What Is The Prognosis For People Who Have Prostatitis
Antibiotics can cure acute bacterial prostatitis. These medications also ease chronic bacterial prostatitis symptoms in approximately 30% to 60% of men. Up to 80% of men with chronic pelvic pain syndrome feel better after receiving appropriate treatments for their symptoms using the UPOINT system. Men with asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis dont need treatment.
What Causes Chronic Prostatitis/chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome
Chronic prostatitis/CPPS is a persistent discomfort or pain that you feel in your lower pelvic region – mainly at the base of your penis and around your anus. It is usually diagnosed if you have had pain for at least three months within the previous six months. The cause of this type of chronic prostatitis is not fully understood.
Symptoms And Signs Of Prostatitis
Symptoms vary by category but typically involve some degree of urinary irritation or obstruction and pain. Irritation is manifested by frequency and urgency, obstruction, a sensation of incomplete bladder emptying, a need to void again shortly after voiding, or nocturia. Pain is typically in the perineum but may be perceived at the tip of the penis, lower back, or testes. Some patients report painful ejaculation.
Acute bacterial prostatitis often causes such systemic symptoms as fever, chills, malaise, and myalgias. The prostate is exquisitely tender and focally or diffusely swollen, boggy, indurated, or a combination. A generalized sepsis syndrome may result, characterized by tachycardia, tachypnea, and sometimes hypotension.
Chronic bacterial prostatitis manifests with recurrent episodes of infection with or without complete resolution between bouts. Symptoms and signs tend to be milder than in acute prostatitis.
Chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome typically has pain as the predominant symptom, often including pain with ejaculation. The discomfort can be significant and often markedly interferes with quality of life. Symptoms of urinary irritation or obstruction also may be present. On examination, the prostate may be tender but usually is not boggy or swollen. Clinically, inflammatory and noninflammatory types of chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome are similar.
Don’t Miss: Is Zinc Good For Prostate
What If My Prostatitis Is Not Caused By Infection
Because we do not understand what causes prostatitis without infection, it can be hard to treat. Your doctor might try an antibiotic to treat a hidden infection. Other treatments are aimed at making you feel better. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines, such as ibuprofen or naproxen, and hot soaking baths may help you feel better. Some men get better by taking medicines that help the way the bladder or prostate gland work. These medicines include oxybutynin, doxazosin, prazosin, tamsulosin and terazosin.
Who Is More Likely To Develop Prostatitis
The factors that affect a mans chances of developing prostatitis differ depending on the type.
Chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome. Men with nerve damage in the lower urinary tract due to surgery or trauma may be more likely to develop chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome. Psychological stress may also increase a mans chances of developing the condition.
Acute and chronic bacterial prostatitis. Men with lower UTIs may be more likely to develop bacterial prostatitis. UTIs that recur or are difficult to treat may lead to chronic bacterial prostatitis.
Recommended Reading: Does Enlarged Prostate Affect Ejaculation
What Are Clinical Trials And Are They Right For You
Clinical trials are part of clinical research and at the heart of all medical advances. Clinical trials look at new ways to prevent, detect, or treat disease. Researchers also use clinical trials to look at other aspects of care, such as improving the quality of life for people with chronic illnesses. Find out if clinical trials are right for you.
What Is Chronic Prostatitis
The prostate is a walnut-sized gland that sits below the bladder in men. This gland makes fluid that mixes with sperm to form semen.
Prostatitis is inflammation or swelling of the prostate gland. When symptoms start gradually and linger for more than a couple of weeks, the condition is called chronic prostatitis.
