What Are The Side Effects
Initially, the urethra and surrounding area will be inflamed, and it will be difficult to urinate. The catheter and flushing process can also be uncomfortable and cause bladder cramping.
The urethra, penis, and lower abdominal area will be tender, red, and swollen for a few weeks after surgery, which can interfere with urination. Most people also feel very weak and tire easily for several weeks.
Common side effects of TURP surgeries include:
- difficulty completely emptying the bladder
- urinary urgency or the sudden urge to urinate
- discomfort during urination
- small dribbles or clots of blood in the urine, for up to 6 weeks
The minor side effects associated with TURP surgeries usually go away as the urethra and prostate tissues become less inflamed, usually within a few weeks.
Though TURP surgeries may or may not be associated with erectile difficulty in some people, they can decrease the volume of semen produced during ejaculation.
As with any medical procedure, especially those involving anesthesia, the surgery for BPH is associated with some medical complications.
Possible but rare risks associated with TURP procedures include:
- excessive bleeding
Who Is A Candidate For Transurethral Incision Of The Prostate
TUIP is most appropriate for patients who have mild to moderate benign prostatic hyperplasia, where the prostate is not severely enlarged.
When successful, TUIP helps reduce the symptoms of BPH including:
- Urgent need to urinate
TUIP is also an option to treat patients who have complications due to urine flow blockages from the following conditions:
- Frequent urinary tract infections
- Bladder stones
How Do I Get Ready For A Turp
Some things you can expect before the procedure include:
- Your healthcare provider will explain the procedure and you can ask questions.
- You will be asked to sign a consent form that gives permission to do the procedure. Read the form carefully and ask questions if anything isnt clear.
- Your healthcare provider will review your medical history, and do a physical exam to be sure youre in good health before you have the procedure. You may also need blood tests and other tests.
- You will be asked not to eat or drink anything for 8 hours before the procedure, generally after midnight.
- Tell your healthcare provider if you are sensitive to or allergic to any medicines, latex, iodine, tape, contrast dyes, or anesthesia.
- Make sure your healthcare provider has a list of all medicines herbs, vitamins, and supplements that you are taking. This includes both prescribed and over-the-counter.
- Tell your healthcare provider if you have a history of bleeding disorders or if you are taking any blood-thinning medicines , aspirin, or any other medicines that affect blood clotting. You may need to stop these medicines before the procedure.
- If you smoke, stop as soon as possible to improve recovery and your overall health.
- You may be given a sedative before the procedure to help you relax.
Based on your medical condition, your healthcare provider may request otherspecific preparation.
Recommended Reading: How Is Radiation For Prostate Cancer Done
What Is Transurethral Incision Of The Prostate
Transurethral incision of the prostate is a procedure to treat an enlarged prostate gland.
The prostate gland is part of a mans reproductive system. It is about the size of a walnut and located between the bladder and the penis. The prostate gland surrounds the upper part of the urethra, the tube that carries urine from the bladder out through the penis. It makes fluid that nourishes sperm and helps carry it out of the body during sex.
When Is It Used
When the prostate gets bigger than normal, it may put pressure on the urethra and cause problems with urination. You may have trouble passing urine, and you may feel the need to urinate more often, sometimes even at night. The need to urinate can come on suddenly. In severe cases, you may not be able to pass urine. This can cause kidney damage if it is not treated promptly.
TUIP is a possible treatment if your prostate gland is not severely enlarged. Itâs best to have this procedure before urine symptoms become severe or the prostate gland gets too large. Ask your healthcare provider about your choices for treatment and the risks.
Recommended Reading: Can Prostate Cancer Be Cured
Prostate Size And Blockage Of The Urethra
If the inner part of the prostate gland obstructs the urethra during urination, this will irritate the bladder and cause urinary symptoms.Urinary symptoms may include:
- frequent urination, particularly at night
- urgency and possible urgency incontinence
- passing drops of urine involuntarily after you think you’ve finished
- blood in the urine although this can never be assumed to be due to the prostate until other causes have been excluded.
