What Does The Prostate Gland Do
09 August 2010
The prostate gland is a male reproductive organ whose main function is to secrete prostate fluid, one of the components of semen. The muscles of the prostate gland also help propel this seminal fluid into the urethra during ejaculation .
The prostate is a muscular gland that weighs about three-fourths of an ounce about the size of a small apricot. It surrounds the urethra just beneath the bladder .
During ejaculation, millions of sperm move from the testes through tubes called the vas deferens into the area of the prostate. At this point, the prostate contracts, closing off the opening between the bladder and the urethra, releasing fluid into the urethra and pushing semen on through.
The fluid excreted by the prostate makes up about one-third of the total volume of semen and contains various enzymes, zinc and citric acid. Though prostate fluid is slightly acidic, another fluid in semen made by the seminal vesicles leaves semen slightly alkaline, or basic. This alkalinity helps protect sperm and prolong their life after they are deposited in the acidic environment of the vagina, according to the biology textbook, “Life: The Science of Biology, Eighth Addition” .
One component of prostate fluid an enzyme called Prostate Specific Antigen also aids in the success of sperm by liquefying semen that has thickened after ejaculation. This thinning action allows sperm to swim more freely, according to the medical reference book “Prostate Specific Antigen” .
Does Surgery On The Prostate Gland Interfere With Sexual Function
Surgery for an enlarged prostate does not usually interfere with a man’s sexual functioning. However, about 10 to 15 percent of men may have trouble getting erections after surgery. Men may have a problem called retrograde ejaculation, which causes semen to go backward into the bladder instead of through the urethra to the outside. This means no longer being able to father children but causes no other harm.
Prostate Gland Physiology And Function
The prostate secretes a slightly acidic fluid, milky or white in appearance, that usually constitutes 2030% of the volume of the semen along with spermatozoa and seminal vesicle fluid. The prostatic fluid is expelled in the first ejaculate fractions, together with most of the spermatozoa. In comparison with the few spermatozoa expelled in seminal vesicular fluid, those expelled in prostatic fluid have better motility, longer survival, and better protection of the genetic material. The prostate also contains some smooth muscles that help expel semen during ejaculation.
To work properly, the prostate needs male hormones , which are produced mainly by the testes. Some male hormones are produced in small amounts by the adrenal glands. However, dihydrotestosterone regulates the prostate. A healthy human prostate is slightly larger than a walnut in adult males, with a weight ranging between 7 and 16 grams.
You May Like: Transitional Zone Prostate
What Is The Male Urogenital System
The term urogenital refers to something that has both urinary and genital origins. The word urogenital is used because the urinary and reproductive systems in males merge. The male urogenital system consists of several parts, including the testes, epididymis, vas deferens, ejaculatory ducts, urethra, penis, prostate and accessory glands.
Common Conditions Of The Male Reproductive System
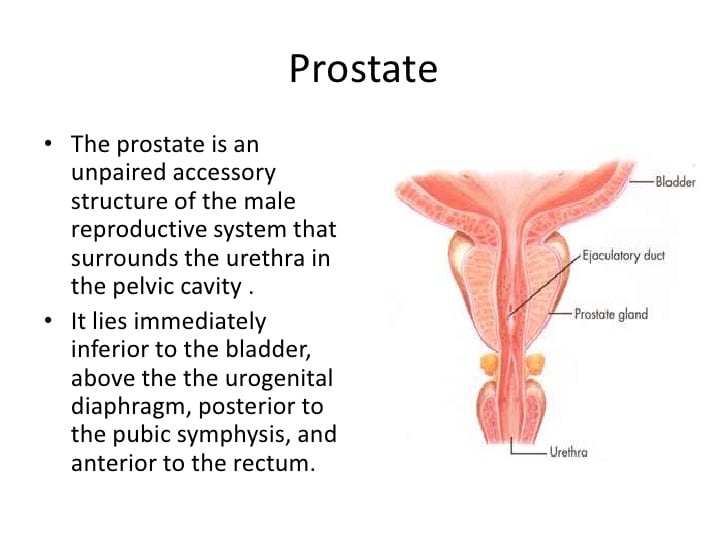
Several urological conditions can affect the male reproductive system, including:
- Hypospadias: A condition that is present at birth , in which the urethra opens anywhere other than the tip of the penis.
