Testing Options For Prostate Cancer
There is no one age for prostate cancer testing, but the American Cancer Society makes recommendations about prostate cancer screenings. According to the ACS, patients in any of these groups should consider asking their doctor about testing:
- Men age 50 or older who have an average risk of prostate cancer and a life expectancy of at least 10 more years
- Men age 45 or older with a high risk, including African-American men and those with a first-degree relative who had prostate cancer before age 65
- Men age 40 or older who have a higher risk, such as more than one first-degree relative diagnosed with prostate cancer at an early age
Expert
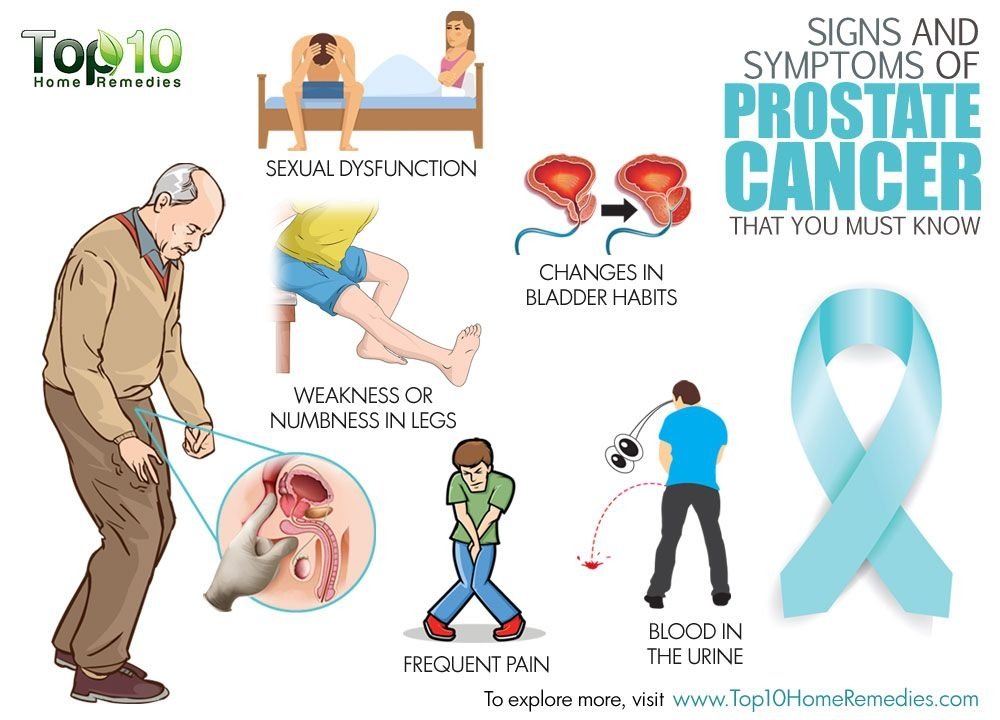
What Are The Symptoms Of Prostate Cancer
If you have any symptoms that worry you, be sure to see your doctor right away. They may be caused by conditions other than prostate cancer.
Different people have different symptoms for prostate cancer. Some men do not have symptoms at all.
If you have any of the following symptoms, be sure to see your doctor right away
- Difficulty starting urination.
- Weak or interrupted flow of urine.
- Frequent urination, especially at night.
- Difficulty emptying the bladder completely.
- Pain or burning during urination.
- Blood in the urine or semen.
- Pain in the back, hips, or pelvis that doesnt go away.
- Painful ejaculation.
Keep in mind that these symptoms may be caused by conditions other than prostate cancer.
Links with this icon indicate that you are leaving the CDC website.
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination websites privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance on other federal or private website.
Knowing How To Read The Common Early Warning Signs Of Prostate Cancer Is Very Important To Ensure You Seek Treatment Early
Prostate cancer develops when abnormal cells in the prostate gland start to mutate and grow uncontrollably and more rapidly than normal cells. These abnormal cells can sometimes grow outside the prostate and into different parts of the body.
