What Are The Stages Of Prostate Cancer
Cancer staging is first described using what is called a TNM system. The “T” refers to a description of the size or extent of the primary, or original, tumor. “N” describes the presence or absence of, and extent of spread of cancer to lymph nodes that may be nearby or further from the original tumor. “M” describes the presence or absence of metastases — usually distant areas elsewhere in the body other than regional lymph nodes to which cancer has spread. Cancers with specific TNM characteristics are then grouped into stages, and the stages are then assigned Roman numerals with the numerals used in increasing order as the extent of the cancer being staged increases or the cancer prognosis worsens. Prognosis is finally reflected by considering the patient’s PSA score at presentation as well as their Gleason score in assigning a final stage designation.
The American Joint Commission on Cancer system for prostate cancer staging is as follows:
The primary tumor
Traditionally, advanced prostate cancer was defined as a disease that had widely metastasized beyond the prostate, the surrounding tissue, and the pelvic lymph nodes and was incurable. However, a more contemporary definition includes patients with the lower-grade disease with an increased risk of progression and/or death from prostate cancer in addition to those with widely metastatic disease.
CT scan is used for the initial staging in select patients including
The regional lymph nodes
The distant metastasis
New Strategies Against Bone Metastases From Prostate Cancer
- Date:
- University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus
- Summary:
- A study suggests a new approach, or, possibly two new approaches against prostate cancer bone metastases: While targeted therapies and anti-cancer immunotherapies have not been especially successful against primary prostate cancers, the study suggests that both these approaches may be effective against the bone metastases that grow from primary prostate cancers, and, in fact, the type of bone metastasis may dictate which targeted therapies and immunotherapies work best.
When prostate cancer spreads, it most often spreads to bone. And while the 5-year survival rate for prostate cancer that has not spread is nearly 100 percent, once the disease reaches bone, the 5-year survival rate is only 29 percent. Now a University of Colorado Cancer Center study published in the Journal for Immunotherapy of Cancer suggests a new approach, or, possibly two new approaches against these bone metastases: While targeted therapies and anti-cancer immunotherapies have not been especially successful against primary prostate cancers, the study suggests that both these approaches may be effective against the bone metastases that grow from primary prostate cancers, and, in fact, the type of bone metastasis may dictate which targeted therapies and immunotherapies work best.
The group is now focused on testing therapies in mouse models of lytic and blastic bone metastases to determine the most promising drugs and drug combinations.
Keeping Health Insurance And Copies Of Your Medical Records
Even after treatment, its very important to keep health insurance. Tests and doctor visits cost a lot, and although no one wants to think of their cancer coming back, this could happen.
At some point after your cancer treatment, you might find yourself seeing a new doctor who doesnt know your medical history. Its important to keep copies of your medical records to give your new doctor the details of your diagnosis and treatment.
You May Like: Can You Have Prostatitis With Low Psa
Staging Spread And Survival Rates
As with all cancers, doctors use the term stage to describe the characteristics of the primary tumor itself, such as its size and how far prostate cancer has spread when it is found.
Staging systems are complicated. The staging system for most cancers, including prostate cancer, uses three different aspects of tumor growth and spread. It’s called the TNM system, for tumor, nodes, and metastasis:
- T, for tumor describes the size of the main area of prostate cancer.
- N, for nodes, describes whether prostate cancer has spread to any lymph nodes, and how many and in what locations.
- M, for metastasis, means distant spread of prostate cancer, for example, to the bones or liver.
Using the TNM system, each man’s prostate cancer can be described in detail and compared to other men’s prostate cancer. Doctors use this information for studies and to decide on treatments.
As far as survival rates for prostate cancer go, however, the staging system is pretty simple. As we’ve mentioned, in terms of survival rates, men with prostate cancer can be divided into two groups:
Show Sources
Intermittent Versus Continuous Therapy
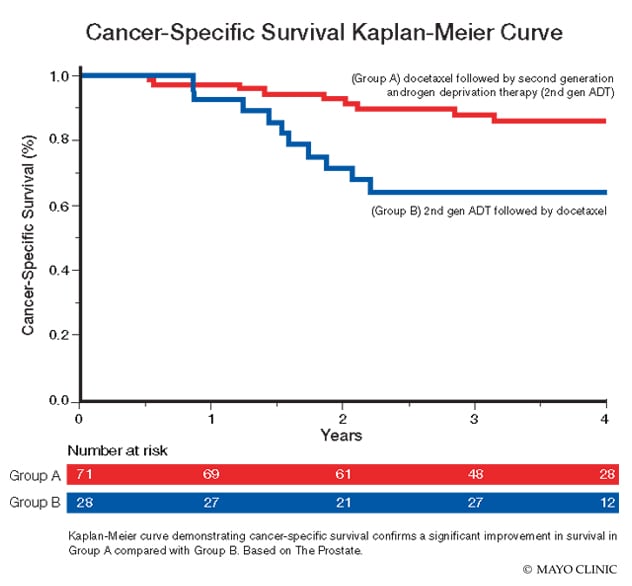
The common complications of androgen deprivation therapy include sexual dysfunction, mood disturbance, change in body composition and osteoporosis.2,3 In view of these adverse effects intermittent dosing has been considered. This is a period of androgen deprivation therapy followed by a break until disease progression, if a good response was attained. The optimal duration of androgen deprivation therapy is fairly arbitrary as the studies have looked into various periods ranging from three months to three years.