The actual size of the prostate does not appear to determine whether or not there is a blockage. Some men with large prostates never develop obstruction, but some men with small prostates can have severe bladder obstruction, which causes difficulty with urinating.Around one in three Victorian men over the age of 50 years have some urinary symptoms. In most cases, these symptoms are due to a blockage caused by an enlarged prostate, but they may be due to other causes.
Other Surgical Procedures For Prostate Disease
Alternative surgical procedures to TURP include:
- open enucleative prostatectomy this involves making a cut in the abdomen to remove a very enlarged prostate. This is the least common form of surgery. The average hospital stay is seven to 10 days
- laser TURP a laser is used to remove prostate tissue from the middle part of the prostate, which has the advantage of less bleeding and therefore safer for people on anti-coagulation therapy for other problems, including coronary stents, heart valve or vascular disease
- transurethral incision of the prostate similar to TURP except that no prostate tissue is taken out. One to three cuts are made in the prostate near the bladder neck to release the ‘ring’ of enlarged tissue and make a larger opening around the urinary tract
- UroLift® this technique is useful for men for whom medication has not been successful but their prostates are not so enlarged that they need a TURP. It involves the transurethral insertion of staples to separate the lobes of the prostate. It has minimal side effects and preserves ejaculatory and erectile function.
Read Also: How To Stimulate Prostate Externally
What To Expect After Surgery
TUIP is a much less invasive procedure than transurethral resection of the prostate . You may be able to go home after surgery, or you may need to stay overnight in the hospital. You may not be able to urinate and may need to have a catheter to drain your bladder. For most men, this lasts for a week or less.
Who Might Need Turp
TURP is sometimes recommended when a man has an obstructed flow of urine due to benign prostatic hypertrophy or benign prostatic hyperplasia , which is a common cause of an enlarged prostate. It is used to treat prostate enlargement only if other non-surgical treatments such as medication have not worked.
The prostate is a gland that surrounds the top part of the urethra and in young men is normally the size of a walnut. It often starts to get bigger from about the age of 40 on. Eventually, it can get big enough to block the flow of urine. Symptoms include
- a weak urinary stream
- feeling that the bladder isnt empty after urinating
- having to pass urine frequently day and night
- having to pass urine urgently
TURP is an option only for men who have severe symptoms from prostate enlargement and whose quality of life is affected.
Recommended Reading: How To Hit The Prostate Just Right
What Is A Transurethral Resection Of The Prostate
The prostate gland is found only in males. It sits below the bladder andwraps around the urethra. The urethra is the tube that carries urine out ofthe body. The prostate helps produce semen.
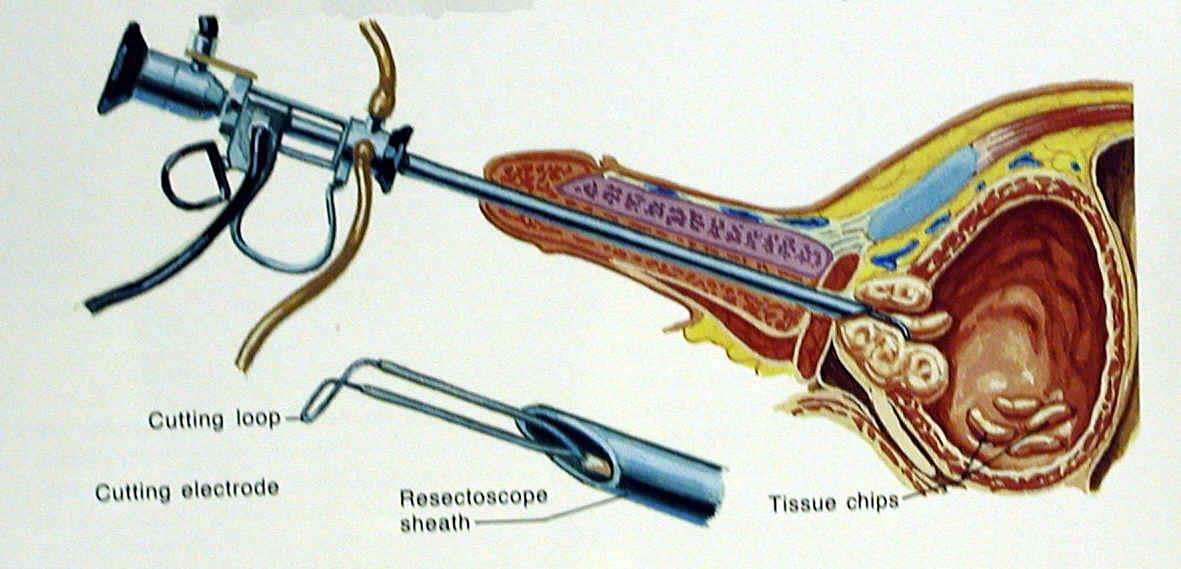
A transurethral resection of the prostate is surgery to remove partsof the prostate gland through the penis. No incisions are needed.