- Hydrocele: A fluid-filled sac around the testicle, which shows up as a swelling of the scrotum.
- Varicocele: The veins of the testicle become dilated and twisted to form a swelling in the scrotum that looks like a bag of worms.
- Cryptorchidism: One or both testicles fails to descend into the scrotum, which can cause sterility if not corrected before puberty.
- Benign prostatic hypertrophy : BPH refers to enlargement of the prostate gland. This occurs with age and often leads to trouble urinating or the need to urinate in the middle of the night .
- Erectile dysfunction: This is the inability to achieve or maintain an erection sufficient for sexual intercourse. This condition can have many causes, from nerve damage, to low hormones, to heart disease.
- Infertility: The inability to get a woman pregnant can result from problems with the number, shape, or movement of sperm, or a blockage in the tubes that carry the sperm from the testicles.
- Infectious diseases: This includes sexually-transmitted diseases like gonorrhea and chlamydia, some of which can affect a mans fertility.
References
Chung BI, Sommer G, Brooks JD. . Anatomy of the Lower Urinary Tract and Male Genitalia. Campbell-Walsh Urology. 10th ed.
Molina PE. . Male reproductive system. Endocrine Physiology. 3rd ed.
Read Also: Does Enlarged Prostate Affect Ejaculation
Can A Man Go Through Menopause
Menopause is a term used to describe the end of a woman’s normal menstrual function. In women, this is marked by changes in hormone production. One of the biggest changes for a woman after menopause is that she can no longer have children. The testes, unlike the ovaries, don’t lose the ability to make hormones. If a man is healthy, he may be able to make sperm well into his 80s or longer.
On the other hand, subtle changes in the function of the testes can happen as early as 45 to 50 years of age, and more dramatically after the age of 70. For many men, hormone production may remain normal into old age, while others may have declining hormone production earlier on. This can sometimes be a result of an illness, such as diabetes.
Its unclear whether decreasing testicular function contributes to symptoms like fatigue, weakness, depression or impotence.
Function Of The Prostate Gland
As part of the male reproductive system, the prostate glands main job is to secrete a slightly alkaline fluid that forms part of the seminal fluid. This is the fluid that carries sperm. During a man’s orgasm, the muscular glands of the prostate help to propel the prostate fluid, and sperm that was made in the testicles, into the urethra. The semen then leaves the body out of the tip of the penis during ejaculation.
Online Medical Reviewer:Online Medical Reviewer:Online Medical Reviewer:Date Last Reviewed:
Recommended Reading: Is Cranberry Juice Good For Prostate Infection
What The Male Reproductive System Does
The main functions of the male reproductive system are:
- Manufacturing, nourishing, and transporting sperm
- Making fluid that protects and supports the sperm
- Depositing sperm inside a womans reproductive system
- Producing and secreting male sex hormones
The urethra, which is part of both the male reproductive system and the urinary system, has the dual function of transporting sperm and urine.
External Male Sex Organs
Most of the male reproductive system is located outside of the mans body. These external structures are the penis, scrotum, epididymis, and testes.
Male Reproductive System: Lateral view of male reproductive system with organs labeled.
The penis is the male organ for sexual intercourse and urination. Semen and urine leave the penis through the urethra. The scrotum is a loose, pouch-like sack of skin that hangs behind the penis, containing the testes.
The scrotum has a protective function, including the maintenance of optimal temperatures for sperm survival and function. For sperm development, the testes must maintain a temperature slightly cooler than normal body temperature. Special muscles in the wall of the scrotum contract and relax in order to move the testes near the body.
The epididymus is located at the back of the testis and connects it to the vas deferens. Its function is to store and carry sperm. The testis is the location for testosterone production. The coiled collection of tubes within the testes are the seminiferous tubules. Within these tubules, spermatogenesis takes place.
Read Also: Flomax Dry Ejaculation
Blood And Lymphatic Vessels
The prostate receives blood through the inferior vesical artery, internal pudendal artery, and middle rectal arteries. These vessels enter the prostate on its outer posterior surface where it meets the bladder, and travel forward to the apex of the prostate. Both the inferior vesical and the middle rectal arteries often arise together directly from the internal iliac arteries. On entering the bladder, the inferior vesical artery splits into a urethral branch, supplying the urethral prostate and a capsular branch, which travels around the capsule and has smaller branches which perforate into the prostate.