In patients with PSA relapse only , intermittent therapy has been shown to be non-inferior to continuous dosing. There was also a better quality of life with intermittent dosing.4
In patients with objective metastases, intermittent androgen deprivation therapy had numerically worse outcomes than continuous treatment, but the study was statistically inconclusive. There was less sexual dysfunction and better mental health in the intermittent group, but this effect disappeared by 15 months when most people were back on continuous treatment.5 If short-term quality of life is important, even at the risk of possible worse survival, intermittent therapy is a reasonable approach.
You May Like: How Long Does Prostate Cancer Take To Develop
Also Check: What Is The Male Prostate
Prostate Cancer Survival Rates Are Favorable Overall
Thinking about survival rates for prostate cancer takes a little mental stretching. Keep in mind that most men are around 70 when diagnosed with prostate cancer. Over, say, five years, many of these men will die from other medical problems unrelated to prostate cancer.
To determine the prostate cancer survival rate, these men are subtracted out of the calculations. Counting only the men who are left provides what’s called the relative survival rate for prostate cancer.
Taking that into consideration, the relative survival rates for most kinds of prostate cancer are actually pretty good. Remember, we’re not counting men with prostate cancer who die of other causes:
- 92% of all prostate cancers are found when they are in the early stage, called local or regional. Almost 100% of men who have local or regional prostate cancer will survive more than five years after diagnosis.
- Fewer men have more advanced prostate cancer at the time of diagnosis. Once prostate cancer has spread beyond the prostate, survival rates fall. For men with distant spread of prostate cancer, about one-third will survive for five years after diagnosis.
Many men with prostate cancer actually will live much longer than five years after diagnosis. What about longer-term survival rates? According to the American Society of Clinical Oncology, for men with local or regional prostate cancer:
- the relative 10-year survival rate is 98%
- the relative 15-year survival rate is 95%
Prostate Cancer In Asia
The incidence of prostate cancer in Asian countries has been historically much lower than their Western counterpart, ranging between 4.5 cases per 100,000 persons for South-Central Asia, 10.5 for Eastern Asia and 11.2 for Southeast Asia . Those values could be explained both by a low susceptibility of Asian men to prostate cancer and the lack of a systematic screening program. However, there is evidence that these figures are increasing in several countries . A review by Ha Chung et al., showed a general increase in prostate cancer incidence across China, India, South Korea, Vietnam, Japan, and Singapore . These figures were supported by data from GLOBOCAN 2008 and 2012 . Sim and Cheng noted that in some centres in Japan, the incidence rate rose from 6.3 to 12.7 between 1978 and 1997, while the incidence rates in Singaporean Chinese men increased to 118% within the same period . The lowest incidence reported in Asia was in Shanghai whereas the highest was in the Rizal Province in the Philippines. shows the differences in incidence and mortality across Asia. Studies have also shown that Asian Men living in the United States develop higher risk of prostate cancer than their counterparts living in Asia suggesting that change in lifestyle, and probabaly increased screening, could be the major contributors .
Recommended Reading: How Long Do Stage 4 Prostate Cancer Patients Live
Metastatic Prostate Cancer: Seeking A Fresh Chance Of Recovery
In 2012, a man in his 50s arrived at the Cleveland Clinic in Ohio with high-grade prostate cancer that had spread to a nearby lymph node. The treatment in such cases would ordinarily have been limited to drugs that block testosterone, a hormone that fuels prostate tumour growth. At the time, metastatic prostate cancer was considered uniformly fatal, and physicians were reluctant to subject someone to the side effects of surgery and radiation if these extra measures were unlikely to prolong life.