The surgeon reaches the prostate by putting an instrument into the end ofthe penis and through the urethra. This instrument, called a resectoscope,is about 12 inches long and .5 inch in diameter. It contains a lightedcamera and valves that control irrigating fluid. It also contains anelectrical wire loop that cuts tissue and seals blood vessels. The wireloop is guided by the surgeon to remove the tissue blocking the urethra onepiece at a time. The pieces of tissue are carried by the irrigating fluidinto the bladder and then flushed out at the end of the procedure.
Fast Facts On Bph Surgery:
- Surgery is rarely the first line of treatment for BPH.
- A doctor who specializes in the urinary tract does most TURP surgeries.
- TURP is considered a fairly safe, effective procedure for treating BPH.
According to the American Urological Association, transurethral resection of the prostate or TURP is the most common type of surgery used to treat BPH. Every year, doctors perform it on around 150,000 American men.
Surgeons perform most TURP procedures when the patient is under general anesthesia and unconscious or asleep.
Alternatively, they use spinal anesthesia, where a needle is placed in the spine to stop any sensation below the waist.
You May Like: What Causes Castrate Resistant Prostate Cancer
What Is A Transurethral Incision Of The Prostate
Transurethral incision of the prostate is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat patients with enlarged prostates, which are typically caused by benign prostatic hyperplasia. The goal of a TUIP is to relieve pressure on the urethra to allow urine to flow from the bladder into the urethra and out of the body.
What To Expect After The Procedure
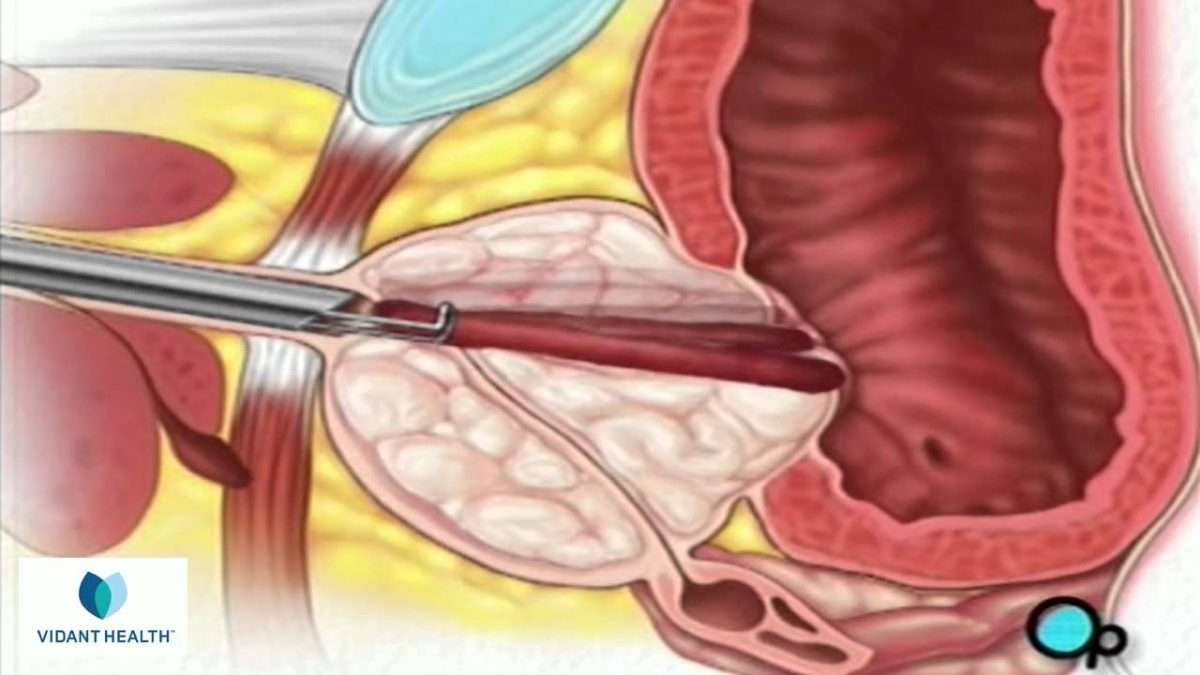
After the procedure, a urinary catheter will be in place to drain urine. This urine will probably have blood in it.
