Can Prostatitis Be Prevented Or Avoided
You cant prevent most cases of prostatitis. However, you should get checked for STDs. To best protect yourself, use a condom during all sexual encounters. This helps prevent getting or spreading the infection.
Men who have frequent UTIs are more likely to have prostatitis. Men who are 50 years of age or older and have an enlarged prostate also have an increased risk.
Prostate Cancer Survival Rates
Answering the question of how curable is prostate cancer? first requires understanding what doctors mean when they refer to curability. Regardless of the type of cancer, doctors consider cancer cured when a patient remains cancer-free for a specified period after treatment. The higher the number of patients who stay cancer-free for five years or longer, the higher the curability of that particular disease.
Prostate cancer, therefore, has one of the highest curability rates of all types of cancer, thanks in large part to early detection standards and advances in treatment, such as the stereotactic body radiation therapy offered by Pasadena CyberKnife. When the cancer is detected in the early local or regional stages that is, before the cancer has spread or when it has only spread to limited areas in the pelvic regions the five-year survival rate is nearly 100 percent.
Survival rates decline significantly when cancer is detected at later stages however, the good news is that only about five percent of men are diagnosed after the cancer has become widespread throughout the body. In short, more than 90 percent of men who are diagnosed with prostate cancer live for five years or longer after treatment, making it one of the most curable forms of cancer.
How Are Bacterial Forms Of Prostatitis Managed Or Treated
Antibiotics can kill bacteria that cause bacterial types of prostatitis. Men with acute bacterial prostatitis may need 14 to 30 days of antibiotics, starting with IV antibiotics in the hospital. Rarely, men need surgery to drain an abscess on the prostate.
Treating chronic bacterial prostatitis is challenging. You may need up to three months of antibiotics to sterilize the prostate. If the prostate cant be sterilized, low-dose antibiotics can be used long term to prevent recurrences. Some men need surgery to remove prostate stones or scar tissue in the urethra. Rarely, surgeons remove part or all of the prostate gland .
Don’t Miss: Female Prostate Equivalent
Diagnosis Of An Enlarged Prostate
In order to establish the possible underlying causes for an enlarged prostate, doctors will perform a variety of tests.
Tests which are commonly used to find the cause of an enlarged prostate include:
- A digital rectal exam. A physician or nurse will insert a gloved finger into the patientâs rectum to digitally examine the prostate for swelling and/or enlargement.
- Swab tests for urethral discharge or urine. To determine underlying conditions such as STIs/STDs and urinary tract infections. A swab of discharge or urine is taken and sent to a medical laboratory for culturing, so that any microorganisms are identified.
- Urinalysis. A urine sample is sent to a medical laboratory for analysis and may be tested for urea nitrogen or creatinine, among other things.
- Blood tests. A sample of blood is sent to a medical laboratory for analysis, which may include tests for creatinine or blood urea nitrogen, as well as antibodies and infectious agents.
- Prostate-specific antigen test. A blood sample is sent to a medical laboratory to be tested for prostate-specific antigen , an enzyme produced by cells in the prostate. A change in PSA levels can indicate that there is a problem with the prostate.
If patients are referred to a urologist, they may have further tests, including:
Before referring the patient for tests, the physician may also ask questions in order to determine the possible causes of the discomfort, their severity, and their duration. Such questions may cover:
Doctor Does Too Much Sex Enlarge The Prostate
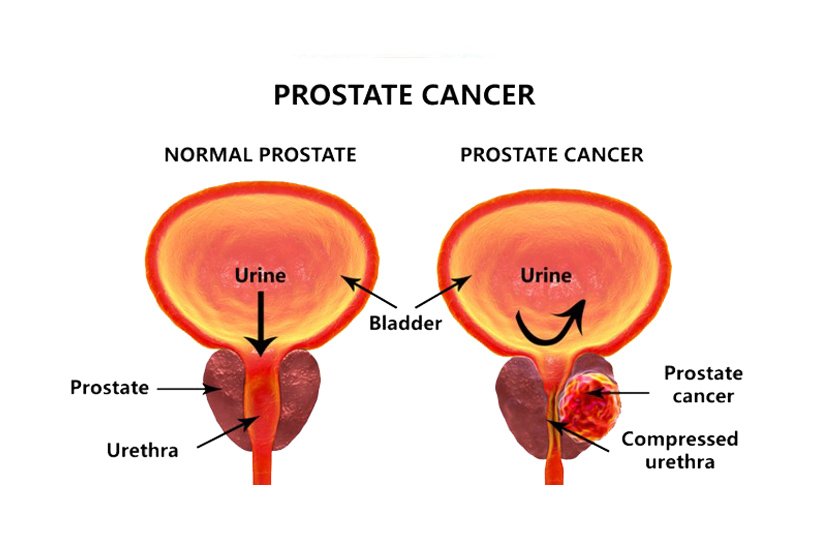
Prostate cancer is the commonest cancer in men. There are concerns on whether frequent sex contributes to the development of prostate enlargement in general and especially in the evolvement of prostate cancer.