Part of Nature Outlook: Prostate cancer
But the man insisted on doing more. In addition to undergoing six months of hormonal therapy, he had his prostate and cancerous lymph node surgically removed. A tumour that was detected in his pelvic bones one year later was treated with radiation. The extra effort paid off. Hes eight years out now with no sign of cancer in his body, says Eric Klein, a urologist at the Cleveland Clinic who consulted on the case. Ever since, Ive been asking if there is a subset of patients like him who would also benefit from more aggressive treatment.
General Prostate Cancer Survival Rate
According to the American Cancer Society:
- The relative 5-year survival rate is nearly 100%
- The relative 10-year survival rate is 98%
- The 15-year relative survival rate is 91%
Note: Relative survival rate means the percentage of patients who live amount of years after their initial diagnosis.
Keep in mind, however, that because the compiled list figures are of cancers diagnosed up to 15 years ago, you may have an even greater chance of survival than these indicate due to advances in prostate cancer treatment technology
You May Like: How To Improve Prostate Health
What Is A 5
A relative survival rate compares people with the same type and stage of cancer to people in the overall population. For example, if the 5-year relative survival rate for a specific stage of prostate cancer is 90%, it means that men who have that cancer are, on average, about 90% as likely as men who dont have that cancer to live for at least 5 years after being diagnosed.
Stage 4 Patients Can Live For Years
The 5 year survival rates listed in the chart above are NOT intended to scare you, but rather to inform you of the average, approximate ratesfor each type of cancer we have explored in this article. The fact is, Stage 4 cancer patients can live for YEARS, and these statistics are just that, statistics. They do not define your experience and do not mean that you cannot beat cancer and thrive!
Don’t Miss: How To Survive Prostate Cancer Without Surgery
Types Of Cancers That Are More Likely To Go Undetected
Some cancers are more easily detected than others. For example, certain types of skin cancer can be diagnosed initially just by visual inspection though a biopsy is necessary to confirm the diagnosis.
But other cancers can form and grow undetected for 10 years or more, as one study found, making diagnosis and treatment that much more difficult.
This table provides an overview of common cancers that often display little or no symptoms early on, and how theyre typically detected and diagnosed:
| Type of cancer |
|---|
Read Also: Prostate Cancer Blood Test Results
Survival Rates By Tnm Stage
The first approach is based on the TNM stage statistical survival times are matched to the stage of the disease.
| TNM Lung Cancer Stage | |
|---|---|
| M1c | 6.3 months |
By contrast, the one-year survival rate for stage 4 lung cancer was reported in one study to be between 15% and 19%, meaning this portion of patients with metastatic disease lived for at least a year.
Also Check: Prostate Cancer That Has Spread
Also Check: Does Drinking Water Help Enlarged Prostate
Where Do These Numbers Come From
The American Cancer Society relies on information from the SEER database, maintained by the National Cancer Institute , to provide survival statistics for different types of cancer.
The SEER database tracks 5-year relative survival rates for prostate cancer in the United States, based on how far the cancer has spread. The SEER database, however, does not group cancers by AJCC TNM stages . Instead it groups cancers into localized, regional, and distant stages.
- Localized: There is no sign that the cancer has spread outside the prostate.
- Regional: The cancer has spread outside the prostate to nearby structures or lymph nodes.
- Distant: The cancer has spread to parts of the body farther from the prostate, such as the lungs, liver, or bones.
Prostate Cancer Is Common With Aging
After skin cancer, prostate cancer is the most common cancer in men. About 1 in 7 men will be diagnosed with prostate cancer in their lifetime. And these are just the men who are diagnosed. Among very elderly men dying of other causes, a surprising two-thirds may have prostate cancer that was never diagnosed.
Only 1 in 36 men, though, actually dies from prostate cancer. That’s because most prostate cancers are diagnosed in older men in whom the disease is more likely to be slow-growing and non-aggressive. The majority of these men eventually pass away from heart disease, stroke, or other causes — not their prostate cancer.
You May Like: What Color Is Prostate Cancer Ribbon
Who Gets This Cancer
Prostate cancer occurs only in men, and it is more common in older men than younger men. It is more likely to occur in men with a family history of prostate cancer and men of African American descent. The rate of new cases of prostate cancer was 111.3 per 100,000 men per year based on 20142018 cases, age-adjusted.
Rate of New Cases per 100,000 Persons by Race/Ethnicity: Prostate Cancer
Males
Also Check: Stage 4 Metastatic Prostate Cancer
Survival By Disease Recurrence
If a man develops an elevated PSA level after cancer surgery, then the disease is viewed as recurrent.
The number of lymph nodes at the time of prostatectomy can influence the risk of recurrence. One study suggests the removal of a large number of nodes is associated with an improvement in odds of recurrence, but this doesn’t appear to impact overall survival.