While the disease is potentially deadly, it is also highly treatable, especially if it is detected in its early stages. However, many men let prostate cancer go untreated because they dont know how to read the signs.
Knowing how to read the symptoms of prostate cancer could mean the difference between radiation treatment and eradicating it with minimal intervention. Lets take a look at some of the early warning signs of prostate cancer.
Recommended Reading: Procedure To Reduce Prostate Size
What About Trans People
People born with a prostate can develop prostate cancer. Individuals born without a prostate cannot develop prostate cancer.
Trans women who use hormone therapy such as estrogen may have a lower risk, but the risk is still present.
Anyone born with a prostate should speak to their doctor about screening for prostate cancer.
What Is Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer affects the prostate glands of men. Prostate cancer is the second-leading cause of cancer deaths for men in the United States.
The prostate is a small organ that lies below the urinary bladder and in front of the rectum . In men, it is normal for the size of the prostate to increase with age. In younger men, it is about the size of a walnut. The prostate makes a milky fluid, which is a part of semen. This fluid feeds the sperm.
Growth in the prostate can be of two types:
- Benign growths: These are noncancerous growths and rarely a threat to life e.g., benign prostatic hyperplasia.
- Malignant growths: These are cancerous growths that can be life-threatening.
Prostate cancer starts in the prostate gland and may spread to other organs.
Also Check: How Deep Is Prostate Gland
Determining The Proper Treatment
There are a number of treatment options for prostate cancer, according to the Mayo Clinic.
- Radiation. Radiation therapy can be delivered in a few different ways. One is external beam radiation, in which a machine outside the body delivers radiation to the prostate tissue. Another form of therapy, known as brachytherapy, involves using radioactive seeds to deliver a low dose of radiation directly to the prostate tissue.
- Hormones. The hormone testosterone acts as fuel for prostate cancer cells inside the body. By blocking the production of testosterone, you can kill off the cancer. Possible treatments include medications that stop the production of testosterone, medications that block testosterone from reaching cancer cells or, in extreme cases, surgery to remove the testicles.
- Surgery. For life-threatening prostate cancer, surgery to remove the prostate gland and surrounding tissues may be recommended.
- Biological therapy. Biological therapy uses your bodys own immune system to fight cancer. In the case of prostate cancer, your bodys immune cells are engineered in a lab to fight prostate cancer, and then injected back into your body.
- Chemotherapy. Chemotherapy is a traditional cancer treatment thats used to stop its spread. It may be needed for prostate cancer that has spread to other areas of the body.
- Cryosurgery or cryoablation. Freezing prostate tissue and then thawing it out has shown some success in killing prostate cancer when other treatments have failed.
Your Role In Prostate Cancer Screening
The time to diagnose, treat and cure prostate cancer is through good screening versus waiting until symptoms arrive. Sometimes patients wait for their primary care doctor to guide them, however, due to some confusion in the frequency PSA testing guidelines, many primary care doctors are not familiar with the current recommendations, so you should be your own advocate and let your urologist be your guide.
A PSA test is a simple and inexpensive blood test that is used to detect prostate cancer. PSA testing works. Prior to regular PSA screening, in the mid 90s, 75% of men who were found to have prostate cancer had metastatic disease. Meaning the cancer had spread outside of the prostate. Today, with regular PSA testing, urologists can find prostate cancer while it is localized to the prostate and when that happens, the cure rate is in the mid 90% range.
Urologists recommend a PSA screening at least every other year and for some at higher risk every year. Men should think about starting PSA testing at age 55 and continue at least until they are 70, and even after 70, if healthy. Some higher risk individuals may need to start screening earlier. For those individuals who have a primary relative who has been diagnosed with prostate cancer and those who are African American it is recommended that they begin screening in their 40s.
You May Like: Best Test To Detect Prostate Cancer
What You Need To Know About Prostate Cancer
Most types of prostate cancer are known as adenocarcinomas, which are cancers that develop from gland cells, the Mayo Clinic says.
While some forms of prostate cancer grow and spread quickly, others grow quite slowly. The American Cancer Society notes that some people can have undetectable prostate cancer for decades without it causing any problems. But the risks of prostate cancer are quite serious, particularly as it begins to spread to other areas of the body.