The veins of the prostate form a network the prostatic venous plexus, primarily around its front and outer surface. This network also receives blood from the deep dorsal vein of the penis, and is connected via branches to the vesical plexus and internal pudendal veins. Veins drain into the vesical and then internal iliac veins.
The lymphatic drainage of the prostate depends on the positioning of the area. Vessels surrounding the vas deferens, some of the vessels in the seminal vesicle, and a vessel from the posterior surface of the prostate drain into the external iliac lymph nodes. Some of the seminal vesicle vessels, prostatic vessels, and vessels from the anterior prostate drain into internal iliac lymph nodes. Vessels of the prostate itself also drain into the obturator and sacral lymph nodes.
-
Microscopic glands of the prostate
When Does A Prostate Problem Need Treatment
BPH requires treatment only if the symptoms are severe enough to be troublesome to the patient, if the function of the urinary tract is seriously affected or if there are other complications, such as bleeding, kidney infections or kidney damage. An enlarged prostate by itself is not enough reason to need treatment.
Don’t Miss: How Long Should You Take Lupron For Prostate Cancer
The Testes Produce Millions And Millions Of Sperm Each Day
The testes are the male gonads and sit below the penis within a sac called the scrotum. They are 4-5 cm long, 2.5 cm in diameter, and covered with two membranous layers, the tunica albuginea and the tunica vaginalis. The testes generate sperm, the male sex cells, as well as testosterone and other sex hormones. The production of sperm is constant and occurs within numerous lobules in each testis. First, structures called seminiferous tubules generate stem cells. These cells, the spermatogonia, divide into spermatocytes, and then divide further to become spermatids. The process is called spermatogenesis. Spermatids move from the testis to the epididymis and mature into sperm.
What Are Clinical Trials And Are They Right For You
Clinical trials are part of clinical research and at the heart of all medical advances. Clinical trials look at new ways to prevent, detect, or treat disease. Researchers also use clinical trials to look at other aspects of care, such as improving the quality of life for people with chronic illnesses. Find out if clinical trials are right for you.
Also Check: How To Massage A Man’s Prostate
How Is A Prostate Problem Diagnosed
A prostate problem is most often diagnosed because of the symptoms that it causes. Your doctor will also do a physical examination called a digital rectal exam, or DRE. Other tests can be done to measure the urine flow, which can help the doctor decide how much the prostate is blocking the urine stream.
How The Male Reproductive System Functions
Three main hormones are involved in the functioning of the male reproductive systemtestosterone, follicle-stimulating hormone , and luteinizing hormone .
Both LH and FSH are made in the pituitary gland, which is located at the base of the brain. FSH is needed for the production of sperm , and LH stimulates the production of testosterone in the testicles. Testosterone plays a role in the development of many male traits, such as muscle strength and mass, bone mass, distribution of fat, and sex drive.
Recommended Reading: Zinc And Prostate Cancer
Clinical Relevance Prostatic Carcinoma
Prostatic carcinoma represents the most commonly diagnosed cancer in men, especially in countries with high sociodemographic index. The malignant cells commonly originate from the peripheral zone, although carcinomas may arise from the central and transition zones too. It is still debatable that the latter tumors may present with lower malignant potential.
However the proximity of the peripheral zone to the neurovascular bundle that surrounds the prostate may facilitate spread along perineural and lymphatic pathways, thus increasing the metastatic potential of these tumors. Malignant cells may invade adjacent structures and/ or lymphatic and blood vessel routes to give distant metastases. Prostate carcinoma also commonly spreads via the Batson venous plexus to the vertebral bodies and cause skeletal metastases.
A DRE may reveal a hard, irregular prostate gland. In most cases the serum PSA values will be increased. However, due to the peripherally-advancing tumor, symptoms may be minimal, as obstruction occurs usually at late stages. One should also keep in mind that the high incidence of prostate carcinoma is found in elderly men, who may already have symptoms due to BPH.
Fig 4 Prostate cancer has the potential to invade nearby structures.
Urinary Tract Infections In Men: Symptoms Diagnosis And Treatment
Nonbacteria microbes may cause a different type of chronic prostatitis, known as chronic pelvic pain syndrome, which may also develop as a result of chemicals in the urine, a urinary tract infection, or pelvic nerve damage.