The prostate gland is an important part of the male reproductive system. It is a major contributor to the formation of the seminal fluid that comes with ejaculation at the peak of sexual intercourse in males.
It produces nourishing materials, especially the sugary fructose, for the wellbeing of sperm cells. It is located just below the bladder where urine is stored, and in front of the rectum the last portion of the large intestine where the feces is stored.
Prostate enlargement: 100 for 100
In anatomical relationship, the prostate surrounds the tube that drains the urine from the urinary bladder, just as the tube is leaving the bladder.
A point of fact is that the prostate gland is destined to enlarge in all men as they get older, albeit at different rates in men of different extractions. Anyhow it goes, it is estimated with corroborative findings on autopsy that all men who lived up to 100 years had enlarged prostate a case of 100 for 100!
The good thing however is that most prostate enlargements are usually of no clinical consequence and are not problematic or symptomatic to the affected men since the prostate growth are mostly non-cancerous and non-strangulating.
Read Also: Is Cranberry Juice Good For The Prostate
What Is The Prostate
The prostate is a walnut-shaped gland that is part of the male reproductive system. The main function of the prostate is to make a fluid that goes into semen. Prostate fluid is essential for a mans fertility. The gland surrounds the urethra at the neck of the bladder. The bladder neck is the area where the urethra joins the bladder. The bladder and urethra are parts of the lower urinary tract. The prostate has two or more lobes, or sections, enclosed by an outer layer of tissue, and it is in front of the rectum, just below the bladder. The urethra is the tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body. In men, the urethra also carries semen out through the penis.
Setting Your Browser To Accept Cookies
There are many reasons why a cookie could not be set correctly. Below are the most common reasons:
- You have cookies disabled in your browser. You need to reset your browser to accept cookies or to ask you if you want to accept cookies.
- Your browser asks you whether you want to accept cookies and you declined. To accept cookies from this site, use the Back button and accept the cookie.
- Your browser does not support cookies. Try a different browser if you suspect this.
- The date on your computer is in the past. If your computers clock shows a date before 1 Jan 1970, the browser will automatically forget the cookie. To fix this, set the correct time and date on your computer.
- You have installed an application that monitors or blocks cookies from being set. You must disable the application while logging in or check with your system administrator.
You May Like: Expressed Prostatic Secretion
Preventing Or Controlling Symptoms
Doctors cant always identify what causes prostatitis, which makes it difficult to avoid prostatitis completely. However, men can take steps to try to reduce the likelihood of experiencing the condition. The same actions can help control symptoms of chronic prostatitis.
- Stay hydrated. Drinking plenty of water helps men to urinate frequently, which flushes out the urethra .
- Avoid irritating the urethra. Avoiding or limiting caffeine, spicy foods and alcohol can help to avoid prostatitis.
- Reduce prostate pressure. Men who ride a bicycle frequently might consider wearing padded shorts and using a split seat to reduce pressure on the prostate region.
- Stay sexually active. Some physicians advise that men ejaculate regularly as another way to flush the urethra.
Request an Appointment
What Are The Risk Factors For Prostate Cancer
The most important factors that increase the risk of prostate cancer are African American race, a family history of prostate cancer, and increasing age. Black men have a 60% higher risk of prostate cancer than white men and are approximately twice as likely to die of prostate cancer. People with a family history of prostate cancer are at increased risk, and having more than one family member with prostate cancer increases the risk further. Older men have a higher risk of prostate cancer than younger men, with more than 50% of all diagnoses occurring after the age of 65 and 97% occurring after the age of 50. There are also certain genetic syndromes that increase the risk of prostate cancer such as BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations and, as new evidence is suggesting, Lynch Syndrome .