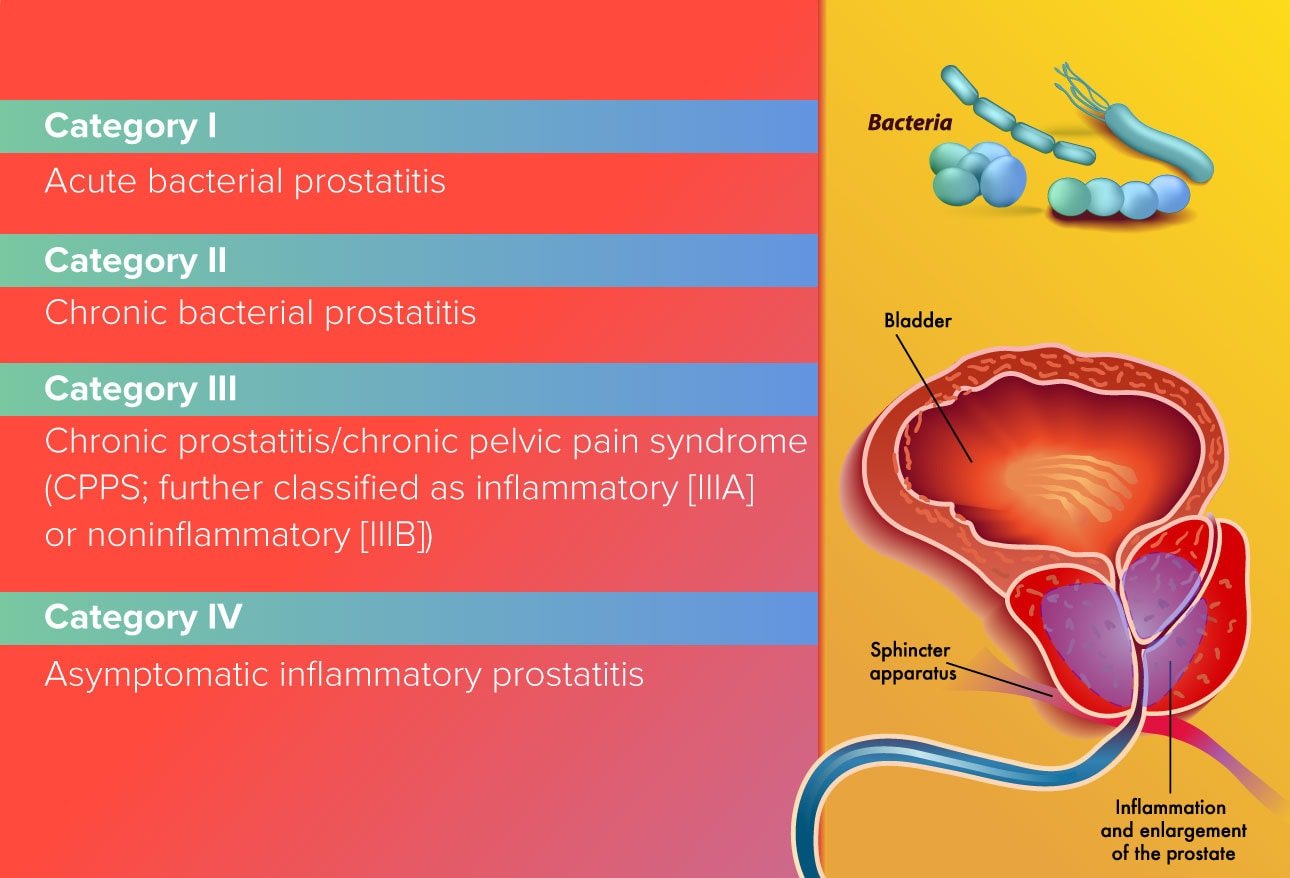
Three major types of chronic prostatitis are:
Chronic prostatitis is common and affects adult men of all ages and from all backgrounds. About five percent of men experience symptoms of chronic prostatitis at some point in their lives. Chronic prostatitis is the reason for up to 25% of office visits to urologists. Urologists are doctors who specialize in diseases of the urinary tract.
Some men develop a chronic infection in the prostate that does not cause any symptoms. Men with this problem may be diagnosed during an evaluation for other urological conditions, such as enlarged prostate or infertility. Doctors often treat the infection with the same antibiotics used for chronic bacterial prostatitis.
Bacterial infection of the prostate gland also can cause acute prostatitis, which starts suddenly and usually causes fever and more serious symptoms. Acute prostatitis is less common than chronic prostatitis.
You May Like: Flomax Ejaculation Problems
Phage Therapy In Bacterial Prostatitis
Phages, bacterial viruses, were used in the treatment of bacterial infections because they show characteristics of infecting and lysing bacteria that have been discovered almost a century ago. Although they were abandoned by the western world after the discovery of antibiotics, the phenomenon of the global effective decline in antibiotic therapy has forced scientists to look for alternative strategies for prophylaxis and control of bacterial infection. Phage therapy may be one of the most popular choices nowadays. Several major advantages, such as host-specificity, self-amplification, biofilm degradation, and low toxicity to humans, are attributed to PT in comparison with antibiotics therapy . Moreover, phages are able to selectively infect and kill bacterial cells, even those that have acquired resistance to antibiotics, such as vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium .
One should be aware that the general use of phages as an alternative to antibiotics will be possible when their efficiency and safety have been verified in large-scale and controlled clinical trials.