Affecting 10 to 15 percent of the U.S. male population, chronic pelvic pain syndrome is the most common type of prostatitis, but also the least understood.
Symptoms vary depending on the type of prostatitis, but can include urination problems, pain , fever, and body aches, among other things.
Some people develop asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis, in which the prostate is inflamed but doesn’t produce any symptoms or require treatment.
Bacterial prostatitis is most often treated with antibiotics. Chronic pelvic pain syndrome may require drugs, surgery, and lifestyle changes.
Over time, prostatitis may cause sexual dysfunction, abscesses in the prostate, inflammation of nearby reproductive organs, and infection of the bloodstream.
Learn More About Prostate Problems and Complications
Read Also: Urinozinc Prostate
Treatment For Prostate Disease
Treatment for prostatitis may include antibacterial drugs and supportive treatments, depending on the type of prostatitis.Treatment for BPH may include medications to relax the smooth muscle of the gland or to shrink the size of the prostate, and surgery to produce a permanently widened channel in the part of the urethra that passes through the prostate.Treatment for prostate cancer is tailored to suit individual circumstances. The nature of the cancer, other health problems the person may have, and their wishes will all be taken into account.Management approaches for prostate cancer include:
- active surveillance
- surgery for example, prostatectomy
- radiotherapy
- ablative treatments such as high-intensity focused ultrasound and NanoKnife®
- hormone treatment
- chemotherapy
Prostatitis: A Common Prostate Problem In Younger Men
Prostatitis, or prostate inflammation, is the most common prostatic and urinary tract problem for men under age 50, according to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases . It accounts for 2 million doctor visits in the United States each year.
There are several types of prostatitis.
Prostatitis caused by bacteria is known as bacterial prostatitis, and it can cause an acute or chronic infection.
Also Check: Prostate Definition Medical
Difference Between Sexual And Asexual Mode Of Reproduction
Both sexual and asexual are two different modes of reproduction. Sexual mode reproduction takes place in all multicellular organisms including humans, animals, and higher plants. Asexual mode reproduction occurs only in lower invertebrates and other simpler living species such as amoeba, bacteria, and hydra.
Cure For Prostate Problems
The prostate is a part of the male reproductive system, which includes the penis, prostate, seminal
vesicles, and testicles. The prostate is located just below the bladder and in front of the rectum. It is
about the size of a walnut and surrounds the urethra (the tube that empties urine from the
bladder).
One of the greatest health issues looked at by means of men in all regions of the planet is trouble
with the prostate. They can be of numerous nature, possibly wear and shape. Pretty tons each
different man beyond 45 years antique previously had a prostate problem and almost, in reality,
theyll all experience this trouble at the off hazard that they stay long. The prostate is a pecan-
measured sturdy organ that is to a point ring-shutting the urethra. Its capability is the introduction
of an emission that conveys sperm. As guys age, they often revel in specific problems with the
prostate, the most famous being prostate extension, extreme and ongoing aggravation, and prostate
cancer.
Prostate cancer is the maximum widely recognized most cancer of fellows, other than
mobile breakdown inside the lungs.
Recommended Reading: Does Enlarged Prostate Affect Ejaculation
What Causes Prostatitis
The causes of prostatitis differ depending on the type.
Chronic prostatitis or chronic pelvic pain syndrome. The exact cause of chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome is unknown. Researchers believe a microorganism, though not a bacterial infection, may cause the condition. This type of prostatitis may relate to chemicals in the urine, the immune systems response to a previous urinary tract infection , or nerve damage in the pelvic area.
Acute and chronic bacterial prostatitis. A bacterial infection of the prostate causes bacterial prostatitis. The acute type happens suddenly and lasts a short time, while the chronic type develops slowly and lasts a long time, often years. The infection may occur when bacteria travel from the urethra into the prostate.
Anatomy Of The Prostate
The prostate is a gland of the male reproductive system. It is located in front of the rectum and just below the bladder, the organ that stores urine. It is about the size of a chestnut and somewhat conical in shape, and consists of a base, an apex, an anterior, a posterior and two lateral surfaces.
The main purpose of the prostate is to produce fluid for semen, which transports sperm during the male orgasm.
You May Like: How To Treat Prostate Cancer That Has Spread To Bones
