Prevention Of Prostate Cancer
The following measures can help prevent or decrease the risk of developing prostate cancer.
- Consume a healthy diet. A diet reduced in dairy and calcium, for example, may help minimize the risk of prostate cancer. The following foods may help reduce the risk of prostate cancer: broccoli, brussels sprouts, and kale, fish, soy, olive oil, which contains omega-3 fatty acids.
- Choose healthy foods over supplements. To date, no studies reported a decreased risk of prostate cancer with supplement use. As an alternative, eat meals that are high in vitamins and minerals to keep the vitamin levels in check.
- Exercise regularly. Exercise can also help the patient reduce weight, which is important because obesity has been linked to prostate cancer according to a 2016 study. Aim for 30 minutes of exercise most days of the week with the doctors consent.
- Consult with the healthcare provider regarding the risk of developing prostate cancer. According to certain studies, 5-alpha reductase inhibitors such as finasteride and dutasteride may reduce the overall risk of prostate cancer. These medications are intended to prevent prostate enlargement and hair loss.
However, some evidence suggests that men who take these drugs may be at a higher risk of developing a more serious form of prostate cancer . Advise the patient to check with the doctor if he/she is concerned about the risk of developing prostate cancer.
How Is Prostate Cancer Diagnosed
A biopsy is when a small piece of tissue is removed from the prostate and looked at under a microscope.
A biopsy is a procedure that can be used to diagnose prostate cancer. A biopsy is when a small piece of tissue is removed from the prostate and looked at under a microscope to see if there are cancer cells.
A Gleason score is determined when the biopsy tissue is looked at under the microscope. If there is a cancer, the score indicates how likely it is to spread. The score ranges from 2 to 10. The lower the score, the less likely it is that the cancer will spread.
A biopsy is the main tool for diagnosing prostate cancer, but a doctor can use other tools to help make sure the biopsy is made in the right place. For example, doctors may use transrectal ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging to help guide the biopsy. With transrectal ultrasound, a probe the size of a finger is inserted into the rectum and high-energy sound waves are bounced off the prostate to create a picture of the prostate called a sonogram. MRI uses magnets and radio waves to produce images on a computer. MRI does not use any radiation.
Prostatectomy Nursing Care Plans
Prostatectomy is the surgical removal of the prostate wherein the procedure could include all or part . Prostatectomy is indicated in the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia while radical prostatectomy is indicated in the treatment of prostate cancer.
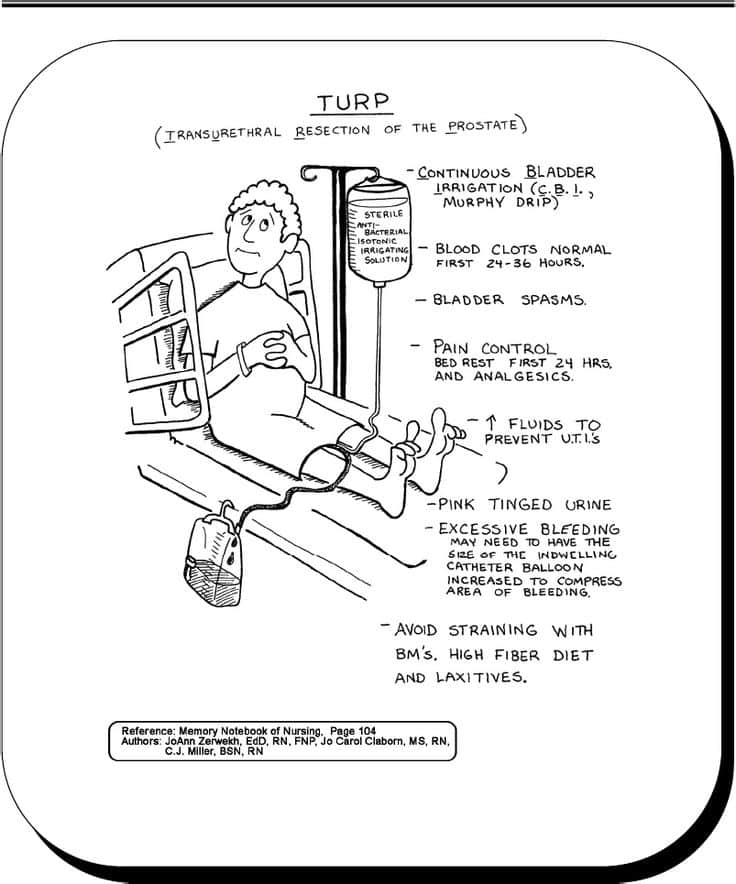
- Transurethral resection of the prostate : Obstructive prostatic tissue of the medial lobe surrounding the urethra is removed by means of a cystoscope/resectoscope introduced through the urethra.