Dont Miss: Is Viagra Good For Enlarged Prostate
Don’t Miss: Tamsulosin And Ejaculation Problems
Causes Of Premature Ejaculation
Various psychological and physical factors can cause a man to suddenly experience premature ejaculation.
Common physical causes include:
- relationship problems
- anxiety about sexual performance
Itâs possible, but less common, for a man to have always experienced premature ejaculation since becoming sexually active. A number of possible causes for this are:
- conditioning itâs possible that early sexual experiences can influence future sexual behaviour. For example, if a teenager conditions himself to ejaculate quickly to avoid being caught masturbating, it may later be difficult to break the habit
- a traumatic sexual experiencefrom childhood this can range from being caught masturbating to sexual abuse
- a strict upbringing and beliefs about sex
- biological reasons some men may find their penis is extra sensitive
Prostate Cancer Survival Rates Are Favorable Overall
Thinking about survival rates for prostate cancer takes a little mental stretching. Keep in mind that most men are around 70 when diagnosed with prostate cancer. Over, say, five years, many of these men will die from other medical problems unrelated to prostate cancer.
To determine the prostate cancer survival rate, these men are subtracted out of the calculations. Counting only the men who are left provides whats called the relative survival rate for prostate cancer.
Taking that into consideration, the relative survival rates for most kinds of prostate cancer are actually pretty good. Remember, were not counting men with prostate cancer who die of other causes:
- 92% of all prostate cancers are found when they are in the early stage, called local or regional. Almost 100% of men who have local or regional prostate cancer will survive more than five years after diagnosis.
- Fewer men have more advanced prostate cancer at the time of diagnosis. Once prostate cancer has spread beyond the prostate, survival rates fall. For men with distant spread of prostate cancer, about one-third will survive for five years after diagnosis.
Many men with prostate cancer actually will live much longer than five years after diagnosis. What about longer-term survival rates? According to the American Society of Clinical Oncology, for men with local or regional prostate cancer:
- the relative 10-year survival rate is 98%
- the relative 15-year survival rate is 96%
Read Also: Prostatic Neoplasms
Pain That Comes And Goes In The Lower Abdomen Around The Anus In The Groin Or In The Back
This pelvic floor pain is a key symptom to diagnose chronic pelvic pain syndrome. This type of pain has varying degrees of intensity. Most cases of pelvic pain are held for a very long time. Patients feel continuous pain and reduce their quality of life. When the problem becomes chronic, it doesnt matter if you have mild or severe pain.