What Is Evaluation Of The Primary Tumor In Prostate Cancer
Evaluation of the tumor :
- TX: Cannot evaluate the primary tumor.
- T0: No evidence of tumor.
- T1: Tumor present but not detectable clinically or with imaging.
- T1a: The tumor was incidentally found in less than 5% of prostate tissue resected .
- T1b: The tumor was incidentally found in greater than 5% of prostate tissue resected.
- T1c: The tumor was found in a needle biopsy performed due to an elevated serum PSA.
It should be stressed that the designation T2c implies a tumor which is palpable in both lobes of the prostate. Tumors which are found to be bilateral on biopsy only but are not palpable bilaterally should not be staged as T2c.
Evaluation of the regional lymph nodes :
- NX: The regional lymph nodes cannot be evaluated.
- N0: There has been no spread to the regional lymph nodes.
- N1: There has been spread to the regional lymph nodes.
Evaluation of distant metastasis :
Also Check: How To Fix A Swollen Prostate
Recommended Reading: How Effective Is Hormone Treatment For Prostate Cancer
Orange County Radiation Oncology Center1100
Get Directions
Privacy Overview
| Cookie | ||
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category “Analytics”. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category “Functional”. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category “Necessary”. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category “Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category “Performance”. |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
How Prostate Cancer Is Diagnosed And Staged
Cancer staging helps you and your doctor understand how advanced your cancer is and how much it has spread at the time of diagnosis. Knowing your cancer stage also helps your doctor determine the best treatment options for you and estimate your chance of survival.
The most widely used staging system for cancer is the TNM system that classifies cancer from stage 1 to stage 4.
TNM stands for:
- Tumor: the size and extent of the tumor
- Nodes: the number or extent of nearby lymph node involvement
- Metastasis: whether cancer has spread to distant sites in the body
The TNM scale is used for many types of cancer. When a doctor uses it to determine your prostate cancer stage, theyll consider several other factors as well, including:
- grade groups
Also Check: Does Prostate Cancer Cause Smelly Urine
Risk Factors For Prostate Cancer
Because prostate cancer tends to not show symptoms in its early stages, risk factors are another useful tool to identify candidates for screening. The Mayo Clinic notes that risk certainly increases as you grow older, and obese men may be more likely to have prostate cancer that is aggressive or difficult to treat.
For unknown reasons, black men are also at a greater risk of prostate cancer than men of other races. Not only are they more likely to get prostate cancer, but the risk of prostate cancer being aggressive or advanced is also higher.
Finally, your family history or genetics can also help determine your prostate cancer risk. For example, men with close relatives who had prostate cancer are more likely to get it. Also, a family history of breast cancer or the presence of the genes BRCA1 or BRCA2 within the family also raises the likelihood of a man developing prostate cancer.
What Is Radical Prostatectomy For Prostate Cancer

Radical prostatectomy is the surgical removal of the entire prostate. This operation is indicated for cancer that is limited to the prostate and has not invaded the capsule of the prostate, any other nearby structures or lymph nodes, or distant organs.
Transurethral resection of the prostate is an alternative to radical prostatectomy.
- Only part of the prostate is removed by an instrument inserted through the urethra.
- An electric current passes through a small wire loop at the end of the instrument. The electrical current cuts away a piece of the prostate.
- This procedure is used to remove tissue that is blocking urine flow in patients with extensive disease or those that are not fit enough to undergo radical prostatectomy. It is not considered a procedure for cure.
Read Also: Can You Give Blood If You Have Prostate Cancer
Where Does Prostate Cancer Spread
The most common place for prostate cancer to spread to is the bones. It can also spread to the lymph nodes, liver and lungs and other organs.
A large tumour in the prostate gland can spread into or press on areas around the prostate, such as the back passage or urethra. The urethra is the tube which carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body.
Key Prostate Cancer Symptoms To Look Out For
Movember is here to raise awareness for prostate cancer one of the most common illnesses in UK men. Here are some of the signs and symptoms to look out for
Shockingly, one in eight men are diagnosed with prostate cancer in their lifetime.
