headaches.
Recommended Reading: Force Factor Prostate Supplement Side Effects
Signs Of Approaching Death
Death from cancer usually occurs after a person has become weaker and more tired over several weeks or months. It is not always possible to predict how long someone will live. But some common signs and symptoms show that a person is entering the final weeks and days of life. Knowing what to expect helps relieve anxiety and allows better planning.
The following are signs and symptoms that suggest a person with cancer may be entering the final weeks of life:
-
Worsening weakness and exhaustion.
-
A need to sleep much of the time, often spending most of the day in bed or resting.
-
Weight loss and muscle thinning or loss.
-
Minimal or no appetite and difficulty eating or swallowing fluids.
-
Little interest in doing things that were previously important.
-
Loss of interest in the outside world, news, politics, entertainment, and local events.
-
Wanting to have only a few people nearby and limiting time spent with visitors.
As the last days of life approach, you may see the following signs and symptoms:
Of course, every person is different. The signs and symptoms that people experience vary. And the order in which signs and symptoms occur may differ.
Possible Changes In Breathing
- Breathing may speed up and slow down due to less blood circulation and build-up of waste products in the body
- Patient may grunt while breathing
- Neck muscles may look tight to help breathe
- Mucus in the back of the throat may cause rattling or gurgling with each breath
- The patient may not breathe for periods of up 10 to 30 seconds
Recommended Reading: Expressed Prostatic Secretion
What Happens When Prostate Cancer Is Left Untreated
Doru Paul, MD, is triple board-certified in medical oncology, hematology, and internal medicine. He is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Weill Cornell Medical College and attending physician in the Department of Hematology and Oncology at the New York Presbyterian Weill Cornell Medical Center.
While most men undergo some form of treatment for their prostate cancer, some men today choose to not be treated for their prostate cancer. Instead, they may choose to have their healthcare providers monitor their cancer.
Known as active surveillance, it is common when the cancer is expected to grow slowly based on biopsy results, confined to the prostate, not causing any symptoms, and/or small. In active surveillance, healthcare providers will initiate cancer treatment only if cancer starts growing.
Others men may choose to not undergo cancer treatment because of a short life expectancy or other serious medical problems. They may feel that the risks or side effects of cancer treatment outweigh their potential benefits.
This option is certainly OK and reasonable in the right circumstancesrequiring a careful and thoughtful discussion with your healthcare provider and family.
Survival For All Stages Of Prostate Cancer
Generally for men with prostate cancer in England:
- more than 95 out of 100 will survive their cancer for 1 year or more
- more than 85 out of 100 will survive their cancer for 5 years or more
- almost 80 out of 100 will survive their cancer for 10 years or more
Survival for prostate cancer is also reported in Scotland and Northern Ireland. But it is difficult to compare survival between these countries because of differences in the way the information is collected.
Cancer survival by stage at diagnosis for England, 2019Office for National Statistics
These statistics are for net survival. Net survival estimates the number of people who survive their cancer rather than calculating the number of people diagnosed with cancer who are still alive. In other words, it is the survival of cancer patients after taking into account the background mortality that they would have experienced if they had not had cancer.
You May Like: Chemo Pill For Prostate Cancer
Should I Make Any Lifestyle Changes Including In My Diet Or Physical Activity
Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight by eating a balanced diet with plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, and staying physically active, can help your overall health. These lifestyle changes can also have a positive effect for men with bone metastases, Tagawa says. Both diet and exercise, he says, are things that are under a mans direct control.
A healthy lifestyle can help you better manage side effects from treatment as well. Try setting small but realistic goals for yourself when it comes to eating a healthy diet and getting plenty of exercise.
While no single food is likely to have a benefit for prostate cancer, smart food choices may help you feel better day to day. Start by cutting out foods high in sugar, saturated fat, and added flavorings and preservatives.
If youre not sure which healthy foods to choose, ask your doctor for a referral to a dietitian. This specialist can help you develop a meal plan that includes foods that offer the best chance of slowing the cancers growth and keeping you as healthy as possible.
As an oncologist, Tagawa says he concentrates on treating the cancer itself, but hes aware that many of the men he sees with advanced prostate cancer are older and more likely than younger men to have health problems that can benefit from diet and exercise.
And if youre on hormone therapy, talk to your doctor about investing in some weights or elastic resistance bands to support your bone strength too.
What Does The Prostate Do
The prostate is a male gland that releases prostate fluid, one of the components of semen.
The muscles of the prostate gland help propel this fluid into the urethra during ejaculation.
It is a muscular gland that is often described as walnut or small apricot-sized.
An enlarged prostate can be a sign of prostate cancer, the third biggest cancer killer.
Recommended Reading: Pseudoephedrine And Prostate
What Causes Prostate Cancer
Experts arent sure why some cells in the prostate gland become cancerous . Genetics appear to play a role. For example:
- Youre two to three times more likely to get prostate cancer if your father, brother or son has the disease.
- Inherited mutated breast cancer genes and other gene mutations contribute to a small number of prostate cancers.
Can You Live 30 Years With Prostate Cancer
The majority of men seeking definitive surgical treatment in contemporary series fall within 55 to 65 years of age and are expected to enjoy an overall life expectancy ranging from about 15 to 30 years, placing these men at long-term risk for disease progression and prostate cancer-specific death if managed expectantly
Read Also: Find Prostate Externally
How Does Cancer Cause Death
Every patient is different, and the way cancer causes death varies. The process can depend on the type of cancer, where it is in the body, and how fast its growing.
For some people, the cancer cant be controlled anymore and spreads to healthy tissues and organs. Cancer cells take up the needed space and nutrients that the healthy organs would use. As a result, the healthy organs can no longer function. For other people, complications from treatment can cause death.
During the final stages of cancer, problems may occur in several parts of the body.
In some cases, the exact cause cant be pinpointed and patients simply decline slowly, becoming weaker and weaker until they succumb to the cancer.
Again, every patient is different and all processes have different stages and rates in which they advance. And some conditions have treatments that can help slow the process or make the patient more comfortable. Its very important to keep having conversations with the patients health care team.
Definitions Of Disease Categories
ICD codes used in the disease categories were the following : myocardial infarction , other coronary heart disease , cerebrovascular accident , arterial disease , heart failure , pneumonia , chronic lower respiratory disease , external causes , complications of diagnostic or surgical procedures , complications of therapeutic drug or vaccine usage , suicide , traffic accident , falls , other heart disease , gastrointestinal disease , dementia , diabetes , complications of heart disease , urinary system disease , symptoms , pulmonary circulation , nervous system disease , hypertensive disease , other bacterial disease , psychic disease , anemia , tumors other than prostate cancer , and prostate cancer .
Don’t Miss: Zinc And Prostate Cancer