Treating Prostatitis Effectively: A Challenge For Clinicians
Nhuan Nguyen, PharmD, MBA, CHEClinical PharmacistGR Health, Georgia Regents Medical CenterAugusta, GeorgiaCharlie Norwood VA Medical CenterAugusta, GeorgiaUniversity of Georgia College of PharmacyAthens, Georgia
US Pharm. 2014 39:35-40.
ABSTRACT: Prostatitis, which affects 5% to 9% of males and occurs mostly in middle age, is classified based on signs and symptoms, with urinary urgency, frequency, and pain typical in nearly all categories. Most physicians are not familiar with prostatitis, particularly chronic prostatitis associated with chronic pelvic pain syndrome . Accordingly, patients are often misdiagnosed and receive ineffective treatment, resulting in poor quality of life. CP/CPPS is challenging to treat, as its causes are not clearly defined and the antibiotics used for therapy have low effective rates. Clinical pharmacists can contribute significantly to patient care by advising physicians and other medical professionals regarding drug efficacy, adverse drug reactions, and drug interactions, and by assisting in the selection of optimal antibiotics and/or treatment regimens for prostatitis.
Prostatitis , which occurs in 5% to 9% of males aged 18 years and older, most often develops in middle age.1 In the early 1990s, prostatitis accounted for about 1% and 8% of office visits to family practitioners and urologists, respectively.1
You May Like: Viagra And Frequent Urination
Symptoms Of Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis
Bacterial infections in the prostate can be very painful.
The symptoms begin slowly and last 3 months or longer. Seek medical attention if you have any of the following symptoms:
Serious complications can arise if an infection isnt properly treated. Complications include:
- urinary retention, which is an inability to urinate
- , which occurs when bacteria spread into the bloodstream
- a prostate abscess, which is a collection of pus that causes inflammation
A bacterial infection causes chronic bacterial prostatitis. Even when the primary symptoms of infection have been treated, bacteria may continue to thrive in the prostate.
Causes of infection include:
- sexually transmitted infections , such as chlamydia and gonorrhea
- E. coli after having an infection of the testicles, urethritis , or a UTI
Certain factors put people at risk for developing this condition, such as:
Predictions For The Future After Chronic Prostatitis Treatment
In most cases, chronic prostatitis responds well to treatment and has no negative health consequences for men.
Prostatitis develops slowly, so the main thing is not to start the development of the disease, and at the first manifestations of the disease, you should consult a specialist.
Early prostatitis responds well to treatment. It should also be warned that prostatitis has the ability to aggravate problems with the genital area. Often, prostatitis causes a man to lose his sexual desire and desire. Men may not even be aware of the presence of inflammation of the prostate gland, attributing short-term symptoms to fatigue or other reasons, so they postpone treatment. This attitude towards your health can have the most negative consequences. Therefore, try to have an ultrasound examination of the prostate gland at least once or twice a year.
Also, men after 40 years should visit a doctor more often, check not only the prostate gland, but also other organs of the reproductive system. Preventing a disease is easier than treating its consequences.
You May Like: How Are Fiducial Markers Placed In The Prostate
Causes & Risk Factors
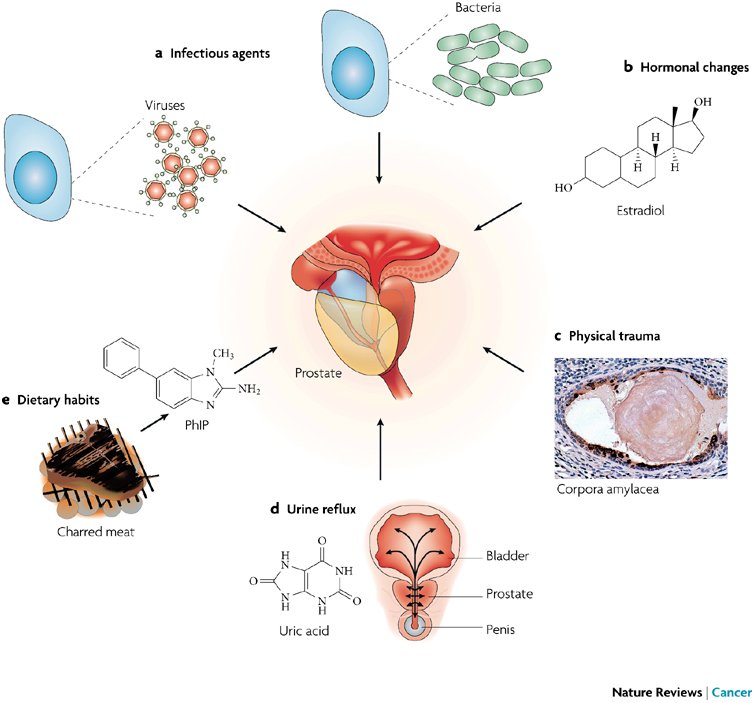
Bacterial prostatitis is caused by a bacterial infection that usually occurs when bacteria travel from the urethra into the prostate. In most cases, bacteria in your urine leak into your prostate and cause an infection. With chronic bacterial prostatitis, bacteria chronically infects the prostate gland, leading to repeated urinary tract infections.