- Suprapubic/open prostatectomy: Indicated for masses exceeding 60 g . Obstructing prostatic tissue is removed through a low midline incision made through the bladder. This approach is preferred if bladder stones are present.
- Retropubic prostatectomy: Hypertrophied prostatic tissue mass is removed through a low abdominal incision without opening the bladder. This approach may be used if the tumor is limited.
- Perineal prostatectomy: Large prostatic masses low in the pelvic area are removed through an incision between the scrotum and the rectum. This more radical procedure is done for larger tumors/presence of nerve invasion and may result in impotence.
You May Like: Is Cayenne Pepper Good For Your Prostate
Abnormal Substances In Urine
At times, abnormal urine contains substances that are not normally found inside blood vessels, and these signs can be used to detect the disease. Common examples are protein, glucose, and blood, which can be easily identified due to their different colors .
The nurse should also be aware that many other conditions can cause impairment in urinary elimination, including:
- Urethral stricture
Recommended Reading: Can Prostate Cancer Spread To The Liver
Prostate Needle Biopsy Nursing Care
The diagnosis of prostate cancer can only be confirmed by histological examination of tissue removed surgically. Fine needle aspiration is a quick, generally painless method done either transrectally or transperineally to obtain prostate cells for cytological examination and to determine the stage of disease that may be present. The procedure typically causes a very brief uncomfortable sensation each time the spring-loaded needle takes a sample. Nurses are involved in the diagnostic process when caring for a patient who has undergone prostate biopsy.
Prostate needle biopsy.
The nurseâs role in the process of obtaining a needle biopsy involves:
- Managing procedure setup
- Patency of urinary drainage system
- Catheter care and wound care
During the home visit, the nurse also reinforces previous education, assesses the patient and familyâs ability to manage required care, encourages ambulation and perineal muscle exercises as prescribed, answers questions, and provides emotional support .
Recommended Reading: Prostate Cancer To Bone Cancer
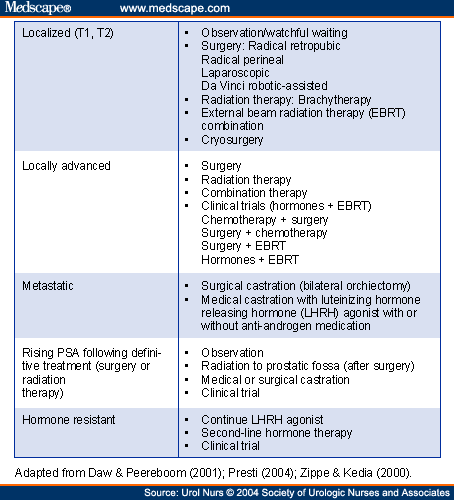
Stages Of Prostate Cancer
A staging method can help the doctor determine how far cancer has spread.
Prostate cancer is staged using the American Joint Committee on Cancer TMN staging system. The system, like many other types of cancer, stages it by:
- the tumors size or location
- involvement of lymph nodes
Prostate cancer has 4 stages with stage 4 being the most advanced stage of the disease.
Nursing Care Plan For Prostate Cancer 3
Nursing Diagnosis: Risk for Deficient Fluid Volume related to difficulty controlling bleeding, restricted intake preoperatively, post-obstructive diuresis, and vascular nature of surgical area secondary to prostate cancer.
Desired Outcomes:
- The patient will demonstrate adequate hydration as evidenced by stable vital signs, palpable peripheral pulses, excellent capillary refill, moist mucosal membranes, and urine output within the normal range.