While the catheter is in place, some men feel bladder spasms or contractions. The catheter is usually removed the following day. A drip may also be in place overnight to help to flush the blood out of the bladder.
At first, you may experience a burning sensation when urinating, or need to urinate frequently. These symptoms should settle with time.
Your doctor is likely to recommend that you avoid strenuous activity, straining and heavy lifting for 6 to 8 weeks after surgery. It is also important to avoid constipation by eating plenty of fibre and drinking 2 to 3 litres of fluid per day.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Know If Your Prostate Is Swollen
Surgical Alternatives To Turp
Surgical alternatives to TURP are designed to decrease blood loss, inpatient hospitalization, and fluid absorption, while still removing or destroying the obstructing prostatic tissue. These include transurethral vaporization of the prostate , bipolar TURP, photoselective vaporization of the prostate , and holmium laser enucleation.
Reports comparing these various prostatic ablative techniques by Van Melick et al, Eaton and Francis, and Gilling et al show that they all demonstrate improvement that is roughly equivalent to TURP in terms of urodynamics, symptom scores, and uroflowmetry parameters for at least 7 years.
Noble and colleagues compared these techniques in a randomized, controlled trial from a strictly economic point of view. They concluded that noncontact laser therapies tended to be the most costly surgical treatment option, while TURP was the most cost-effective.
Electrovaporization of prostate
Electrovaporization of the prostate uses a ridged or pitted cylindrical metal roller electrode instead of the standard wire loop. This roller electrode conducts the electrical cutting current at very high energy levels, resulting in complete vaporization of the prostatic tissue it contacts. This method results in relatively good hemostasis with less bleeding and fluid absorption than the standard TURP.
Bipolar TURP
Holmium enucleation of prostate
Why It Is Done
TUIP may be a good option for men who have only slightly enlarged prostates and who are bothered a lot by their symptoms.
TUIP may be chosen instead of TURP by men who:
- Are at higher risk for complications from surgery and anesthetic, including men with serious health problems. TUIP involves less blood loss and can be done more quickly than TURP.
- Want to avoid the risk for retrograde ejaculation, a condition in which semen flows backward into the bladder. This side effect is more common with TURP than with TUIP.
Also Check: Can An Enlarged Prostate Cause Gas
How To Prepare For A Transurethral Incision Of Prostate
There are several steps you can take to prepare for your TUIP surgery.
Common preparations include:
- Tests Your doctor may want to run various tests to check your health before your procedure.
- Medications Your doctor may inquire about any medication you take. Your doctor may also ask you to stop certain medications that might interfere with the TUIP procedure.
- Transportation You will likely need to organize transportation to and from the hospital for your surgery.
- Overnight Bag A TUIP surgery can be performed as an outpatient procedure. However, sometimes, your doctor may want you to stay overnight in the hospital.
- Restrictions Your doctor will likely advise you what to eat and drink in the 24 hours leading up to your procedure. You may also want to avoid any strenuous activity for a few weeks after your surgery.