The cause of chronic pelvic pain varies. It can come from an initial infection of the prostate, an injury, surgery involving the prostate or lower urinary tract, and spasms of the pelvic floor muscles.
A 2016 study published in Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Diseases indicates potential risk factors for chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain. The most common risk factors include stress, smoking, alcohol consumption, minimal water intake, imbalanced diet, frequent sexual activity, delaying ejaculation, holding urine and nightshift work. Living a sedentary life, drinking caffeinated drinks and not drinking enough water were found to be associated with severe pain in patients with prostatitis.
Some other risk factors associated with prostatitis include having an infection in the bladder that spreads to the prostate having pelvic trauma having a prostate biopsy or having a catheter inserted into the urethra to drain your bladder.
Prostate Massage And Ejaculation
Before the availability of broad-sprectum antimicrobials, prostatic massage was the mainstay of treatment for patients with prostatitis . Mechanistically, prostate massage could help drain occluded prostatic duct and increase penetration of the gland by antimicrobial agents . It could also disrupt bacterial biofilms or massage a neuromuscular trigger point along the pelvic side wall. In a non-controlled study, prostate massage 23 times per week for 46 weeks with concurrent antibiotic treatment had some clinical benefit in patients with CP/CPPS . Frequent ejaculation achieves similar results . It has also been demonstrated that 40% of CP/CPPS patients treated with antibiotics and prostatic massage had lasting clinical improvement, especially if there was large volume of clumpy expressed prostatic secretions at the first visit or if prostate cultures remained positive despite adequate antibiotics .
You May Like: How To Find The Prostate Gland Externally
Antibiotics Combinate With Antibiotics
The improvement of eradication rates on bacterial prostatitis through the combination of antibiotics has also been reported by many randomized trials. Magri et al. found that the pathogen eradication under the combination of levofloxacin and azithromycin was 11% increased compared with the cases treated with levofloxacin as a single agent and recommended this as an interesting option in both first-referral and relapsing cases . Owing to a series of distinct PK and pharmacodynamic properties , macrolide antibiotics are emerging as noteworthy options for enhancing the rates of clinical symptom improvement and pathogen eradication on the treatment of CBP . A study of the fluoroquinoloneâmacrolide combination therapy for CBP has shown that fluoroquinolones combined with macrolides can effectively eliminate pathogenic bacteria and reduce CBP symptoms, such as painful dysuria and sexual dysfunction . Khryanin et al. substantiated the superiority of the combination therapy of ornidazole and ofloxacin for CBP, with the background of general decline in sexually transmitted infection incidence .
The Revival Of Fosfomycin
Considering that the evolving changes in resistance rates for fluoroquinolones have a serious impact on treatment, alternative antibiotic therapies are urgently needed. Studies have demonstrated fosfomycin has a strong killing effect in vitro against antimicrobial-resistant E. coli . This new discovery inspires the treatment of refractory bacterial prostatitis . Fosfomycin, an old drug used before for therapy of females uncomplicated cystitis and transrectal prostate biopsy prophylaxis, has been recently rediscovered as a treatment for MDR infections with an effective rate > 90% in lowering UTIs . In addition, fosfomycin-susceptibility rate of ESBL-producing E. coli, ESBL-producing K. pneumoniae, and E. faecalis reported lately by a systemic review was 95%, 83.8%, and 96.8%, respectively . Clinically, a case report of the successful administration of oral fosfomycin on patients with CBP who were infected by a complicated vancomycin-resistant Enterococci demonstrated that fosfomycin is available .
Recommended Reading: Do Females Have Prostate Cancer
What Is The Prostate Gland
The prostate is a gland that lies just below a man’s urinary bladder. It surrounds the urethra like a donut and is in front of the rectum. The urethra is the tube that carries urine out of the bladder, through the penis and out of the body. Your doctor may check your prostate by putting a finger into your rectum to feel the back of your prostate gland.