Longstanding pain is still tough to live through and requires not only medications but also psychological therapy. Theres an understanding that the symptoms of chronic pelvic pain syndrome are an interplay of psychological, neurological, immune, and endocrine problems .
The 4 Causes Of An Enlarged Prostate
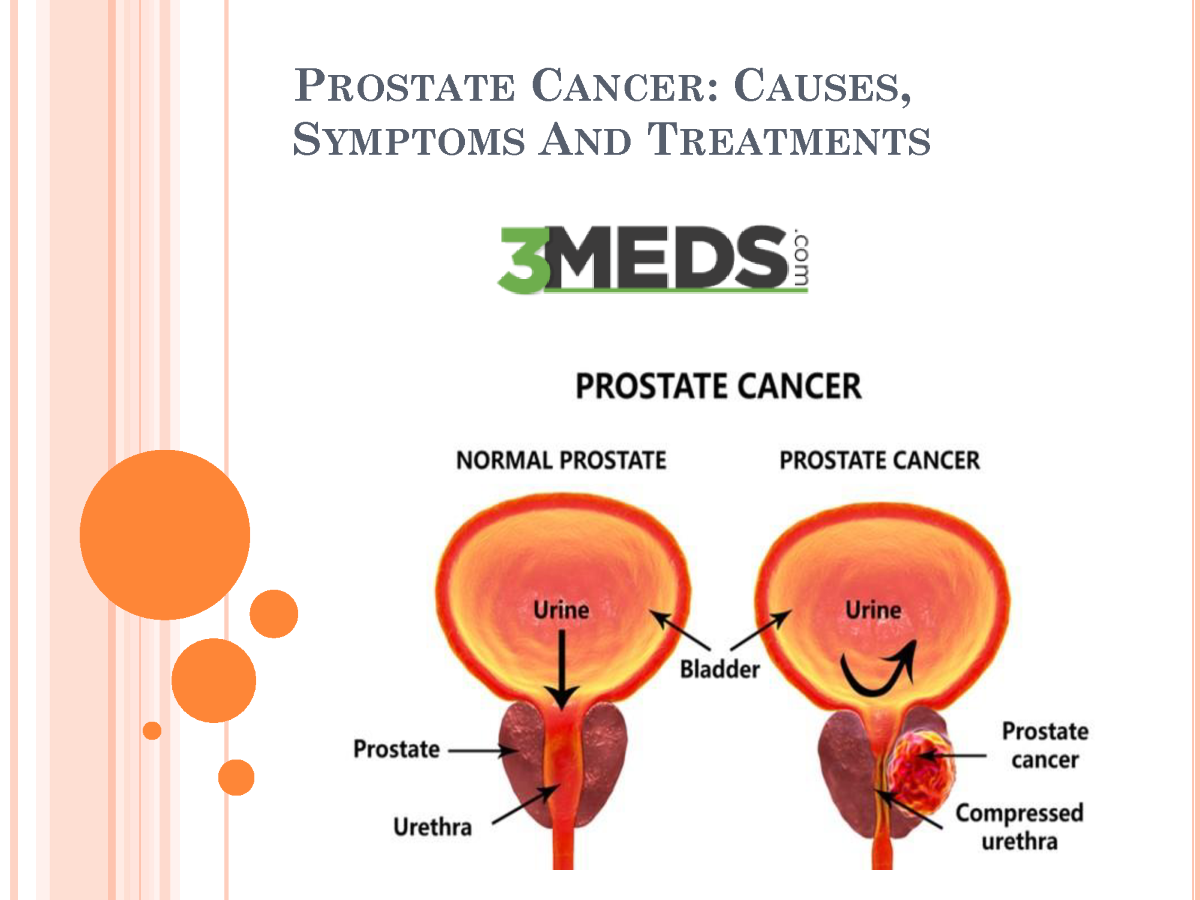
It is normal for a prostate to become enlarged as a man ages. The prostate is approximately the size of a walnut in younger men but can grow to be much larger as they get older. An enlarged prostate can cause no visible symptoms but will eventually impact urinary and erectile functions if not properly treated.
There are many reasons a prostate gets enlarged, and most of them arent cancerous. Here are the most common:
You May Like: Chemo Pills For Prostate Cancer
Treating Prostatitis Effectively: A Challenge For Clinicians
Nhuan Nguyen, PharmD, MBA, CHEClinical PharmacistGR Health, Georgia Regents Medical CenterAugusta, GeorgiaCharlie Norwood VA Medical CenterAugusta, GeorgiaUniversity of Georgia College of PharmacyAthens, Georgia
US Pharm. 2014 39:35-40.
ABSTRACT: Prostatitis, which affects 5% to 9% of males and occurs mostly in middle age, is classified based on signs and symptoms, with urinary urgency, frequency, and pain typical in nearly all categories. Most physicians are not familiar with prostatitis, particularly chronic prostatitis associated with chronic pelvic pain syndrome . Accordingly, patients are often misdiagnosed and receive ineffective treatment, resulting in poor quality of life. CP/CPPS is challenging to treat, as its causes are not clearly defined and the antibiotics used for therapy have low effective rates. Clinical pharmacists can contribute significantly to patient care by advising physicians and other medical professionals regarding drug efficacy, adverse drug reactions, and drug interactions, and by assisting in the selection of optimal antibiotics and/or treatment regimens for prostatitis.
Prostatitis , which occurs in 5% to 9% of males aged 18 years and older, most often develops in middle age.1 In the early 1990s, prostatitis accounted for about 1% and 8% of office visits to family practitioners and urologists, respectively.1
The Initial Causes What Can Cause Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis
One of the first symptoms of prostate issues is pain or tenderness in the groin or lower back. This can be the result of a noncancerous condition called enlarged prostatic tissue, or it could be an infection of the bladder. In either case, its important to see a doctor as soon as possible. If youre suffering from prostate pain, you may want to consider reducing your caffeine intake.