- The patient will demonstrate the absence of active bleeding.
You May Like: Is A Small Prostate A Problem
Nursing Care Of Patients With Cancer
The outlook for patients with cancer has greatly improved because of scientific and technologic advances.
Maintaining Tissue Integrity
- Stomatitis. Assessment of the patientâs subjective experience and an objective assessment of the oropharyngeal tissues and teeth are important and for the treatment of oral mucositis, Palifermin , a synthetic form of human keratinocyte growth factor, could be administered.
- Radiation-associated skin impairment. Nursing care for patients with impaired skin reactions includes maintaining skin integrity, cleansing the skin, promoting comfort, reducing pain, preventing additional trauma, and preventing and managing infection.
- Alopecia. Nurses provide information about hair loss and support the patient and family in coping with changes in body image.
- Malignant skin lesions. Nursing care includes cleansing the skin, reducing superficial bacteria, controlling bleeding, reducing odor, protecting the skin from further trauma, and relieving pain.
Promoting Nutrition
- Anorexia. Anorexia may occur because people feel full after eating only a small amount of food.
- Malabsorption. Surgical intervention may change peristaltic patterns, later gastrointestinal secretions, and reduce the absorptive surfaces of the gastrointestinal mucosa, all leading to malabsorption.
- Cachexia. Nurses assess patients who are at risk of altered nutritional intake so that appropriate measures may be instituted prior to nutritional decline.
Relieving Pain
Causes And Risk Factors Of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
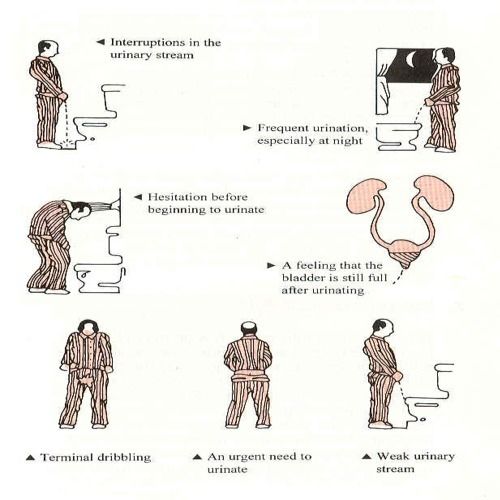
In normal urination, urine flows out outwards the urethra unobstructed. In BPH,, the prostate enlarges, thereby obstructing the urethra by decreasing its diameter and consequently blocking urine flow.
The real cause of BPH is not clear but is often associated with older men. With these, it has been concluded that increasing age and dropping testosterone levels plays a major role for its development.
The risk factors of BPH include the following:
- Aging Men aged 40 may have enlarged prostates but will not experience symptoms. Men aged 60 may develop moderate symptoms. Those 80 and above may experience sever symptoms.
- Family history having relatives with BPH has been linked to the development of BPH latter in life
- Diabetes and heart disease Diabetes and use of beta blockers predisposes patients to BPH
- Obesity and sedentary lifestyle play a role in BPH development.
You May Like: What Is Your Prostate Gland For
When Do You Need Us
Combating prostate cancer is a difficult affair, and is sure to be stressful to the patient as well as his immediate family members. For patients, providing prostate cancer care can be difficult. Since the disease usually affects the aged, nurses for prostate cancer patients are also hard to find. The nurses may have to take the patient to various prostate cancer tests, too. In such situations, Portea can provide care to patients in the early stages or those recovering from the treatment procedures at late stages.
Cancer Nursing Care Plan And Nanda Guidelines
Cancer is a potentially fatal disease caused mainly by environmental factors that mutate genes encoding critical cell-regulatory proteins. The resultant aberrant cell behavior leads to expansive masses of abnormal cells that destroy surrounding normal tissue and can spread to vital organs resulting in disseminated disease, commonly a harbinger of Imminent patient death.
Most types of a cancer cells clumps together to form a mass or tumor. When a cell breaks away from the tumor, it can be swept into the lymph system or bloodstream and carried to other parts of the body where new tumors can be formed.