The prostate gland makes a fluid that provides nutrients for sperm. This fluid makes up most of the ejaculate fluid. We do not yet know all of the ways the prostate gland works.
Prostatitis Causes And Risk Factors
Prostatitis can be caused by bacteria entering the prostate gland from the urinary tract or from a sexually transmitted disease, specifically gonorrhea, chlamydia, or HIV. E. coli is also a common bacterium that can cause UTIs, which may lead to prostatitis.
Risk factors for prostatitis include a prior history of prostatitis, developing a UTI, use of a catheter or other urologic procedures, an enlarged prostate gland, engaging in anal intercourse, having a structural or functional urinary tract abnormality, dehydration, and local pelvic trauma.
Don’t Miss: How To Stimulate Prostate Gland
Antibiotics For Acute Bacterial Prostatitis: Which Agent And For How Long
Eric A. Dietrich, PharmD, BCPS, and Kyle Davis, PharmD, BCPS
Citation:Dietrich EA, Davis K. Antibiotics for acute bacterial prostatitis: which agent, and for how long? Consultant. 2017 57:564-565.
Acute bacterial prostatitis is an infection of the prostate that is most commonly seen in older men. Approximately 8% of men will experience prostatitis-like symptoms, but the overall incidence of acute prostatitis is unknown.1 Acute bacterial prostatitis can be diagnosed by way of a history and physical examination.1 Symptoms commonly mirror those of a lower urinary tract infection , and patients may or may not present with fever. Evaluation also should include urinalysis and cultures, as well as prostatic fluid cultures if needed.
Antimicrobial therapy is the cornerstone of treatment for bacterial prostatitis. Pharmacotherapy should include agents with activity against traditional UTI-causing organisms. Special attention should be given to tissue penetration into the prostate and the duration of therapy.2 Which antibiotics achieve adequate penetration, and how long should clinicians treat patients with acute bacterial prostatitis?
Patient Case
Causes Of Prostatitis Food Allergies
Food allergies can cause prostate inflammation and prostatitis. Symptoms of food allergy can include abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, as well as diarrhea. A food allergy is known as an immune system response, so its symptoms can affect the whole body. Besides, food allergy can lead to itchy skin, a sudden decrease in blood pressure, shortness of breath and difficulty swallowing.
One reason why food allergy can be a cause of prostatitis is that some patients experience a flare-up of signs and symptoms when consuming certain foods. Some products such as pasta, breads as well as baked goods are commonly associated with food allergy. So, you should try a wheat-free diet to help determine whether or not wheat is the cause of your prostatitis. Besides, some other men reported that their symptoms become worse after they consume spicy or acidic foods.
Keep reading this entire article to discover other causes of prostatitis that can make you experience some of the symptoms of prostatitis.
You May Like: Does An Enlarged Prostate Affect A Man Sexually
Is Neglected Chronic Prostatitis Dangerous
In most cases, men ignore some of the symptoms of the disease, which exacerbates the further development of prostate inflammation. This “negligence” request for health can lead to a reduction in the normal production of hormones in men, and problems with hormone levels can lead to a decrease in men’s libido . Erectile function problems may also occur. Taken together, these diseases are difficult to treat.
During prostate inflammation, the normal production of secretions slows down, so sperm loses activity. In most cases, the consequence of advanced chronic prostatitis is infertility and decreased efficacy.
The Shift In Bacterial Etiology
As early as 2003, Bundrick et al, have described that E. faecalis and E. coli were the most common isolates the former was the major infection among cohorts of patients with CBP . An epidemiological investigation of the uropathogens among 6221 Italian patients with CBP from January 1997 to December 2008, showed that incidence of gram-positive was higher than gram-negative bacteria, and E. faecalis prevalence increased within 2006â2008 . Moreover, E. faecalis prevalence has also been reported in North America not just to Italy. Recently, a clinical and microbiological survey of 332 cases of CBP showed that E. faecalis was the main etiologic agent , followed by E. coli among patients diagnosed microbiologically with CBP . These results indicate that the predominant etiologic determinant of CBP is gradually transferring to E. faecalis, which belongs to gram-positive microorganisms. Wagenlehner indicated that the improved clinical use of fluoroquinolones for CBP patients increased the trend of gram-positive infections .
The evaluation of microbiological characteristic for each CBP patients to perform a correct, appropriate, and personalized treatment schedule is essential . Therefore, Magri, V et al. proposed to dismiss empirical therapy to avoid catastrophic consequences in terms of chemoresistance and poor clinical practice .
Recommended Reading: Does Enlarged Prostate Affect Ejaculation