Another symptom of a potentially enlarged prostate is difficulty starting a stream of urine, leaking, or dribbling. These symptoms are not serious, but theyre still alarming. Most men put up with an enlarged prostate for years before seeking medical attention, but they typically seek treatment as soon as they notice symptoms. Even if you dont have symptoms, its worth getting checked to determine if you have any prostate issues.
If you experience nightly bathroom runs, you may be experiencing an enlarged prostate. You may be having difficulty starting a stream of urine, or you may even be dribbling or leaking during the day. These problems arent life-threatening, but can become a nuisance. You should not ignore these signs and seek treatment as soon as you notice them. If you feel any of these symptoms, you should consult a doctor.
You May Like: Does Retrograde Ejaculation Go Away
When To Seek Medical Care
A person may have urinary symptoms unrelated to prostatitis that are caused by bladder problems, UTIs, or benign prostatic hyperplasia. Symptoms of prostatitis also can signal more serious conditions, including prostate cancer.
Men with symptoms of prostatitis should see a health care provider.
Men with the following symptoms should seek immediate medical care:
- complete inability to urinate
- great discomfort or pain in the lower abdomen and urinary tract
What Are Grade Groups
Grade Groups are a new way to grade prostate cancer to address some of the issues with the Gleason grading system.
As noted above, currently in practice the lowest Gleason score that is given is a 6, despite the Gleason grades ranging in theory from 2 to 10. This understandably leads some patients to think that their cancer on biopsy is in the middle of the grade scale. This can compound their worry about their diagnosis and make them more likely to feel that they need to be treated right away.
Another problem with the Gleason grading system is that the Gleason scores are often divided into only 3 groups . This is not accurate, since Gleason score 7 is made up of two grades , with the latter having a much worse prognosis. Similarly, Gleason scores of 9 or 10 have a worse prognosis than Gleason score 8.
To account for these differences, the Grade Groups range from 1 to 5 :
- Grade Group 1 = Gleason 6
- Grade Group 2 = Gleason 3+4=7
- Grade Group 3 = Gleason 4+3=7
- Grade Group 4 = Gleason 8
- Grade Group 5 = Gleason 9-10
Although eventually the Grade Group system may replace the Gleason system, the two systems are currently reported side-by-side.
Anatomic structures and major veins of the male pelvis.
FIGURE 1.
Anatomic structures and major veins of the male pelvis.
FIGURE 2.
FIGURE 2.
Recommended Reading: Describe The Effect Of An Enlarged Prostate Gland On The Urinary Function Of A Male
Is Prostatitis Cancer
No. Prostatitis is a benign ailment, which, while not always curable, is almost always treatable with antibiotics. Occasionally, inflammation due to prostatitis can raise your PSA level . However, it does not lead to cancer.
Prostate cancer is believed to be due to a combination of factors including diet, lifestyle, genetics, and environmental exposures. There is, however, a question as to whether continued inflammation of the prostate may lead to the eventual development of prostate cancer, and studies are being done to determine if reducing inflammation can prevent prostate cancer.
Features Of Pin Cells
Basal cellspecific monoclonal antibodies directed against highmolecular weight keratin are used to identify HGPIN cells. Normal prostatic epithelial cells are consistently stained with these antibodies, showing a continuous, intact, circumferential basal cell layer. Cancer cells have lost their receptors for these antibodies.
Basal cell disruption affects 56% of patients with HGPIN and is usually found in glands adjacent to invasive cancer. The degree of disruption correlates with HGPIN. More than one third of the basal cell layer is lost in 52% of foci that contain HGPIN.
In persons with HGPIN and in many with low-grade cancer, the basement membrane that surrounds the prostatic glands remains intact. The expression of collagenase type 4 in PIN and associated cancer cells is abnormally high. The presence of collagenase type 4 and other enzymes is associated with a degradation of the basement membrane, allowing cell invasion into the stroma. Concurrently, the basal cell layer is diminished. This seems to occur primarily at sites of glandular outpouching.
Increased angiogenesis with an increased number of microvessels is associated with the progression of HGPIN to cancer. The microvessels in HGPIN are shorter than those in benign epithelium and have irregular contours and open lumens, an increased number of endothelial cells, and a greater distance from the basement membrane.
Also Check: Can An Enlarged Prostate Cause Constipation
You May Like: Super Beta Prostate Advanced Side Effects