Read Also: Cryoablation Success Rate For Prostate Cancer
You May Like: How Often To Get Checked For Prostate Cancer
Nursing Care Plan Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia 1
Nursing Diagnosis: Infection related to urinary retention secondary to BPH as evidenced by presence of leukocytes and nitrates in the urine upon urinalysis, positive bacteria urine culture result, foul-smelling urine, temperature of 38.9 degrees Celsius, and increased frequency of urination
Desired Outcome: The patient will be able to avoid the development of an infection.
Possible Nursing Diagnoses And Related Factors
Risk for infection related to inadequate primary defenses
Risk for infection related to immunosuppression/immunosuppressive effects of therapy
Risk for infection related to presence of foreign objects in the body
Risk for infection related to lack of information about proper infection control measures
Note: evidenced by is not usually applicable for a risk diagnosis since the presence of signs and symptoms already makes the nursing problem an actual diagnosis.
Also Check: Does An Enlarged Prostate Affect A Man Sexually
Nursing Management In Chemotherapy
Nurses play an important role in assessing and managing many of the problems experienced by patients undergoing chemotherapy.
- Assessing fluid and electrolyte balance.Anorexia, nausea, vomiting, altered taste, mucositis, and diarrhea put patients at risk for nutritional and fluid electrolyte disturbances.
- Modifying risks for infection and bleeding. Suppression of the bone marrow and immune system is expected and frequently serves as a guide in determining appropriate chemotherapy dosage but increases the risk of anemia, infection, and bleeding disorders.
- Administering chemotherapy. The patient is observed closely during its administration because of the risk and consequences of extravasation, particularly of vesicant agent.
- Protecting caregivers. Nurses must be familiar with their institutional policies regarding personal protective equipment, handling and disposal of chemotherapeutic agents and supplies, and management of accidental spills or exposures.
Tumor Staging And Grading
A complete diagnostic evaluation include identifying the stage and grade of the tumor.Staging. Staging determines the size of the tumor and the existence of local invasion and distant metastasis.
- Tumor, nodes, and metastasis system. The TNM system is frequently used, where T is the extent of the primary tumor, N is the absence or presence and extent of regional lymph node metastasis, and M is the absence or presence of distant metastasis.
- Grading. Grading refers to the classification of the tumor cells, and it seeks to define the type of tissue from which the tumor originated and the degree to which the tumor cells retain the functional and histologic characteristics of the tissue of origin.
- Grade I to IV.Grade I tumors, also known as well-differentiated tumors, closely resemble the tissue of origin in structure and function while Grade IV tumors do not clearly resemble the tissue of origin in structure and function.
Don’t Miss: How Are Prostate Exams Performed
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Scan
Like CT scans, MRI scans show detailed images of soft tissues in the body. But MRI scans use radio waves and strong magnets instead of x-rays.
MRI images are very useful in showing cancer that has spread outside of the bladder into nearby tissues or lymph nodes. A special MRI of the kidneys, ureters, and bladder, known as an MRI urogram, can be used instead of an IVP to look at the upper part of the urinary system.
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Bph Nursing Care Plans Diagnosis And Interventions
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia NCLEX Review and Nursing Care Plans
Its primary function is the production of seminal fluid, which serves as the transport medium of the sperm during intercourse.
In benign prostatic hyperplasia or benign prostatic hypertrophy, the prostate enlarges and in turn causes obstruction problems.
Because of its anatomical placement, urinary problems arise which in turn significantly affects the patient.
The condition is more common in men above 50 years of age.
Read Also: What Does The Prostate Gland Do
Nursing Considerations For Prostate Cancer Survivorship Care
Prostate cancer is the most common cancer among those assigned male at birth, with one in eight diagnosed during their lifetime. But with five-year survival rates of 90%, its also one of the most successful cancers to treat, making survivorship care even more important.
Many patients live with the disease or receive long-term maintenance therapies, and patients often have comorbidities prior to diagnosis. With the advancements in treatment, many are outliving their prostate cancer diagnosis and their death is related to other comorbidities. Survivorship care requires an interprofessional approach that involves primary care, urology, and oncology specialists to address the wide range of late and long-term effects and comorbidities.