But disease recurrence doesn’t always influence survival times. If a recurrence does occur, the 15-year survival rate at the time of diagnosis may be as high as 94% in those with low-risk recurrence.
The main factors influencing survival rates are:
- The Gleason score
- The PSA doubling time
- Whether the recurrence occurred within three years or after three years
A recurrence that occurs within three years reduces survival rates by anywhere from 15 to 20%and even more, if the doubling time is short.
You May Like: How Do They Do A Prostate Biopsy
The Frequency Of Bcr Cp Crd And Rates Of Bpfs Cpfs Css
Median time of follow-up after RP was 64 months. Over this time, 207 men experienced BCR. One hundred twenty-seven men had BCR in the following year after RP, 27 in the second year, 16 in the third, 14 in the fourth, 7 in the fifth, and 16 patients had BCR after 5 years . Of 207 men, 181 received salvage radiotherapy or hormone therapy or both sRT + HT due to BCR.
Figure 1. Risk of biochemical recurrence by the following year after radical prostatectomy .
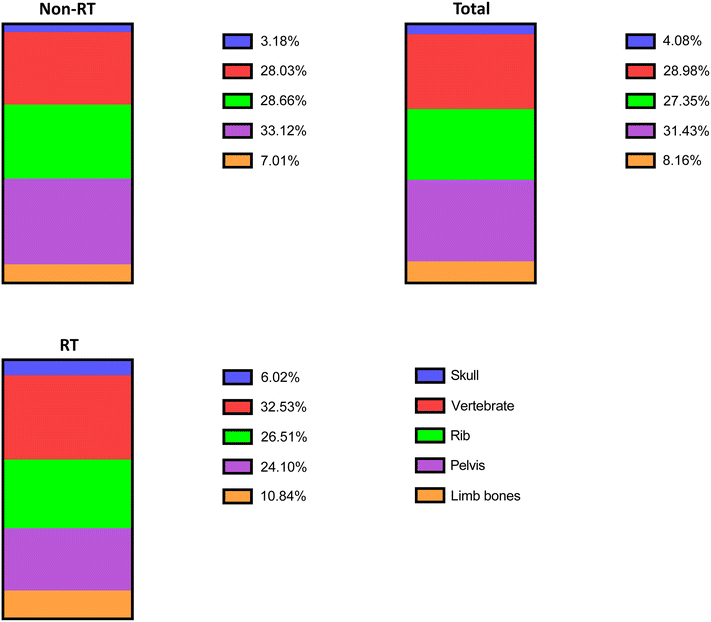
CP was diagnosed in 49 cases. Median time from BCR to CP was 17 months. Twelve men had metastases in lymph nodes, 11 had metastases in bones, 19 had metastases in lymph nodes and bones, 1 had visceral metastases, and 6 had local recurrence in the surgical bed. During the follow-up, 72 patients died. In 24 cases PCa was the cause of death.
According to the DAmico risk classification, the 5-year BPFS rate after RP of patients with one risk factor was 57.7%, and that with two factors was 34.4%. All patients with three risk factors had BCR in the first 5 years after RP .
In all study cohorts, 5- and 10-year BPFS rate was 49.2 and 34.2%, respectively. CPFS rate was 89.2 and 81% and CSS rate was 95.6 and 90.1%, respectively.
Read Also: Elevated Prostate Levels Blood Test
The Truth About Stage 4 Metastatic Cancer
The most advanced stage of any types of cancers is stage 4 metastatic cancer. Stage 4 cancer of any kind is hard to treat. This still means that there is a chance for curing. There are many clinical trials that are improving that contribute in the increase of survival rates of patients.
Stage 4 Metastatic Cancer
However, the improvement of prognosis depends on the treatment. How a patient responds to the treatment matters a lot. Having the right treatment is very important for survival.
Stage 4 metastatic cancer life expectancy is not good at all. It has the lowest percentage when it comes to the five-year survival rate. This is because the cancerous cells have already spread to other parts of the body. Therefore, the stage 4 metastatic cancer prognosis of patient is poor and not progressive. Lets take an example such as in stage 4 metastatic cancer liver. This is the condition wherein the cancer has spread from the liver to others parts of the body. This cancer of the liver which is already in its most advanced stage has originated from the lungs that spread to breast, pancreas, large intestines and stomach. This is a condition that may be difficult to cure. Another example is the stage 4 metastatic cancer spine is the cancer in the spine that has widely spread the cancer cells to the whole spine and to other parts of the body too.Treating this stage cancer very extensively is needed for patients to survive.
Recommended Reading: What Happens When You Have A Prostate Removed