Why Might I Need Turp
TURP is most often done to relieve symptoms caused by an enlarged prostate.This is often due to benign prostate hyperplasia . BPH is not cancer.It is a common part of aging. When the prostate gland is enlarged, it canpress against the urethra and interfere with or block the passage of urineout of the body.
Sometimes a TURP is done to treat symptoms only, not to cure the disease.For example, if youre unable to urinate because of prostate cancer, butsurgery to remove the prostate isnt an option for you, you may need aTURP.
There may be other reasons for your healthcare provider to recommend aTURP.
Recommended Reading: How To Speed Up Nerve Regeneration After Prostate Surgery
Recovery After The Procedure:
After the surgery, the patient is observed in the recovery area, then prepared for discharge home. Typically, there is no need for a catheter to drain the bladder.
After surgery one can anticipate mild discomfort including slight burning with urination, urgency, and frequency. One may notice a small amount of blood in the urine this should not be cause for alarm as this is part of the healing process. Patients will notice improvements in the urinary symptoms gradually.
Men can expect to return to normal activity approximately 3 days after the TUIP procedure. Patients should avoid strenuous exercise, heavy lifting or pushing, and avoid equipment that vibrates for about 2 weeks. These types of activities may aggravate the urogenital region and can cause bleeding.
Generally, patients can resume normal sexual activity about 4 weeks after the surgery.
Why Turp Is Carried Out
TURP is often recommended when prostate enlargement causes troublesome symptoms and fails to respond to treatment with medication.
Symptoms that may improve after TURP include:
- problems with starting to pee
- a weak flow of pee, or stopping and starting
- having to strain to pee
- a frequent need to pee
- waking up frequently during the night to pee
- a sudden urge to pee
- being unable to empty your bladder fully
Read Also: Can You Have Sex If You Have Prostate Cancer
What Are The Alternatives To Turp
If you have an enlarged prostate, there are a number of options, including:
- do nothing some men will find the symptoms get no worse
- take medicines
- laser therapy, using heat to remove tissue from the prostate
- microwave treatment, using microwave energy to shrink the prostate
- other operations, such as transurethral incision of the prostate or open or retropubic prostatectomy
You should think about the benefits and risks of all approaches.
What Are The Risks Of This Procedure
Every procedure or treatment has risks. Some possible risks of this procedure include:
- You may have problems with anesthesia.
- You may have infection, blood clots, or bleeding.
- It may be harder for you to have an erection. Also, when you have an orgasm, semen may not come out of your penis. Instead it may flow backward into your bladder.
- Rarely, you may have trouble controlling your urine.
Ask your healthcare provider how these risks apply to you. Be sure to discuss any other questions or concerns that you may have.
Read Also: How To Screen For Prostate Cancer
What Are The Benefits Risks And Side Effects Of Turp
This treatment has well known long-term outcomes. Other treatments are generally compared with it. Symptoms generally improve markedly. The effects of treatment last for 15 years or more.
TURP does not remove the entire prostate. No incisions are needed. The hospital stay is 1 to 2 days or until there is no significant blood in your urine. TURP does require anesthesia. As with any surgery, anesthesia poses a risk.
Side effects of TURP may include retrograde ejaculation, erectile dysfunction, urinary tract infections right after surgery, and urinary incontinence. Full recovery takes about 4 to 6 weeks.
When To Seek Medical Advice
While you’re recovering, you should contact the hospital clinic or your GP if you develop:
- a high temperature of 38C or above
- severe pain while urinating
- an inability to urinate
- persistently severe or worsening blood in your urine
These symptoms can be a sign of a problem such as internal bleeding or a urinary infection that needs to be treated.
Recommended Reading: What Does Prostate Cancer Feel Like
Risks Of A Transurethral Incision Of The Prostate
A transurethral incision of the prostate is a generally safe procedure, but complications can arise. Complications may include:
- Difficulty urinating without a catheter – This side effect typically only lasts a few days.
- Urinary tract infection
- Need to treat again – If TUIP is not effective after the first procedure, you may need an alternate treatment to relieve your symptoms.