Prostate Cancer: Survivorship Care Case Study Care Plan And Commentaries
Michelle Delcioppo
This case study highlights the patients status in care plan format and is followed by commentaries from expert nurse clinicians about their approach to manage the patients long-term or chronic cancer care symptoms. Finally, an additional expert nurse clinician summarizes the care plan and commentaries, emphasizing takeaways about the patient, the commentaries, and additional recommendations to manage the patient. As can happen in clinical practice, the patients care plan is intentionally incomplete and does not include all pertinent information. Responding to an incomplete care plan, the nurse clinicians offer comprehensive strategies to manage the patients status and symptoms. For all commentaries, each clinician reviewed the care plan and did not review each others commentary. The summary commentary speaks to the patients status, care plan, and nurse commentaries.
Recommended Reading: How To Decrease Risk Of Prostate Cancer
Nursing Care Plan For Prostate Cancer 5
Nursing Diagnosis: Situational Low Self-Esteem related to biophysical factors such as disfiguring surgery, chemotherapy, or radiotherapy side effects and psychosocial such as threat of death, doubt regarding acceptance by others, fear, anxiety, and feeling lack of control secondary to prostate cancer as evidenced by alteration in self-perception, lack of follow-through, not taking responsibility of self-care, verbalization of change in lifestyle, and feelings of helplessness, hopelessness and powerlessness.
Desired Outcomes:
- The patient will verbalize and express an understanding of body changes and self-acceptance of the situation.
- The patient will start developing coping mechanisms to effectively deal with problems.
- The patient will demonstrate adaptation to changes or events that occurred as evidenced by setting realistic goals and active participation in leisure activities and personal relationships as appropriate.
Prostate Cancer: A Guide To Diagnosis
Key learning points:
Prostate cancer is the most common cancer in men
Current diagnostic tests for prostate cancer can give false negatives and false positives and are therefore currently unsuitable for a national screening programme
Men need support to make an informed decision on whether or not to be tested for prostate cancer
Prostate cancer is the most common cancer in men. Every year over 44,000 men are diagnosed with the disease in the UK and it kills more than 10,000. With no national screening programme, diagnosing prostate cancer remains one of the biggest challenges facing health professionals.
Nurses play a vital role in ensuring that all men concerned about prostate cancer are armed with the information they need to make an informed decision about testing.
Signs and symptoms
Most early stage prostate cancers do not cause any symptoms, mostly because either the tumour is small or in the outer part of the prostate and is therefore not putting any pressure on the urethra.
Risk factors
Due to the fact that most men with early stage prostate cancer will not have any symptoms, being aware of a mans risk is essential. There are three key risk factors to think about:
1. What is the mans ethnicity?
We know that in the UK one in four black men will be diagnosed with prostate cancer, which is double the risk of a white man .
2. Does he have a family history of prostate cancer?
3. How old is he?
What to do after an assessment?
The pros and cons of the PSA test
Also Check: How Do You Know If You Have An Enlarged Prostate
Causes Of Prostate Cancer
The cause of prostate cancer is unknown. Prostate cancer develops when cells in the prostate have DNA alterations, according to doctors. The alterations cause the cells to divide and expand more quickly than normal cells. Aberrant cells grow continuously and form a tumor, which can spread and invade neighboring tissue. Some aberrant cells can break away and spread to other places of the body .
Risk Factors to Prostate Cancer
Predisposing factors may increase the risk of developing prostate cancer.The risk factors for developing prostate cancer are as follows:
- Old age. the risks of acquiring prostate cancer rise as the patient get older. It gets increasingly common beyond the age of 50.
- Race. For unexplained causes, black men have a higher risk of prostate cancer than other races. Black males are also more likely to have aggressive or advanced prostate cancer.
- Family background. A family history of prostate cancer increases ones risk. Furthermore, if the patient have a strong family history of breast cancer or a gene that raises the risk of breast cancer , the chances of developing prostate cancer are higher.
- Obesity. Obese people may have a higher risk of prostate cancer than people who are regarded to be of normal weight, while studies have produced inconsistent results. Furthermore, this risk group is also prone to develop a more aggressive caner posttreatment.