As Movember comes around once again, it is important for men to know the signs of prostate cancer and how to check for it.
There are around 11,900 prostate cancer deaths in the UK every year, an average of 32 a day and, according to Cancer Research UK, there are around 52,300 new prostate cancer cases in the UK every year, which is around 140 every day.
This makes it the most common form of cancer in men, trans women, non-binary and intersex people in the UK.
Older men are far more susceptible to get prostate cancer. Between 2016-2018, 34% of diagnosed cases were men aged 75 or over.
So what are the symptoms of prostate cancer?
Don’t Miss: Where Is A Mans Prostate
Early Signs And Symptoms Of Prostate Cancer
Most prostate cancers grow slowly. As a result, prostate cancer can be present for years without causing any problemsit has few early warning signs or symptoms. In fact, men often don’t know they have the disease. Because of the silent nature of this cancer, doctors often rely on a blood test to check for the disease in its early stages. A specific physical exam can also help detect it early on. It’s only as prostate cancer progresses that men usually begin to notice symptoms.
The closeness of the prostate gland to the urethra explains some symptoms of prostate cancer. The prostate gland surrounds the urethrathe tube that releases urine from the bladder. The prostate helps control the flow of urine. It also plays a role in sexual functioning. It supplies fluid that goes into semen. Prostate cancer causes the prostate to grow larger.
As prostate cancer grows, men may experience the following symptoms:
A noncancerous condition called benign prostatic hyperplasia also can cause problems urinating and maintaining an erection. Thats why its important to see your doctor regularly as well as when you have symptoms. Doctors examine the prostate gland, order blood tests, and look at imaging test results to diagnose or rule out prostate cancer.
Prostate Cancer Symptoms Early Advanced And Recurrent Signs
As referenced before, the prostate malignancy will, for the most part, give practically zero indications explicitly during the beginning period. The manifestations may change for every person. It is imperative to understand that a significant number of symptoms can also be present because of other underlying diseases. You can schedule a screening test, which is often through a rectal examination to look for the prospects of an abnormality if there is any.
Read Also: What Is Level 7 Prostate Cancer
Recommended Reading: Prostate Cancer Treatment Alzheimer’s
Sure Signs You Have Prostate Cancer
Cancer is the second leading cause of death in the United States behind heart disease and prostate cancer is one of the most common types for men. The American Cancer Society estimates, “268,490 new cases of prostate cancer” and almost 35,000 people will die. While that’s an alarming number, the good news is not only is prostate cancer successfully treatable, it can be curable according to Dr. Mahdi Taha, Medical Director ofMedical Oncology at Delray Medical Center, Part of thePalm Beach Health Network who shares what to know about prostate cancer and symptoms to watch out for. Read onand to ensure your health and the health of others, don’t miss these Sure Signs You’ve Already Had COVID.
What Are The Stages Of Prostate Cancer
The primary staging assessment of prostate cancer is usually made by digital rectal examination , prostate specific antigen measurement, and bone scan, supplemented with computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging and chest X-ray in specific situations.
Staging is a system of classifying tumors by size, location, and extent of spread, local and remote.
Staging is an important part of treatment planning because tumors respond best to different treatments at different stages.
Stage is also a good indicator of prognosis, or the chances of success after treatment.
Clinical staging provides the initial information about the extent of disease that is used to plan therapy. However, clinical staging can underestimate the extent of the tumor, when compared with results based upon pathologic examination of a resection specimen .
Conventional stages of prostate cancer are as follows:
- Stage I : The cancer cannot be felt on digital rectal exam, and there is no evidence that it has spread outside the prostate. These are often found incidentally during surgery for an enlarged prostate.
- Stage II : The tumor is larger than a stage I and can be felt on digital rectal exam. There is no evidence that the cancer has spread outside the prostate. These are usually found on biopsy when a man has an elevated PSA level.
- Stage III : The cancer has invaded other tissues neighboring the prostate.
- Stage IV : The cancer has spread to lymph nodes or to other organs.
Recommended Reading: How Often Should Males Get Their Prostate Checked
